The fourth month of pregnancy “opens” the most pleasant and safest trimester in general – the second. By the fourth month, all the unpleasant phenomena associated with toxicosis should have subsided, in any case, their intensity has noticeably decreased. Nausea and vomiting are often replaced by increased appetite - the baby continues to actively grow and develop, requiring nutrients and beneficial substances in the required quantities. The fetus is now growing, as if in a fairy tale - by leaps and bounds, and by the end of the fourth month, a woman for the first time, with a sinking heart, can feel its first tremors and movements. However, it should be taken into account that the issue of feeling the first tremors is very individual: many mothers can feel the first movements of the baby only next month. It all depends on the woman’s physique, anatomical features, and whether the woman is “expecting” for the first time or again.
Despite the fact that the second trimester of pregnancy, which begins with the fourth month, is considered the calmest and safest, the expectant mother, as before, needs to be careful. Among other things, eat well, walk in the fresh air, rest and get enough sleep, monitor your weight and blood pressure.
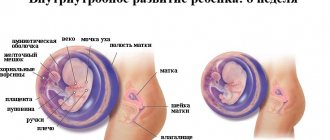
Baby four months pregnant
This month, the formation of the child’s internal organs is almost completed: the kidneys independently excrete urine into the amniotic fluid, the adrenal glands produce hormones, all functions of the small body are controlled by the nervous and endocrine systems, and the immune system is actively developing. The development and growth of the baby's brain continues: the fourth month is marked by the formation of the cerebral cortex.
Now the placenta performs the function of transporting all nutrients and useful substances to the child, it is also responsible for removing harmful substances and waste products, and for protecting the baby from harmful viruses and bacteria.
In the fourth month of pregnancy, the baby already bends his legs and arms, clenches his palms into fists, and develops grasping and sucking reflexes. In the same month, hair on the head, eyebrows and eyelashes will begin to grow, and nails will begin to form. At the same time, an embryonic fluff, lanugo, appears on the baby’s body, which will retain a special protective lubricant secreted by the skin.
The child already knows how to squint his eyes, and by the end of the month he will open his eyes completely. At the end of the fourth month, the baby will grow to 16-20 cm, its weight reaches 200 g.
Fetal development
By the beginning of the second trimester, all the baby’s organs have already been created. Within a month they increase in size and continue to ripen.
At the beginning of the month, the child is 6.5 cm in length and weighs just over 120 g. By the end of the month, the weight is 90 g and the height is 10–11 cm.
What has changed in fetal development:
- In the 4th month of pregnancy, the baby's body stretches. From now on, his movements will train the muscles of the back and neck. Facial features are now clearly visible on the ultrasound image. The facial expression becomes more and more baby-like.
- A baby's skin is thin and transparent, so blood vessels are clearly visible.
- At this point, the fetus closes its eyelids and opens them again at 26–27 weeks.
- His joints and limbs are flexible, he moves more and more, clenches his hands into fists, and changes his position.
- From the 16th week you can feel its movements as a faint fluttering.
- The fetus trains the diaphragm through breathing attempts and hiccups. He often sucks his thumb.
- The creation of organs is completed, the stomach, intestines and kidneys are already working. Nutrients are absorbed through the placenta, and waste is sent to the mother through the umbilical cord.
- The pancreas and liver begin to function.
- The heart is also fully developed in the middle of 4 months. At this point, it pumps about 28 liters of blood per day, and immediately after birth, the newborn's heart will pump about 350 liters of blood. The baby's heart sounds are clearly audible during a medical examination.
- By the end of the month, the production of insulin in the pancreas and, consequently, glucose in the child’s blood leveled out. The thyroid gland begins to produce hormones at the 4th month.
- The baby develops a lanuto hair covering, an atavistic echo of prehistoric times, which serves to protect the skin from vibration, noise and pressure. In addition to lanuto, the child’s skin has a lubricant similar to cheese. It protects it from softening by amniotic fluid and will also disappear after birth.
- Hair and eyebrows grow, but the color and structure of the hair are determined only at the time of birth.
- The child already has a fingerprint that is unique.
- The foundations for sensory perception are laid. Now the child can hear the first sounds and respond to them, for example, to music.
Feelings and possible problems in the fourth month of pregnancy
This month there is a gradual improvement in overall well-being: toxicosis goes away, increased appetite appears, and activity increases. The figure changes more noticeably: the uterus grows quickly, accordingly, the tummy is rounded and the waist is smoothed, the mammary glands enlarge even more, but, fortunately, their soreness and swelling gradually disappears.
In the fourth month, age spots may appear on the skin, and existing freckles may appear or darken. In addition, the stripe on the abdomen becomes more pronounced, and the nipples and areolas also darken.
Due to the large amount of fluid in the body, increased sweating and a slight increase in whitish vaginal discharge are possible. For any changes in the nature of the discharge - if its color, consistency changes, the discharge is accompanied by itching and/or burning - you should consult a doctor, because with such symptoms, treatment of the associated infection is most likely necessary.
At 4 months of pregnancy, periodic headaches and dizziness are still possible, and slight bleeding of the gums may occur when brushing your teeth. There may be some nasal congestion, and if small vessels cannot stand it, nosebleeds.
Constipation can become an extremely unpleasant problem, as a consequence of hormonal changes in the body and the pressure of the enlarged uterus on the intestines. It is better to avoid constipation by carefully monitoring your diet, and if constipation does occur, try to quickly improve the functioning of the digestive system and intestines in particular. After all, constipation is often the cause of a painful and delicate disease - hemorrhoids.
In the fourth month, the uterus already extends beyond the pelvis, and its growth continues in the abdominal cavity. A significant enlargement of the uterus is accompanied by sprained ligaments, which many expectant mothers feel in the form of nagging pain in the lower abdomen. But in order to establish the nature of the pain and eliminate the possible risk of losing the child, you should definitely consult a doctor about the pain.
More on the topic
Pain in the first month of pregnancy
Signs of pregnancy in the first month
Fifth month of pregnancy
Second month of pregnancy
Seventh month of pregnancy
Bleeding
The appearance of bloody discharge accompanied by pain in the abdomen and lower back is a very dangerous symptom, indicating the onset of spontaneous abortion. The discharge is bright red and may contain blood clots. If such symptoms appear, you should immediately seek emergency help. If timely measures are taken, miscarriage can be prevented.
Minor, painless discharge that appears after intimate relations may be a sign of cervical erosion. This condition should be treated after delivery.
Nutrition in the fourth month of pregnancy
One can only envy the appetite of a pregnant mother at this stage of bearing a baby: toxicosis has become just an unpleasant memory, and now the woman is increasingly drawn to “eat, snack, nibble.” At the same time, it is now simply necessary to monitor your weight in order to prevent excessive weight gain and to avoid less or more severe complications associated with it (for example, stretch marks on the skin or, worse, diabetes mellitus in pregnant women).
Therefore, it is important to properly organize your diet and choose those products that can satisfy the needs of the woman’s body and the life growing inside her for useful and nutritious substances. When compiling a daily menu, it should be taken into account that on average a woman should gain within a month in the range of 2-2.5 kg.
Experts recommend organizing nutrition in the 4th month of pregnancy in such a way as to prevent hunger and consume food to its maximum benefit. So, you should eat more often, but in small portions, eat most of the food in the first half of the day: the first and second breakfasts should be sufficiently nutritious, lunch should be the most satisfying, and in the evening you should eat easily digestible foods. At the same time, you are allowed to eat fruits and vegetables in almost unlimited quantities throughout the day (with the exception of citrus fruits, fresh cabbage, which causes bloating, and potatoes, which are rich in carbohydrates and starch).
Food for a pregnant woman should be as natural as possible: fast food, semi-finished products, smoked foods, marinades are prohibited. In addition, you should give up salty foods (salt provokes fluid retention in the body and the development of edema), sweets and confectionery delights (“fast” carbohydrates contribute to very rapid weight gain, in addition, they do not provide any “benefits” to a developing baby).
The diet of the expectant mother must include lean meat and fish as the main source of protein. Milk and cottage cheese will provide the body with the necessary calcium, and fermented milk products will have a beneficial effect on intestinal function. Again, for normal intestinal motility, you will also need fruits and vegetables, which will also supply vitamins, macro-, and microelements. Cereal porridges, whole grain bread, vegetable and butter, and nuts should also be integral “elements” of a pregnant woman’s diet. To avoid anemia, you should enrich your diet with foods rich in iron - beef, liver, pomegranates, dried apricots.
However, it should be taken into account that iron is poorly absorbed from food; it may be necessary to take it additionally as part of a vitamin-mineral complex. In addition to the increased need for iron at this stage, the pregnant woman’s body, and with it the baby in her mother’s tummy, needs sufficient amounts of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium, and B vitamins. Therefore, it is quite possible that the doctor will decide to take the pregnant woman one or more other vitamin and mineral complex.
TEDDIE Club responds:
Are there norms for weight gain during pregnancy?
Traditionally, pregnant women think about the issue of weight gain. Today there are no clearly defined norms for weight gain by week, it’s just worth remembering the following: the more excess body weight before pregnancy, the less weight gain should be while expecting a child. And vice versa - thin mothers-to-be usually gain more weight and faster.
The main thing is not the number of kilograms gained, but what foods your diet consists of. Food should be varied and moderate. It is better to eat in small portions, but often (5-6 times a day).
The average energy expenditure of a pregnant woman's body increases by 200-300 kcal per day in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters, and in the first it remains almost unchanged! Therefore, we wish to always adhere to the ideal body mass index – 20-25.
Sex in the fourth month of pregnancy
Is sex acceptable in the fourth month of pregnancy? Very much so, but: provided that the doctor leading the pregnancy did not voice warnings about the impossibility of intimacy during this period. Sex in the fourth month of pregnancy also acquires new colors and shades because now, after the first months of the body’s adaptation to the new state, the woman seems to be “reborn” and is capable of physical love with new strength and rapture. All this, of course, is great, but there are very clear contraindications for which it is better to refuse intimacy now.
These could be:
- spotting, vaginal bleeding;
- high risk of miscarriage;
- damage to the amniotic sac;
- placenta previa or low-lying placenta;
- genital tract infection in women;
- sexually transmitted infections in a spouse.
The appearance of whitish discharge from the vagina.
Usually, watery milky discharge (leukorrhea) is not a pathology, it is similar to the discharge that occurs before menstruation. If the discharge causes discomfort, use sanitary pads. Wear cotton underwear and avoid wearing tight clothing. Be sure to tell your doctor about this. You may need to take an additional genital tract smear. If candidiasis (so-called thrush) is diagnosed, the doctor will advise treating it. Do not ignore his recommendations, because usually this infection does not go away on its own, and during the passage of the birth canal the child may become infected (children may develop oral candidiasis, treatment-resistant diaper rash).
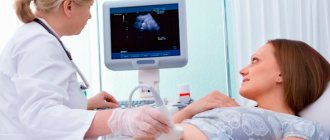
Tests and examinations at 4 months of pregnancy
In a normal pregnancy, the pregnant woman will have a “date” with the doctor only once this month. During a routine visit, a specialist will measure the expectant mother’s weight and blood pressure, listen to the fetal heart, and perform palpation to determine the size and height of the uterine fundus. In addition, a urine test will traditionally be taken to identify protein and determine sugar levels.
The woman may be advised to undergo a so-called triple (or “simplified” double) test. This screening test measures the blood concentrations of three substances produced by the mother's body and placenta: alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and estriol (E3). The optimal time for it is considered to be 15-16 weeks of pregnancy. Prenatal screening in the form of a triple test can identify the risks of chromosomal abnormalities and fetal malformations, such as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, and neural tube defects. However, it should be remembered that the triple (double) test is in no way diagnostic; it can only be used to suggest increased risks. If the results of the analysis are unsatisfactory, the woman will be recommended an in-depth examination.