What it is
At the moment of ovulation, the egg is in “free flight”, and unprotected sexual contact leads to its fertilization. Then it moves to the uterine cavity to be secured to one of its walls. This stage takes at least 14 days.
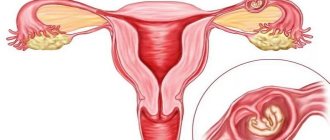
With anembryony, a fertilized egg is formed, but life either does not develop in it, or the embryo dies immediately after fertilization of the egg.
The pathological process is a malformation of pregnancy and requires the removal of the fertilized egg by mechanical curettage of the walls of the uterus. Empty egg syndrome is in second place after sudden loss of pregnancy in the early stages.
The disease can be detected in the first month of gestation, if at least 2 weeks have passed since the expected date of fertilization.
With a transvaginal ultrasound examination, the doctor is able to determine the presence of an embryo in the egg; if the data is questionable, the examination is repeated after 1 month.
Why does anembryonia develop?
Anembryonia is formed as a result of stopping the reproduction and division of the internal cell mass - a subgroup of cellular elements that normally give rise to the tissue structures of the fetus. The deviation is registered in the primary stages of gestation - from 2 to 4 weeks of pregnancy. At the time of the process, there is no change in the development of the membranes.
The result of the disease is the formation of an empty fertilized egg, which continues its spontaneous growth and development.
Important factors in the development of the disease are:
Congenital (inherited from parents) or acquired chromosomal errors and other anomalies of a genetic nature. They are capable of leading to:
- gross disruption of the synchronous development of embryonic tissues;
- changes in the structure of collagen and other protein structures;
- disruption of logical cell division and migration.
- Common autosomal abnormalities include:
- trisomy - the presence of three chromosomes in places where there should be a pair;
- monosomy – the presence of one of a pair of chromosomes;
- triploidy – an additional set of chromosomes;
- Tetraploidy is a lethal mutation at the organismal level.
An excess of circulating immune complexes in the body of a pregnant woman. Their presence in the area of small blood vessels leads to thromboembolism and other serious disturbances of local circulation at the site of the implanted egg. Experts consider antiphospholipid antibodies especially dangerous.
During the course of the pathological process, a complex of substances is produced in the pregnant woman’s body, provoking a further prolongation of gestation. In a large number of cases, spontaneous abortion is not observed. The patient experiences a further increase in HPP (determined by blood tests), and symptomatic signs of pregnancy.
Primary ultrasound confirms the successful implantation of the fertilized egg into the uterine cavity - conception has occurred, but further development takes place without an embryo.
Main causes and risk factors
The diagnosis of “anembryonia” is perceived extremely negatively by women.
A pregnancy test and hCG level test indicate that pregnancy has occurred, but its outcome is already predetermined. Patients must understand that there is no life in the fertilized egg, and there are reasons for this.
- Sexually transmitted diseases that stop mitotic processes and cause the death of the embryoblast. These diseases include TORCH infections, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis.
- Bacterial and viral infections that cause the death of the trophoblast. The embryogenesis process can be worsened by taking antiviral or antimicrobial medications.
- Irradiation after alleged fertilization - X-rays, fluorography, radiation, or being in an area with an increased risk of radiation.
- Substance abuse on the part of the father or mother, taking drugs before or during pregnancy.
- Illnesses on the father's side, in particular, genetic disorders under the influence of alcohol.
- Female alcoholism.
- Nicotine addiction.
- Abnormal pregnancies ending in fetal death.
- Being stressed or depressed.
- Endocrine system disorders, the presence of chronic systemic pathologies: diabetes, thyrotoxicosis, hormonal imbalance.
- Chromosomal mutations of the embryo that led to its early death.
Despite the large number of reasons, empty egg syndrome occurs without obvious tendencies. Doctors believe that a malfunction of the genetic bookmark is to blame.
Don't retreat and don't give up
“Why did this happen to me?” — even the strongest and most self-possessed among us succumb to despair over what happened. Alas, there is no answer to this question - dispassionate statistics claim that the threat of anembryonic pregnancy hangs over every woman, without exception, and ranges from 15% to 20%. You should not blame yourself and grumble at fate - this path leads to self-destruction. If it is impossible to change the situation, you need to try to change your attitude towards it: perhaps, if the body had not recognized the pathology of the fetus and had not stopped its development in time, then a non-viable baby with severe defects would have been born. Look to the future with optimism and firmly believe that your next attempt to become a mother will definitely be successful.
Especially for the site Babyplan.ru Zhanna Metlenkova
Symptoms
The primary symptoms of the pathology are similar to signs of pregnancy:
- no periods;
- mood changes;
- Breast enlargement and nipple pain occur;
- early toxicosis occurs;
- increased sensitivity to odors;
- the uterus increases in size, but it is impossible to determine this on your own, but an ultrasound can determine the size of the organ;
- when performing a hormonal pregnancy test, 2 stripes appear;
- When donating blood to check the hCG level, its rise is determined.
Based on the characteristic sensations, a woman may suspect the development of a new life, but to confirm her guesses, an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs should be performed.
Patients with an increased sensitivity threshold may notice nagging pain in the abdominal area, the appearance of brown discharge and a slight rise in temperature. Such signs are typical at 10-12 weeks of gestation.
Diagnostics
Pathology can be diagnosed by examining the uterine cavity and its appendages with ultrasound equipment.
At 6 weeks, the diagnostician detects the presence of a fertilized egg. It is not possible to determine whether there is life in it due to the short gestation period. The woman is advised to repeat the study no earlier than after 2 weeks.
It is impossible to rely on data from laboratory tests on the level of hCG, since the hormone increases both in anembryonics and in the case of tubal pregnancy. Unfortunately, it is impossible to make a diagnosis before 8 weeks of gestation.
In the process of enlarging the fertilized egg, it becomes possible to examine its cavity:
- absence of a yolk sac;
- lack of heartbeat;
- discrepancy between embryo growth and gestational age.
In addition to diagnostic procedures, the doctor differentiates anembryonia from other pathological processes of reproduction. Due to the fact that the structure of the reproductive organs is different, doctors repeat the procedure 10 weeks from the moment of conception. It happened that by this time the embryo was found alive.
There is also another type of pathological process: biochemical pregnancy. This is a condition in which an early miscarriage occurs, unnoticed by the woman. The reason for this phenomenon is also the lack of life of the fertilized egg.
What to do with anembryonia with high hCG
During these few days I re-read the entire Internet. Hope appears and disappears.
My last menstrual period was April 17th.
The tests were already completed in mid-May, on the 5th day of delay.
On May 19, I passed the first hCG test - 621
May 24 second hCG - 3849
Then I decided to wait.
My chest became swollen and began to hurt, sometimes I felt sick, felt nauseous, I became picky about food, I ate little, I felt nauseous from everything. I lost 2 kg.
I had my first ultrasound on June 7 (according to 7 weeks (from conception 5)
PU - 22mm, no embryo or yolk sac detected, anembryonia + hematoma.
They told me to immediately go for a cleaning or take pills for a miscarriage.
Moreover, the uzist woman asked various questions (as I understood, to confirm her diagnosis). But my answers did not agree with her diagnosis. I felt pregnant, I didn’t have any spotting, my stomach didn’t hurt, my chest hurt.
To say that I was shocked is to say nothing!
Having roared, she came to her senses. And the next day I went for another ultrasound. To another clinic. The doctor looked and said, I can’t tell you anything, for me this is not a common case. The egg is empty, but sometimes I got the impression that somewhere near the edge I heard something. And he sent me to another doctor-colleague, more experienced.
USEFUL INFORMATION: High D-dimer after transfer
He looked and made the same diagnosis as the first one, only he wrote a period of 6 weeks 5 days (June 8). And with him was a girl trainee. She looked for a long time. And he says to the doctor, “Look, like this when I look - it’s empty, but like this (at the same time he somehow turns the unit) - it’s as if there’s something there.”
The doctor agreed, but did not change the diagnosis.
He said we need to clean it up. But after my questions, is it urgent? He suggested waiting 3 days and looking again, if there are no changes, delete it.
On the same day I passed the hCG test - 50800!
But I read that hCG increases even with an empty PU.
On Sunday I’m going to have an ultrasound again, and on Friday I’ll have another hCG test.
Girls, what do you think, if they hope for anything, or is it too late?
Treatment
There is no drug treatment for the disease. To eliminate the empty egg, the “pregnancy” is terminated for medical reasons.
Artificial termination is carried out in two ways: surgical and medicinal. The treatment tactics are determined by the doctor and depend on the duration of the pseudopregnancy, clinical signs of pathology and the causes of the development of the disease.
The surgical method is reduced to vacuum cleaning of the walls of the uterine cavity under general anesthesia. Such an interruption is acceptable if the patient has uterine bleeding, and if a spontaneous miscarriage has begun.
Drug therapy comes down to taking the drug according to the regimen. Taking the medicine should cause detachment of the fertilized egg and menstruation to evacuate the anembryon.
Despite the fact that the method is non-invasive and more gentle, the desired effect may not be achieved, and therefore surgical intervention may be required.
Afterwards, a histological examination of the material is mandatory to establish the possible cause of the pathological process and prevent recurrence of the syndrome.
The next pregnancy is planned no earlier than in 6 months. After an abortion, the patient is prescribed antibiotic therapy and sedatives.
Anembryonia and hCG growth
List of messages in the topic “Anembryonia and hCG growth?” forum I want a child > I want a child
I think everything will be fine.
I didn’t hear a heartbeat at 6 from conception - three days ago. However, they saw the embryo. Tomorrow I have a second ultrasound and I’m shaking.
GOOD LUCK to you and @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@. Since we saw the embryo, maybe everything will work out. God willing.
So pull yourself together and better wait.
I had the same thing: hCG growth is excellent, growth dynamics are normal, but the fertilized egg is empty.
At this stage, hCG is not an indicative test - that’s what the doctors explained to me.
an easy pregnancy for you.
Take care of yourself and don't worry anymore.
When there is a threat, by the way, the level of hCG usually increases in order to increase the production of progesterone and remove this very threat, when everything becomes normal, the growth of hCG is correspondingly inhibited.
All rights to materials posted on the site are protected by copyright and related rights legislation and cannot be reproduced or used in any way without the written permission of the copyright holder and placing an active link to the main page of the Eva.Ru portal (www.eva.ru) next to with the materials used.
The editors are not responsible for the content of advertising materials. Certificate of registration of mass media El No. FS77-36354 dated May 22, 2009 v.3.4.168
Possible consequences and complications
Complications can arise both from treatment and from refusal to terminate the pregnancy.
If the patient refuses to terminate the pregnancy due to anembryonia, the risk increases:
- infectious processes of the uterine cavity;
- further infertility;
- occurrence of uterine bleeding.
Abortion is also accompanied by a number of possible consequences:
- coagulopathy;
- allergy to anesthesia;
- perforation of the uterine wall;
- DIC syndrome;
- secondary infertility;
- isosensitization by the Rh factor of the blood;
- uterine rupture;
- insufficient cleansing of the organ cavity;
- endometriosis;
- infection of the patient with viral hepatitis;
- septic shock and further death.
It is important to note that the earlier the disease is diagnosed, the sooner treatment should be provided. In this way, the estimated risk of complications can be significantly reduced.
Forecasts
The prognosis of obstetric pathology depends on several factors:
- age of future parents;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- number of pregnancies in history;
- method of conception.
With timely removal of the fertilized egg, the chance of a successful pregnancy and childbirth increases significantly.
Planning a pregnancy should be postponed for six months to a year. During this time, the endometrium will recover, the couple will undergo examination and, if necessary, treatment.
Prevention recommendations
A recurrence of anembryonia is not excluded, and it is impossible to prevent it. However, you can reduce the risk of illness. To do this, the patient should give up bad habits, eat right, and be thoroughly examined by a family doctor together with her partner.
If the problem is serious deviations in the spouse’s spermogram, it is possible to carry out artificial insemination using reproductive technologies.
Embryology does not stand still, and gives the most desperate couples a chance for pregnancy and childbirth.