With the arrival of winter, many of us think about how to supplement ourselves with vitamins, because in winter the body is “depleted” and does not receive important elements. But along with a lack of vitamins, there is also a risk of an excess of vitamins - hypervitaminosis. Excess water-soluble vitamins are eliminated from the body without problems. In this case, it is appropriate to talk about the harm of vitamins. Yes, yes, exactly harm. The fact is that excess fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E and K accumulate in the body and lead to unwanted side effects. We tell you why this is dangerous.
It is almost impossible to get an overdose of vitamins that enter our body from foods.
It is almost impossible to get an overdose of vitamins that enter our body from foods. Most often this happens due to taking synthetic vitamin complexes. In some cases, this, of course, may be justified, but only after consulting a doctor and conducting the necessary tests. Although taking synthetic vitamins is unlikely to lead to an overdose - after all, no one takes a loading dose - scientists suggest that even a slight excess of the daily norm can manifest itself in sleep and concentration problems, numbness, and increased irritability.
How does hypervitaminosis manifest itself?
What is hypervitaminosis - the reasons for its appearance
Hypervitaminosis is a condition that can be caused by uncontrolled use of vitamins of various groups without prior consultation with a therapist or nutritionist. Such exposure leads to poisoning of the body with characteristic manifestations. If the disease is not recognized in time, malfunctions of various internal organs and systems may occur.
Hypervitaminosis can be diagnosed based on laboratory data. In addition, an initial examination conducted by a nutritionist, gastroenterologist or therapist is important.
Primary diagnosis consists of the following steps:
- Studying a lifestyle that will tell you which of the vitamins provoked poisoning of the body.
- Examination of the external condition of the skin, nails, hair, measurement of body temperature, blood pressure and heart rate.
- A survey that will help the doctor get an overall picture of the symptoms and signs of the disease.
The following laboratory tests will help determine the presence of the disease:
- general blood analysis;
- hormone tests;
- general urine analysis.
It may be necessary to conduct instrumental diagnostics to confirm or refute malfunctions in any of the internal organs, as well as to assess the condition of the bones. Such measures include x-rays of bones, ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, collection of biological material and endoscopic procedures.
Children are most susceptible to hypervitaminosis, as they have a fast, but not always stable metabolism.
Signs of hypervitaminosis in children and adults appear when:
- constant uncontrolled consumption of foods containing an excessive dose of vitamins, for example A or C;
- regularly taking medications that include vitamins;
- single use of a drug that contains an excessive dose of any vitamin;
- the use of various dietary supplements;
- intolerance to one or more organic substances.
Chronic diseases and heredity also contribute to the development of hypervitaminosis.
The symptoms of hypervitaminosis depend on the substance that led to intoxication.
The “forgotten” vitamin for heart and bones
The name “vitamin K” refers to 2 substances – (found in plant foods) and K2 (found in foods of animal origin). And both of them are not interchangeable substances. After all, if K1 is largely needed for blood clotting, then K2 is responsible for heart health and bone strengthening. Although sometimes K2 is called the “forgotten vitamin”, because it often remains in the shadows, overlooked.
Like A, D, E, it is a fat-soluble substance. Synthetic analogs are K3, K4 and K5. In the human body, K2 is synthesized in the gastrointestinal tract. People with gastroenterological diseases or taking antibiotics for a long time are at risk of becoming a victim of hypovitaminosis K.
Significance in the body
In the human body, vitamin K plays a physiological role as a substance responsible for normal blood clotting. Supports bone health, especially in menopausal women. It is part of therapy for Alzheimer's disease and various types of tumors (there is evidence of effectiveness in the treatment of liver cancer). Responsible for the synthesis of proteins needed by the blood and kidneys. Like retinol, K2 is an important supplement to vitamin D (these substances will not work properly if you are deficient in one of them).
A lack of vitamin K often causes calcification of the arteries, cardiovascular diseases, and varicose veins. Has anti-aging properties. At one of the research institutes, scientists conducted an experiment. For some time, pensioners were given 2 servings of food rich in K-substance (spinach, cabbage, spicy greens) daily. They began to look 11 years younger. At the cellular level, rejuvenation also occurred.
Sources
Greens are the best product for replenishing vitamin K reserves. But for the substance to “work”, it is important to combine the consumption of greens with healthy fats (dress salads with vegetable oils: soybean, cottonseed, rapeseed, olive).
Good sources of the vitamin: spinach, cauliflower, broccoli, turnips. There is not much substance in animal products. Also found in coffee, tea, bacon and cheese. Table of vitamin-rich foods
| Products | Availability per 100 gram serving (in mcg) |
| Cabbage | 882 |
| Chard | 830 |
| Dandelion greens | 778 |
| Italian chicory | 255 |
Dosages
The main danger of insufficient vitamin K intake is the risk of bleeding. Deficiency can occur in children and in people taking antibiotics or anticoagulants (blood thinners). Also at risk are the category of patients with various intestinal diseases and chronic diarrhea.
Excess vitamin K can cause the death of red blood cells and liver disease. Typically, only synthetic forms of the vitamin have a toxic effect on the body.
Daily rate:
- for adults – 80 mcg.
Combines well with fats, does not combine with tocopherol, calcium and antibiotics.
Comparison table for fat-soluble substances
| Category of people | Vitamin A (mcg) | Vitamin D (mcg) | Vitamin E (mcg) | Vitamin K (mcg) |
| Newborns | ||||
| 0-6 months | 400 | 10 | 4 | 2 |
| 6-12 months | 500 | 10 | 5 | 2,5 |
| Children | ||||
| 1-3 years | 300 | 15 | 6 | 30 |
| 4-8 years | 400 | 15 | 7 | 55 |
| Men | ||||
| 9-13 years | 600 | 15 | 11 | 60 |
| 14-18 years old | 900 | 15 | 15 | 75 |
| 19-30 years old | 900 | 15 | 15 | 120 |
| 31-50 years | 900 | 15 | 15 | 120 |
| 51-70 years | 900 | 15 | 15 | 120 |
| More than 70 years | 900 | 20 | 15 | 120 |
| Women | ||||
| 9-13 years | 600 | 15 | 11 | 60 |
| 14-18 years old | 700 | 15 | 15 | 75 |
| 19-30 years old | 700 | 15 | 15 | 90 |
| 31-50 years | 700 | 15 | 15 | 90 |
| 51-70 years | 700 | 15 | 15 | 90 |
| Over 70 years old | 700 | 20 | 15 | 90 |
| Pregnant | ||||
| 14-18 years old | 750 | 15 | 15 | 75 |
| 19-30 years old | 770 | 15 | 15 | 90 |
| 31-50 years | 770 | 15 | 15 | 90 |
| Breastfeeding | ||||
| 14-18 years old | 1200 | 15 | 19 | 75 |
| 19-30 years old | 1300 | 15 | 19 | 90 |
| 31-50 years | 1300 | 15 | 19 | 90 |
Classification
All vitamins can be divided into two groups: fat-soluble and water-soluble.
Fat-soluble include organic substances A, D, E, K. Vitamins of this group can accumulate in large quantities in the liver and adipose tissue, which means that their reserves in the body may exceed the permissible dose. It is more difficult to get rid of excess accumulations of substances of this group, so the appearance of hypervitaminosis most often occurs with an excess of vitamins of this group.
Vitamins B and C are water soluble. They are able to be eliminated from the body on their own, so poisoning with these substances occurs less frequently. An overdose of water-soluble vitamins is possible only in one case - when they are introduced into the body by injection. If vitamins of this group enter the body with food, then the necessary part is absorbed, and the excess is excreted.
A
Vitamin A (retinol) is necessary for the synthesis of hormones, improves metabolism, stimulates receptors, helps the growth of bone tissue and epithelium, and strengthens the immune system.
Intoxication of the body with retinol can occur in the case of a one-time use of an exceeded dose of the drug. In addition, accumulation of the vitamin occurs due to the use of dietary supplements without observing the required dosage.
Hypervitaminosis A has the following symptoms:
- insomnia;
- decreased ability to work at full capacity, general weakness;
- emotional instability;
- hair loss, dry skin, brittle nails;
- diarrhea, nausea and vomiting;
- blurred vision;
- abnormal heart rate, slight increase in body temperature;
- painful sensations in muscles and joints.
Symptoms of liver and kidney dysfunction occur. Exceeding the concentration of vitamin A in the body in a pregnant woman can cause a miscarriage.
IN
B vitamins help the nervous system function properly and promote energy metabolism in the body. The most toxic substances in this group are B6 and B12.
Hypervitaminosis B1 (thiamine)
An excess of this substance can manifest itself as weakness, the development of various disorders of the functioning of the kidneys and liver, and the occurrence of allergy symptoms.
Hypervitaminosis B2 (riboflavin)
Excess riboflavin in the body leads to liver dysfunction, there is a high probability of primary damage to the heart muscle (cardiomyopathy), and allergies develop. An excessive dose of vitamin B2 can lead to clogging of the kidney tubules, which subsequently accumulate fluid.
Relationship between A, D and K
Vitamin A and D contribute to the effective functioning of the immune system. Nevertheless, experiments on isolated cells showed: D-substance can affect the body only with the participation of retinol. Other studies suggest that vitamin A can negate the benefits of vitamin D if there is too much of the carotenoid. One of the simplest ways to adjust the balance is to regularly receive calciferol from the sun, and carotene in the form of colorful vegetables.
Vitamins A and D also cooperate in the production of vitamin K-dependent proteins. After K2 activates these proteins, they begin to mineralize bones and teeth, protect arteries and soft tissues from infections, and prolong the life of cells.
Calcium, magnesium and K2 (or D3) also tend to work more efficiently in tandem. This must be taken into account when taking one of the named elements.
Treatment
The treatment of hypervitaminosis also depends on the excess of any vitamin. Regardless of the concentration of which substance in the body is exceeded, first aid must be provided:
- Carry out neutralization of toxic substances (detoxification).
- Adjust your diet and stop taking medications.
Pharmacy drugs
If there is an excess of vitamins B and D, diuretics (diuretics) are prescribed in order to remove excess toxic substances from the body along with fluid.
If hypervitaminosis threatens a person’s life, the administration of glucocorticoids is indicated. The most effective in this regard are Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone, Prednisone.
An effective remedy in case of excess organic matter is activated carbon. It is used to remove excess concentrations of the vitamin from the body.
Traditional methods
Folk remedies are intended primarily to relieve symptoms of poisoning. You can do this as follows:
- Take 100 g of watermelon rinds, chop them finely, put them in a saucepan and add 1 liter of water. Place on the stove and cook for at least 1 hour. Wait until the broth cools down and strain. Add the juice of 2 lemons to the resulting broth and mix everything. Drink in any quantity.
- Prepare a decoction of viburnum fruits or leaves and drink 1 liter every day.
- Make a rosehip decoction and drink 1 glass 2 times a day.
- Effective remedies in the fight against hypervitaminosis are ginger tea with honey and tea made from rowan fruits.
How to replenish supplies?
It is not difficult to pamper your body with fat-soluble elements - they are found in many traditional foods. But it is not enough to eat a vegetable containing, for example, carotene. In order for the substance to “work”, it needs fats. Simply put, be sure to eat something fatty along with a vitamin product. Well, or remember another feature: the fattier the food, the higher the likelihood of the presence of elements A, D, E or K in it.
Fat-soluble elements have their advantage. They, unlike water-soluble substances, accumulate in the body and are stored until their “services” are needed. This means you don't have to take them every day.
And yet, it is important to remember that there is always a risk of accumulating more fat-soluble substances than the body needs, and this is already a problem.
Safety rules and possible complications
If treatment is not started in time, complications may arise:
- kidney failure;
- pulmonary edema;
- numbness of the limbs;
- diabetes;
- infertility or pathologies during pregnancy, miscarriage.
If you decide to take vitamins and supplements without first consulting a doctor, remember that it is easier for the body to tolerate vitamin deficiency or hypovitaminosis than to exceed the concentration of these compounds.
To avoid the consequences of an overdose, be sure to take breaks between taking vitamin complexes. In the summer, adjust your diet and try to get nutrients from vegetables and fruits.
In addition, think over a menu in which natural products will predominate. Give preference to fresh herbs, vegetables and fruits, cereals and dairy products.
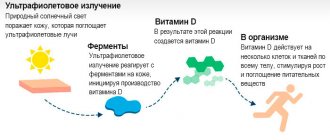
Vitamin D hypervitaminosis
Vitamin D is known as the “sunshine vitamin” and is responsible for the deposition of calcium and phosphorus in the bones. Without this vitamin we would be “soft”, in the literal sense of the word. Although vitamin D overdose is rare, it does occur due to taking vitamin supplements. Signs of hypervitaminosis D include general weakness, bone weakness, kidney stones and other kidney problems, deafness, nausea, vomiting, headache, unquenchable thirst, fatigue, excessive urination and loss of appetite. In addition, blood cholesterol levels and blood pressure increase.
Prevention
Vitamins are the same medications, so the dosage of vitamin-mineral complexes must be selected by the doctor individually. The most important preventive measure for hypervitaminosis is rational and correct intake of vitamins. It is also worth paying attention to products that are enriched with these substances. Prevention of hypovitaminosis C should be carried out in spring and winter, when there are no foods rich in this vitamin, thereby reducing the risk of developing hypervitaminosis. To prevent rickets, vitamin D is recommended to everyone without exception in a dosage of 400 IU per day, but this applies to residents of the middle and southern zone. For children from the Far North, the daily intake of vitamin D should be at least 1500 IU, without interrupting treatment in the summer. This dosage is not capable of causing hypervitaminosis, but you should always remember about it and immediately consult a doctor if symptoms appear.
Possible consequences of hypervitaminosis A
Acute overdose of the drug usually does not cause serious consequences. They are caused by chronic intoxication, which develops during a long course of treatment with high doses of retinol.
These consequences include:
- liver failure;
- renal failure;
- acute pancreatitis;
- in children - increased intracranial pressure, hydrocephalus;
- in women - hormonal imbalance with menstrual irregularities;
- in severe cases - coma and death.
Several signs that you do not have enough vitamin A in your body:
· Wounds and cuts do not heal for a long time. · Various types of skin lesions: rash, peeling, signs of aging, dermatitis. · Frequent infections with infectious diseases · Increased sensitivity of teeth · Deterioration of vision · Inflammation in the genitourinary tract · Nails grow slowly and break easily. · Insomnia · Decreased appetite. · Appearance of dandruff and hair loss · Decreased erection · Premature ejaculation.
Excess Vitamin A
With proper functioning of the body and a balanced diet, it is almost impossible to obtain an excess of vitamin from food. A healthy body can safely remove everything unnecessary or superfluous from the body. Here the main danger comes precisely from drugs from pharmacies; as a rule, they are all synthetic and can be deposited in the liver in large quantities, and this only happens if you take 100.00 IU daily and for a period of time one month.
Diagnostics
In most cases, the diagnosis of any form of hypervitaminosis without exception is based on the history of the disease, clinical manifestations, that is, symptoms, as well as the results of instrumental and laboratory data.
It is noteworthy that the diagnosis has practically no specificity either for an excess of water-soluble vitamins or for an overdose of fat-soluble vitamins.
It all starts with a thorough study of the patient’s medical history and medical history. It is important for the doctor to find out when and how it all started, what clinical signs preceded this disease, what foods were included in the patient’s diet and in what quantity, whether such conditions arose previously, and how they could manifest themselves. It is important to clarify which medications containing a particular vitamin the patient may have taken recently.
It is worth noting that in most cases, hypervitaminosis develops against the background of abuse of vitamin complexes, usually in childhood, when parents try to give their baby as many vitamins as possible, without thinking at all about the likely consequences.
The next step is to analyze the presence of clinical symptoms. In 95% of cases these are general symptoms - headache, weakness, malaise. Specific symptoms typical of a particular type of poisoning appear in 95 percent of cases. In this case, local manifestations are more characteristic of a certain type of disease.
In conclusion, it is important to determine the level of vitamin content in the blood plasma. The concentration can be increased three to five times, and in some cases even a hundred times.
For all types of hypervitaminosis, the diagnosis ends here, and then treatment begins.