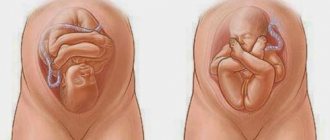
Structure of the ventricular system of the brain
The ventricular system is a capacitive structure of the brain. Its purpose is to synthesize and store cerebrospinal fluid. This fluid, called cerebrospinal fluid, is responsible for a number of functions in the body. It acts as a shock absorber, protecting the thinking organ from external damage, and helps stabilize intracranial pressure. Without cerebrospinal fluid, metabolic processes between the brain and blood cells would be impossible.
How is the structure responsible for the synthesis of this essential fluid represented in the human body? A table illustrating the normal four-cavity structure of the ventricular system of the brain in humans will help answer the question:
Treatment of ventriculomegaly
The goal of treatment for ventriculomegaly:
- eliminate the causes of the disease;
- prevent negative consequences that may manifest themselves later.
Since the disease is detected in the fetus in the womb, treatment is prescribed to the expectant mother. Mild degrees of the disease generally do not require drug intervention. In such cases, constant monitoring and monitoring of the condition of the mother and fetus is indicated.
Serious pathological phenomena in the fetus require immediate intervention, so expectant mothers are prescribed the following groups of drugs:
- antihypoxants;
- diuretics;
- vitamins.
Massage and exercise therapy are indicated.
A pediatrician and neurologist prescribe antihypoxants, diuretics and vitamins as drug therapy.
To treat ventriculomegaly, massage and physical therapy (static exercises with loads on the pelvic muscles and pelvic floor) are prescribed.
As medications intended to prevent the development of neurological disorders in a child, drugs are prescribed that are aimed at retaining potassium in the body.
Normal ventricle sizes
The volume of each ventricle directly determines how much cerebrospinal fluid is synthesized or stored in it. If the size of the structure exceeds normal, there is a risk of overproduction of cerebrospinal fluid or problems with its removal, which cannot but lead to malfunctions in the functioning of the thinking organ.
What is the usual ventricular depth in newborns? According to the observations of neonatologists, normal values will be approximately as follows:
Over time, as the newborn's brain begins to grow, the depth of its internal cavities will gradually increase. If the expansion of the ventricles occurs sharply, and their proportions cease to be linearly consistent with the size of the skull, this, like a congenital deviation from normal values, is a reason to sound the alarm.
What will you need for an ultrasound?
Carrying out ultrasound diagnostics does not require special preparation. The procedure itself is also not a complex manipulation. At this stage, there is no need to fill the bladder, since there is already enough amniotic fluid to examine the structure of the areas of interest. Eating food before the procedure does not in any way affect the results of the ultrasound.
Many clinics do not indicate the need to bring anything with you; otherwise, you will be warned about this in advance. Most often, for the procedure, the patient may need a diaper and napkins. The diaper will need to be placed on the couch, since the ultrasound is performed in the supine position. Wipes are used to wipe away excess gel.
Causes of enlarged ventricles of the brain
Sometimes a slight discrepancy between the size of brain structures and normal values is genetically determined. This feature is detected already during the initial examination of the baby and, as a rule, is not considered pathological. At the same time, noticeable dilatation or asymmetry of the ventricles may be the result of a serious chromosomal abnormality that arose during the intrauterine development of the fetus.
Doctors have also identified a number of non-genetic factors that provoke the expansion of brain cavities. These include:
- infections suffered by the child's mother during pregnancy;
- pathologies of fetal development caused by chronic diseases of the parent;
- sepsis;
- entry of a foreign body into the liquor spaces;
- hydrocephalus of unknown etiology;
- the occurrence of tumors and other neoplasms in the brain;
- birth injuries and complications.
Information content of ultrasound at 19 weeks
With the help of ultrasound diagnostics, at this period it is possible to ascertain the degree of formation and development of the functional systems of the fetal body, and to assess the condition of the woman’s reproductive organs. The baby at the 19th week of pregnancy is already developed so much that an ultrasound will tell about:
- The activity of movements and their purposefulness
- Formation of tooth buds
- Development, first of all, of the nervous, urinary and muscular systems
- Child's field (with body position available for viewing)
- Body proportions, anatomical features
- The size of the fetus - its weight and height
- The number of heartbeats and respiratory acts
- The presence of pathologies such as: hydrocele of the brain, Down syndrome, developmental retardation, malnutrition, abnormal body constitution, fetoplacental insufficiency)
- Condition of the umbilical cord
- Degrees of placenta maturity
- Condition of the uterus
- Quantity and quality of amniotic fluid
An addition to the standard ultrasound procedure is vascular Doppler. This study is carried out in the same way as ultrasound. Doppler ultrasound allows you to evaluate blood circulation in the functional system “uterus-placenta-fetus”: the direction of blood movement through the vessels, its speed.
Consequences of pathology in children
Depending on the severity and location of the problem, the consequences of enlarged cerebral ventricles for the child also vary. As a rule, the pathology in question is completely harmless. The prospects for its development are unpleasant, but not fatal. Enlargement of the ventricles leads to an increased concentration of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain spaces, which increases the pressure on local nerve endings. As a result, complications arise such as:
- defecation disorders;
- problems with urination;
- periodic failure of the senses (temporary blindness or deafness);
- impaired coordination of movements;
- delays in mental and physical development.
The resulting hemorrhage can lead to:
- epilepsy;
- permanent loss of hearing or vision;
- paralysis or coma;
- instant death.
Normative and pathological parameters of BZ
Analysis of fetal brain structures is carried out in the second trimester, between 18 and 27 weeks of pregnancy.
In most cases, pathological changes are detected on routine ultrasound. The diagnosis is also made at 30-33 weeks of pregnancy. Table of the norm of the lateral ventricles (LV) in the fetus
| Age of the fetus/child | BZ width in mm |
| 18 weeks | 4,9 – 7,5 |
| 27 weeks | 5,6 – 8,7 |
| newborn | 23,5 |
| 3 months | 36,2 |
| 6-9 months | 60,8 |
| 12 months | 64,7 |
Discrepancies in parameter measurements of 0.1-0.3 mm are normal.
Degrees of ventricular dilatation (by how many mm do they increase from standard values):
- 1st (mild, insignificant) – an increase in the depth of the bodies of the 1st and 2nd basins from 5 to 8 mm, the lateral curvature is smoothed out, the outlines become more rounded, the 3rd and 4th ventricles remain unchanged;
- 2nd (moderate severity, moderate) - the body expands to 9-10 mm above the norm, the increase is uniform on all sides, the 3rd ventricle increases by 6 mm, 4 - within the anatomical norm;
- 3rd (severe, pronounced) - the depth of the bodies expands by 10-21 mm or more in all ventricles, the subarachnoid cisterns of the brain increase.
The disease is unilateral (left-sided, right-sided) or bilateral (biventriculomegaly).
- The first degree is characterized by dilatation of the ventricles up to 12 mm.
- Second degree, the ventricles are enlarged to 15 mm. Complete fluid outflow is impaired, contributing to the formation of neurological symptoms.
- Third degree with ventricular dilatation from 16 to 20 mm. The newborn is diagnosed with abnormalities in the formation of the brain.
Features of the clinical picture depending on the stage of the disorder:
- The first stage of the disease, in which the ventricles dilate from 10 to 12 mm, generally does not produce severe symptoms. Therefore, a diagnosis can be made after passing through an open fontanel on the newborn’s head. The child’s mother may notice that he is too capricious, whiny, any change in the weather entails hysterics and sleep disturbances. In rare cases, the child’s behavior is apathetic, lethargic, and he may refuse to eat.
- Moderate ventriculomegaly (second stage) entails abnormalities in the brain, development of the heart and skeletal system, genetic abnormalities, Down syndrome. Such pathologies are diagnosed before the child is born. Symptoms of the first degree include convulsions, rapid head growth, visualization of veins on the temples and forehead. As they grow, a lag in physical and mental development appears.
- The third degree is also the most severe, in which the ventricles can be dilated up to 20 mm. Excessive increase leads to the fact that the child will begin to sit, crawl, stand and walk late. Speech development is inhibited. In addition to the above symptoms, cramps and headaches are added. The head is disproportionate to the size of the body and exceeds the permissible norms by 3 cm. And often appears.
It must be taken into account that the ventricles are asymmetrical and can have different sizes. During the examination, the results of the data obtained must correspond to the norm and not go beyond their limits. If a diagnosis of borderline ventriculomegaly has been made, this means that the ventricles are dilated, but not more than 10 mm.
Such deviations in the ventricular system do not indicate the presence of pathologies, but the risk of abnormalities in the formation of the brain increases significantly.
Most often, ventricular enlargement develops as an independent disease. But sometimes Turner, Down, Edwards syndrome, etc. are jointly diagnosed. Symptoms appear if a woman has various anomalies during pregnancy, and these do not necessarily have to be chromosomal diseases.
- intrauterine infections;
- heredity.
What exactly provoked the expansion of the ventricles can only be determined by a neurologist after a thorough examination.
Ventriculomegaly is more often detected in newborns if the mother’s age exceeds 35 years. After reaching this age mark, a woman may develop deviations that must be taken into account when conceiving a child:
- the risk of genetic disorders increases;
- the maternal chromosome may be mutated;
- oxygen starvation in the fetus doubles;
- the risk of infectious diseases increases.
Based on this, we can say that in women under 35 years of age, the risk of developing the disease in their unborn child is unlikely, and after that it increases sharply, two to three times.
Acquired ventriculomegaly in a newborn is diagnosed during a comprehensive examination. Laboratory tests and instrumental studies are performed as part of differential diagnosis. The disease must be distinguished from hydrocephalus.
With ventriculomegaly, the width of the ventricular bodies varies from 0.6 to 1 cm. Signs of neuronal maturation are poorly expressed. The ratio of the width of the germinal and new zones of the cerebral cortex is 1:2.
With internal hydrocephalus, the ventricles expand evenly in all directions by more than 1 cm. The brain parenchyma is atrophied, with a jelly-like consistency. The cortical plate narrows. The germinal layer is much wider than the neocortex, their ratio is 2:1.
Indicators of ultrasound and MRI performed before and after childbirth differ significantly in 57-83% of cases. If ventricular dilatation is detected in the fetus, do not panic.
To confirm or refute the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a repeated ultrasound and tomographic examination of the newborn.
Such arguments are presented in the publication “Frequency and causes of discrepancies in diagnostic images in children with ventriculomegaly” GM Senapati, 2010.
The purpose of the third screening is to confirm or refute the identified deviations and malformations suspected during the second screening.
It is mandatory to examine the same structures of the brain and facial skeleton.
The purpose of ultrasound screening of the fetal head is to thoroughly study the structures of the brain and facial structure in order to identify abnormalities.
If the prognosis is favorable, then parents will be able to get advice from specialists on surgical correction of the defect and begin treatment in a timely manner after the birth of the baby.
Oksana Ivanchenko, obstetrician-gynecologist, especially for Mirmam.pro
Treatment depends on when ventriculomegaly is diagnosed—during pregnancy or after the birth of the child.
If ventricular enlargement is detected during fetal development, the doctor will take into account the amount of enlargement. If a severe degree of disorder is diagnosed, as well as concomitant diseases and anomalies in the development of the child, the woman is offered an artificial termination of pregnancy.
Moderate severity of ventricular dilatation is not a reason for abortion. Treatment begins during pregnancy, and the main thing that needs to be done is to determine the cause of the abnormal dilatation of the ventricles.
A woman's blood is taken to identify infectious diseases. Additional tests are performed for Down, Edwards and Turner syndrome. If all the results are negative and no abnormalities are identified, the gynecologist prescribes diuretics (diuretics) that will help remove excess fluid from the body.
- Together with taking diuretics, potassium supplements and medications that provide tissues with oxygen are prescribed to prevent fetal hypoxia.
- If the disease is detected after the birth of the child, drug therapy will be selected depending on the severity of the disorders.
- When the ventricles dilate to 12 mm, doctors are of the opinion that treatment is necessary when the symptoms that appear against the background of ventriculomegaly cause significant discomfort to the child.
- , which are selected strictly according to the age of the child. These include,;
- diuretics – Diacarb or Furosemide;
- B vitamins;
- drugs to improve blood circulation;
- potassium preparations.
A massage is prescribed for 15 days, with a break of two months, and so on for two or three courses.
If third-degree enlargement is detected, drug therapy is not effective. Surgical intervention is required to carry out.
During the operation, the surgeon installs a shunt that will drain excess fluid. After surgical treatment, the child’s general condition improves, symptoms quickly disappear. This is due to the fact that excess fluid does not put pressure on the brain.
According to research, 11% of children diagnosed with ventricular enlargement suffer from physical and psychological developmental delays. Symptoms may be obvious or subtle.
If a child is diagnosed with an isolated form of the disease, i.e. no other developmental defects or genetic mutations have been identified, the prognosis will be favorable, provided that treatment is started immediately from the moment the child is born.
Ventriculomegaly requires mandatory treatment and monitoring of the course of the disease over time; if this is not done, the child will develop neurological diseases and other consequences that will significantly affect his health and development.
What processes in a woman’s body during pregnancy can cause ventriculomegaly in the fetus? Is it possible to carry and give birth to a healthy baby, despite a frightening diagnosis? Is ventriculomegaly treated and at what stages? The answers to these and other questions will help expectant mothers understand the current situation.
Ventriculomegaly with chromosomal consequences in the fetus after birth is manifested by Down syndrome in 70% of children. In 30% of cases, trisomy on the X chromosome is diagnosed - the eyes are set at a great distance from each other, a characteristic type of curvature of the fingers, epicanthal (Mongolian) folds of the upper eyelid hanging over the inner corner of the eye.
Rare consequences associated with chromosomal mosaicism (scientific publication “Prenatal finding in a fetus with mosaicism due to two chromosomal rearrangements” RJ Hastings, SG Watson, LS):
- Klinefelter syndrome - manifests itself only in boys during puberty (erectile dysfunction, infertility, endocrine disorders - diabetes, thyroid disease);
- Edwards syndrome - diagnosed 3 times more often in girls - birth weight does not exceed 2 kg, while pregnancy proceeds normally; there are anomalies in the structure of the skull, narrow palpebral fissures, deformed ears, heart defects;
- Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome – malformations of internal organs, gonads, short stature;
- de la Chapelle syndrome - typical for boys - when they become adults, infertility appears, the absence of secondary sexual characteristics (male pattern hair), mental and physical development remains normal.
Diagnosis of pathology
In order to prevent the sad consequences described above, it is very important to detect deviations in a timely manner. What modern tools allow you to most accurately diagnose the pathology in question?
Usually, asymmetry or enlargement of the cerebral ventricles in an infant is detected at the very first routine ultrasound, which any child under one year of age must undergo (we recommend reading: what does an ultrasound of the brain show in newborns and how is it done?). To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe a number of additional examinations for the baby:
- examination by an ophthalmologist;
- MRI under general anesthesia;
- CT.
Questions about ventriculomegaly
Ventriculomegaly in the fetus is a developmental defect in which the size of the lateral ventricles of the brain exceeds 10 mm. Doctors from Art-Med medical clinics answer patients’ questions about ventriculomegaly.
You have a slight deviation in size from the average norm. Based on such figures, one cannot speak of any pathology. For control, you can repeat the ultrasound with the specialists of our center.
In your case, the size of the fetus is within the limits of individual fluctuations. An expert ultrasound scan is required after 3-4 weeks and a face-to-face consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist.
The upper limit of normal for the posterior horns of the lateral ventricles in the II and III trimesters is 10 mm. The dimensions of your baby correspond to the normal range of fetometric parameters for a period of 19-20 weeks.
Judging by the data provided, your baby is doing fine. The upper limit of normal for the posterior horns of the lateral ventricles in the II and III trimesters is 10 mm.
The width of the occipital horns up to 10 mm is considered normal. Your next scheduled ultrasound is at 30-32 weeks.
Enlargement of the occipital horns of the lateral ventricles can be isolated or combined with other developmental defects. In addition, ventriculomegaly can occur as a result of structural changes in the brain (pathology of the corpus callosum, cerebellum, spinal cord) or be a consequence of certain pathological conditions (colds or infectious diseases in the mother, intraventricular bleeding, tumor in the fetus, etc.). In each specific case, the prognosis for the baby’s health will be different. To clarify the diagnosis and prognosis, it is advisable to conduct an expert ultrasound.
The diagnosis of “Ventriculomegaly” is made if the size of the occipital horns of the lateral ventricles exceeds 10 mm. To fully assess your situation, it is advisable to conduct an expert ultrasound to clarify the presence of ventriculomegaly and find out its cause. Only after this will it be possible to talk about a correct forecast and further actions on your part.
Theoretically, it can lead to the child having (optionally) hydrocephalus. It is necessary to observe after birth and do an ultrasound of the brain.
Be sure to redo the ultrasound to more accurately determine the size of the left ventricle of the brain. Carry out complex antiviral therapy and monitor the dynamics of ultrasound.
If you haven't had the flu, then no way. A TVP of 2.6 mm, although formally within the normal range, should have alerted the patient to fetal pathology. Since the exact diagnosis is not known, it is impossible to say about the prognosis for future children. It is possible that a recent mutation has occurred with a low risk of recurrence. In any case, it is advisable for you and your spouse to have a karyotype analysis done.
Most likely we are talking about ventriculomegaly. Theoretically, it can develop into hydrocephalus. In this case, surgical treatment is performed after the birth of the child. Now it’s impossible to say for sure. Dynamic observation is needed.
After childbirth, regression may occur, but hydrocephalus may also develop. It is not clear what caused the hemorrhage. There may be consequences because of this.
If the measurements are carried out correctly, then it most likely will not decrease. But this may be compensated ventriculomegaly without significant consequences for the child.
It is unlikely that a nasopharyngeal infection caused the ventriculomegaly. It is impossible to give a forecast in advance. There are different options – from compensated hydrocephalus to decompensated.
We recommend doing an expert ultrasound to clarify the type of multiple pregnancy, consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist and a geneticist.
Fetal hydrocephalus can develop very quickly. If in doubt, it is worth repeating the ultrasound by an independent specialist. Predictions can be made after delivery and examination of the baby by a neurologist.
Theoretically possible. That there will be compensated or subcompensated hydrocephalus with minimal clinical manifestations, but the final prognosis is possible only after the birth of the child.
It is impossible to give a forecast in advance. It may lead to nothing, or it may end in hydrocephalus. There is no point in doing a fetal MRI now. Wait for the birth, and then examine the baby.
The child develops hydrocephalus. Possible Dandy-Walker syndrome. Antibiotics cannot help in such a situation. And the situation is very serious. Urgently go for a consultation with pediatric neurosurgeons.
In this case, it is ventriculomegaly. Whether it will develop into hydrocephalus or not will become clear only some time after the birth of the child.
It is theoretically possible that a child will be born with compensated hydrocephalus, which has virtually no effect on development.
The fetus has 2-sided ventriculomegaly. In your situation, a repeat ultrasound is required in 2-3 weeks.
Hydrocephalus may develop. The influence of previous influenza is unlikely.
The width of the posterior horns of the lateral ventricles is 9 mm—the upper limit of normal. More often, these are passing changes, are not dangerous for the child, and no treatment is required. Observation by an obstetrician-gynecologist, treatment of pregnancy complications, if any, and ultrasound at 30-32 weeks are necessary.
There is a form of hereditary ventriculomegaly in boys. In addition to PEP, it can also be a consequence of infection during pregnancy.
Your baby is developing internal hydrocephalus. Most likely, the baby will have developmental disabilities. I would recommend that you immediately show your child to a good pediatric neurologist.
The child may be born alive, but no one can tell you exactly how long he will live. It's unlikely that it's been more than a year.
The child will be born with severe pathology of the central nervous system. The operation is possible, but no one can predict its outcome.
The fetus develops hydrocephalus. After birth, observation and treatment under the supervision of a good pediatric neurologist is necessary. It is also worth showing the baby genetics. The method of delivery depends on the specific obstetric situation; it is impossible to answer this question in absentia.
Anyone can make mistakes. The doctor is no exception. If in doubt, get an expert ultrasound from another specialist (2D is enough).
Treatment methods
If the diagnostician’s suspicions of enlarged or asymmetrical cerebral ventricles are confirmed, the child receives a referral to a neurosurgeon or neurologist, who will develop an individual treatment regimen for his little patient. Usually, drug therapy methods are used to normalize the patient’s condition. For children with obvious neuropathological abnormalities, doctors recommend:
- Diuretics. Accelerated removal of fluids from the body helps eliminate cerebral edema.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes with high potassium content. Due to frequent urination, the body loses many useful substances, the deficiency of which must be compensated in a timely manner. In addition, regular intake of vitamins helps the patient recover faster.
- Nootropic medications. Improved blood supply due to increased elasticity of blood vessels facilitates the normal functioning of brain structures.
- Sedatives. Sedatives reduce the manifestation of neurological symptoms of the disease (tearfulness, irritability, etc.).
For children suffering from this pathology in a mild form, drug treatment shows excellent results. If the enlarged cerebrospinal fluid spaces are the result of a mechanical head injury received during childbirth, the problem takes on a completely different scope. It is usually impossible to solve it without the help of a qualified surgeon.
What kind of disease is this
Most often, ventricular enlargement develops as an independent disease. But sometimes Turner, Down, Edwards syndrome, etc. are jointly diagnosed. Symptoms appear if a woman has various anomalies during pregnancy, and these do not necessarily have to be chromosomal diseases.
Dilatation of the ventricles is provoked by infectious diseases that a woman suffered while pregnant. The following provoking factors of ventriculomegaly are also identified:
- intrauterine infections;
- heredity.
What exactly provoked the expansion of the ventricles can only be determined by a neurologist after a thorough examination.
Ventriculomegaly is more often detected in newborns if the mother’s age exceeds 35 years. After reaching this age mark, a woman may develop deviations that must be taken into account when conceiving a child:
- the risk of genetic disorders increases;
- the maternal chromosome may be mutated;
- oxygen starvation in the fetus doubles;
- the risk of infectious diseases increases.
Based on this, we can say that in women under 35 years of age, the risk of developing the disease in their unborn child is unlikely, and after that it increases sharply, two to three times.
A pathological process affecting the fetal brain, in which the ventricles of the brain swell (change their shape), is called ventriculomegaly. Pathology has a negative impact on the developing nervous systems of the body (central and peripheral). As a result of ventriculomegaly, the fetus suffers from:
- spinal cord;
- brain;
- nerve processes and roots;
- autonomic nervous system.
Not only individual organs, but also entire body systems suffer from excess fluid.
The cerebral ventricles communicate with each other through canals. They perform a very important function for the body - they synthesize cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Normally and in the absence of abnormalities, this fluid flows into a certain space called the subarachnoid space. If an anomaly is present, then the outflow stops, fluid (CSF) accumulates in the ventricles, creating many problems for the baby.
With a mild degree, the lesions are isolated, quickly respond to treatment and pass without consequences for the baby. Complex drugs are not required, the ventricles quickly return to normal.
The average degree implies an increase in the ventricles (one or more) up to 15 mm inclusive. This happens because the natural outflow of fluid is disrupted. The functionality of the ventricles is also impaired.
With severe ventriculomegaly, the ventricles are greatly enlarged (up to 21 mm) due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in them. Serious treatment and monitoring of the condition and intrauterine development of the baby is required.
Ventriculomegaly is a rather dangerous disease that can provoke the death of the fetus in the womb, or manifest itself in the form of anomalies (mental and physical disorders), as a prospect - disability in the future. In order, if possible, to protect the baby from the harmful consequences of ventriculomegaly, it is necessary to select the most effective treatment, identifying the real causes of this pathology.
- the age of the pregnant woman is over 35 years;
- abnormal genes and chromosomes in expectant mothers;
- the presence of pathological processes during pregnancy;
- all kinds of infections (including intrauterine ones);
- obstructive fetal hydrocephalus;
- physical injuries;
- strokes;
- periventricular leukomalacia;
- lissencephaly.
The threat can be detected as early as 17 weeks of pregnancy using ultrasound screening. From the 17th to the 34th week, the doctor pays special attention to the development of the brain, as well as the size of its ventricles. Ventriculomegaly is indicated by an increase in one or more ventricles, ranging from 12 mm to 20 mm. If ventriculomegaly is suspected, the doctor recommends undergoing additional tests and repeating the ultrasound after another 2 weeks.
Ventriculomegaly in the fetus - the consequences of this disease, which began in the womb, can be very severe, starting with the death of the child in the womb (due to developmental defects), premature birth (accounts for up to 4% of all known cases), severe and disability.
If a genetic factor plays a role in the appearance of ventriculomegaly, then the following deviations and syndromes are possible:
- Down syndrome;
- hydrocephalus;
- Patau;
- Edwards;
- Turner (with gonadal dysgenesis);
- vascular malformations of the brain;
- mental retardation;
- retardation in physical development.
We invite you to read: Fitness for the brain, which workouts will have a neuroprotective effect
It has been noted that female infants are more susceptible to anomalies and defects as a result of ventriculomegaly, compared to male infants.
Despite everything, children born with a similar diagnosis have a very good chance of further normal life. So, in 80% of cases out of a hundred, babies outgrow this condition and subsequently develop fully without deviations.
Among all known cases of ventriculomegaly, 10% of infants are susceptible to serious pathologies. Deviations of moderate severity were noticed in 8% of children born with this diagnosis.
Predictions for a child
If small deviations in the size of the first and second lateral, as well as the third or fourth cerebral ventricles were detected in the baby immediately after birth, the prognosis for his recovery is quite favorable. In most cases, such anomalies are caused by the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of infants, so with age the problem goes away on its own. To guarantee a favorable outcome, parents need to register their child with a neurologist, who will closely monitor changes in the baby’s condition for the next few years and, if necessary, prescribe appropriate treatment.
For children whose pathology was identified at an older age, the prospects are not so rosy. The later the deviation is discovered, the higher the likelihood that, in the absence of observation and therapy, the disease has managed to contribute to the formation of various abnormalities in brain development, which is fraught with complications. Of course, such a diagnosis is not a death sentence. However, parents need to prepare themselves and their child for the inevitability of the upcoming long and complex treatment, and possibly for surgery.
Identification of pathology and its causes
Deviations in the values of the MRM and its structure during ultrasound imaging indicate the presence of pathologies. It could be:
- Violation of morphogenesis (formation). Anomalies of the structure of the cerebellum and posterior cranial fossa: Gendry-Walker malformation (hypoplasia of the vermis, its low location; dilatation of the 4th ventricle, increase in the size of the posterior cranial fossa), aplasia, hypoplasia. Anomalies in the development of the rhombencephalon - rhombencephalosynapsis, in which the cerebellar hemispheres merge with the dentate nuclei uniting along the midline, tectomerbellar dysraphism - the “small brain” is located inside the 4th ventricle.
- Hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis.
- Disorders of cortical organization. Defects in the structure of the cerebellar cortex are a fairly common pathology of the central nervous system. Due to the fact that its influence on the organization of the central nervous system is not great, it is rarely diagnosed. Usually this is degeneration (destruction) of the granular layer of the rudimentary cortex, hypertrophy (increase in volume) of the granular layer.
- Cysts, neoplasms.
A large number of factors can cause the development of pathologies of the cerebellar structure, including:
- Heredity. It plays an important role, for the reason that any physiological abnormalities in parents in the future can affect the development of the child. Before planning a pregnancy, a woman and a man must undergo a series of examinations and tests to identify the risk of developing pathologies in their offspring.
- Unfavorable environment. Pollution of nature by products of the petrochemical industry, exhaust gases, high content of carcinogens and pesticides in food affects the health of future parents. Therefore, the risk group for developing various pathologies of the central nervous system includes children whose parents work in hazardous industries, interact with toxic substances, or live near large industrial plants or in areas with high background radiation.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle. Smoking, alcoholism, and drug use by parents affect the health of future children.
- Infection. The penetration of dangerous viruses and pathogenic bacteria into the body of the expectant mother can result in dangerous pathologies for the baby. Pregnancy can end badly if infection occurs before 12 weeks of pregnancy. Over long periods of time, pathogens can cause various pathologies in the fetus. For example:
- toxoplasmosis provokes the development of microcephaly, meningoencephalitis, hydrocephalus, and central nervous system damage in a child.
- rubella causes deafness, blindness, glaucoma and damage to the fetal skeletal system;
- hepatitis B is dangerous due to the high probability of the virus penetrating the fetus through the placenta, in which case approximately 40% of children do not live to see 2 years of age;
- cytomegaly, can cause blindness, deafness, liver cirrhosis, gastrointestinal damage, encephalopathy;
- Treponema pallidum – damage to the skeletal system, liver, kidneys, central nervous system, congenital syphilis;
- gonococcus - eye diseases, sepsis, conjunctivitis, in a pregnant woman - inflammation of the fetal placenta.
Prevention of the development of various pathologies of the central nervous system consists of preventing exposure to the above risk factors. Expectant parents are advised to take care of their health long before conception and monitor their diet and lifestyle. During pregnancy, a woman needs to undergo routine screening (especially at 20 weeks of pregnancy) and monitor her condition.
Ultrasound of the fetal head during pregnancy: interpretation
Ultrasound for pregnant women is a screening method of examination. The medical term “ultrasound screening” is an examination of absolutely all pregnant women within a specified period of time in order to identify intrauterine malformations of the fetus.
A screening test is carried out three times during pregnancy:
- I screening – at 11-14 weeks;
- II screening – at 18-22 weeks;
- III screening - at 32-34 weeks.
Fetus at 19 weeks gestation
All parameters that can be assessed using ultrasound diagnostics are determined by the rapid development of the child. At week 19, the following processes occur in his body:
- The baby’s movements become more conscious and orderly, thanks to the strengthening of neuromuscular connections. The child can move his jaws, push away from the walls of the uterus, and suck his fingers.
- The body takes on more proportional shapes: the limbs have the correct length ratio, the head also begins to look natural in relation to the size of the body. The phalanges of the fingers have formed.
- The skin begins to lighten a little due to the accumulation of subcutaneous fat. But the skin still looks wrinkled. The sebaceous glands produce a special lubricant that envelops the baby’s entire body and protects it from damage and infections, from the constant influence of amniotic fluid, and ultimately helps it to be born. In addition, the entire body is covered with vellus hair, which is also intended to perform a protective function.
- Centers responsible for analyzers and sense organs are formed. Receptors are actively developing.
- The digestive system will improve and it will be able to digest nutrients. Therefore, original feces are formed in the intestines.
- The child’s daily routine changes - the duration of the activity phase increases to 6-7 hours. The rest of the time he remains in a state of sleep.
- In the respiratory system, the formation of bronchioles occurs.
- The reproductive system is practically formed, and it is already possible to determine gender with great certainty. Most of the genital organs, both internal and external, are already laid. In girls, the rudiments of eggs have already been formed in the ovaries.
- The heart is fully formed.
- The immune system begins to form, the child’s body is already able to independently produce substances that can protect against infections and viruses.
At week 19, all systems are close to the final stages of their formation, the baby becomes an original organism that will soon be ready for birth.
Ultrasound of the fetal head at 1st screening
At the end of the first trimester, the expectant mother is prescribed the first ultrasound screening in utero in order to exclude such gross malformations of the fetal head as pathology of the brain, skull bones and facial skeleton.
The doctor evaluates the following fetal structures:
- contours of the bones of the cranial vault for their integrity;
- brain structures that normally look like a “butterfly”;
- measures the length of the fetal nasal bone (at 11 weeks its presence or absence is indicated, and at 12-14 weeks the norm is from 2 to 4 mm);
- biparietal size (BDS) of the head - measured between the most prominent points of the parietal bones of the fetus. The average normative value of BPR in the period of 11-14 weeks is from 17 to 27 mm. The doctor will look at these indicators in a special table.
If everything is fine with your fetus, the doctor will write down the following in the ultrasound report:
- bones of the cranial vault – integrity preserved;
- BPR -21 mm;
- the choroid plexuses are symmetrical, in the shape of a “butterfly”;
- the length of the nasal bone is 3 mm.
What head pathology occurs during the first ultrasound screening?
Particular attention is paid to assessing the length of the fetal nasal bone. This is an informative criterion for early diagnosis of Down syndrome.
Examination of the skull bones already at the end of the first trimester makes it possible to identify such severe developmental abnormalities as:
- acrania;
- exencephaly;
- anencephaly;
- cranial hernia.
Anencephaly
- the most common defect of the central nervous system, in which brain tissue and skull bones are completely absent.
Exencephaly - the skull bones are also absent, but there is a fragment of brain tissue.
Acrania is a developmental defect in which the fetal brain is not surrounded by the bones of the skull.
It is important to know! With these three defects, the death of the child occurs. Therefore, if they are detected at any stage of pregnancy, it is proposed to terminate it for medical reasons. In the future, the woman needs genetic counseling.
A cranial hernia is a protrusion of the meninges and brain tissue through a defect in the bones of the skull. In this case, a consultation with a neurosurgeon is required to find out whether it is possible to correct this defect with surgery after the birth of the child.
Lateral ventricles of the brain: norm in the fetus by week, table
Pregnancy is always accompanied by certain risks, therefore, to eliminate or correct them, prenatal screening is used, which is a mandatory study of complex pregnancies in modern medicine. During screening, biochemical and ultrasound parameters are examined, which consist of a blood test for hormones and ultrasound to determine the size of all vital signs of the fetus.
During a normal pregnancy, only a routine ultrasound is required, but screening is prescribed if any deviation from the norm is suspected or at the request of the pregnant woman for 100% confidence in the correct development of the fetus inside her.
There is a risk group of women who require mandatory fetal screening:
- age after 35 years (especially if this is the first pregnancy);
- hereditary predisposition to the development of defects or deviations in the functioning of any system or organ;
- past viral and infectious diseases in the first trimester;
- treatment with pharmaceuticals dangerous to the fetus;
- frozen previous pregnancy, stillbirth, miscarriages.
The first screening is performed at 11-14 weeks and consists of 2 stages: ultrasound and blood drawing.
During the study, the specialist determines the gestational age, the number of fetuses, and their size. The results determine whether the embryo is developing correctly and whether there are any deviations in the indicators.
The second - 16-20 weeks - is prescribed only for deviations identified during the first study. Ultrasound helps to examine the internal organs of the fetus, their size and full development; the brain and its constituent parts are examined.
There is a table of normative values, which shows the normal size of the lateral ventricles of the fetal brain by week.
Enlargement of the ventricles of the brain means the development of ventriculomegaly.
Normally, the fetus should have 4 ventricles, two of them located inside the white medulla. All of them are connected to each other using vessels. The size of the lateral ventricles should be no more than 10 mm; their expansion is considered the beginning of a pathological process that entails negative consequences for the whole organism.
Reasons for education
Ventriculomegaly can occur in isolation or exist against the background of other abnormal developments in the body. But often the enlargement of the ventricles is not accompanied by chromosomal pathologies in the child’s body.
The main cause of the pathology is genetic disorders in a pregnant woman, whose condition is complicated by various negative processes.
The most common reasons include:
- infections and viruses in a woman that have entered the womb;
- injuries during pregnancy;
- impossibility of normal outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, causing dropsy;
- fetal hypoxia;
- hereditary predisposition, hereditary pathology;
- internal hemorrhage;
- brain damage (destructive).
An increase in the size of the ventricles can cause ailments such as Down, Edwards or Bonnevie-Ulrich syndrome in a newborn. In addition, pathology can cause disruption of the functionality of some important structures of the body, for example, the brain, musculoskeletal system or heart.
The first ultrasound cannot be the basis for making a diagnosis. To do this, it is necessary to conduct at least two studies with an interval of 3 weeks to assess the dynamics of changes. A consultation with a genetics specialist, karyotyping of the fetus, and analysis of identified abnormalities in the chromosomal structure are also necessary.
Types of Ventriculimegaly
Pathology of the lateral ventricles of the brain in modern medicine is divided into 3 types:
- mild – in the form of a lesion that does not require surgical action;
- medium – the maximum size of the ventricles is 15 mm, which creates difficulty in the outflow of fluid;
- severe - a characteristic increase in the size of the cerebral ventricles, which is only one of many components that disrupt the functioning of the brain and the entire body.
It is important to know that the human body has a distinctive feature: the ventricles of the brain are slightly asymmetrical, this can be detected even during the period of gestation. In boys, these differences are slightly more pronounced than in girls. If the width ranges from 10 to 15 mm, such cases are called “borderline” ventriculomegaly and this increases the risk of disruption of the central nervous system and other life-supporting organs. It can be asymptomatic for a certain time, but it is the beginning of the development of a complex pathological process and can lead to the development of heart defects, impaired brain development, infections and many other negative aspects of intrauterine development.
Complications and negative consequences
Abnormal development of the cerebral ventricles can lead to very serious complications, and even the death of an unborn child. This pathology can provoke premature birth, disability of the baby, and serious dysfunction of systems and internal organs. If the appearance of these disorders was caused by a genetic predisposition, the following deviations may be observed:
- dropsy of the brain (hydrocephalus);
- mental retardation or Down syndrome;
- physical underdevelopment, dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system;
- Patau or Turner syndrome;
- improper connection of veins, arteries, lymph nodes.
Treatment methods
The main principle of treating this disease is timely identification and elimination of the cause that provoked this disease. When an infection occurs inside the womb, doctors are faced with the task of killing this infection with the help of drug therapy.
The goal of treatment is to eliminate the provoking factor and prevent possible complications and consequences that may appear during the course of the disease and cause irreparable harm, including death.
Since the pathology appears in utero, pharmaceutical treatment is intended for the expectant mother. Mild forms of the disease can be managed without medications; regular monitoring of the dynamics of development and constant monitoring by a doctor are sufficient.
For moderate and severe forms, treatment is prescribed immediately, including the following groups of drugs:
- vitamin complexes and minerals;
- antihypoxants in order to increase tissue resistance to lack of oxygen in the body;
- diuretics to remove excess fluid;
- nootropics that improve blood circulation;
- diuretics;
- To prevent neurological disorders, special agents are used that prevent potassium from being washed out of the body.
In combination with medications, a course of massage and physical therapy classes are prescribed. These measures are also prescribed for children who were born with pathology in order to strengthen their muscles. In any case, with timely measures taken, there is a great chance for a small child to gain a normal, full life.
According to statistics, more than 75% of children outgrow this condition and develop further without deviations from the normal indicators of their peers.
However, there are situations in which drug therapy does not give the desired results either in the womb or at birth. Such pathologies can be solved exclusively by surgical methods. During the operation, a special drainage tube is installed in the child’s skull, which will help drain excess fluid from the brain.
Preventive measures
To prevent the development of pathologies, a woman during the planning period should follow the principles of a healthy lifestyle, as well as take folic acid, carry out prevention and timely treatment of various chronic ailments, viral infections, etc. A medical consultation with a geneticist is mandatory.
Ventriculomegaly is a very dangerous disease that poses a direct danger to the life and health of the baby. That is why examinations and observations by a doctor should not be neglected during pregnancy. If a problem is identified early and corrected early, it increases the chances of a healthy future for your children. With the help of therapy, the consequences and complications of the disease can be eliminated.
This disease is also diagnosed in adults using CT and MRI, but deviations from the norm may not interfere with the normal functioning of the brain and central nervous system; it is only important to control these processes and constantly monitor the development of the disease.
nashinervy.ru
Enlarged ventricles: manifestation
As is known, one of the functions of the ventricles is the secretion of cerebrospinal fluid into the cavity between the meninges and spinal membranes (subarachnoid space). Therefore, disturbances in the secretion and outflow of fluid lead to an increase in the volume of the ventricles.
But not every increase and change in size is considered a pathology. If both lateral ventricles become symmetrically larger, then there is no need to worry. If the increase occurs asymmetrically, that is, the horn of one of the lateral ventricles increases, but the horn of the other does not, then pathological development is detected.
Enlargement of the head ventricles is called ventriculomegaly. It exists in 3 types:
- Lateral (dilatation of the right or left ventricles, enlargement of the posterior ventricle).
- Cerebellar (the size of the cerebellum and medulla oblongata changes).
- Pathological release of cerebrospinal fluid in the frontal region.
There are 3 degrees of the disease:
- Easy.
- Average.
- Heavy.
Sometimes the disease is accompanied by disruption of the central nervous system. Enlargement of the ventricles in large children with a non-standard skull shape is considered normal.
With venticulomegaly, due to a large amount of cerebrospinal fluid, the pressure inside the baby’s skull rises; swelling of the cortex, gray matter, and tissues appears. The pressure disrupts the blood supply to the brain, and deterioration and disruption of the central nervous system are also observed.
The following symptoms are observed with enlarged ventricles:
- Increased muscle activity.
- Deterioration of vision (defocus, squint, downcast gaze).
- Trembling of limbs.
- Strange gait (movement on tiptoes).
- Inactive reflexive manifestations.
- Lethargic, apathetic behavior.
- Increased moodiness and irritability.
- Insomnia, sleepwalking.
- Lack of appetite.
An obvious symptom of venticulomegaly is regurgitation and vomiting, the amount of which exceeds the norm. This occurs due to irritation of the vomiting center in the fourth ventricle, which is located at the bottom of the diamond-shaped fossa.
Not in every situation, expansion of the ventricles of the brain causes the development of unfavorable symptoms. Usually the child does not feel much discomfort, which clearly indicates the development of a rather complex pathology. But with more severe disorders, the baby may experience the following adverse effects:
- Visual disturbances manifested in the form of poor focusing or strabismus. Sometimes a child may experience double vision, and this condition intensifies when looking at small objects.
- Disturbed gait: the child stands on his heels or walks on his toes.
- Disproportional head.
- Behavioral disorders: the little patient becomes drowsy and lethargic, even somewhat apathetic, and finds it difficult to get involved in recreational activities.
- Changes in muscle tone, revitalization of tendon reflexes.
- Dizziness and pain in the head area.
- Vomiting may develop.
- Bulging, tension and enlargement of the fontanelles in linear dimensions.
- Optic disc congestion.
- Decreased appetite: The newborn usually does not eat well and has increased regurgitation. High cerebrospinal fluid pressure can affect the vomiting center, which is located at the bottom of the rhomboid fossa.
- Decreased sucking and swallowing reflexes.
- Disturbed sleep: the child has difficulty falling asleep and may walk in his sleep.
- Pronounced veins in the forehead, which causes obstructed blood flow from the head.
Are the ventricles of the brain enlarged in an infant? This pathology has varying degrees of severity during its course. When initial symptoms are detected, a mild course of the disease is noted. If a baby develops the above symptoms, which indicate high pressure inside the head, the illness may become more severe. If the baby’s condition generally deteriorates, it is recommended to carry out rather severe treatment, always in a hospital.
It is important to understand that all of the above symptoms do not necessarily indicate the development of brain enlargement. A slight increase in these structures and their slight asymmetry, changes in the fundus, and the presence of reflexes may not bother parents in any way. The main thing is to constantly monitor the baby’s condition and regularly perform neurosonography.
Ventriculomegalic state
With it, the cavity system of the ventricular apparatus is enlarged, which will result in dysfunction of the central nervous system.
Depending on the severity, the pathology occurs in mild, moderate and severe; location determines the following types:
- lateral, in which there is a pronounced increase in some of the ventricles in a small child, such as the posterior and lateral;
- another type, where the pathology is located in the area near the visual thalamus and frontal region;
- in the next case, the focus affects the cerebellar region with the medulla oblongata of the brain.
The main root cause of possible pathology in newborns is considered to be a chromosomal abnormality in pregnant women. Other circumstances that determine why certain ventricles of the brain zone in a small child are enlarged include infectious diseases, physical trauma, hydrocephalic obstruction, hemorrhagic manifestations, and complicated heredity.
Symptoms of the disease
Dilated certain ventricles of the brain in a small child are the root cause of the Down, Turner, and Edwards syndrome conditions. In addition, enlarged certain ventricles of the brain area in a small infant affect cardiac activity, brain structures and the musculoskeletal system.
Diagnostic measures
This condition in children is diagnosed using an ultrasound examination of the head.
How is it treated
In a condition where the lateral ventricles of the child’s brain are dilated, the main thing is to prevent complicated conditions in the body. Diuretics, vitamin preparations, and antihypoxants are prescribed. Additional methods of treatment for this condition are massage procedures with special physical therapy. To prevent complicated conditions, potassium-sparing agents are used.
Diagnostics are carried out to clarify the diagnosis. A doctor can notice a chronic form of venticulomegaly as early as three months of age using an ultrasound. The examination includes the following procedures:
- Examination by an ophthalmologist (this will reveal swelling of the eyes and hydrocephalus).
- Magnetic resonance imaging (the MRI procedure helps monitor the growth of the ventricles after the fusion of the cranial bone. To carry out the examination, which takes from 20 to 40 minutes, the baby is put to sleep with the help of drugs).
- CT scan. In this case, medicated sleep is not required because the procedure does not take much time. So CT is the best option for children who cannot tolerate anesthesia.
Ultrasound is prescribed for children born after a pregnancy during which there were complications. It is done in the first year of life, and if there are no neurological abnormalities, then it is repeated after three months.
To determine the exact dimensions of the ventricles, doctors prescribe the following informative methods:
- Computed tomography makes it possible to identify the size of the ventricles, as well as their structure. This procedure does not cause any particular inconvenience to the newborn and does not harm him.
- Ultrasound examination describes the size and quantitative indicators of the ventricles of the brain, and also calculates their index. This method helps to estimate the available volume of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain collectors.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is used if the diagnosis is quite difficult to establish. This procedure is performed for older children. But even for small children, MRI, if the ventricles of the brain are enlarged in an infant, is carried out after putting them into anesthesia.
- Neurosonography.
- Examination of the fundus of the eyes.
After complete closure and narrowing of the fontanelles, the doctor begins to monitor changes in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, performing MRI and X-ray CT. Magnetic resonance imaging describes the soft tissue structures of the brain as completely as possible, but, as noted above, you need to lie in the ring of the device for quite a long time, and this will be very difficult for a small child. It is also worth remembering that there are some contraindications for this procedure.
In such a situation, computed tomography, which quickly determines the size of the ventricles, will be very effective. But it is worth understanding that tomography has a small radiation dose on the newborn, and the quality of the information will be less.
Are the ventricles of the brain enlarged in an infant? This could be caused by subarachnoid or subdural hemorrhage. In this case, an MRI will detect excessive blood accumulation. Typically, pathological dilatation of parts of the brain begins with the horns at the back of the head. To examine them, screening methods are used - neurosonography, or ultrasound through the fontanel to identify the size of the ventricles and brain.
Why do you need to know the size and weight of the fetus?
The weight and height of the fetus are the most important characteristics that give doctors the opportunity to assess how well the child is developing and feeling well. When the baby’s formation proceeds normally and neither he nor his future mother has any pathologies or abnormalities affecting the embryo, he grows according to established standards.
A small fetus may indicate problems with the development of the child - if there is a lack of oxygen or nutrients, the embryo grows more slowly than it should. The reasons for this are usually:
- bad habits - alcohol, smoking;
- insufficient nutrition of a pregnant woman;
- problems with the placenta;
- diseases of the internal organs of the expectant mother, causing fetoplacental insufficiency.
Frozen pregnancy is another reason that can cause the fetus to weigh too little because it has stopped developing.
An excessively large baby may be a consequence of diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman. Overeating or poor nutrition can also cause increased weight in the embryo.
But deviations in a child’s weight or height are not always caused by pathologies - this can also be a hereditary trait, because a miniature mother and a small father will most likely give birth to an equally small baby. Therefore, if a deviation from the norm is detected in the fetal parameters, it is important to accurately determine its cause. Unhealthy lifestyle (drinking alcohol, smoking, malnutrition, excess food consumption) is quite easy to correct. If deviations from the norm are caused by problems in the pregnant woman’s body, the doctor refers her for auxiliary examinations and prescribes the necessary treatment - the woman is usually hospitalized and measures are taken to improve uteroplacental blood flow so that the child receives enough vital substances for the full development and formation of all organs.
Excessive consumption of sweets during pregnancy leads to excessive weight gain in the child
Another reason why doctors need to know the physical parameters of the child is to establish the due date. The 11th week of pregnancy is considered the most ideal time for calculations - it is at this period that, using some parameters of the embryo, one can determine its age (with an error of 1-3 days) and, accordingly, predict the day when the gestational age reaches 40 weeks. Of course, this does not give any guarantee that the birth will occur on this day, but it is the preliminary date of birth that is taken as the starting point.
In addition, the parameters of the fetus are used to determine how the child will be born. If the size of the baby exceeds the size of the expectant mother's pelvis, then a caesarean section is prescribed.
My first child was born quite big - a little more than 4 kilograms. When I became pregnant with my second, I carefully monitored the pounds I gained because I didn’t want to carry an overly large baby again. Until 30 weeks, my daughter’s weight did not raise any suspicions. At the third screening, however, I was told that the expected due date had moved forward a week due to the fact that the baby was slightly overweight. The next ultrasound was performed 5 weeks before the PDR - and again there was a shift, an even greater weight gain. A week before my due date, I ended up in the maternity hospital with contractions - they turned out to be training contractions, but just in case, I was admitted to the hospital, and also had another ultrasound. His result shocked me - the baby already weighed 4100! Fortunately, I didn’t have to test whether I could independently give birth to a baby over 4.5 kilograms - after a couple of days, real contractions and labor began. The final weight of the child turned out to be only 3800 grams, so calculating the child’s weight using ultrasound also does not, as it turned out, provide complete accuracy. However, this method gave a smaller error than my attempts to calculate the body weight of the baby growing inside me using formulas using my parameters - they gave a range from 3.5 to 4.5 kilograms.