Finding an effective method of contraception is a pressing issue for most modern women. The most effective technique among the variety of methods is considered to be blocking the fallopian tubes. The option is radical and irreversible, popularly called “sterilization.” The procedure requires compelling medical reasons and is carried out with the written and legally certified consent of the patient. Tubal ligation often takes place during a caesarean section, so the consequences for the patient’s body are minimized, because there is no need for another separate surgical intervention.
Sorry, there are no surveys available at this time.
Principle of manipulation
The procedure is carried out when a woman is sure that she no longer wants to have children.
Also, if pregnancy can cause irreparable harm to the woman, tubal ligation may be recommended. How are fallopian tubes tied? There are several ways to make a woman completely infertile. Let's look at them. The essence of the procedure is to artificially create obstruction of the fallopian tubes, thereby preventing the conception of a child. After maturation, the egg from the ovary enters the fallopian tubes, is fertilized and then enters the uterus. Restricting the passage makes the process impossible. During sterilization, the fallopian tubes may be clamped, cut, tied, or covered with implants.
Is it possible to restore tubes after ligation?
Of course, doctors believe that after surgery it is no longer possible to get pregnant, but history remembers situations when the functions of the uterus were restored naturally. This is explained by the fact that during the procedure the doctors violated the procedure or did a poor job.
If a woman decides to undergo restoration, it will take time to find a clinic that can perform uterine plastic surgery. If this does not happen, IVF is prescribed for pregnancy, which does not guarantee further fertilization of the body.
The health consequence of tubal ligation is the cessation of reproductive function, which women begin to regret over time (in half the cases). In medical practice, there are methods for performing surgical interventions to improve tubal patency, but their successful outcome is directly influenced by the ligation technique.
Manipulations to restore reproductive abilities are classified as difficult, incurring large time and material costs, which do not guarantee effectiveness, even taking into account the highly professional qualifications of the surgeon. According to statistics, from 2 to 26% of women decide to improve their reproductive function after tubal ligation.
The algorithm for restoring reproductive function consists of two stages:
- It is necessary to bring a postoperative report to the gynecologist, which indicates the method of tubal ligation: the possibility of carrying out the recovery procedure depends on it.
- A surgical method for restoring reproductive function is selected. Most often, the operation is performed laparoscopically. During the intervention, foreign objects (clamps, rings, inserts) are removed, tissue is cut, and the pipes are then sewn together.
The success of tubal restoration depends on the method of tubal ligation, the amount of time that has passed (the shorter the period, the greater the likelihood of a positive result), and the condition of the tubes (the more damaged the tubes, the less likely they are to be restored).
After the intervention, gynecologists do not provide any guarantees of a successful pregnancy. Another alternative method of conception is IVF. Statistics show 30% of cases of successful fertilization.
Contraindications
Before agreeing to such a procedure, a woman must undergo a consultation, during which the patient is explained all the intricacies of the intervention, consequences and indications. The girl must receive objective information in order to make a choice, agreeing or refusing DHS. In addition, the available indications for such intervention are explained.
- The patient is completely and unconditionally sure that she does not want to have children ever in her life;
- If a woman already has a child and her age has exceeded 35 years;
- For dangerous cardiovascular pathologies, pulmonary hypertension, active hepatitis forms, etc.;
- The presence of pathologies that can negatively affect the process of pregnancy or somehow aggravate the pregnancy;
- If the first three births occurred via surgical delivery (cesarean);
- If a woman has a severe hereditary disease that can pass on to her children;
- With liver failure, leukemia or diabetes;
- The patient has no pathologies that could be an obstacle to DHS.
Many patients mistakenly believe that the cesarean section procedure and subsequent tubal ligation are two interrelated surgical procedures, but this is incorrect. Even if during a cesarean section it turns out that it is dangerous for the patient to become pregnant and give birth to offspring in the future, doctors cannot perform sterilization without the woman’s consent.
Vitamins should only be taken on the recommendation of a specialist.
There are a number of certain conditions in which voluntary surgical sterilization is contraindicated. Such conditions include obesity and allergic intolerance to drugs used for anesthesia, oncological pathologies, and malignant neoplasms. If a woman is under 35 years of age or if there are adhesions or inflammatory processes in the genitourinary and reproductive structures, DHS is also contraindicated.
Bandaging is not performed on single patients who do not have a single child or women with unstable sexual and family relationships. After all, circumstances can always change, then a woman will want to give birth, but will no longer be able to, because the sterilization procedure is irreversible, and a ligated canal in both tubes makes pregnancy impossible.
The only absolute contraindication to surgical sterilization is the woman’s desire. But tubal ligation is also considered as a method of solving some problems:
- if a woman has serious pathologies that can threaten the life of the mother during pregnancy and childbirth;
- if there are contraindications to installing an IUD or taking oral contraceptives;
- genetic pathologies with a high probability of the child inheriting the disease.
Relative indications for PMT (tubal ligation) include age over 35 years and the presence of one or more children.
- inflammation of the pelvic organs;
- high BMI (body mass index);
- extensive adhesions in the pelvic cavity;
- tumors of benign and malignant nature;
- severe diseases and chronic pathologies in acute form (due to a possible negative reaction to anesthesia).
Main contraindications
Blockage of the tubes during a caesarean section is not possible when:
- the patient is severely obese;
- she has been diagnosed with malignant neoplasms in the reproductive system or intestines;
- there are inflammations or adhesions in the pelvic cavity;
- the administration of anesthesia and, accordingly, the surgical intervention itself are risky due to certain severe pathologies of internal organs;
- Allergic intolerance to substances used for anesthesia is observed.
In addition, tubal ligation during cesarean section, as well as sterilization at any other time, are not recommended for patients:
- under 30 years old;
- single, without stable sexual relationships;
- survivors of a difficult pregnancy or difficult childbirth.
The procedure is excluded when a woman is ready to undergo it under pressure from family members or, despairing of finding effective contraceptive protection for herself. Ligation of the fallopian tubes is a serious, radical and irreversible operation; doctors strongly recommend resorting to it, having carefully weighed all the pros and cons, being fully confident that you will no longer want to become a mother in the future.
Recommendations after surgery
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- tests for blood clotting, group and rhesus;
- examination and examination by a gynecologist;
- tests for HIV, syphilis and viral hepatitis;
- ECG and ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs.
It is very important to establish the fact that there is no pregnancy. One must be prepared for the fact that before a tubal ligation, a woman is constantly asked questions about refusing the procedure.
If for any reason the patient begins to doubt the need for sterilization, she may interrupt preparations for tubal ligation.
If there are no absolute contraindications to PMT, the woman will have to undergo an interview with a specialist who will notify her that after the dressing the chances of restoring fertility are minimal.
Before the intervention, the patient undergoes standard preoperative preparations with laboratory tests and other studies.
- About a week before the cesarean and ligation, the patient should stop taking all medications.
- You should not eat or drink before the intervention.
- After surgical sterilization, any physical activity is strictly prohibited; you cannot drive or get the wound wet.
- In general, contraindications after ligation surgery are similar to those after a cesarean section.
- If the intervention was carried out as an independent laparoscopic procedure, then it is necessary to avoid stress, the bath is also strictly prohibited, but you can go to the shower, having previously covered the wound from water.
- Sexual rest is also necessary; the doctor will determine its exact timing individually.
- A bloody mass may be released from the vagina in the first day or three.
- Sometimes constipation may occur in the first days, which doctors recommend avoiding with a special diet.
After resuming sexual activity, there is no need to use contraception.
If the doctor is sufficiently qualified, and during surgical sterilization all necessary standards were met, then you should not expect any negative complications. If the operation was performed poorly, then there is a possibility of serious complications and severe consequences such as sepsis, vascular damage, bleeding, inflammatory damage or allergic reactions due to the anesthesia used.
After the dressing, the woman is forever deprived of the opportunity to bear children, but the patient does not experience any hormonal problems as a result of the operation, nor does she experience menstrual irregularities.
If tubal ligation occurred during a cesarean section, then it is necessary to comply with all restrictions on the main intervention during childbirth; this will be sufficient for recovery after an additional procedure. In general, after dressing you need to:
- observe sexual rest for a month, use protection for 3-6 months;
- do not shower for 3-5 days;
- do not wear heavy items for a month;
- do not engage in active physical activity for a month;
- do not use tampons;
- do not douche for 4-6 weeks;
- After laparotomy, bed rest for 24 hours is recommended.
Rules for preparing for tubal ligation surgery
The time for tubal ligation is selected individually. It is recommended to do this after the end of menstruation, but delayed sterilization in the second phase of the cycle is not contraindicated. The procedure is also carried out 6 weeks after an uncomplicated birth, during an induced abortion using colpotomy access.
Preparation for the operation is carried out according to the standard scheme. The woman undergoes an examination during which the following diagnostic methods are used:
- clinical blood and urine tests;
- vaginal smear;
- biochemical blood test;
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the pelvis;
- blood test for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis.
The operation is carried out strictly on an empty stomach as planned. The evening before the intervention, it is not recommended to have a large dinner, drink alcohol or fatty foods.
Consequences of anesthesia
Before the procedure, it is necessary to weigh the pros and cons of surgery and eliminate the possibility of impulsive decisions, since the operation is associated with risks:
- damage to internal organs;
- inflammatory processes;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- hormonal imbalances;
- tissue necrosis.
Immediately after tubal ligation, bleeding from the genital tract may occur. During laparoscopy, women experience temporary bloating and pain in the back.
Unpleasant symptoms disappear after two to three days, when carbon dioxide is completely eliminated from the body.
Two weeks after the operation, you must visit a doctor to conduct a follow-up examination and rule out the development of late complications.
Situations in which women regret their decision to undergo sterilization are common.
After all, even an attempt to restore tubal patency (using gentle PMT methods) does not guarantee that a woman will be able to have children. Against this background, depression and mental disorders may occur.
Depending on which method of procedure you choose, various complications may occur. Every woman who decides to undergo such a procedure should know about them. So, what could be the consequences of tubal ligation in women? Let's look at each of them in detail.
If the ligation of the fallopian tubes was carried out using laparoscopy or laparotomy, then the woman was under general anesthesia. This is a prerequisite for the manipulation. After such a procedure, the patient may experience memory impairment and absent-mindedness. Another fairly common consequence of anesthesia is hair loss and deterioration of the skin.
Female sterilization methods
There are several methods of tubal ligation.
They are divided according to the type of access and the type of achieving obstruction of the fallopian tubes. Dressing is carried out using several methods:
- Ligature dressing. It is used less frequently than other methods.
- Bandaging and incision.
- Cauterization.
- Using clips. With this method, reproductive function can be restored after removing the clips.
- Tubal implants that cause inflammation in the tube and scarring. Within three to four months, the tube heals and the lumen closes.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GxRJH2f—P0
By type of surgical intervention:
- Laparoscopy. Can be performed under local anesthesia. The method is considered safe; no scars remain after the intervention. Two cuts are made - upper and lower.
- Minilaparotomy. Tubal ligation after cesarean section or some time after natural childbirth, which is agreed upon with the doctor in advance. During the operation, two small incisions are made.
- Laparotomy. It is used for inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs in women, when other methods are not applicable.
- Colpotomy. Access is made through the back wall of the vagina, so after this intervention there are no scars left on the woman’s body. But there is a restriction on sexual activity in the first month after surgery.
- Endoscopy. One of the new methods is to block the ends of the fallopian tubes with plastic tampons.
The procedure is carried out only with the woman’s consent. She undergoes a consultation and signs documents of her consent. The intervention itself lasts no more than half an hour under general or local anesthesia, depending on the type of surgical intervention and the patient’s condition. The woman goes home a few days after the procedure.
What is tubal ligation during caesarean section?
Tubal ligation is a surgical method of contraception in which the tubes are ligated (cauterized) or sutured, making them completely obstructed, and is often done during a caesarean section. Tubal ligation makes it impossible for the sperm and egg to meet: the female reproductive cell cannot move into the uterine cavity, so fertilization does not occur.
The dressing itself, that is, the obstruction of patency, can be carried out in different ways:
- by pulling with a silk ligature (ligation);
- blockage with special implants;
- laser coagulation;
- cauterization and clipping (installation of special plastic or metal clamps).
Each option has its advantages and disadvantages. When blocked by implants, recanalization of the lumen is possible, as well as the development of inflammatory reactions of an allergic nature, although the material of the implants does not imply such reactions. It is also possible to restore patency after applying metal clips. But coagulation of the lumen leads to irreversible consequences, and the risk of adhesions at the cauterization site also increases.
The fallopian tubes are ligated during the operation by laparotomy, which was performed for the cesarean section itself, and the tubes are ligated with clips or coagulation; ligation is now rarely used, as is the use of implants.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NlvL-6yOeQ8
The process looks like this:
- The dressing begins after the baby is removed and the bulk of the placenta has passed.
- The surface of the uterus is sutured, the cavity is examined and the tubes are found: they are tied or tied and cauterized, or cut and cauterized. The choice of method depends on the surgeon's skill and preferred techniques. With cauterization and intersection, the possibility of restoring patency is zero.
- After the manipulation is completed, the cavity is re-examined and sutured in layers. There is no need to leave drains.
Irving sterilization method Pomeroy sterilization method Uchida operation
Preparation
Both of these interventions are performed under anesthesia, so an allergic history should be collected and the condition of other organs and tissues should be assessed. Before the operation, a woman needs to do:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- general urine analysis;
- determination of glomerular filtration rate, urine analysis according to Nechiporenko, ultrasound of the kidneys for pathologies of the excretory system;
- blood test for infections: HIV, hepatitis B and C, syphilis;
- Rh factor and blood group;
- ECG, echocardiography for heart pathologies, as well as Holter monitoring;
- Ultrasound of the pelvis;
- coagulogram;
- consultation with a therapist;
- examination by a gynecologist, taking a smear from the vagina and cervix.
During pregnancy, X-ray examinations of the lungs are not performed, so you need to take with you the latest available fluorogram and conclusion. A week before surgery, you need to follow a gentle diet and exclude foods that can aggravate existing gastrointestinal pathologies or cause flatulence. You should not eat or drink 8 hours before surgery.
In the morning before the intervention, the woman is given an enema, and the patient is given a hygienic shower. All medications prescribed for other diseases are discussed with your doctor.
Early complications can occur during the first days to weeks after surgery. These include:
- infection;
- inflammation of the uterus and appendages;
- inflammation of the bladder or intestines;
- trauma to the bladder or intestines;
- bleeding.
Late negative consequences should be expected after a certain time, usually several months:
- adhesive disease;
- chronic adnexitis, endometritis;
- failure of ligatures or clips and recanalization of the lumen;
- ectopic pregnancy with impaired surgical technique and incomplete obstruction;
- displacement of the uterus and internal organs in the pelvis.
After anesthesia, a woman may experience severe headaches, dizziness, impaired attention and memory, mood disorders, and emotional lability.
If after surgery
If the decision to have a tubal ligation is made after a caesarean section, it is necessary to restore the body before subjecting it to similar stress again. It is recommended to perform the operation 3-6 months after cesarean by laparoscopic method.
If a woman has a history of two cesarean sections, then the third pregnancy will also be resolved promptly, at which time it is advisable to perform a tubal ligation, since a larger number of surgical births is not recommended at all.
Consequences
The consequences of tubal ligation are most often positive if the woman performed this intervention according to the following indications:
- there is no risk of getting pregnant;
- no effect on libido and hormonal function.
However, if the surgical technique is incorrect or the surgeon is insufficiently qualified, tubal restoration and pregnancy, often ectopic, can occur. And this represents a formidable complication up to and including hysterectomy (that is, removal).
Also, a woman may change her mind if the operation was performed at her request at the appropriate age and the presence of children, which will lead to a complex recanalization procedure with a low success rate.
There is an opportunity to do IVF, but this option of conception is also quite difficult and expensive.
Most women, after bandaging, experience psychological discomfort from the inability to have more children, even if they themselves wanted it. Therefore, in the early stages, the help of a psychologist is necessary.
Immediately after surgery, there are also restrictions on activity: a gentle regime is indicated for several weeks, as well as strict contraception for 3-4 months, especially after ligation or clipping of the tubes.
Is it worth using this method of contraception?
Tubal ligation is a radical type of contraception that is almost impossible to reverse in the future.
Voluntary sterilization is allowed for women of reproductive age who already have at least one child and do not want to have children in the future. Tubal ligation is indicated for a number of diseases that during pregnancy can pose a threat to life and health.
Many women have contraindications to taking hormonal contraceptives and using intrauterine devices, then sterilization becomes the only reliable means of protection. Tubal ligation is highly effective and is the most popular method of contraception among mature couples who have already had children. However, a serious complication of sterilization is the increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Although doctors warn that tubal ligation is irreversible and ask that you think carefully before doing it, if necessary, you can try to restore the function of the tubes, after which pregnancy occurs in 60-80% of women. These are microsurgical operations that take place under general anesthesia; difficulty arises with the reunification of the cut ends of the fallopian tubes.
Before you make a decision, you should keep in mind the statistics that show that many women who have tubal ligation surgery regret it. Science does not stand still, and today a new, simpler and safer method has been developed, which does not require intervention in the abdominal cavity. Its essence is the introduction of various drugs or devices into the uterus, causing local damage and an inflammatory reaction, as a result of which the connective tissue grows and the fallopian tubes become impassable.
The effectiveness of this method is more than 99%, but it is not yet used in clinics in the CIS countries.
The most reliable way is to simply dissect the pipe with a scalpel or an electric knife, after which a needle with a nylon ligature is used to puncture it in two places in the pipe in its middle part. The ends of the threads are tied and cut off. Also no less reliable is sterilization by resection of a part of the tube with immersion of its ends under the peritoneum.
Inability to conceive a child
Experts say that tubal ligation as a method of contraception is not dangerous, but it has the consequence of infertility. This may be exactly what you need right now. But everyone knows that life changes, and sometimes a person finds himself in a completely unexpected situation. Sometimes it happens that a woman deliberately makes herself infertile.
If the procedure was done by tying or tying the fallopian tubes, they can be undone. However, this does not guarantee that the woman will subsequently be able to conceive a child on her own.
In the case where implants were installed, tubal ligation in women has irreversible consequences. Such a representative of the fair sex will never be able to conceive a child on her own.
Reviews from doctors
Vlasova Lidiya Vasilievna
Surgical sterilization is a serious decision, a woman needs to carefully weigh everything, she needs to clearly understand that the chances of becoming pregnant after the operation are almost zero. Yes, ligation of the fallopian tubes is the most reliable method of contraception, but it is better to find a good gynecologist and choose a more gentle method of protection against unwanted pregnancy.
Ligation of the fallopian tubes protects against unwanted pregnancy 100%, but sterilization is a responsible step, since the process is irreparable. Operations are performed using laparoscopy, minilaparotomy, laparotomy, hysteroscopic and colpotomy access - each method takes a little time and does not have serious negative consequences.
Find out more on the topic: Women's health
Tubal ligation and consequences
Tubal ligation does not affect hormonal function, which means that menstruation will occur without changes after this. There may be a slight delay in the first cycle as the surgery is stressful on the body. Some women report a change in the amount of menstruation, but this is unlikely to be related to the dressing.
Changes in the menstrual cycle can cause inflammatory and infectious complications of surgery, as well as severe adhesions in the abdominal cavity and pelvis.
pros
The issue of choosing an effective method of contraception is always relevant in gynecological practice.
The tubal ligation technique has the following advantages:
- High contraceptive effect. Compared to other methods of preventing unwanted pregnancy, this method is considered the most reliable. The effectiveness of the procedure tends to 100%.
- There is no effect on the balance of hormones in the body. As a result, libido and general well-being are not disturbed, weight remains at the same level, and the cyclicity of menstruation does not change.
- If the operation is performed correctly, the risk of side effects is minimized, and the woman’s general health does not suffer.
- It is possible to perform an operation during a caesarean section, which eliminates the need for additional surgical interventions. Tubal ligation after childbirth is acceptable.
to contents ^
Ectopic pregnancy
If tubal ligation is done, what other consequences may there be?
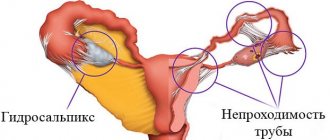
A serious complication of this procedure is ectopic pregnancy. If the manipulation is performed poorly and the fallopian tubes are poorly tied, then the male sperm can penetrate through the small lumen to the egg. In this case, fertilization will occur, but the fertilized egg will not be able to descend into the uterine cavity. As a result, the embryo will begin to develop in the blocked tube.
At this moment, the woman is sure that pregnancy is impossible. The lady is not even aware of her interesting situation, which can lead to death. If the fact of pregnancy is not established in time, then after a few weeks the fallopian tube will simply rupture under the influence of the growth of the fertilized egg, and extensive internal bleeding will begin.
Side effects after tubal ligation in women
In 98% of cases, intervention for tubal ligation takes place without consequences for patients (subject to the conditions for correct execution of the operation).
But depending on the method of the procedure, negative consequences may occur:
- bleeding through damage to blood vessels, fallopian tubes, intestines (when using a Veress needle, trocar);
- injury to nearby tissues during coagulation;
- there is a possibility of a puncture of the uterus;
- Side effects may appear after the administration of anesthesia (allergic reactions, headache);
- Infections are unlikely, but possible;
- isolated cases of disturbances in monthly cycles were observed;
- pregnancy (in 5 cases per 1000 procedures);
- neuropsychiatric disorders in the form of depression;
- the appearance of sexually transmitted infections is possible, so barrier contraception is necessary in the future;
- after more than 50% of operations, patients regret the manipulations and have a desire to restore fertility (after a while, changes in everyday situations are possible in the form of remarriage, death of children);
- general malaise of the body during the rehabilitation period (powerlessness, dizziness, indigestion, flatulence);
- rarely the appearance of inflammatory reactions in the lumbar region.
World medical practice knows of rare cases of conception after surgical tubal ligation, but mostly they ended in ectopic conception, which is possible if the technique of the procedure is violated. In 50% of cases, the phenomenon occurred due to the coagulation method of cauterization of organs.
Inflammatory processes
Tubal ligation in women has consequences in the form of inflammatory processes. It is always necessary to conduct an examination before the procedure. If this is not done, then minor inflammation can lead to serious complications. Such consequences occur especially often after the installation of implants. It happens that pathogenic bacteria are present in the uterus, but under the influence of immune defense they cannot penetrate the fallopian tubes and infect the ovaries. When implants are installed, these same bacteria penetrate along with a foreign body into the fallopian tubes and affect the gonads.
Do you want to have a tubal ligation? Read the reviews of those who have done this first. In most cases, such a procedure always ends with an adhesive process. This phenomenon in itself causes a woman considerable discomfort. The lady constantly complains of pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies during menstruation. Also, after fertility is restored, the adhesive process can cause infertility.
Reasons for visiting a specialist
You should consult a doctor immediately if you experience symptoms of pregnancy. This may be a disruption in the menstrual cycle, increased breast sensitivity, and nausea. Causes for concern should be considered pain on either side of the lower abdomen, loss of consciousness and dizziness.
Risks and complications after dressing
What is characteristic of tubal ligation is that there are no serious complications after it. Less serious consequences include infection and dehiscence. This occurs in 11% of women after mini-laparotomy and in 6% after completion of laparoscopy. More serious complications include significant and dangerous blood loss, problems caused by general anesthesia, as well as damage to organs during the operation and the need for even more significant dissection.
Despite the fact that laparoscopy has fewer complications than other types of tubal ligation operations, such complications can be more threatening. Let’s say that when inserting a laparoscope, damage to the bladder or intestines is likely. The risk of surgery increases if a woman has diabetes, excess weight, nicotine addiction or cardiovascular disease.
Risks and complications after the introduction of tubal implants
After implantation, pain in the pelvic area may not go away. In such situations, the implants are removed six weeks after insertion into the fallopian tubes. This increases the risk of developing pelvic organ diseases. It is recommended to undergo examination before carrying out the intervention. This will make it possible to make sure that the patient does not have infectious diseases of the reproductive system.
Risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy
If the process of resection of the fallopian tubes or implantation was unsuccessful, and the woman nevertheless became pregnant, then her likelihood of developing an ectopic pregnancy increases many times. This can happen several years after surgery, and most likely after three years or more.
Sterilization and tubal ligation - what's the difference?
Sometimes a woman’s life circumstances are such that she does not want or is absolutely forbidden to have children. Today, gynecologists can offer a lot of contraceptive methods. But if pregnancy is contraindicated for the patient for the rest of her life, then it is better to refuse lifelong use of contraceptive hormonal drugs and undergo a surgical sterilization procedure.
This procedure is usually performed under anesthesia and is often combined with a cesarean section, which is very convenient and does not require unnecessary incisions on the patient’s abdominal wall to gain access to the fallopian tubes. All manipulations are carried out after the baby is removed from the uterus, through the same incision. Tubal ligation, unlike other methods of contraception, gives the patient a 100% guarantee that pregnancy will never occur.
Such an operation, as already mentioned, is carried out only with the consent of a woman whose age is over 35 years old and she already has 2 or more children. If there are medical indications, then the presence of children and age characteristics are no longer taken into account, although the patient’s written consent is also necessary. DHS (or voluntary surgical sterilization) has a number of indications and contraindications, which are also taken into account when deciding on an intervention.
Sterilization involves the removal of the ovaries, resulting in a woman going through artificial menopause. This is possible, for example, if complications arise during a caesarean section and the uterus and ovaries have to be removed. Or if it is discovered during the intervention that the ovaries are cystic and there is a suspicion of cancer, in this case it is also necessary to remove everything.
During tubal ligation, only the patency of the fallopian tubes is disrupted, which does not in any way affect the woman’s hormonal system, her ovaries, that is, all genital organs are in place and working as usual. But pregnancy does not occur because there is an obstacle on the way to the egg - fertilization does not occur.
Indications
- Tubal ligation at the request of a woman over 35 years of age with two or more children, who is absolutely sure that she does not want to have any more offspring.
- Severe diabetes mellitus.
- Heart defects accompanied by pulmonary hypertension and circulatory failure stage II-III.
- Severe pathologies of the kidneys, liver, lungs, etc.
- Oncological diseases.
- It is possible for a court to make a decision on sterilization in relation to a woman with severe mental illness who has been declared incompetent.
- Multiple caesarean sections in the presence of living children.
- Severe genetic pathology that can be passed on to offspring.
to contents ^
How to “untie” the fallopian tubes
After a ligation operation, it is quite difficult to “untie” the fallopian tubes; for this, the following techniques are used:
- Balloon: patency is restored in the initial sections by introducing a catheter with a balloon with its gradual expansion, dilatation of the lumen is carried out by mechanical stretching.
- Laser: a laser light guide is inserted through the fimbrial segment (located on the ovarian side) to the site of obstruction, then the site is irradiated for 40 seconds and removed, then the procedure is repeated for up to 5 minutes. And at the end they contrast the skylight. The manipulation is performed laparoscopically.
Before performing any lumen-restoring procedures, obstruction is diagnosed using one or more of the following methods:
- echohydrohisterosalpingoscopy – washing the uterus and tubes with saline under ultrasound control;
- X-ray hysterosalpingography;
- fertiloscopy or transvaginal hydrolaparoscopy;
- diagnostic laparoscopy.
Echohydrohisterosalpingoscopy
There are contraindications for manipulations:
- uterine bleeding;
- active inflammatory process in the pelvis;
- Less than 30 days have passed since gynecological surgery;
- high arterial hypertension;
- blood system disorders;
- decompensation of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems;
- acute infectious diseases;
- severe course of endocrine pathologies.
All laparoscopic techniques require anesthesia, which causes restrictions on other organs and systems. The effectiveness of restoring the lumen after tubal ligation is quite low: if intersection or coagulation was performed, then the procedure is completely impossible. But ligation and clipping leave a chance for success.
According to statistics, out of 100 cases of tubal ligation, 18 patients subsequently became pregnant.
Tubal ligation is a reliable and practically irreversible method of contraception. Can be performed during a caesarean section. Used only in women who already have children and are over 35 years old or for medical reasons. The procedure does not in any way affect the sexual function or general well-being of the woman, but only prevents pregnancy.
Indications for dressing
According to the law, the procedure is performed only on females who have reached their 35th birthday and have at least one child. Also, dressing is mandatory after the second, and especially the third, caesarean section. In the absence of the above conditions, surgical sterilization is permitted only for medical reasons. Basically, when conception and further bearing of a baby are fraught with death, and the use of certain contraceptives is contraindicated for the patient.
Other indications for dressing:
- the presence of severe genetic diseases in the fairer sex that can be transmitted to the fetus;
- private medical pathologies - heart defects, severe diabetes mellitus, malignant tumors, leukemia, uterine rupture, etc.;
- serious mental disorders of the patient, calling into question the possibility of her viability as a mother.
Important! Blockage of the fallopian tubes during a cesarean section and the procedure for giving birth to a child are two independent, unrelated surgical processes. If, upon opening the uterus and removing the baby, it turns out that the patient can no longer become a mother without risk to health, sterilization is impossible without the prior written permission of the mother in labor.
This surgical operation is permitted when a woman consciously decides not to have any more children and clearly understands the radical nature of such a step. But the absence of pathologies that prevent dressing is mandatory even in this case.
Damage to internal organs
Such consequences occur quite rarely, but they have the right to life. If laparoscopy is performed, the doctor using the manipulators can damage neighboring organs: the uterus, intestines, bladder or ovaries. As a result, bleeding occurs.
If the laparotomy method is chosen, an unskilled surgeon may accidentally make an incision into the uterus or bladder. Such cases end rather disastrously, since the woman then becomes disabled.
If the procedure is performed on a gynecological chair, then when implants are inserted, perforation of the uterine wall may occur. This phenomenon requires immediate surgical intervention, as it can threaten the woman’s life.
Useful video
- Planned caesarean: preparation, at what time it is done...
What is worth knowing and what to prepare for if there is a planned caesarean. At what time is the operation performed, what preparation is required at home and in the maternity hospital. The course of the operation, its features, how long it takes to perform a planned caesarean section, when they are admitted to the maternity hospital. How is it different from emergency? - Spinal anesthesia for caesarean section: how...
How spinal anesthesia is performed during caesarean section, complications and consequences after it for the woman and child. Which anesthesia is better for a CS - epidural, general. Contraindications to spinal anesthesia. How long does anesthesia last, how long does it take to wear off? How does a woman feel with him?
- How to remove belly fat after cesarean section: home methods...
The main ways to remove the belly after a caesarean section, if it is large. How long does it take to recover, is it possible to lie on your stomach. How to get rid of and lose weight with a roller, wraps, vacuum. Popular abdominal surgeries after caesarean section.
- Discharge after cesarean section: what is normal in color...
Which discharge after cesarean section will be normal and which will be pathological in color and smell. How long do lochia last, what is its nature in the days after childbirth. Do you need to worry if clots, small or abundant, bright red, black, yellow, began and then ended?
- Suture after caesarean section: what happens, how to treat...
What are the sutures after a caesarean section - vertical, longitudinal transverse, their features, what they look like, which one is better. How long does it take for a suture to heal after a cesarean section, how to properly treat it and what to apply. Possible complications with the suture: inflamed, festered, itchy, hard, split. How long does it take for a seam to heal, how to remove it.
How is the operation performed?
There are different methods for ligating the fallopian tubes, all operations are performed under general anesthesia, sometimes spinal anesthesia is used, the average duration of sterilization is 30–60 minutes.
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy procedure
The most popular method of tubal ligation has a short recovery period, can be performed under local anesthesia, and after the operation, stitches and scars are practically invisible.
How to tie the tubes:
- The doctor makes a small incision on the abdominal wall, and the necessary devices and instruments are inserted into it.
- The abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide to improve vision.
- The surgeon examines the internal organs of the reproductive system, reaching the tubes.
- To obstruct patency, laser, electrocoagulation, photocoagulation are used, clips, staples, and rings are used.
- To avoid burns to surrounding tissues, the abdominal cavity is washed with saline solution.
After the procedure is completed, the woman is transferred to the ward, and if there are no complications, she is discharged after 2-3 days.
Minilaparotomy
A simple, inexpensive method of surgical intervention that does not require highly qualified surgeons.
Operation stages:
- The doctor makes an incision 2–3 cm long under the symphysis pubis.
- Examines the pelvic organs, finds the tubes.
- Cauterizes tissue or installs clips to obstruct patency.
This method of operation is used after childbirth, but it is not suitable in the presence of uterine fibroids or obesity.
Laparotomy
During laparotomy, the abdominal cavity is completely opened
During the operation, a suprapubic or midline incision is made and the abdominal cavity is completely opened. The operation has many disadvantages - a long recovery period, a high probability of developing infectious complications, noticeable scars, which is why it is used during or after a caesarean section.
You will have to spend 7–10 days in the hospital under the supervision of a doctor, after which the stitches will be removed.
Hysteroscopic and colpotomy access
Hysteroscopic access requires special equipment that allows you to influence the inner lining of the pipes through coagulation. The advantage is that there are no incisions; the device is inserted through the vagina into the uterine cavity, then advanced to the tubes, and the woman is discharged from the clinic within a day.
Hysteroscopy procedure
Colpotome access - small incisions are made on the back surface of the vagina, they go to the tubes, and pull them into the hole. The part is excised, tied with surgical threads, or a clamp is installed, or cauterized, returned to its place, and sutures are placed on the incision.
The advantage is low cost, the disadvantage is that there is a high probability of infection.
Ligation is carried out in the second phase of the menstrual cycle, 1.5 after an abortion, 2–7 days after a natural birth, or during a cesarean section.