Third screening studies
The third screening includes the following studies:
- Ultrasound of the fetus . The doctor checks the visual condition of the fetus, the correct functioning of the placenta and its presentation, and the level of amniotic fluid.
- Cardiotocography (CTG) allows you to determine the heartbeat and assess the general condition of the fetal heart muscle. During a CTG test, two devices are attached to the abdomen: one records uterine contractions, the other records the condition of the fetus. Measurements are taken at the moment of maximum activity of the fetus and at the moment of rest, lasts about half an hour, depending on the activity of the fetus at the time of the procedure.
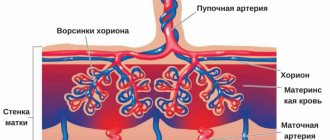
- Dopplerography allows you to assess the state of the circulatory system in the placenta. Doppler research is no different from ultrasound diagnostics.
In addition to basic studies, if indicated or at the request of a pregnant woman, additional biochemical studies , which includes the following indicators:
- AFP (alpha fetoprotein);
- gonadotropin (hCG);
- marker to determine the risk of Down syndrome;
- PL (placental lactogen).
Procedures
The list of mandatory studies includes ultrasound diagnostics, and instead of biochemical screening, CTG with Dopplerometry is prescribed. But if there are certain risks, then blood biochemistry is also prescribed.
A blood test can provide detailed information.
Ultrasound
When conducting ultrasound diagnostics, the state of fetal development, the level of motor activity and location in the uterine body, the state of the placental structures and the volume of amniotic fluid are assessed. When conducting this examination, the specialist clearly examines the baby’s skull and face, so he can accurately determine whether the baby has a cleft palate or a cleft lip.
If the results of the third ultrasound screening reveal abnormalities, the specialist may prescribe an additional ultrasound examination a little later, for example, after 35 weeks of gestation.
CTG
Carrying out a cardiotocographic examination helps to timely identify problems with oxygen supply based on the baby’s heartbeat in various phases of life (for example, while awake or asleep). Ultrasonic equipment is also used during the process, but the image is not displayed on screens. Instead, the monitor records the heart rate, slowing down or excessively accelerating the heart rate in accordance with the method of stimulation used during the testing process.
If such an examination shows the presence of negative conditions, the doctor may decide on hospitalization. Sometimes there is even a need for early birth.
Doppler
Doppler ultrasound is the name given to ultrasound diagnostics of blood vessels in the circulatory system. As a rule, such an examination is carried out in an ultrasound room, only on a device equipped with similar functions. During the examination, the specialist evaluates the uterine vascular canals, as well as the blood umbilical or placental structures, the maturity and functionality of the child’s vascular system.
During pregnancy, many suffer from skin irritations
Using Doppler ultrasound, the speed of vascular blood flow, arterial-venous patency, how blood moves through the vascular channels, etc. are assessed. The data obtained help the specialist assess the sufficiency or insufficiency of fetal oxygen supply, the presence of nervous system or cardiovascular disorders, etc.
Biochemistry
If necessary, biochemical laboratory blood diagnostics are prescribed.
- During biochemistry, indicators of hormonal substances such as hCG, ACE, free-form estriol and placental lactogen are determined.
- These hormonal substances are informative indicators of successful fetal development, without any chromosomal abnormalities.
- If the level of these elements exceeds acceptable standards, then suspicions arise regarding the presence of developmental defects and genetic abnormalities in the fetus (Edwards, Shereshevsky or Down syndromes, etc.).
- If previous screening studies made it possible to assess the risk of developing such conditions, now experts speak with complete confidence about the presence or absence of these pathologies.
Depending on the specific period of the test, the results obtained will be more or less accurate.
Screening indicators 3: what they look at
The third screening is an important step in preparing for the birth of the baby .
At the third screening, the position of the baby in the womb (presentation), the functioning and thickness of the placenta, the general condition of the fetus and cervical pharynx are determined, which is the determining factor when choosing between a cesarean section and natural birth.
- An ultrasound examines the fetus in more detail: the approximate weight of the fetus and the diameter of the head are determined, and the development of the brain is assessed.
- Cardiotocography determines the state of the fetal oxygen supply system, reveals the presence or absence of hypoxia, which occurs as a result of disruption of the placenta or when the umbilical cord is entangled in the neck.
- Dopplerography determines the state of the myocardium and nervous system of the fetus, assesses blood flow in the placenta, which also helps to identify a lack of oxygen (hypoxia).
After a general assessment of the results of Dopplerography and cardiotocography and receipt of results indicating hypoxia, the doctor can admit the pregnant woman to the maternity ward for observation, and if the life of the fetus is threatened, perform an emergency cesarean section.
If a general ultrasound of the fetus reveals abnormalities, additional biochemical studies will help confirm or refute concerns. Analysis for AFP allows us to identify fetal death and a predisposition to the birth of a child with chromosomal abnormalities (Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome). An analysis of hCG levels can reveal a predisposition to chromosomal abnormalities, gestosis, developmental delay and missed abortion.
Indications for screening
In fact, third trimester screening is an opportunity to obtain important information about fetal development and take timely measures to eliminate existing abnormalities or pathologies. Screening studies are usually prescribed for each trimester of pregnancy, but sometimes there is a need to repeat them and additional studies. There are a number of factors under which a third screening is necessary:
- If the mother has suffered a viral infection;
- When the parents are related by blood;
- If there have been previous cases of stillbirth or miscarriage;
- If the mother has unhealthy habits such as alcohol addiction or drug use;
- If prenatal developmental abnormalities were detected during previous screenings;
- If during pregnancy the mother is forced to take dangerous medications;
- When the pregnant woman is over 35 years old;
- If there are any abnormalities or pathologies of hereditary origin in the family history;
- If the patient works in an occupation that is harmful to health, or is intensively engaged in physical or mental activity.
Typically, in such situations, traditional ultrasound screening is supplemented by other studies.
At what stage, how many weeks 3 screening during pregnancy
When to do the third screening during pregnancy? This screening is planned in the last trimester of pregnancy, namely in the period from 32 to 36 weeks. At this stage, many of the fetal organs are already fully formed and the baby will maintain its position in the uterus until birth (head or pelvic presentation). If a pregnant woman’s condition is suspected of deteriorating, the doctor may send her for a third screening a little earlier.
First, mandatory studies are carried out: ultrasound, cardiotocography and Dopplerography. As prescribed by the doctor, additional biochemical screening is performed after 2 days. It is worth noting that when pathologies are detected in the fetus, only the woman makes the decision to continue the pregnancy. This applies only to those cases where there is no danger to the life of the mother in labor (intoxication due to fetal death, bleeding).
Third screening during pregnancy: what is looked at during the diagnostic process
The latter screening consists of ultrasound diagnostics and cardiotocography, and the determination of biochemical parameters can be indicated only in exceptional cases when there is a risk of genetic abnormalities.
Ultrasound in the third screening
Ultrasound screening is necessary to measure the physical parameters of the fetus and their compliance with established standards, as well as to assess its general condition. At the time of the study, the following fetal parameters are determined:
- movement activity;
- location in the uterus;
- degree of aging of the placenta;
- amniotic fluid norms;
- level of physical development.
On a note! During this gestational period, the diagnostician excludes the presence of a cleft palate in the fetus, as well as a cleft lip.
Doppler testing in the third screening during pregnancy
Another component of the third screening is Doppler monitoring. Doplegorrhaphy is performed during an ultrasound using a special device that displays the state of placental blood flow. This helps to establish the presence of oxygen starvation in the baby, the degree of hypoxia, as well as most cardiovascular abnormalities.
CTG in the third screening
Additionally, the woman undergoes cardiotocography. A special device measures the baby’s heart rate, its activity, reaction to external stimuli, as well as the frequency of uterine contractions in a woman.
During the study, two sensors are attached to the abdomen: one records the fetal cardiac activity, the other displays the activity of the uterus. The procedure lasts from 15 to 40 minutes, which depends on the baby’s mood: the device needs to record the work of his heart at the peak of activity and rest.
Important! CTG is not included in the latest screening, but obvious signs of hypoxia are the reason for its implementation.
Blood test in the third screening during pregnancy
If two previous screenings showed abnormal development of the baby, the third screening also shows a biochemical blood test. The following blood parameters are determined:
- hCG (gonadotropin);
- AFP (alphafetoprotein);
- PL (placental lactogen).
Important! The test results allow us to assess the risk of such abnormalities in the baby as Down Syndrome, as well as Shereshevsky, Edwards. However, it is important to remember that many factors influence blood counts, so you need to adhere to the rules for donating blood.
Indications for screening
The third screening is a routine test in the third trimester. But a woman, according to her own convictions, may refuse to carry it out, thus jeopardizing not only the baby’s life, but also her own. General ultrasound of the fetus, cardiotocography and Doppler ultrasound are prescribed to all women who are registered for pregnancy.
Additional biochemical screening is carried out for special indications:
- the age of the woman in labor is more than 35 years;
- the presence of children with chromosomal pathologies;
- serious pathologies in a previous pregnancy and fetal death.
Additional research is not necessary, since some women are convinced that they will give birth to any child: sick or healthy.
When is the third screening done?
The third screening during pregnancy is carried out from the 30th to the 36th week of gestation. It is indicated for all women. Carrying out the 3rd screening, including ultrasound of the fetus and placenta, cardiotocography, is indicated for absolutely all women according to the standards for examining pregnant women.
There are no contraindications to conducting research.
If desired, a pregnant woman has the right to refuse the examination; for this purpose, a written refusal is issued.
Indications for additional examination include:
- The woman is over 35 years old. Every year, the risk of having a child with genetic abnormalities increases, as well as deterioration in the functioning of the placenta.
- Existing children with Down syndrome. This situation requires control by a geneticist.
- Frozen pregnancy, history of intrauterine fetal death. These problems are often associated with developmental defects and poor functioning of the placenta.
- Exposure to radiation on one of the parents before pregnancy, taking medications that have a teratogenic (disturbing the normal development of the fetus) effect. These factors influence the quality of the genetic material and cause defects and structural anomalies.
In addition, watch the video:
Preparing for the third screening
Standard third screening studies (ultrasound, CTG and Dopplerography) do not require special preparation. By the third trimester, the uterus has reached a large enough size to allow the fetus and placenta to be viewed without the need to fill the bladder, as happens in early pregnancy.
It is recommended to spend more time in nature and be less nervous so that the baby can move more actively during CTG. You can stimulate fetal activity with a small sweet snack before CTG.
If, in addition to the standard set of studies, you need to undergo biochemical screening, then in order to obtain correct results you must prepare for it in advance and follow the following rules:
- Refusal to eat 12 days before the test.
- Two days before the test, exclude sweets, fried and salty foods.
3rd trimester screening – mandatory or not?
The comprehensive examination to which pregnant women are referred is called screening; Doctors also say “prenatal screening” - that is, prenatal. Each trimester has its own screening, which means that the diagnosis is carried out three times during pregnancy. Only the first examination is included in the list of mandatory ones; the remaining two women undergo it at will, however, gynecologists recommend not to refuse the second and third screenings in order to detect possible pathologies in the fetus and diseases in the mother in time.
The third comprehensive examination of a pregnant woman is carried out between the 30th and 36th weeks. By this time, important changes have occurred in the baby’s body that require medical supervision:
- by the 3rd trimester, the baby should gain significant weight and grow in length;
- the skin becomes denser, a source of energy is formed under the skin - a fat layer;
- the day before, in the 2nd trimester, the brain and central nervous system developed intensively;
- the development of the lungs is in full swing, which will begin to function immediately after birth;
- the volume of amniotic fluid increases;
- the unborn child is located in the uterus in a certain way relative to the internal os (cephalic, pelvic and other presentations); however, on the eve of birth the baby sometimes changes position.
In the middle of the 3rd trimester, organs and tissues are formed, the fetus becomes a full-fledged little person.
The set of procedures for the third screening varies - depending on the preliminary diagnoses. The woman will:
- Ultrasound - examination of the fetus using ultrasound;
- Dopplerometry is a type of additional ultrasound that determines the speed of blood flow in the umbilical cord and placenta;
- cardiotocography (CTG) - assessment using heartbeat sensors of the unborn child; the study is prescribed when the doctor suspects hypoxia (oxygen starvation) in the fetus;
- biochemical blood test - taken when a threat of a genetic abnormality in the fetus is detected, usually 2-3 days after the hardware examination; Blood taken from a vein is examined in the laboratory.
Of course, the expectant mother has the right to refuse prenatal diagnostics on the eve of childbirth, especially if she feels excellent and previous tests showed that everything is fine with the fetus. But in the later stages, unpleasant surprises cannot be ruled out in the form of sudden sores - for example, gestosis (a dangerous pathology that occurs exclusively in pregnant women) or dysfunction of the placenta - a temporary organ that nourishes and protects the fetus. Such misfortunes often begin asymptomatically. A comprehensive examination will help; your health is still normal - you feel calmer; if any deviations are found, the doctor will select a therapy that will avoid premature birth and other undesirable consequences.
In a number of situations, the timing of the third screening is shifted - diagnosis is carried out earlier, at 28–30 weeks. This happens if:
- the woman’s health deteriorates;
- signs of fetal hypoxia appear: the number of movements decreases, the amplitude of movements decreases;
- The doctor suspects genetic disorders in the baby.
Who needs the third check first?
Expectant mothers whose pregnancy is not considered successful or is accompanied by increased risks need screening in the last weeks without any reservations. These are those women who:
- based on the results of previous examinations, problems with fetal development were discovered;
- past pregnancies ended in miscarriages and stillbirths;
- age exceeded 35;
Doctors strongly advise older expectant mothers to undergo screening in the 3rd trimester - the partner and father of the unborn child is a close relative;
- a viral infection was diagnosed during pregnancy;
- problematic heredity - there were cases of genetic abnormalities in the family;
- Harmful conditions at work, heavy physical or mental stress.
The risk group also includes irresponsible mothers who are prone to alcoholism and drug use; Those who, during pregnancy, took medications prohibited for pregnant women should also be checked.
Tasks of the last screening
The fetus grows, the mother’s body adapts to the developing child. At this time, it is important to find out whether the baby’s weight and height are normal, and whether any developmental anomalies have appeared; whether female organs can cope with the increased load. The same hypoxia of the fetus is sometimes caused by vessels compressed by the grown uterus, through which blood flows more slowly; namely, the baby receives nutrients and oxygen through the bloodstream.
During screening the following is diagnosed:
- fetoplacental insufficiency - pathological changes in the condition of the placenta that interfere with the normal functioning of the temporary organ;
- fetal hypoxia;
- intrauterine growth retardation - including due to poor functioning of the placenta, hypoxia;
- diabetic fetopathy in the unborn child - disturbances in the development of organs due to diabetes mellitus in the mother;
- fetal infection;
- genetic abnormalities (they are generally determined during the second screening, when the baby’s organs are already formed; subsequent diagnostics confirm or refute previous data);
- entwining the baby with the umbilical cord.
Based on the results of the examination, doctors decide whether the birth will be natural or by caesarean section.
How to prepare for your 3rd trimester screening
For an early ultrasound, the expectant mother needed to drink a couple of glasses of water half an hour before the procedure to fill her bladder; then the uterus would temporarily shift and assume a position in which the device could better “see” the tiny embryo. By the 30th week, the fetus is quite accessible for hardware examination; even small details of the body are visible, as well as a “photo portrait” of the grown-up baby. A pregnant woman no longer needs to fill her bladder with water, and the woman comes to the ultrasound without preparation.
For accurate CTG readings before the examination:
- avoid worries and stress;
- get a good night's sleep;
- walk more in the fresh air;
Walking in nature will strengthen the nervous system, which is important before undergoing a comprehensive examination - on the eve of the procedure, eat candy or other sweets - then the sweet tooth in the womb will perk up; if the baby is lethargic or even falls asleep, the CTG will be uninformative.
When a pregnant woman has a blood test for biochemistry, she will have to prepare more seriously:
- biomaterial is donated in the morning, on an empty stomach, so you need to eat your last meal 12 hours before the procedure;
- 2–3 days before the test, exclude fried, spicy foods, smoked foods, and marinades from the menu; refrain from foods that provoke allergies - citrus fruits, chocolate.
Well, don’t tremble with fear in front of the doctor’s office; The “torture” will end quickly, but your nervousness will be transmitted to the child, which will lead to erroneous results.
Ultrasound in the 3rd trimester of a pregnant woman is performed free of charge - there is an order from the Russian Ministry of Health in this regard. If the study shows that the fetus most likely has developmental defects, the doctor will refer the expectant mother for additional examination (Doppler testing, CTG) - there is also no need to pay for this.
But when a woman decides to check her health using additional diagnostics without a doctor’s prescription, she will have to shell out money. Some pregnant women do not trust specialists at public medical institutions at all and go to private ones. A lot of clinics offer services; in the capital, a set of diagnostic procedures will cost expectant parents about 2,300 rubles. There will also be those who are ready to examine a pregnant woman for 600 rubles, but be careful: cheap does not mean quality and safety.
Interpretation of the results of screening 3: norms
Indicators of the norm of ultrasound of the third screening:
| Index | Normal (32 weeks) |
| Placenta thickness | 25.3-41.6 mm |
| Maturity of the placenta | I-II (degree) |
| Amount of amniotic fluid | 81-278 mm |
| Condition of the cervix | Closed |
| Cervix | 3 cm or more |
| Head circumference | 309-323 mm |
| Fetal weight | 1790-2390 gr |
| Abdominal girth | 266-285 mm |
| Humerus length | 55-59 mm |
| Femur length | 62-66 mm |
| Fruit length | 43-48 cm |
The normal CTG result indicators are 8-12 points. When assigning a total number of points, doctors summarize the indicators of the following parameters: basal rhythm and amplitude of heart contractions, deviations from the usual rhythm, slowdown and acceleration of heart rate. If the CTG indicator is from 6 to 7 points, then we can talk about possible deviations in the condition of the fetus. If the CTG value is below 5 points, the pregnant woman is strongly recommended to undergo conservation.
The permissible number of fetal heart beats is from 140 to 160 beats/min.
Doppler ultrasound normal indicators:
| Index | Norm |
| Blood flow in the uterus | 0.34-0.59 (resistance index) |
| Blood flow in the umbilical cord | 0.50-0.74 (IR) |
Biochemical screening norm indicators:
| Index | Norm |
| hCG | from 2,700 to 78,100 mIU/ml |
| AFP | from 100 to 150 units |
| Placental lactogen (PL) | from 3.2 to 10.1 mg/l |
It should be noted that the norm indicators are averaged .
In some cases, a deviation from the norm of up to 5 units is acceptable, which is explained by the physiological structure of the child, since it is individual for each person.
Norms and decoding
A standard ultrasound performed during the third screening includes determining the absolute and relative sizes of the baby and its organs (fetal fetometry). Also, during an ultrasound, the level of amniotic fluid, the degree of maturity of the placenta and its thickness are determined.
Fetometry standards for the third screening:
Degree of maturity of the placenta:
In the absence of pathologies, the maturity of the placenta should correspond to the data given in the table below. The maturity of the placenta is characterized by the presence of compactions and depressions in some places. Deviations from normal indicators indicate premature aging of the organ.
The thickness of the placenta is also an important indicator, and should normally range from 24 to 44 mm. Less thickness may be due to previous infections, low body weight or hypertension. Large - may indicate the development of Rh conflict, diabetes mellitus in the mother, as well as anemic manifestations.
Amniotic fluid level:
A significant excess of these indicators indicates polyhydramnios. This phenomenon threatens with many negative consequences, among which the most dangerous is perinatal death of the fetus. Oligohydramnios can cause delays in fetal development.
KGT indicators:
The results of this survey are indicated in points:
- if the condition of the fetus is assessed at 8-10 points, its development is normal;
- 5-7 points – average score, indicates the initial level of development of hypoxia in the fetus;
- less than 4 points – the presence of serious developmental pathologies.
If poor results are obtained, the issue of emergency surgical intervention is decided - delivery by cesarean section.
Dopplerography includes the determination of two main indicators: the speed of uterine and umbilical blood flow.
Norms of uterine blood flow:
Umbilical cord blood flow rates:
High values indicate increased vascular resistance, low values indicate decreased resistance. Both high and low indicators indicate the presence of deviations in the baby’s development.
In any case, it is worth remembering that the normal indicators of all studies conducted during the third screening are averaged and in some cases deviations of several units are acceptable.
Also, a decision about the condition of the fetus is made only after all the necessary studies have been carried out, and if any problems are detected, additional procedures are carried out that most fully reveal the picture of what is happening.
Signs of pathologies at the third screening
Ultrasound abnormalities and consequences:
- Infection of the fetus or diabetes mellitus is manifested by a large amount of amniotic fluid.
- An increase in fetal abdominal girth compared to head girth may indicate hemolytic disease or an enlarged fetal liver.
- The small size of the femur indirectly indicates dwarfism (dwarf disease).
- Low placenta previa can cause premature birth.
- A rapid or slow heartbeat indicates possible fetal hypoxia (lack of oxygen).
Deviations from the norm of biochemical screening:
- Elevated hCG and decreased AFP indirectly indicate Down syndrome.
- Reduced hCG and AFP indirectly indicate Edwards syndrome.
What is included in the third screening and when is it carried out?
Third trimester screening includes ultrasound, cardiotocography, and possibly biochemical screening. Doppler testing as part of screening is not performed in all pregnant women and strictly according to indications. The ultrasound method is the main examination; its results are compared with accepted standards and correlated with data from previous studies, on the basis of which conclusions are drawn.
The third screening during pregnancy has vague timing. They range from 30 to 37 weeks and are determined individually in each case.
- In a normal pregnancy, the period for performing an ultrasound in the 3rd trimester is 32-34 weeks of pregnancy.
- Doppler testing can be done on any day of the 3rd trimester.
- It is advisable to start recording cardiotocography from 28-30 weeks with the frequency required in a particular case.
Factors influencing screening results
It is not recommended to make decisions about the condition of the fetus based on one ultrasound examination, since the result may be affected by a faulty ultrasound machine and human factor. If, as a result of ultrasound diagnostics, serious pathologies characteristic of chromosomal abnormalities and other diseases incompatible with fetal life are revealed, it is recommended to consult specialists from other clinics .
False results from the third screening may be due to an incorrectly determined gestational age. An error of 2-4 weeks will not allow identifying deviations and making an accurate diagnosis.
Multiple pregnancies also cause false results from the third screening, since it is difficult to see each baby individually.
What does the third screening include?
In addition to ultrasound examination, the woman is sent for CTG (cardiotocography), Doppler measurements and blood tests for hormone levels.
Thanks to ultrasound studies in the 3rd trimester, it is possible to determine the development of the child, his approximate weight and diameter of the head, how active he is, what is the location of the child in the uterus (head or pelvic). At the same time, the doctor carefully examines the cervix, placental condition, and the volume of amniotic fluid.
Dopplerography is similar to an ultrasound procedure and is often performed simultaneously with it. Based on the screening results, the doctor assesses the risk of developing pathologies of the cardiovascular system, central nervous system, the sufficiency of oxygen supply to the fetus, and the strength of blood flow.
Cardiotocography is one of the third trimester screening procedures. This method is necessary to assess the fetal heart rate during uterine contractions. It detects hypoxia of the baby due to entanglement in the umbilical cord or placental insufficiency. If the life of the child is at risk, based on the results, the woman may be sent to a hospital for observation, or a premature birth may be performed.
The doctor includes a blood test in the 3rd trimester screening when studies of earlier weeks of fetal development have shown the likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities. Based on the results of the level of human chorionic gonadotropin, placental lactogen, free estriol, alpha-fetoprotein, the doctor makes a conclusion about chromosomal changes, frozen pregnancy and gestosis.
Screening options
A routine screening examination makes it possible to evaluate the main parameters of the fetus using ultrasound, identify possible developmental abnormalities (genetic or other), and analyze the health status of the woman’s reproductive system. A laboratory blood test is performed to determine the level of hormones responsible for pregnancy:
- AFP (protein component, which indicates the abundance or deficiency of nutrients in the embryo);
- hCG hormone (responsible for the complete preservation of the embryo);
- E3 (determines the degree of progress of the uterus and the quality of uteroplacental blood circulation).
The results of the study are considered only as a whole. To avoid discrepancies, doctors advise donating blood and doing an ultrasound on the same day. In case of a complicated pregnancy, in addition to the mandatory 3 screenings, the doctor may prescribe an additional ultrasound examination. Ultrasound diagnostics is harmless to the pregnant woman and the fetus. You can undergo the procedure as many times as the doctor deems necessary.
How the research is carried out
Ultrasound of the fetus, uterus and provisional organs (these include the placenta, umbilical cord, amniotic fluid) is performed transabdominally. The woman lies on the couch on her back, puts her legs horizontally or keeps her knees bent. The doctor moves a regular sensor over the stomach and sides, then the device receives information, analyzes it and gives a result.
Dopplerography is carried out using a surface ultrasound sensor. The doctor moves it over the woman’s stomach, having previously applied a special gel that helps the signal pass through. Doppler ultrasound is usually performed immediately after an ultrasound.
CTG during third trimester screening is performed in a certain way:
- the woman sits in a chair or sits on a couch;
- 2 sensors are attached to the abdomen - one to the right or left of the navel (it will detect the baby’s heartbeat), the second in the lower abdomen (needed to monitor the contractility of the uterine muscles in response to movement);
- The pregnant woman is given a special remote control with a button, which the woman must press when she feels movement.
All this helps to understand how pronounced the activity of the fetus is, determine the number of heartbeats, their rhythm, and track the reaction of the uterus to the movement of the baby.
When conducting CTG, there are special criteria; compliance with them is a signal to complete the examination. These are specific indicators that the doctor needs to assess the child’s well-being. They are based on the number of movements, the dynamics of changes in heartbeat, muscle contractions, so the time of analysis depends on whether the baby is sleeping or awake. The maximum period for which one examination is designed is 40 minutes.
If the child is sleeping, the criteria will not be met. This does not indicate a problem, but does not provide a complete picture for the doctor, so the baby needs to be woken up.
To do this, the woman is asked:
- It is easy to pinch or stroke the belly;
- eat sweets;
- get up, walk around.
Recommended actions in case of deviations from the norm
The third final screening helps to identify pathological processes in the intrauterine development of the fetus. When undergoing diagnostics, you should not worry or panic. Since any negative emotions can affect the results of the study and the baby.
It is important to remember that a negative diagnosis does not always truly indicate the presence of a disease. To be sure of the veracity of the diagnosis, the girl should undergo additional laboratory testing. The obstetrician-gynecologist should prescribe the girl auxiliary tests and a repeat ultrasound to clarify the latest conclusion.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, there is no need to be upset. By identifying the cause of ill health in time, you can correct it. If there are pathological processes in the body of the expectant mother, the doctor will prescribe conservative treatment that helps get rid of the problem and preserve the health of the mother and child.
But we must not forget that when certain diagnoses are made (frozen pregnancy, fetal death), an artificial termination of pregnancy or a cesarean section is inevitable.
Why diagnostics of the fetal condition is needed, how it is carried out and what can be revealed in the expectant mother will be told in the video.
Screening in the third trimester as a set of tests
In the last trimester of pregnancy, screening is carried out at 32–34 weeks. This final examination is necessary to:
- determine the method of delivery: by cesarean section or natural birth;
- confirm or, conversely, refute the results of previous screenings;
- identify the readiness of the woman’s body for the upcoming birth, in particular, the condition of the placenta and uterus;
- assess the degree of development of the baby’s organs.
Many Western countries do not have 3rd trimester ultrasound screening. If nothing worries you and the observing obstetrician-gynecologist, then most pregnant women there do without an ultrasound in the later stages of pregnancy. This does not mean that these newborns do not have problems. As I already wrote, according to numerous foreign studies conducted over the years, the detection rate of congenital malformations of the fetus averages 45–55%.
Kurgannikov A. S., ultrasound specialist
https://www.cironline.ru/blogs/?page=post&blog=cironline-blog&post_id=277
The final screening consists of:
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- Dopplerography;
- cardiotocography (CTG);
- biochemical blood test.
A woman has the right to sign a waiver of all research, but then all responsibility for the life of the child and the outcome of the pregnancy falls on her shoulders. But it is worth remembering that failure to detect pathologies in a timely manner is fraught with a deterioration in the baby’s condition and problems at the time of birth.
Indications and contraindications for the examination
Screening has no contraindications, as it does not pose a potential danger to the woman and child. Moreover, there are even certain indications for its mandatory implementation:
- poor screening results in previous trimesters;
- the age of the expectant mother is over 35 years;
- father's age - over 45 years old;
- family ties between future parents;
- genetic abnormalities in first children or other relatives;
- bad habits: alcohol, drugs, smoking;
- taking toxic medications during gestation;
- hazardous health conditions in the workplace;
- exposure of the expectant mother to radiation before or during pregnancy;
- paternal exposure to radiation before conception;
- viral diseases.
What organs and systems are examined as part of the 3rd screening?
What do doctors look for during the final examination? At the last examination before childbirth, the doctor examines and evaluates the health status of the mother and child. After receiving the results, he compares them with the results of the second examination and makes a conclusion based on this.
In the third trimester, during diagnosis, the gynecologist carefully examines the following:
- Condition and location of the placenta.
- Condition of the cervical canal.
- Reproductive organ health.
- The amount of amniotic fluid.
- The umbilical cord.
- The structure of the baby's skull and spine.
- Correct formation of the abdominal cavity, heart, and genitourinary system.
The doctor also determines whether the fetus is entangled in the umbilical cord, and how it is located in the womb. Diagnostic measures help to determine the conditions of the placenta as accurately as possible and make predictions for future births.
Diagnostic screening techniques
Ultrasound and Dopplerography are mandatory examinations at the final stage of gestation. CTG and biochemical blood tests are carried out for medical reasons when abnormalities in the development of the fetus or reproductive organs of a woman are detected, or at the request of the woman herself. There is no need to carry out all procedures on the same day.
Ultrasound as a mandatory part of the examination
At the final stage of gestation, it is important for the uzist to evaluate the following indicators:
- degree of maturity and thickness of the placenta. The quality of supply of all useful substances to the fetus depends on these factors;
- volume of amniotic fluid;
- condition of the cervix.
- fetometric features of the fetus: biparietal head size;
- Head circumference;
- abdominal diameter;
- thigh length;
- shin length;
- shoulders, forearms;
- fronto-occipital lobe;
- height and weight indicators;
- brain;
- heart rate;
Using an ultrasound machine, the doctor can see the real picture of what is happening in the womb of a pregnant woman.
Doppler
Doppler measurements are most often performed after an ultrasound procedure using the same device. The purpose of this examination is to study blood circulation in the vessels of the fetus, placenta, umbilical cord and uterus, which are responsible for providing the baby with oxygen.
Subjects of Dopplerometry research:
- uterine arteries;
- umbilical cord arteries;
- fetal middle cerebral artery;
- fetal aorta;
- venous duct.
The need to examine the venous duct, middle cerebral artery and fetal aorta arises only if there is a suspicion of intrauterine pathologies of the child’s development and hydrocephalus.
Dopplerometry is aimed at identifying pathologies associated with blood circulation in the placenta, umbilical cord, uterus and fetal vessels
Reasons and purposes of performing cardiotocography
Cardiotocography is performed for all pregnant women and outside screening. In a normal pregnancy, two or three such procedures are sufficient. But CTG is performed more often if ultrasound results reveal complications such as:
- umbilical cord entanglement;
- low heart rates;
- Rh conflict (a condition when mother and child have different Rh factors);
- gestosis;
- diabetes;
- premature aging of the placenta.
This test helps monitor the fetal heart rate and uterine contractions. Experts say that performing CTG before the 32nd week is not informative. If there are no deviations, the procedure takes about 20 minutes, otherwise it can take up to an hour.
Cardiotocography can take from 20 to 60 minutes
Using the results of cardiotocography, you can determine:
- basal heart rate (average heart rate maintained over 10 minutes);
- amplitude of the fetal heartbeat;
- short-term increase in heart rate by 15 beats per minute;
- a short-term decrease in heart rate by 15 beats per minute. Normally, this condition should not be diagnosed.
The results of the CTG are displayed on paper and then deciphered by the gynecologist. But as independent indicators, they do not provide a complete picture of the condition of the fetus and uterus, so they must be considered in conjunction with the results of other tests.
At the 34th week of pregnancy, I was admitted to the pathology department due to intrauterine growth retardation and oxygen starvation of the fetus, so I had to do cardiotocography daily. It was not always possible to get the result on the first try, sometimes it took a whole hour, so many doctors recommend that expectant mothers take a blanket with them to put under their back during the procedure. It is worth noting that even despite the diagnosis given to me, all CTG indicators were normal and did not show any abnormalities. And this once again suggests that only the results of all tests are informative.
Blood chemistry
A biochemical blood test is not mandatory and is carried out only when the results of previous tests have revealed pathologies in the development of the baby. The fact is that while carrying a baby, a woman’s body begins to produce specific proteins, the level of which is a kind of indicator of the well-being of fetal development, the functioning of the placenta and the course of pregnancy in general. This study is carried out to monitor the level of these blood proteins.
This analysis determines the level of:
- AFP (alpha fetoprotein). The level of this protein is an indicator of fetal health;
- pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (Pregnancy-associated Plasma Protein-A; PAPP-A). By the level of this one can judge chromosomal abnormalities in fetal development;
- free estriol. The level of this hormone can be used to judge the functioning of the placenta and umbilical cord, as well as the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in fetal development: Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome and pathologies in the development of the neural tube;
- human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). The hormone is responsible for carrying a pregnancy;
- PL (placental lactogen). The hormone is synthesized by the placenta and is an indicator of its condition.