What it is
Fetometry is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure performed at least 2 times during the entire gestation period. It is carried out in a medical institution using a special ultrasound device.
The numbers obtained from fetometry help determine the size of the ovum. With their help, the diagnostician identifies the presence of disorders in the mother’s body, which can lead to irreversible negative consequences during pregnancy.
In later periods of gestation, the formation of the embryo and its individual organs is monitored using research. If a pathological process is detected, the woman is recommended to terminate the pregnancy.
Ultrasound 10-14 weeks
At this stage of pregnancy, the fetus has formed its main systems and organs. The specialist prescribes this routine ultrasound examination for the first trimester to every woman awaiting the birth of a new life. At this time, doctors do not have as a goal to determine the sex of the child, as pregnant women mistakenly think.
The purpose of ultrasound at 10-14 weeks is:
- Confirmation of the expected gestational age by the gynecologist. An experienced specialist will install it during this period with maximum accuracy. Only thanks to such accuracy will an obstetrician-gynecologist be able to determine whether the baby’s development is in accordance with the established gestational age.
- Detection (if any) of gross malformations in the development of the fetus. It is thanks to ultrasound that echoscopists can determine the presence of certain defects in the baby. In such cases, women are advised to terminate pregnancy using low-traumatic methods. Of course, the decision depends only on the pregnant woman, her religious and aesthetic views.
Ultrasound helps determine the gestational age. There are discrepancies between the dates of the last menstruation and ultrasound. If there is a difference of a week or a week and a half, doctors give preference to the results of an ultrasound examination. It determines the CTE and establishes according to the table compliance with the size norm at a certain period of development.
If the difference is more than two weeks, then the period is determined by ultrasound.
Ultrasound examination at this time is also called “genetic”. Already by 10-14 weeks, specialists can visualize swelling of the collar space using ultrasound. In most of these pathologies, the fetus subsequently showed signs of Down syndrome. Thus, this pathology can be determined already at 10-14 weeks.
If the thickness of the fold is about 3 mm, this is considered a pathology. During this period of development, the thickness of the collar space of most fruits is less than a millimeter. With increased thickness, the specialist does not make an unambiguous diagnosis. He recommends that the pregnant woman undergo further examination by geneticists. It is thanks to this screening that gynecologists identify a risk group among the entire stream of pregnant women.
What are they watching?
During fetometry, the diagnostician pays attention to:
- gestational age (if clinical and anamnestic information is insufficient);
- correspondence of changes in the embryo;
- diseases of individual organs and systems – skeletal dysplasia, microcephaly;
- risk group, taking into account chromosomal aberrations.
A doctor who evaluates fetal fetometry week by week has the opportunity to calculate the risk of disorders and failures at the genetic level.
In 1st trimester
In the first trimester, the diagnostician determines and confirms PDR. The results help to exclude or not malfunctions at the chromosomal level.
The doctor also examines the embryo for gross developmental pathologies and whether all organs have developed. The coccygeal-parietal size and abdominal circumference are measured - these are the main indices in the early stages.
In the 2nd trimester
At this stage, the procedure is prescribed to check the absence of defects in the baby. Also, the diagnostician can already determine the gender of the unborn baby.
Parameters that gynecologists look at:
- biparietal diameter;
- frontoccipital value;
- Head circumference;
- average abdominal diameter;
- abdominal circumference;
- femur length;
- intersemilutar diameter of the cerebellum.
Interpretation of fetal fetometry is carried out only by a doctor. Minor anomalies from standard numbers are determined individually for each woman.
At the same time, the characteristics of her body and the presence of chronic diseases are taken into account.
In the 3rd trimester
In the last stages of pregnancy, the percentile during pregnancy is calculated taking into account changes in relation to previous indices. Diagnostics are carried out to measure the weight and height of the child, the symmetry of its changes and once again confirm the expected date of birth.
Possible developmental disorders of the ovum
Under the influence of certain factors, the development of the fertilized egg can occur with certain pathologies. You can find a description of the most commonly diagnosed anomalies in the following table.
Table. Pathologies of the development of the ovum
| Pathologies | Description |
| Form violations | The shape of the fertilized egg in both scans up to 5-6 weeks is usually round. By 6-7 weeks, the fetal egg becomes oval in a longitudinal scan, but remains round in a transverse scan. Along with this, the development of form can occur with various kinds of deviations. Most often, this is caused by various types of tumors in the uterine cavity. Also, this pathology can occur in the case of partial placental abruption. |
| Pathologies of location | In the absence of deviations, implantation of the fertilized egg most often occurs in the fundus of the uterus or its posterior wall, sometimes in the area of the internal os or at the top of the uterus. Other options for the location of the ovum are assessed by a specialist. He also makes a decision on further actions in relation to a particular patient. |
| Dimensional violations | Information regarding changes in the size of the ovum as pregnancy progresses has been provided previously. Significant deviations from the given values in both directions are considered pathological, and conclusions about their significance are made by a specialist. |
| Functional pathologies |
It is impossible to give any definite answer regarding the causes of the development and treatment of pathologies in the development of the ovum - each case requires individual consideration by a qualified specialist. Only a doctor can objectively assess the situation and make the most appropriate decision.
Regularly undergo the necessary examinations, follow the recommendations of your treating specialist and be healthy!
What to pay attention to
It is impossible to track all intrauterine abnormalities at once, so indicators are monitored until the moment of birth. This makes it possible to identify possible violations and enable parents to decide on measures to eliminate them.
During the research process, it becomes possible to determine possible developmental delay. There are 3 degrees of lag reflected in the standards:
- 14 days;
- menstruation;
- up to 2 months.
With subsequent studies, the difference returns to normal. If this does not happen, the leading gynecologist will prescribe additional methods to identify the causes of the failure.
Baby's weight
The child's conditional height and weight are monitored from the first planned ultrasound. The numbers cannot be exact, only approximate.
Even with a weight of 2300 g, healthy children are born if the pregnancy was multiple. Also, the weight of 4500 g of a newborn should not be alarming and be a reason for panic if one of the parents is large.
Approximate baby weight by week:
- 11 – up to 16 g;
- 22 – up to 500 g;
- 32 – before 1950;
- 40 – 3500 g.
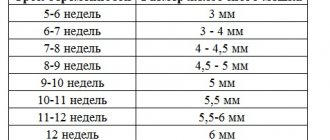
Coccygeal-parietal indicators
CTE is determined at the first screening. The results obtained are the main criterion for assessing the formation of the embryo. CTE is also compared with fetal weight and gestational age.
They allow you to control the progress of the baby’s maturation over time and monitor possible deviations. Certain data are compared with average standards in a special table.
Bipareital size
BDP on ultrasound during pregnancy is the distance between the outer and inner contour of the bones of the crown. In other words - from one temple to another.
Along with this information, the fronto-occipital size is taken into account. At the first screening, it should not exceed 31 mm. Using the BTR, it is possible to determine the period only up to the 23rd week, and after the 29th week the reliability of the results decreases.
The indicators allow you to evaluate the structure of the brain, skull bones, and detect the presence of neoplasms.
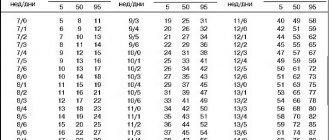
Table of fetal BPD norms by week:
- 12 – 21 mm;
- 16 – 34 mm;
- on the 32nd – 82 mm;
- on the 40th – 96 mm.
Thigh length
The length of the femur allows you to calculate the gestational age and identify visible disturbances in the growth and formation of the baby. In the second month, the length of the thigh should be 9-12 mm, starting from the 22nd month - 40 mm, and at the 40th - 77 mm.
Abdominal circumference
Abdominal circumference is measured at the second and third screening. Measurements are taken along the line of the liver, stomach, and umbilical vein. Monitoring is necessary to assess the baby's growth. The standards are compared using a special table.
Sternal volume
Results are informative at 14-22 weeks. But doctors use several parameters to evaluate a child's changes. The conformity of the formation of other organs is taken into account.
Biparental fetal size by week
Another important indicator that experts take into account in their research is the biparietal size, represented by the distance between the outer surface of the upper contour and the inner region of the lower contour between the parietal bones.
As is the case with other indicators, when analyzing the resulting biparietal size, minor deviations from the norm are allowed. If the established data is exceeded, the specialist must evaluate other parameters, represented by abdominal circumference and limb length.
Analysis of this indicator is extremely important, because its deviations from the norm in many cases may indicate serious pathologies, represented by hernias, tumors and other space-occupying formations, in which the only way out may be termination of pregnancy. Insufficient development of the baby’s head or a decrease in its size is also considered undesirable, which may be due to underdevelopment or absence of anatomical structures of the brain. In this case, experts also strongly recommend termination of pregnancy.
Often, in the third trimester, reduced indicators of BPD are diagnosed, which, if detected in a timely manner, can be successfully corrected.
As a rule, in this case, a diagnosis of intrauterine growth retardation is made, and the pregnant woman is prescribed treatment with medications that help improve uteroplacental blood flow and ensure the transport of necessary nutrients.
In medical practice, the following average indicators of biparietal dimensions of the fetus are used:
- 8 week – 6 mm;
- 9 week – 8.5;
- 10 week – 11 mm;
- 11 week – 15 mm;
- 12 week – 20 mm;
- 13 week – 24 mm;
- 14 week – 26 mm;
- 15 week – 32 mm;
- 16 week – 35 mm;
- 17 week – 39 mm;
- 18 week – 42 mm;
- 19 week – 44 mm;
- 20 week – 47 mm;
- 21 weeks – 51 mm;
- 22 week – 54 mm;
- 23 week – 58 mm;
- 24 week – 61 mm;
- 25 week – 64 mm;
- 26 week – 67 mm;
- 27 week – 69 mm;
- 28 week – 72 mm;
- 29 week – 75 mm;
- 30 week – 78 mm;
- 31 weeks – 80 mm;
- 32 week – 82 mm;
- 33 week – 84 mm;
- 34 week – 86 mm;
- 35 week – 88 mm;
- 36 week – 90 mm;
- 37 week – 91 mm;
- 38 week – 92 mm;
- 39 week – 94 mm;
- 40 week – 95 mm.