Few of us have heard of celiac disease, a congenital disease caused by protein intolerance to certain grains. Just a few years ago it was believed that this was a fairly rare disease. However, today doctors come to disappointing conclusions: the number of people suffering from celiac disease is growing every year.
Gluten is a plant protein found in some grains. Approximately 1% of people on the planet suffer from congenital intolerance to this substance or celiac disease. Once in the intestines, gluten in such people disrupts the natural functioning of the body, causing a number of unpleasant symptoms. Patients with celiac disease are forced to follow a lifelong gluten-free diet.
Where did celiac disease come from?
Celiac disease has been known for a long time, since the beginning of our era. Actually, the name of the disease comes from the Greek word κοιλιακός (koiliakόs, “abdominal”). An ancient Greek physician used this term to describe chronic diarrhea. The classic symptoms of gluten intolerance can be found in medical records throughout the centuries, but it was only in the mid-20th century that the disease began to receive real attention.
The discovery of the nature of celiac disease belongs to the Dutchman William Dick. During World War II, a scientist noticed that some children's condition worsened when they ate white bread. But as soon as the kids switch to rice, their digestion is normal again. At the same time, the main conclusion was made - celiac disease (celiac enteropathy or simply an allergy to gluten) occurs due to the toxic effects of the protein of certain types of cereals. Gluten damages the lining of the small intestine and leads to atrophy and severe malabsorption.
Why is this happening? Predisposition to celiac disease is inherited along with certain genes. Moreover, there is no connection to the female or male line of inheritance. The presence of genes for gluten intolerance in one of the parents suggests a high degree of predisposition of children to this pathology, but not in 100% of cases.
Celiac disease is a congenital disease that has nothing to do with a food allergy such as wheat. The development of these diseases is based on different mechanisms. Perhaps only one thing unites the two illnesses: the reaction requires a substance coming from outside. Allergy symptoms are similar to those of the common cold: rhinitis, swelling, cough, itching. With celiac disease, atrophy of the mucous membrane of the small intestine develops, due to which intestinal absorption is impaired and chronic diarrhea develops.
Reasons for development
Previously, it was believed that celiac disease was a rare disease that most often manifested itself only in children and adolescents. But recent scientific and practical research by gastroenterologists has shown that every 10th person who has this gene from birth is susceptible to developing celiac disease. People who have first-degree relatives with the problem - parents, brothers, sisters and children - are also at risk.
The causative factors for celiac disease include:
- damage, trauma to the mucous membrane on the walls and surfaces of the small intestine;
- the appearance of specific antibodies in the blood serum;
- release into the systemic circulation of a large dose of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL 10, 15, IFN, etc.).
Celiac disease can begin to progress at any age - in childhood, adolescence (due to hormonal imbalances), in adulthood and in old age.
There are factors that provoke the development of celiac disease. This could be stress, a change of place of residence, or a radical change in diet. The development of the disorder can be triggered by taking medications or antibiotics.
Symptoms of celiac disease: see the main thing
Celiac disease is insidious in that it skillfully hides under the guise of many other diseases. As a rule, gluten allergies first appear in childhood, when the child begins to eat foods containing gluten. However, the symptoms of celiac disease are not always correctly recognized by parents and doctors. Accordingly, the prescribed treatment does not work. So it is not uncommon for adults to be diagnosed with celiac disease after 30-40 years of age.
Gluten causes atrophy of the mucous membrane of the small intestine, which impairs intestinal absorption and develops chronic diarrhea. An inflamed intestine is unable to absorb even processed substances, which leads to various health problems. Celiac disease in children manifests itself primarily in the form of weight loss or insufficient weight gain, growth retardation, delayed psychomotor development and various so-called deficiency syndromes.
The typical appearance of a person with celiac disease is a large belly and thin arms and legs.
In addition, celiac disease can provoke deterioration of stools: more frequent, thinner, or larger in volume (polyfeces). A change in appetite may indicate gluten intolerance. For example, a child either begins to eat a lot and at the same time rapidly loses weight, or, conversely, refuses to eat.
In some cases, celiac disease may cause swelling in the legs, and spontaneous bone fractures may occur due to a lack of calcium. Then there are symptoms of multivitamin deficiency (dry skin, stomatitis, dystrophy of teeth, nails, hair, and others).
Gluten intolerance is an unexpected and unpleasant immune reaction that ranges from rashes in people of any age to chronic diarrhea and stunted growth in children.
An important symptom of celiac disease in a child is the child’s mental state: he is whiny, anxious, and has decreased interest in life. An experiment was conducted: children with gluten intolerance were given colored pencils and paper. Of all the colors, they painted only black, which indicated their depressed state.
Gluten intolerance: symptoms of celiac disease in adults
Symptoms of gluten intolerance in adults can vary. Often with celiac disease, people do not tolerate physical activity well, suffer from insomnia, and chronic fatigue.
About 60% of patients suffer from anemia due to a lack of iron in the blood, which is not absorbed in the intestines due to chronic inflammation. Celiac disease can cause problems with the female reproductive system. Thus, in girls, an allergy to gluten can cause a delay in the onset of menstruation, and in adulthood, dysmenorrhea (a menstrual disorder).
Reduced bone calcium is another common symptom of gluten intolerance. Half of children with celiac disease and 75% of adults with the disease have signs of osteoporosis.
If celiac disease is not diagnosed in time and the patient is not put on a gluten-free diet, the disease can be fatal.
Basic principles of nutrition for celiac disease
Transferring patients to a diet will help restore the intestinal mucosa and eliminate its disorders. Within a few months of starting a gluten-free diet, your body's condition can improve.
This method of treatment is based on avoiding wheat, rye and barley. Some doctors also advise avoiding oats. But studies show that its presence in the diet in an amount of 50 g does not provoke an exacerbation of the disease. It is advisable to give preference to rice, millet, corn, and buckwheat.
To increase energy value in accordance with physiological standards, the content of proteins and carbohydrates is increased. Fats are consumed in smaller quantities. They make sure that patients consume enough vitamins, calcium, iron and other useful components for normal functioning of the body.
During the diet, excessive mechanical and chemical effects on the digestive organs should be avoided. Dishes are chopped and wiped before consumption; only boiled or steamed foods are allowed. You should eat small portions up to five times a day. Additionally, doctors prescribe complexes of vitamins and minerals. If the stool has returned to normal, then it is not necessary to grind food. Cold and hot foods should be excluded. Permissible temperature is from 15 to 62 degrees.
Diagnosis of celiac disease: symptoms and harmful gene
The symptoms of celiac disease resemble other diseases, so doctors use special diagnostic methods.
- 1 Genetic analysis: allows you to detect special genes in human DNA - HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8, which are responsible for the development of gluten intolerance. If the genes are found, this indicates a very high degree of predisposition to celiac disease.
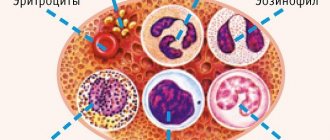
- 2 Immunological analysis: allows you to detect antibodies characteristic of celiac disease in the blood. Two types of proteins can indicate the presence of the disease: antibodies against tissue transglutaminase and antibodies (or immunoglobulins: IgA, IgG) against endomysium.
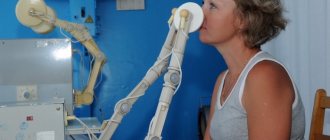
- 3 Histological analysis: allows for a definitive diagnosis. To do this, fibrogastroduodenoscopy is performed, during which a biopsy of the small intestine is taken. The presence of characteristic signs of inflammation confirms the diagnosis of celiac disease.
Skin tests for allergies are, unfortunately, not suitable for diagnosing celiac disease. Gluten intolerance can be detected using immunological and genetic tests (blood tests). A biopsy of the small intestine, which is taken during fibrogastroduodenoscopy, will help make a final diagnosis.
Bread and porridge are not our food: treatment of celiac disease
There are currently no medications for celiac disease, so the only treatment for the disease is a lifelong gluten-free diet. If you follow it, after a few weeks you can feel an improvement in your well-being.
By the way, even 100 milligrams of flour causes the same atrophic processes in the intestinal mucosa in patients with celiac disease as a whole loaf.
So, if you have gluten intolerance, the following foods should disappear from your diet forever:
- Wheat, rye, barley, oats and their derivatives: bread, cereals, starch, flour, pasta, kvass and so on.
- Semi-finished products, canned goods, sausages, ready-made sauces, chocolate, candies, products with flavors and dyes often contain gluten, so they can only be consumed if the label states that the product does not contain gluten.
- Alcoholic drinks such as beer, some types of vodka, made from wheat.
Most foods on supermarket shelves contain gluten. Often, there is practically no information about the amount of gluten in food products. In European countries, there is a law in which on the label of each of them there is an icon in the form of a crossed out spikelet, which indicates the absence of gluten in the composition.
There are currently no medications for celiac disease, so the only treatment for the disease is a lifelong gluten-free diet. If you follow it, after a few weeks you can feel an improvement in your well-being.
Criteria for treatment effectiveness
Celiac disease in adults is considered compensated if:
- stable clinical picture without exacerbations and progression;
- restoration of the small intestinal mucosa;
- absence of specific antibodies (serological markers of the disease).
The effectiveness of treatment is assessed after 6 and 12 months from the start of therapy, then once a year. The persistence of specific antibodies (immunoglobulins) for more than one year from the start of therapy indicates that the patient is not adhering to a gluten-free diet or is unintentionally consuming foods containing hidden gluten.
This disease cannot be completely cured, since the pathological reaction to gluten-containing foods will persist throughout life. However, it is quite possible to achieve stable remission, when the disease does not manifest itself and does not affect the patient’s quality of life.