A fracture is most often the result of an injury that disrupts the integrity of the bone. Soft tissues can also be damaged, swelling and hematomas form, and the person experiences severe and prolonged pain. Of particular danger are ruptures of arteries and nerves. Incorrect actions of others when independently transporting a patient can even lead to death.
First aid for fractures should not only relieve the victim of pain, but also eliminate the risk of additional complications, prevent wound infection and prepare the person for evacuation.
Types of fractures
The most common cause of a fracture is injury from a fall or blow. There are a number of diseases that reduce bone strength. Even with minor loads and occasional muscle tension from everyday work, the integrity of bone tissue is disrupted, which leads to fractures. Such diseases include:
- Osteoporosis;
- Tuberculosis;
- Malignant bone tumors;
- Osteopetrosis;
- Osteomyelitis.
The fracture can be partial or complete; in the first case, a crack or break is formed; in the second, bone fragments move freely relative to each other, which often leads to deformation of the damaged area.
Fractures are classified as open, when the integrity of the skin is broken; there are also closed and complicated ones. With the latter, the surrounding tissues are torn, severe bleeding, serious wounds and large hematomas are observed. Based on the type of fragments, fractures are divided into:
- Longitudinal;
- Transverse;
- Helical;
- Oblique;
- Splintered.
A very serious danger is posed by ruptures of large vessels, arteries and important nerves, which result in large blood loss, traumatic shock, and with an open fracture there is a high probability of tissue infection.
For this reason, it is very important to provide the victim with first aid after an injury, but all actions and their sequence must be competent. Otherwise, the risk of complications increases.
Local clinical signs
Clinical manifestations at the site of injury arise as a result of the action of a traumatic factor and subsequent damage by bone fragments to soft tissues (muscles, blood vessels, nerves). These include pain, swelling, hematoma formation or hemarthrosis, limb deformation, impaired innervation, deterioration of blood and lymph outflow.
Pain syndrome
Pain of varying severity is the first and constant sign of a bone fracture. In cases of severe injuries to large tubular bones, the spine, and joints, the pain syndrome is highly intense, which forces patients to seek medical help immediately after the injury. In the case of incomplete fractures of the fissure type, the pain is weak and aching, intensifying with movement. Such patients do not immediately consult a doctor and continue to lead a normal lifestyle. This leads to the development of complications and impairs fracture healing.
Bone is visible at the bottom of the wound - an open fracture
The intensity of pain depends on the individual threshold of pain sensitivity. People with a labile psyche do not tolerate pain well, which increases the risk of developing traumatic shock. Victims under the influence of alcohol or drugs at the time of injury weakly feel painful stimuli. In such cases, the intensity of pain does not always reflect the severity of bone damage.
High-intensity pain syndrome occurs when the integrity of the nerves is disrupted and can subsequently lead to disruption of various types of sensitivity. Children usually feel pain acutely and react to its occurrence. In older people, pain is less pronounced even when severe injuries occur.
Swelling, hemorrhage, hemarthrosis
After the injury, smoothing of the contours and thickening of the limb occurs within a few hours. This occurs due to impaired blood circulation and lymph outflow, which causes swelling in the fracture area. Edema is most pronounced in areas of the body not covered by muscles, with well-developed subcutaneous fat.
As a result of bone trauma, hemorrhages often occur:
- subcutaneous,
- subperiosteal,
- intermuscular,
- subfascial,
- intra-articular (hemarthrosis).
Hemarthrosis due to intra-articular fracture
Subcutaneous hematomas form within an hour after injury and are easily identified by examining the area of injury. Intermuscular and subfascial hemorrhages can form at some distance from the grass due to the movement of spilled blood between the fascia or muscle fibers. Hemarthrosis causes stretching of the joint capsule, increases its volume and impairs the motor function of the arm or leg. Hematomas can fester with the formation of phlegmon, which complicates the course of the pathological process and worsens the general condition of patients.
Limb deformity
Deformation of an injured arm or leg occurs with open fractures and closed injuries, which are accompanied by displacement of bone fragments. Violation of the anatomical integrity of the bone occurs with crushed or splintered injuries, as well as with significant displacement of fragments under the influence of traction of large muscles. Changes in the shape and volume of the limbs are facilitated by the formation of hematomas and hemorrhages in the joints.
Disturbance of innervation, blood and lymph outflow
Compression of peripheral nerves by bone fragments or hematoma leads to impaired sensitivity and motor activity of the limbs. Based on the nature of the neurological symptoms, it is possible to determine which nerve trunks are damaged by the pathological process. Compression of blood vessels and lymphatic pathways causes congestion and impaired blood flow (ischemia).
Clinical symptoms of impaired blood and lymph outflow:
- paleness of the skin, marbled skin pattern;
- decrease in local temperature, cold extremities;
- swelling;
- decreased pain sensitivity;
- trophic disorders (dry skin, destruction of nails);
- weak pulsation or absence of pulse in the peripheral vessels of the arms or legs.
Bone damage is confirmed by radiography
Violation of blood flow and microcirculation causes a deterioration in the motor activity of the limb, and in severe cases leads to the formation of gangrene.
Signs of a fracture
The victim may only notice acute pain in the area of injury, which becomes stronger with movement and changing body position. With microcracks and small fractures, symptoms may resemble a severe muscle strain or torn ligament. Diagnosis of such injuries is carried out by X-ray examination. Relative signs of a fracture are:
- Acute or prolonged aching pain in the injured area;
- The presence of edema and hematoma (not observed immediately);
- Limited mobility;
- Deterioration of motor functions of the limbs;
- Bone deformation is visually noticeable;
- Mobility in the area of damage.
If a crunch is heard, bone fragments move, fragments are visible in the wound, or the length and shape of the limb changes, in this case absolute signs of a fracture are observed. The victim urgently requires medical attention, and all measures must be taken to avoid causing major damage.
Kinds
Before providing first aid for fractures of the extremities, it is necessary to take into account the main symptoms that confirm that a violation of the integrity of the bone has occurred. These include deformation of the limb, loss of motor function, swelling and swelling in the injured area, a characteristic crunch when moving the affected part of the body, and severe pain. If it is not possible to determine whether a fracture or other injury has occurred, the rules applicable to a fractured limb must be followed.
In any case, you need to immobilize the limb. Immobilization is carried out with the application of a Kramer transport splint. If there are no special transport tires, then you can use boards, cardboard, an umbrella or other dense material.
Carrying out first aid for limb fractures, depending on the type and nature of the injury, the degree of severity, includes a set of the following actions:
- Emergency care for upper limb injuries consists of ensuring complete immobility of the injured arm and fixing the injured limb to the body with a bandage. If the shoulder joint is damaged, fixation is carried out using two splints. One of them is bandaged on the outside of the shoulder, the other - from the armpit to the elbow joint. If a special splint is not at hand, then the bent arm is suspended on a scarf and bandaged well to the body. The victim is transported in a sitting position. To prevent the occurrence of hematoma, swelling, and reduce pain, apply ice or a cold compress to the injured area. It is important to ensure complete calm of the patient; you can give a drug with a calming effect. If there is severe pain, painkillers should be taken.
- First aid for a lower limb injury should be provided by ensuring complete rest of the injured leg. You need to immobilize one joint located above the fracture site to another, which is located below the injury site. Secure the injured leg by tying it to the healthy limb. If swelling has formed, a bandage should be applied to it.
It is also useful to know how to provide first aid for a broken arm.
First aid after a fracture
Having assessed the person’s condition, you should contact an ambulance, where they will advise you to wait for the medical team to arrive or take the victim to the nearest medical facility. When talking with the medical service dispatcher, you need to inform about the nature of the injury, the patient’s well-being, and the presence of wounds.
If bleeding is observed, first aid is necessary to stop it. When an artery is damaged, bright scarlet blood flows out in a powerful and strong stream. In this case, a tourniquet is applied above the wound; it can be made from durable fabric of sufficient length, a tie or a belt. When dark blood slowly leaks out, the victim's veins are damaged.
It is necessary to use a pressure bandage that is placed below the wound. The time of application of the tourniquet should be accurately recorded and then reported to the arriving doctor. After about 1.5 hours, be sure to loosen the tourniquet for a few minutes to prevent tissue necrosis.
The damaged part of the body must be immobilized by making a splint from improvised means. Such first aid will eliminate pain, prepare the person for evacuation and reduce the risk of injury. Any solid object of sufficient length can be used as the surfaces that form the tire: sticks, pipes, plastic or metal parts.
In the absence of such, the damaged part of the body is bandaged to the healthy one. The hand is applied to the body, and the legs are fixed together. The limb is secured tightly and firmly to immobilize the joints in the immediate vicinity of the fracture site.
Wounds should be treated with a solution of hydrogen peroxide or any non-alcoholic antiseptic. The skin is lubricated with iodine, but it should not get into the wound itself. A sterile gauze bandage is applied on top. In emergency cases, you can apply a clean scarf or piece of cloth, after which the damage must be bandaged.
A cold pack or compress wrapped in a cloth is applied to the injured area. It is important not to place it directly on bare skin, this will only increase the pain and damage the blood vessels. As cooling elements, you can use any available materials from the refrigerator or freezer: frozen vegetables or pieces of meat, ice, bottles and cans of drinks. If a person is outside, his body is warmed by covering him with a blanket or warm clothes.
Hot drinks are allowed only if there is no damage to internal organs.
The victim is administered drugs that relieve pain (Analgin, Promedol, Morphine). Before the doctors arrive, you can give any painkillers in tablets, after making sure that the person is not allergic to them. Sleeping pills and sedatives should be avoided.
What not to do for fractures
Until doctors arrive, you should not move bone fragments in an attempt to restore its normal shape. When moving, fragments can easily damage arteries and nerves and disrupt the functioning of internal organs. There is no need to set the bone yourself if it comes out during an open fracture.
You should not change the position of the victim’s body or move him without fixing the damaged bone motionless. The load on the injured area should be minimal.
When securing the splint, there is no need to undress the patient, freeing the injury site from clothing.
All immobilizing bandages are applied to the pant leg or sleeve. They should stay tight on the body, but also not interfere with the blood supply.
If, with a fracture of the upper extremities, a person is often able to get to the hospital or emergency room on his own, then if the lower extremities are damaged, it is better to wait for an ambulance to arrive. If a spinal fracture is suspected, it is not recommended to move the victim; he should not be tilted or lifted by his arms and legs.
X-ray symptoms
Even if there are obvious signs, the patient should be given an x-ray in two projections - in front and from the side of the injury. Looking at the x-ray, the doctor sees that the bone is damaged, determines what direction the fracture line is, whether the fragments are displaced and how many bone fragments there are. For severe fractures, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may be performed. Thanks to these studies, the doctor can assess the condition of joints, ligaments, muscle tissue, blood vessels and nerve endings.
Knowing what signs occur when a bone is broken, a person can distinguish this injury from other injuries and consult a doctor in a timely manner. Based on clinical, local, general and x-ray symptoms, the doctor makes a diagnosis and selects the optimal tactics of therapeutic therapy and rehabilitation measures.
First aid for various types of injuries
Leg fractures
If you break your leg, you will need two splints.
They are attached to the straightened injured limb, one is placed on the outer surface of the leg, the other on the inner. The end of the first splint should reach the armpit and grip the foot. The second splint is placed from the perineum to the foot, after which the entire structure is tightly bandaged to the body. In case of a hip fracture, the splint should cover the hip, knee and ankle joints. If the foot or toes are injured, a small board is attached to the sole.
Damage to hands and fingers
The fingers are carefully shaped into a grip, and a piece of cotton wool the size of a small apple or a similar lump of soft improvised materials is placed in the palm itself. Then the hand is bandaged to the tab, and the hand is suspended on a scarf or piece of fabric, having previously applied a splint.
Nose fracture
First aid for a person with a broken nose is to sit him up, tilting his head slightly forward so that the leaking blood does not enter the trachea. Wounds and abrasions should be treated with antiseptic agents, and cotton swabs should be placed in the nostrils. To stop bleeding, it is better to apply a cooling bag or a package filled with ice to the bridge of the nose.
Jaw fracture
A fracture of the lower jaw can lead to suffocation if the victim loses consciousness, and a retracted tongue blocks the airway. The patient is placed in a sitting position with his head tilted to the side, or placed on his stomach. It is very important to ensure normal breathing and clear the oral cavity of blood clots and foreign bodies. Bleeding is stopped with a cotton-gauze bandage, and in the most severe cases, stitches are applied.
If the upper jaw is damaged, take a bandage, bandage or piece of cloth, carefully pull the chin up and fix it. If the victim's teeth do not close, a piece of plywood is placed between them, and then the head is bandaged.
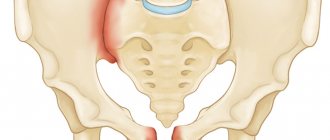
Pelvic bones
When the pelvic bones are damaged, soft stretchers cannot be used. To create a hard surface during transportation, a sheet of plywood or boards are placed on top of them. The victim is placed on his back with his legs spread apart (frog pose). A large roll made from clothing and other soft objects is placed under the knees, after which the legs are secured with bandages, belts or strips of fabric.
Forearms
If there is a suspicion of a forearm fracture, first aid consists of applying a splint and quickly transporting the person to a doctor. Although the injured person may be able to walk and be able to get to a medical facility on their own, they should not be left alone due to possible post-traumatic shock.
The splint should be applied to the arm, for which it is bent at the elbow joint. The angle between the forearm and the upper arm should be close to straight. The hand is carefully turned with the palm towards the stomach.
The hard objects at hand for creating the splint are selected in such a size that one end of the structure is in the area of the fingers, and the other extends beyond the elbow joint.
Fractures of ribs and clavicle
If you fracture your collarbone, it is very important to immobilize your arms and entire upper body. Typically, such injuries are the result of a fall on a straight arm. On the side of the injury, a large roll of fabric or cotton wool is placed in the armpit, and the shoulder is tightly bandaged to the body. The hand can then be placed on the knotted garment. The forearm is suspended on one bandage, and the other arm is fixed closer to the body.
One of the signs of a rib fracture is difficulty breathing, which is accompanied by chest pain. A thick, wide bandage is applied to the upper part of the body; it must be secured as the injured person exhales.
Spine
A spinal fracture is a very serious injury; even slight displacement of bone fragments can lead to paralysis or death. The patient must not be turned over, moved, tried to sit up, or otherwise changed the position of his body. A person with a spinal injury can only be transported on a stretcher or on a hard surface under the supervision of medical personnel. To avoid painful shock, the victim is given an increased dose of pain medication and waits for the ambulance to arrive. Signs of a spinal fracture are:
- Loss of sensation or paralysis of limbs;
- Labored breathing;
- Spontaneous urination and defecation;
- Severe pain in the back;
- Visual deformation of the vertebrae.
Self-transportation of the victim is carried out only in an emergency or desperate situation, when it is impossible to wait for medical help. A person is placed on a hard surface in one step, and he cannot be lifted by his legs, arms or shoulders. Only objects that are longer than his height are suitable for transporting a patient. It is best to move the victim with a team of several people, carefully lifting him by the edges of his clothing and acting in concert.
After a person is placed on a stretcher, he is firmly secured to it using available means - belts, ropes or bandages. You need to place a thick fabric roll under your neck. If a fracture of the upper spine is suspected, such a cushion should be wrapped around the entire neck, and the head should be secured with other soft objects. The patient is transported only in a horizontal position, without sudden movements and without tilting the stretcher.
First aid for fractures of the femur, tibia and pelvic bones
To apply a splint bandage in case of a hip fracture, you need to have at least two large splints. The first of them is applied to the outer plane of the leg, with one of its ends located under the armpit. The second is to slightly protrude beyond the foot area. It is important that the second splint is applied strictly along the inner plane of the leg so that one end reaches the perineum, while the other protrudes beyond the foot itself. In this position, the splints must be bandaged to the body.
When special splints or similar devices are not available, the injured limb must be bandaged to the uninjured leg. In case of a tibia fracture, first aid is provided in the same way as for a hip injury.
A characteristic feature of pelvic bone fractures is that internal organs are damaged, and therefore bleeding and shock are likely. The victim’s pelvic bones should be placed in a position that will create a minimum of pain.
in a horizontal position on your back with a bolster under your feet;
your hips should be slightly apart.
The cushion can be made from a pillow, outer or warm clothing, or any other fairly soft material. The victim can be transported only on a hard board or board. It would be best to carry out various anti-shock measures before this, for example, relieving pain or stopping bleeding.
Skull fracture
When the skull is fractured, a change in its shape may be observed, and there are dents and breaks on the head. The most dangerous thing in this case is damage to the brain, when it is compressed, hemorrhage occurs, as a result of which the person loses consciousness. The victim may bleed from the nose or ears, or cranial fluid may leak out.
First of all, it is necessary to secure the head and neck with rollers made of fabric and clothing. The person is placed on a stretcher, a mat with a small depression is placed under the head, a soft collar is placed on the neck, and bolsters are placed on the sides for reliable fixation.
Much depends on timely first aid for a fracture and the correct sequence of actions; wrong decisions by others often provoke complications of injuries and infection of the wound. The victim's life may be in danger, especially for injuries to the skull and spine.
An incorrectly applied splint, tourniquet or pressure bandage leads to a number of problems, the elimination of which will require long and difficult treatment. If you suspect a fracture, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.