In a situation where a woman cannot become pregnant for a long time, she turns to family planning centers to undergo a full examination of the reproductive system. One of the mandatory methods is ultrasound of the pelvic organs and ovaries. Based on the condition of the organ, contours, structure, size, the doctor receives important information for making a diagnosis and predicting pregnancy.
An important indicator when planning pregnancy or IVF is the size of the follicle before ovulation. What does this mean and what other parameters matter?
Physiology
The reproductive period of a woman lasts from 12-16 to 45-50 years. By the beginning of puberty, a girl’s ovaries contain about 300 thousand follicles (FL), of which only 200–400 will mature in subsequent years.
Every month, cyclic changes occur in the ovaries:
- growth of several and maturation of dominant PL;
- ovulation;
- formation, development and regression of the corpus luteum - a temporary endocrine gland.
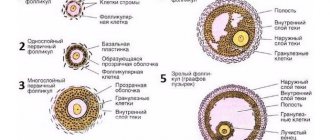
In the first days of the new menstrual cycle, under the influence of sex hormones, from 3 to 30 primary follicles begin to mature in the ovaries. These are special formations consisting of several layers of cells and one immature egg (oocyte) in each.
Gradually, the oocytes grow, become covered with shiny, dense membranes, and cavities (secondary PL) filled with liquid are formed around them.
On the 7th day of the menstrual cycle, one of these bubbles is noticeably larger than the others. This is the dominant follicle in which the egg matures and ovulation occurs. Its size during this period is about 9-10 mm, which makes it possible to see the growing follicle on an ultrasound. Other secondary FL gradually undergo reverse development - atresia.
About 2 days before ovulation, the size of the dominant follicle increases to 21 mm. The protrusion of Graaf's vesicle becomes clearly visible on the ovary. If 2 or more vesicles mature, followed by fertilization, a multiple pregnancy with fraternal twins develops.
a failure is possible in which the PL increases, but the maturation of the egg does not occur. This is an anovulatory cycle in which pregnancy will not occur.
Double ovulation, signs and detection
Double ovulation
In practice, it is not always possible to track the presence of two ovulations. Because there are no special changes in the menstrual cycle, as well as the presence of any characteristic signs. You can track it during an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Most often, doctors encounter double ovulation in women who are planning their pregnancy.
With an ultrasound examination, it is possible to see two follicles with dominant features. Their size and density are identical.
There are specialized tests based on the detection of luteinizing hormone, and basal temperature measurements can also be taken.
Dimensions
The parameters of growth and development of the dominant vesicle can be influenced by hormonal stimulation. Also, the values for each woman will vary slightly depending on the length of the menstrual cycle and age. There are no clear values for what size a follicle should be for ovulation.
The table shows the main numerical parameters of the growth of the dominant FL:
The method of observing and monitoring the development of follicles using ultrasound is called folliculometry. This is an accessible, simple and informative way to monitor changes occurring in the ovaries, which does not require special training for the woman. But the study needs to be carried out several times to determine the dynamics.
What to do if there are practically no follicles
If there are almost no follicles in the ovaries, this indicates their dysfunction or the onset of early menopause. In this case, the patient usually has a too short menstrual cycle.
In reproductive age, the causes of pathology can be:
- genetic characteristics;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- some viral infectious diseases;
- use of inappropriate hormonal drugs;
- severe nicotine addiction;
- alcohol abuse;
- malnutrition;
- undergoing chemotherapy or radiotherapy;
- surgical interventions on the pelvic organs in the past.
Since the production of hormones is largely determined by the state of the nervous system, deviations from the norm can be caused by constant stressful situations or depressive states, the elimination of which plays an important role in normalizing reproductive health.
Therapy is based on eliminating the causes of identified disorders. Thus, patients with endocrine pathologies are usually prescribed special medications. In case of deviations caused by the use of inappropriate hormonal agents, the treatment regimen is reviewed. Hormone replacement therapy is often prescribed.
Frequently asked questions
At what follicle size does ovulation occur?
On average, ovulation occurs when the FL size is from 22 to 25 mm.
Is it possible to conceive with a small follicle before ovulation?
With values less than 21 mm, impaired egg maturation can be predicted. Conception in such cases is problematic.
On day 10 of the cycle the follicle is 19 mm, when will ovulation occur?
Most likely, there is early ovulation or a woman’s natural cycle of less than 28 days. The release of a mature egg can be predicted after 24–36 hours when the peak concentration of estradiol in the blood is reached.
What is the size of the egg at ovulation?
A mature egg before fertilization has a size of 0.12 mm. It is the largest cell in the body. Compared to others, it is huge, but invisible during ultrasound examination. For your information, sperm is 85,000 times smaller.
What is the normal maximum follicle size before ovulation?
In medical practice, there is information about the size of the follicle at ovulation up to 35 mm. The larger the bubble, the more likely it is that the woman will feel pain when the egg is released.
What follicle size at ovulation is the norm for conception?
For natural fertilization of an egg, many factors must be observed. The size of the follicle does not play a decisive role. Conception is possible with FL sizes from 16 mm. It should be remembered that fertilization is most likely within 24 hours after ovulation. And sperm fertility lasts up to 2 days.
Reasons for deviations
The causes of any folliculogenesis disorders may be:
- dietary disorders - hypovitaminosis, malnutrition, etc.;
- obesity and metabolic syndrome;
- chronic or significant one-time stress;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs, incl. birth control pills;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- hormone-dependent tumors;
- autoimmune systemic diseases;
- high prolactin levels during breastfeeding.
Monitoring your health and the cyclicity of your monthly cycles will help a woman identify problems in a timely manner and avoid infertility.
Knowing what size a follicle should be ready for ovulation, you can use ultrasound to monitor its formation and plan conception.
Where do twins come from?
The “main” follicle is determined approximately on days 7-10 of the cycle. All others shrink and die naturally. But sometimes it happens that there are two “leaders” at once. In a natural cycle (that is, without the use of hormones to stimulate ovulation), this happens quite rarely - in one woman out of ten, and not every monthly cycle.
It happens that two dominant follicles in different ovaries (or in one - this is also possible) ovulate, that is, burst. And then there is a chance that both eggs will be fertilized. This means that fraternal twins will be born.
Unlike twins (when one egg is fertilized by two sperm), twins are not identical, not identical. They can be of different sexes or the same sex, and look alike, like ordinary brothers and sisters.
So, the correct growth of the dominant follicle and subsequent ovulation are clear signs of women’s health. And possible violations should alert you (and your doctor), but not frighten them. Indeed, in most cases such deviations are successfully treated.
Follicle size by cycle day
With the onset of puberty (14-15 years), he completely completes his development. It is considered normal if during the follicular phase, when the menstrual cycle begins, several follicles mature in both ovaries, of which only one reaches a significant size, which is why it is recognized as dominant.
The dominant follicle, whose size increases on average by 2-3 mm every day, reaches its normal diameter (18-24 mm) at the time of ovulation.
This is an ultrasound diagnostic test, through which the process of development and growth of follicles can be monitored. Most often, women suffering from infertility or menstrual irregularities resort to it. The manipulation in question allows us to track the dynamics of ovulation using ultrasound.
At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, it becomes possible to monitor the process of endometrial growth, and in a later period, the evolution of the follicle. So, you can determine the exact size of the follicles by the days of the cycle.
This diagnostic study allows:
- determine the onset of ovulation accurate to specific days;
- determine the size of the follicle before ovulation;
- analyze the performance of the follicular apparatus;
- plan the gender of the child;
- establish the integrity of the phases of the menstrual cycle;
- calculate the optimal day to conceive a child;
- monitor the progress of multiple pregnancies;
- diagnose menstrual irregularities;
- assess the patient’s individual hormonal background;
- monitor the progress of appropriate treatment.
From the very first days of the next cycle, using ultrasound, you can notice that in the ovaries there are several antral anatomical formations in question, which will subsequently grow. Their increase is due to the influence of special hormones, the main ones being follicle-stimulating hormone (FHS) and estradiol.
Antral follicles in the ovaries, the size of which is insignificant, should be present, according to the norm, in both sex glands in an amount not exceeding nine. As a rule, they are no more than 8-9 mm in diameter. Subsequently, it is the antral follicles, under the influence of appropriate hormones, that will give rise to such an important anatomical formation as the dominant follicle, the size of which is 2.5 times larger in diameter.
On average, the menstrual cycle is 30 days. Somewhere by the tenth day, a dominant one emerges from the entire set of antral follicles.
Often patients have a question: “What size should the follicle be at this stage?” At the first folliculometry session, its size is practically no different from the others (12-13 mm). It is worth recalling that this diagnostic ultrasound examination allows you to determine the size of the follicles by day of the cycle.
Also, at the first appointment, the specialist will be able to tell exactly how many dominant follicles have already formed. Most often it is the only one (in the right or left ovary). However, in the case when the patient undergoes a course of special stimulation of ovulation, there may be several such follicles, resulting in a multiple pregnancy, of course, subject to the maturation of two or more dominant anatomical formations.
The second session is carried out after three days. During this process, the doctor:
- confirms the presence of a dominant follicle;
- determines the size of the follicle based on menstrual cycles;
- records (if this occurs) the reverse development of the follicle.
The specialist carefully examines both of the woman’s ovaries. If you track the size of the follicles by day of the cycle, then at the second session it is 17-18 mm in diameter. It's already about day 13.
At the third session (transvaginal ultrasound), you can see that the size of the follicle before ovulation (its peak size) took on a value of 22-25 mm. This indicates its imminent rupture (in the next few hours), as a result of which the mature egg will move into the abdominal cavity and then penetrate the fallopian tube.
There are also cases when the dominant follicle grows at a different rate, which is why more than three sessions of this ultrasound may be required. If the patient has repeatedly recorded its regression, then, as a rule, the doctor prescribes daily folliculometry (from the 9-10th day of the cycle). This will identify the onset of regression and then determine the cause of this phenomenon.
So, it is worth recalling once again that it is possible to determine the size of the follicle by cycles during a diagnostic ultrasound examination - folliculometry. It will allow not only to monitor the maturation of the dominant anatomical formation in question, but also to identify the causes of deviations that inhibit this reproductive process (if any).
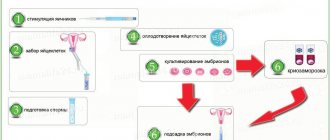
In other words, its induction. This is a complex of various types of medical manipulations, the purpose of which is to achieve pregnancy. It is in demand within modern gynecology in relation to female infertility due to many reasons.
To begin with, it is worth interpreting the concept of infertility - a condition when a woman under the age of 35 cannot become pregnant for 12 months, subject to an active sex life, as well as couples (a woman over 35 and a man over 40) in whom pregnancy does not occur. six months.
Induction is carried out in two cases:
- anovulatory infertility;
- infertility of unknown origin.
The main contraindications for this procedure are:
- violation of the patency of the fallopian tubes;
- the impossibility of conducting a full diagnosis using ultrasound;
- male infertility;
- depletion of the existing follicular reserve.
Stimulation of ovulation is not carried out during long-term treatment of infertility problems (more than two years).
It is not possible to determine the size yourself. For such purposes, there is a special procedure called folliculometry. This is an ultrasound examination, during which it is possible to determine the size, number and growth dynamics of embryonic cells.
Folliculometry is indicated for women who have problems with natural conception and menstrual irregularities. Also during the examination you can determine:
- exact date of ovulation;
- improper functioning of the appendages;
- the effectiveness of the therapy.
Folliculometry makes it possible to identify the presence of pathological diseases:
- follicular cyst - a neoplasm in the appendage, which is an egg that did not come out after the rupture of the epidermal cocoon into the fallopian tube;
- atresia – pathological underdevelopment of the DF;
- persistence – the presence of a virus in the tissues of the appendage, which prevents the full development of the egg;
- luteinization is a violation of the development of the “vesicle”, when the corpus luteum begins to develop into still immature cells.
The specificity of folliculometry is as follows:
- During the first procedure, the doctor identifies the antral follicles, one of which will subsequently become dominant.
- After 3 days, another ultrasound is performed, during which the presence or absence of DF is determined.
- And during the third procedure, the doctor determines the maximum value of DF, which indicates the approach of ovulation.
Every day it changes, grows. There are special tables, the data in which was obtained on the basis of folliculometry, indicating the norm of development.
Stimulation of follicle growth in the ovaries
Even an apparently healthy woman may not become pregnant for a long time due to the fact that her ovaries do not form a healthy egg. In such cases, if conception has not occurred for more than a year (or six months in older patients), drug stimulation of ovulation may be prescribed.
Indications for stimulation:
- anovulatory infertility accompanied by hormonal disorders;
- anovulation due to the woman’s high weight;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- preparation for IVF;
- infertility of unknown origin.
The choice of a drug regimen for stimulating the growth and maturation of follicles depends on the woman’s age, her body weight, and the results of the preliminary examination.
What groups of drugs are used to stimulate ovulation:
- menopausal gonadotropins (obtained from the urine of menopausal women) - Menopur;
- recombinant gonadotropins (synthesized by genetic engineering) - Gonal, Puregon. Details about Gonal stimulation;
- antiestrogens (drugs that block estrogen production and increase FSH levels) - Clostilbegit, Clomid, Clomiphene;
- drugs that promote timely rupture of the follicle - Prophase, Horagon, Pregnil, Ovitrel.
When planning pregnancy, as a rule, various combinations of the drugs presented above are used. The most effective drugs have proven to be those containing FSH, a hormone that stimulates the growth and maturation of follicles in the ovary.
Drug stimulation of ovulation is allowed to be carried out no more than 6 times. If successful conception does not occur, then they resort to other methods of treating infertility.
If the size does not correspond to the standards
If the follicle is 11 mm on the 11th day of the cycle or 13 mm on the 13th day of the cycle, then this size is not normal. This means that the egg matures too slowly and ovulation is unlikely. The reason for this condition is most often hormonal abnormalities: improper functioning of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland, ovaries, or this entire “ligament”.
This condition requires additional examination (in particular, you need to find out the level of hormones) and medical correction. Gynecologists often use hormonal drugs, but this does not always happen. In some cases, vitamins, drugs that improve blood circulation, herbal medicine, and physiotherapy are sufficient.
Sometimes anovulation (lack of ovulation) is associated with natural causes:
- Stress, overwork, lack of sleep;
- Poor nutrition (strict diets, in particular low-fat diets);
- Obesity or extreme thinness;
- Heavy physical work or exhausting sports training.
If these factors are excluded, there is a chance that ovulation will return on its own.