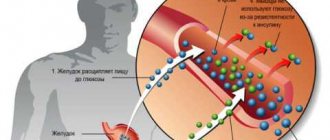
Consultation with a doctor and repeated testing is important if, after receiving the first results, it is discovered that blood glucose is elevated.
It is necessary to find out what this means and what is the reason for the violation.
Most often, an increase in dextrose is indicated by disruptions of the endocrine system, which lead to diabetes mellitus.
Letters from our readers
Topic: Grandma's blood sugar has returned to normal!
From: Christina ( [email protected] )
To: Administration diabeto.ru
Christina, Moscow
My grandmother has been suffering from diabetes for a long time (type 2), but recently there have been complications in her legs and internal organs.
I accidentally found an article on the Internet that literally saved my life. They gave me a free consultation over the phone and answered all my questions and told me how to treat diabetes.
2 weeks after completing the course of treatment, my grandmother’s mood even changed. She said that my legs no longer hurt and the ulcers are not progressing, next week we will go to see a doctor. I am sending a link to the article
Causes
Risk factors that can cause high blood sugar include:
- genetic predisposition;
- poor nutrition (especially consumption of large quantities of baked goods and sweets);
- irrational use of medicines;
- bad habits (especially alcohol abuse);
- heavy blood loss;
- deficiency of vitamins in the body (especially B1 and C);
- excessive physical activity;
- carbon oxide poisoning;
- frequent stressful situations.
With the development of gestational diabetes in the early stages of pregnancy, there is a risk of developing fetal pathologies, including serious ones.
Elevated sugar levels are observed in diabetes mellitus, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, stroke, heart failure, epileptic seizures, and some pathologies of the thyroid gland, stomach and intestines. The risk group includes women with polycystic ovary syndrome, as well as people with low potassium concentrations in the blood.
In women, an increase in sugar can also be observed during premenstrual syndrome, during pregnancy. Hyperglycemia in pregnant women is caused by changes in hormonal levels and the associated low susceptibility of body tissues to the action of insulin. This condition is called gestational diabetes. Often it occurs in the absence of any clinical manifestations, is detected only during laboratory diagnostics and goes away after childbirth. When gestational diabetes develops in the early stages of pregnancy, there is a risk of developing fetal pathologies, including serious ones: heart defects, cerebral palsy, congenital cataracts, etc. In some cases, gestational diabetes can turn into true diabetes. The risk group includes pregnant women with a family predisposition to diabetes, obesity, arterial hypertension, and a history of repeated miscarriages.
Doctors note an increase in the frequency of detection of hyperglycemia in children. This phenomenon is associated with regular consumption of large amounts of fast food, early introduction of cow's milk and/or grains into the diet, drinking water with excess nitrates, and nervous disorders caused by an unfavorable psychological climate in the family. In addition, hyperglycemia in children is often observed after influenza or rubella.
Who is at risk for decreased glucose tolerance?
The process of carbohydrate metabolism and the risk of excess insulin production threatens not only people with a congenital predisposition and the above risk factors. It is recommended to regularly take sugar tests if you have previously been diagnosed with:
- diseases of the liver, heart, blood vessels and intestines;
- increased blood lipid levels;
- hypothyroidism;
- gout;
- atherosclerosis;
- high cholesterol levels.
Pressure in diabetes mellitus - diagnosis, treatment
Such diseases do not mean the presence of diabetes mellitus (even in the early stages), but indicate that the body is predisposed to its occurrence. The only way to protect yourself is timely examination and prevention of pathology.
Symptoms
The main signs of a long-term increase in sugar:
- constant thirst (even when drinking a large amount of liquid), the inability to completely quench it;
- dryness of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity;
- frequent urge to urinate, increased volume of urine produced, night urination;
- decreased visual acuity;
- skin itching;
- weakness, fatigue;
- irritability;
- arrhythmia;
- dyspnea;
- causeless weight loss (even with adequate nutrition);
- smell of acetone from the mouth.
In addition, patients with hyperglycemia complain of numbness of the lips, numbness and coldness of the upper and/or lower extremities, causeless debilitating headaches, nausea, frequent constipation or diarrhea, dizziness, chills, flashing spots before the eyes, and susceptibility to infectious diseases.
Symptoms of hyperglycemia may indicate the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus
In men with elevated sugar levels, sexual dysfunction and inflammation of the foreskin are common.
These signs allow one to suspect hyperglycemia, but the final diagnosis is established after examination.
Steroid drugs
Long-term use of steroid hormones can cause secondary insulin-dependent type 1 diabetes mellitus in men. In people with good carbohydrate metabolism, the condition returns to normal after stopping the medications. But if there is a predisposition, drug-induced diabetes may develop. The risk is increased in patients who have to take high doses of steroids for a long time, as well as in those who are overweight. Risk group drugs include dexamethasone, prednisolone, and hydrocortisone.
Such glucocorticoids are used in the treatment of bronchial asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune diseases, and multiple sclerosis.
Diagnostics
In addition to laboratory determination of the concentration of glucose in the blood, if the development of a pathological condition is suspected, a test for glucose tolerance (glucose tolerance test) is performed. In this test, fasting blood glucose levels are measured and the patient then takes glucose dissolved in water. After this, several consecutive measurements are taken at intervals of 30 minutes. Normally, the glucose concentration two hours after a glucose load does not exceed 7.8 mmol/l. At a glucose level of 7.8–11.0 mmol/l, the result is regarded as impaired glucose tolerance; at higher levels, diabetes mellitus is diagnosed.
To avoid distortion of test results, it is recommended to adhere to certain rules for its preparation:
- blood must be donated on an empty stomach, the last meal should be no later than 10 hours before the test;
- the day before the study, you should stop playing sports and avoid heavy physical activity;
- You should not change your usual diet on the eve of the study;
- Avoid stressful situations before taking the test;
- Get a good night's sleep the night before the test.
If hyperglycemia is suspected, patients are prescribed a general blood and urine test (with the detection of ketone bodies), tests for the determination of C-peptide, glycosylated hemoglobin, and antibodies to pancreatic β-cells.
For long-term elevated sugar levels, it is recommended to evaluate the function of the heart, liver and kidneys (ECG, ultrasound, etc.).
In order to exclude complications developing against the background of hyperglycemia, the patient, depending on the indications, is referred for consultation to an endocrinologist, ophthalmologist, urologist or gynecologist, cardiologist, or neurologist.
Blood sugar levels
The unit of measurement for sugar in Russia is millimoles per liter (mmol/l). When assessing fasting glycemia, the upper normative limit should not exceed 5.5 mmol/l, the lower limit is 3.3 mmol/l. In children, the standard value is slightly lower. In older people, a slight increase in values is allowed due to an age-related decrease in cell sensitivity to insulin.
If the indicators do not meet the standards, you need to find out why your blood sugar is rising. In addition to diabetes, there are other causes of increased glucose levels related to lifestyle and general health. Glycemia is classified as:
- Stable (constant).
- Temporary.
- On an empty stomach.
- After eating (postprandial).
Table of normal values
To determine the true cause and form of hyperglycemia, differentiated diagnosis is necessary. Hypoglycemia, otherwise a drop in blood sugar below normal, is also an abnormal state of the body, often dangerous to health.
What to do
A physiological increase in sugar usually does not require special treatment; glucose levels, as a rule, normalize when the factor that caused it is eliminated.
Treatment of pathologically high sugar is complex and should be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician. It is important to remember that self-medication can aggravate the situation and lead to adverse consequences.
When a patient is diagnosed with diabetes, therapy is prescribed depending on its type. In addition to diet therapy, it may include subcutaneous insulin injections and oral hypoglycemic drugs. In the absence of compensation for diabetes mellitus, there is a risk of developing hyperglycemic coma, which is a life-threatening condition.
You should give up sugar, if it is difficult to do this right away, leave a small amount of it, gradually reducing it until it is completely removed from the diet.
In some cases, patients with hyperglycemia are prescribed vitamin and herbal therapy (blueberry tea, hibiscus tea, tea from lilac leaves, sage).
Hibiscus helps normalize sugar levels
Moderate physical activity (gymnastics, swimming, aerobics and water aerobics, badminton, tennis, golf, volleyball, basketball, cycling) helps normalize glucose levels. Walking, climbing stairs on foot, and running at a moderate pace are also effective. Even half an hour of physical therapy exercises a day helps normalize blood sugar levels. Among other things, regular physical activity is one of the measures to prevent the development of type 2 diabetes.
Patients with hyperglycemia should avoid stress, physical and mental overload, even changing jobs if necessary. It is necessary to get rid of bad habits and spend more time in nature.
Diet
The main way to normalize blood glucose levels is diet. The number of calories consumed is calculated depending on your body type and physical activity. Fractional nutrition is indicated - eating 5-6 times a day in small portions at regular intervals. In addition to lowering sugar levels, the goal of diet therapy is to normalize weight. With increased body weight, the daily calorie intake should be reduced by 250-300 kcal from the daily value recommended for a given age and lifestyle.
The basis of the diet is vegetable protein; foods containing carbohydrates are allowed only those that have a low glycemic index. Recommended:
- vegetables in raw and thermally processed form (fresh vegetables should be eaten daily, their share should be at least 20% of all vegetables);
- lean meat, offal, fish, seafood;
- eggs (no more than two per day);
- natural dairy and fermented milk products;
- cereals (buckwheat, millet, barley, pearl barley, oat flakes);
- bakery products from unleavened dough, whole grain, rye;
- legumes;
- berries, fruits, as well as fresh juices from them;
- black natural coffee, black, green, white, herbal tea, unsweetened compotes, fruit drinks;
- some sweets (marshmallows, marshmallows, marmalade, small amounts of honey, dark chocolate);
- vegetable oils.
In case of hyperglycemia, it is necessary to adhere to a plant-protein diet, excluding high-carbohydrate foods
For hyperglycemia, it is recommended to drink at least 1.5-2 liters of water per day.
Even half an hour of physical therapy exercises a day helps normalize blood sugar levels. Among other things, regular physical activity is one of the measures to prevent the development of type 2 diabetes.
Exclude from the diet are confectionery products except those permitted, baked goods made from butter and puff pastry, rice, semolina, sausages, bacon, ham, rich meat broths, fatty, smoked and pickled foods, pasta, fatty and hot sauces, fast food. , snacks. You should give up sugar, if it is difficult to do this right away, leave a small amount of it, gradually reducing it until it is completely removed from the diet. Alcohol is also prohibited, with the exception of a small amount (1-2 glasses) of natural dry red wine 1-3 times a week.
Treatment of glucose metabolism disorders in men
Sustained hyperglycemia is the main symptom of diabetes mellitus. The disease is classified into two main types. The first (insulin dependent or juvenile). Formed in childhood or adolescence due to hereditary predisposition or activation of autoimmune processes. Characterized by a failure of the endocrine pancreas to produce insulin.
The second (insulin-independent or insulin-resistant). Occurs in adults over the age of 30 under the influence of bad habits and excess weight. A distinctive feature is the stable production of insulin against the background of the inability of body cells to adequately perceive and use the hormone.
Excessively high blood sugar in diabetics is a consequence of:
- Violations of dietary rules.
- Incorrect use of glucose-lowering drugs.
- Refusal (missing an injection) during insulin therapy.
- Nervous shocks.
- Physical activity that does not correspond to the patient’s capabilities.
Diabetics often experience sugar spikes in the morning. Fasting hyperglycemia, or the so-called dawn syndrome, occurs when overeating, the presence of infections, or an insufficient dose of insulin administered before bedtime. In children, this phenomenon is due to the active production of growth hormone (somatotropin) in the morning.
In people who do not have diabetes, an increase in blood glucose may be associated with the presence of other diseases:
- Chronic infections affecting metabolic processes.
- Diseases of the hepatobiliary system (in particular, the liver).
- Pathologies of the pancreas.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Obesity.
- Postoperative period after surgical intervention in the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract).
- Chronic alcoholism.
- TBI (traumatic brain injury) affecting the hypothalamus region of the brain.
People with excess body weight are most susceptible to prediabetes and diabetes.
Exacerbations of diagnosed cardiovascular diseases can increase sugar levels.
In a healthy person, an increase in sugar occurs under the influence of the following factors:
- Distress (permanent neuropsychological tension).
- An abundance of simple carbohydrates (confectionery, sweet drinks, baked goods, etc.) in the daily diet.
- Incorrect therapy with hormone-containing drugs.
- Excessive passion for alcoholic beverages.
- Polyavitaminosis of vitamins B and D.
In women, blood glucose concentrations often increase during the perinatal period. Hyperglycemia in the second half of pregnancy can be caused by:
- Changes in hormonal status. Active synthesis of the sex hormone progesterone and endocrine hormones of the provisional organ (placenta) blocks the production of insulin.
- Overstrain of the pancreas. A pregnant woman's body requires more glucose to provide nutrition for the baby. In response to the increased supply of sugar, the pancreas is forced to increase insulin production. As a result, insulin resistance develops—cell immunity to the hormone.
This condition is diagnosed as GDS (gestational diabetes mellitus). This is a pregnancy pathology that requires timely diagnosis and treatment. Otherwise, there is a risk of abnormal fetal development, complicated delivery, and negative consequences for the health of the mother and child. Another reason for the increased sugar content in women is the hormonal changes in the body during menopause.
At the age of 50, the production of sex hormones (progesterone, estrogen) and thyroid hormones, which take an active part in metabolic processes, sharply decreases. At the same time, the pancreas increases insulin production during menopause. Hormonal imbalance prevents stable metabolism, which provokes insulin resistance.
Even without a significant deterioration in health during menopause, it is recommended to regularly monitor blood sugar levels
Increased glucose in children is observed in type 1 diabetes mellitus, due to an unbalanced diet (abuse of sweets and fast food) against the background of low physical activity, and in a state of stress. In newborns, elevated sugar levels are most often a consequence of active therapy with glucose injections given to underweight infants.
Many factors can provoke an increase in glucose levels.
This can happen in a completely healthy person in the following cases:
- With an unbalanced diet high in carbohydrates. In a healthy body, the increase in the indicator will be temporary, insulin will return everything to normal. If you are overly fond of sweets, you should think about the inevitability of obesity and the deterioration of blood vessels.
- When taking certain medications. This includes non-selective beta blockers, some diuretics, and glucocorticoids.
- Stress, excessive physical and mental stress lead to loss of immunity, disruption of hormone production and slowdown of metabolic processes. It is known that during anxiety and stress, the production of glucagon, an insulin antagonist, increases.
- Insufficient physical activity (physical inactivity) causes metabolic disorders.
- For severe pain, in particular with burns.
In women, increased blood sugar may also be associated with premenstrual syndrome. Alcohol consumption provokes hyperglycemia.
Glucose obtained in the digestive organs not only enters the cells, but also accumulates in the liver and the cortex of the kidneys. If necessary, it is removed from the organs and enters the blood.
Regulation of glucose levels is carried out by the nervous, endocrine systems, adrenal glands, pancreas and part of the brain - the hypothalamic-pituitary system. Therefore, it is difficult to answer the question of which organ is responsible for high sugar levels.
Failure of this entire complex mechanism can lead to pathology.
She is provoked by:
- diseases of the digestive tract, in which carbohydrates are not broken down in the body, in particular, postoperative complications;
- infectious lesions of various organs that disrupt metabolism;
- liver damage (hepatitis and others), as a storage facility for glycogen;
- disturbances in the absorption of glucose into cells from blood vessels;
- inflammatory and other diseases of the pancreas, adrenal glands, brain;
- hypothalamic injuries, including those received during medical procedures;
- hormonal disorders.
A short-term increase in the indicator occurs during epileptic seizures, heart attack and angina pectoris. If your blood sugar level is higher than normal, this does not always indicate diabetes.
Some people experience persistently elevated glucose levels. However, this value does not reach the figure at which diabetes is diagnosed. This condition is called decreased glucose tolerance (from 5.5 to 6.1 mmol/l).
This condition was previously classified as prediabetic. In 5% of cases it ends in type 2 diabetes. People who are obese are usually at risk.
If diabetes is not diagnosed, it is necessary to identify the reasons for the increase in glucose levels. If the problem is caused by taking medications, the doctor must choose other means of treatment.
For diseases of the digestive tract, liver or hormonal disorders, therapy methods are being developed that, along with treating the underlying disease, will stabilize sugar and bring it back to normal. If it is impossible to reduce the indicator, insulin or sugar-burning agents are prescribed.
Ways to reduce sugar are a specially selected diet, physical activity and medications.
Developing a diet helps normalize blood composition, and sometimes completely get rid of the problem. To stabilize glucose, diet No. 9 is indicated. Meals are recommended in small portions 5-6 times a day. You shouldn't go hungry. Foods need to be controlled on their glycemic index and calorie content.
You can eat lean meats, poultry and fish. Foods rich in fiber are beneficial. Alcohol must be excluded.
There are food groups that should be excluded from the menu, some should be consumed infrequently and with caution.
Prohibited:
- sausages (all, including boiled sausages and frankfurters);
- baked goods, cookies;
- sweets, sugar, jams;
- fatty types of meat, fish;
- butter, cheese, fat cottage cheese.
You can consume it in moderation by reducing the portion by 2 times:
- bread, loaves;
- fruits, giving preference to sour ones;
- pasta;
- potato;
- porridge.
Doctors recommend eating a lot of vegetables, fresh, boiled and steamed. As for cereals, you should avoid semolina and rice. The healthiest thing is barley porridge. Almost anything can be used for cereals. However, you should not eat instant cereals or muesli; you should use only natural cereals.
Rich broths are contraindicated; it is better to eat vegetable broths. Lean meats and fish can be boiled separately and added to the soup. Despite many restrictions, you can eat varied.
Physical training
Moderate exercise and enjoyable sports help improve metabolic processes in the body. It doesn't have to be intense training.
You should choose a method that is pleasant and not difficult:
- walking;
- swimming - in the summer in an open reservoir, at other times in the pool;
- skiing, biking, boating - according to season and interest;
- Swedish walking or running;
- yoga.
Classes do not have to be intense, but must be regular. Duration – from half an hour to one and a half.
The selection of medications to lower glucose is carried out by a doctor, if necessary.
Phytotherapy
Some plants, fruits and roots will help to successfully reduce sugar levels:
- Place laurel leaves (10 pieces) in a thermos and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Leave for 24 hours. Drink ¼ cup warm 4 times a day.
- 1 tbsp. a spoonful of chopped horseradish is poured with 200 ml of yogurt or kefir. Take a tablespoon three times a day before meals.
- Boil 20 grams of walnut partitions in a glass of water for an hour over low heat. Take a tablespoon three times a day before meals. You can store the decoction for several days in the refrigerator.
- Blueberry berries and leaves give a good effect. 2 tbsp. spoons of raw materials are poured into a glass of boiling water and left for an hour. Take ½ glass before meals.
How to prevent
To prevent high blood sugar, it is recommended:
- healthy eating, avoiding excess sugar, sugar-containing foods and alcohol, avoiding any unbalanced diets;
- maintaining normal body weight;
- regular physical activity, while avoiding excessive exercise;
- monitoring blood glucose concentrations (especially for people at risk);
- development of stress resistance;
- rejection of bad habits;
- timely treatment of diseases that can lead to hyperglycemia.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Why is glucose needed in the body?
Normally, blood glucose is one of the main energy substrates in the body.
When glucose molecules are broken down, energy is released to meet the metabolic needs of the body. More than half of all the energy consumed by the body is generated in the process of glucose oxidation. The main sources of glucose in the body are:
- molecules of sucrose and starch that enter the body during food intake;
- glycogen synthesized by liver tissues;
- amino acids and lactate.
Regulation of blood glucose levels is carried out by the hypoglycemic hormone - insulin and counter-insular hormones (glucagon, somatotropin, thyrotropin, thyroid hormones, cortisol and adrenaline).