A pelvic fracture is not just damage to the integrity of the bones, but a life-threatening condition. Inside the pelvic ring there are internal organs, vessels, and nerves. In the event of a fracture, the fragments can injure soft tissues, which leads to massive blood loss, which can be up to 3 liters. Damage to the nerve endings causes painful shock up to loss of consciousness. Emergency care should be provided as quickly as possible, because with every minute the risk of complications and death increases.
Causes
Fractures of the pelvic bones occur due to the action of great force. Athletes who engage in weightlifting, elderly people with impaired mineral metabolism, diseases of the thyroid gland, and adrenal glands are at risk.
The immediate causes of a pelvic fracture include:
- Pressure on the pelvic ring with a heavy object (during an accident, earthquake, house collapse, natural disasters).
- A strong blow to the pelvic area during fights and training.
- Athletes may experience a fracture of the pelvic bone like a crack. When lifting a barbell with a large weight, the gluteal muscles and hamstrings work. Most of them are attached to the ischium. With sudden movements, muscle fibers contract, which leads to cracks.
- When falling from a height, the entire force of the impact often falls on the pelvis. Especially in cases where there is a fall in a horizontal position.
- Osteoporosis (decreased bone density); hereditary or acquired disorders of mineral metabolism increase the risk of fractures.
- In women, healed fractures of the pelvic bones may complicate the birth process in the future. A large fruit, high water supply, and a narrow pelvis lead to cracks and bone damage. This is rather the exception than the rule. Timely diagnosis during pregnancy will help avoid complications.
Patient rehabilitation
When pelvic injuries occur, rehabilitation begins only after complete and comprehensive treatment. The rehabilitation course is an integral part of therapy, which is aimed at quickly restoring motor activity and returning a person to a normal lifestyle. This event is carried out strictly under the supervision of a doctor. Rehabilitation activities include:
- Exercise therapy to prevent the development of ankylosis and contractures, normalize muscle tone.
- The use of vitamin and mineral complexes to strengthen osseous tissue.
- Physiotherapy and massage.
- Therapeutic traction.
It is important to eat properly during this period, including sea fish, dairy products, vegetables and fruits, nuts, sesame seeds and rose hips in your diet. Doctors recommend walking in the fresh air to restore the functionality of the musculoskeletal system.
Patients with pelvic fractures during treatment and the recovery period should include in their daily diet a sufficient amount of foods that are rich in calcium:
- fish;
- dairy products;
- legumes (green beans, soybeans, etc.);
- fresh vegetables and herbs;
- nuts, sesame, poppy seeds;
- rose hips and other berries;
- persimmon and other fruits.
The duration of fusion of the pelvic bones is determined by many factors, and it is impossible to give an exact time frame for restoring their integrity. The rate of their fusion depends on age, type of bone, area of fracture, quality of blood supply to the damaged area, the presence of concomitant diseases in the victim that impede bone fusion, bad habits, etc.
Compliance with all doctor’s recommendations is important when healing the pelvic bones. If such recommendations are not followed, the fragments may heal incorrectly and cause complications in the future.
Only a doctor guided by X-ray data can give the exact time frame for bone restoration. As a rule, the healing period is about 1-1.5 months, and the patient’s full recovery is possible several months after the injury.
To ensure a complete recovery of the patient, the rehabilitation program includes the following activities:
- taking medications to restore bones;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- therapeutic traction;
- cryomassage;
- use of ointments, creams and gels;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
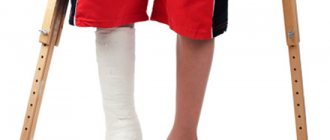
After examination by a doctor, the patient is allowed to walk using crutches or a walker. Even after stable fractures, the use of such devices is necessary for 3 or more months. In this case, the person limps for some time. The duration of walks for such injuries should be increased gradually and recommended by a doctor.
Fractures of the pelvic bones are serious and dangerous injuries. When they appear, it is important to correctly provide first aid and quickly and gently transport the victim to a medical facility. In some cases, such fractures can be treated conservatively (i.e., by immobilization), but in case of a complicated course they require surgery.
Types of fractures
Signs of a pelvic fracture depend on the type of injury and the presence of complications. If the pelvic ring, which is the plane of entrance to the small pelvis, is disrupted, the patient’s condition sharply worsens, movements of the lower limbs are almost impossible, and stability is lost. The risk of blood loss with this type of fracture is high. Emergency assistance must be provided as soon as possible. Damage to one bone is not so life-threatening, but it should not be treated negligently. Immobilization and transportation are carried out slowly, so as not to damage blood vessels, internal organs, or worsen the situation.
The following types of pelvic fractures are distinguished:
- isolated - fractures of the pubic, ischial or iliac bones are usually called stable. Under the influence of a traumatic force, a fracture of the most protruding parts occurs: the crests or wings of the ilium, the tuberosities of the ischium, the branches of the pubis;
- unstable fractures are accompanied by disturbances of the pelvic ring. In most cases, internal organs are injured. Depending on the location of the damage, vertically unstable fractures are distinguished, when displacement occurs in the vertical plane. Rotation fractures are characterized by horizontal displacement of fragments;
- damage to the acetabulum. A fracture of the hip bone occurs as a result of a violation of the integrity of the bottom or edges of the articular surface of the socket.
- combined injury: fractures of the pelvic bones are accompanied by dislocations in the pubic or sacroiliac joint.
Possible consequences
Possible complications:
- Development of paresthesia.
- Injuries to nerve endings, blood vessels, tendons, muscles.
- Osteomyelitis, osteoarthritis.
- Bleeding.
- Disorders of the genitourinary area.
- Infections.
- Incorrect fusion.
- Bone growths.
- Atrophy.
In serious cases, patients experience shortened limbs, delayed bone healing, and complete or incomplete loss of mobility. According to statistics, the mortality rate in these cases does not exceed 5%.
Local manifestations
Despite some differences in the clinical picture, there are common signs of a pelvic fracture. These symptoms indicate the presence of damage and the need for emergency assistance.
- The pain syndrome is expressed as strongly as possible. When trying to touch the pelvis, the patient begins to scream and tries to pull away.
- There is deformation of the bones and an unnatural position of the limbs.
- Hematomas and hemorrhages under the skin are characteristic symptoms of fractures. Under the influence of a traumatic factor, the vessels burst, which leads to bruises.
- In severe cases, bleeding occurs.
- When the fragments are displaced, crepitus (crunching) can be heard in the damaged area.
- Poor circulation and increased vascular permeability lead to swelling.
- A fracture of the hip bone is accompanied by limited mobility of the lower extremities. It is impossible to lift or move the leg due to increasing pain (symptom of a stuck heel).
Immobilization and transportation of victims
If it is necessary to independently immobilize and transport the victim to a medical facility, they must be carried out in such a way as to prevent the displacement of bone fragments, which can damage muscles, nerves and blood vessels, as well as internal organs. To do this, you can use any available means: sticks, pieces of cardboard, boards, scraps of fabric, gauze or bandages.
Immobilization must be carried out carefully and carefully, since any incorrect movement can provoke a painful shock and a person may lose consciousness. The victim should not move his limbs; he should be placed comfortably and bandaged, fixing the damaged area as much as possible.
General symptoms
In addition to local changes, severe general symptoms are observed with pelvic fractures. Violation of bone integrity, pain, and blood loss lead to traumatic shock. As a rule, the patient is excited immediately after the injury and does not feel pain. Within a few minutes the condition begins to deteriorate. There is pale skin, cold, sticky sweat. The pressure drops sharply, which is due to the presence of bleeding from the vessels and the pelvic bones themselves, which have a spongy structure.
Increased heart rate is a protective mechanism. To ensure the supply of nutrients and oxygen to the brain and other organs when there is insufficient blood, the heart is forced to work faster. The release of adrenaline as a reaction to a stressful situation also plays an important role.
Sometimes the condition is complicated by fainting. Loss of consciousness occurs due to severe pain, which significantly exceeds the threshold of pain sensitivity. Another mechanism is oxygen starvation of the brain during massive bleeding.
Damage to internal organs
The urinary system, lower intestines, uterus, tubes and ovaries in women are most susceptible to injury. Signs of a pelvic fracture are varied and depend on the degree of damage to a particular organ:
- urinary retention and the presence of blood in the urethra indicate a rupture of the urethra. It is impossible to insert a catheter due to severe pain and mechanical obstacles;
- if the bladder is damaged, hematuria (blood in the urine) is observed;
- blood in the rectum or vagina is a sign of damage to the relevant organs.
Iliac fractures
If the ilium is damaged, shortening of the limb and pain in the area of the wing or crest on the corresponding side are observed. There is a specific symptom of backward movement, when it is easier for the patient to move backwards.
Pubic bone fractures
Most often, with this type of injury, the pelvic ring is not broken. The patient takes a forced position, in which the pain decreases: lying on his back, legs bent at the knee joints, spread to the side. For clarity, the posture of a person with pelvic fractures (frog pose) is shown in the photo.
Fractures of the ischium
Damage occurs when falling on the pelvis, more often in winter or during sports. The patient complains of acute pain, swelling, and redness on the buttocks.
Fractures with disruption of the integrity of the pelvic ring
Fractures of the pelvic bones with a violation of the integrity of the anterior and posterior semi-rings are characterized by pathological mobility with slight pressure on the pelvis, asymmetry. The pain syndrome is severe and leads to loss of consciousness. There are bruises and bruises on the skin.
How to treat a pubic bone fracture
A fracture of the pubic bone of the pelvis is a very complex injury. The pubic (pubic) bone consists of a main body and two branches located on either side of it.
A fracture of this bone is often accompanied by severe blood loss and injury to the pelvic organs. The risk of becoming disabled as a result of such damage is very high.
Causes
The main reasons for such a fracture are:
- strong external impact of a shock nature;
- strong squeezing or pressing of the body; falling from height.
What is a stress fracture
More often than others, athletes, as well as elderly people suffering from osteoporosis, suffer from fractures of the pubic bone.
Symptoms
Unilateral fracture of the ischium and pubic bones of the pelvis
A fracture of the pubic bone is characterized by:
- traumatic shock;
- loss of blood;
- decrease in pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- pale skin;
- the appearance of sticky sweat;
- loss of consciousness (in some cases);
- sharp pain, intensifying with leg movement and palpation;
- the symptom of “stuck heel”, manifested by the inability to lift the heels off the ground (when the symphysis (the pubic symphysis, which has a cartilaginous structure and connects the lateral bones of the pelvis) is ruptured);
- the presence of blood when urinating, urinary incontinence (due to a bruise of the bladder or injury to the urethra);
- pronounced asymmetry of the legs, when one leg is shorter than the other;
- crunching (crepitation) of bone fragments;
- deformation of the pelvic region;
- swelling, subcutaneous hemorrhage.
Diagnostics
During the diagnostics, the following points are analyzed:
- circumstances and mechanism of injury;
- patient complaints if he is conscious;
- X-ray (general view, photo of the pubic bone);
- MRI, CT (if necessary).
If there is any damage to the pelvis, the integrity of the internal organs should also be checked. For this purpose, ultrasound, urethrography (x-ray examination of the urethra), and cystography (x-ray examination of the bladder) are performed.
First aid
In the event of a fracture of the branches of the pubic bone, it is important to provide the victim with quick, high-quality first aid. To this end, you should perform the following steps:
- call an ambulance;
- ensure the immobility of the victim’s body by placing the victim on his back, placing a cushion or other suitable object under his feet;
- give painkillers to prevent painful shock;
- exercise control over the general condition of a person, his pulse, heart rate;
- treat the wound with disinfectants and cover the wound with a cloth (for complicated open injuries);
- apply a tourniquet (if there is rupture of blood vessels and blood loss);
- wait for the ambulance to arrive; If calling an ambulance is not possible, then take the victim yourself to the nearest medical center.
First aid for a fracture of the pubic pelvis
Treatment
The success of treatment for a fracture of the pubic pelvis largely depends on proper diagnosis, during which the severity of the injury and the affected area are established. This damage can be treated with both conservative and surgical methods.
The ICD-10 code for pubic bone fracture is defined as S32.5.
In case of fractures of the pubic bone without displacement and changes in the condition of the pelvic ring, the healing of the fragments occurs due to immobilization and does not require surgical intervention. In addition, the following medications are taken:
- painkillers;
- vitamin complexes, calcium;
- antibiotics (in case of an open fracture).
Surgical treatment of a fracture is performed when:
- presence of internal organ injuries;
- rupture of the symphysis pubis and divergence of the pubic bones;
- significant displacements of bone fragments and lack of effectiveness of conservative treatment.
The duration of treatment for a fracture of the pubic pelvis without displacement, as well as with displacement, depends on various factors: the severity of the injury, the general condition of the patient, and the timeliness of seeking medical help.
On average, healing of a fracture lasts three to four months. If there are any complications, the treatment period increases.
Relieving pain shock
To relieve pain shock, the Shkolnikov-Selivanov method is used.
To do this, a one percent novocaine solution is injected into the tissue of the iliacus muscle, the effect of which gradually spreads to the area of the iliopsoas muscle.
Also, intraosseous anesthesia is used for pain relief by injecting a solution of novocaine into the crest of the iliac wing.
The above methods of anesthesia are used when the anterior or posterior part of the pelvic ring is damaged.
If the marginal bones that do not form the pelvic ring or the anterior semi-ring break, then a one percent novocaine solution is injected into the bruise formed just above the fracture site.
Fighting blood loss
Bilateral fractures of the pubic and ischial bones
To prevent blood loss, compression is created on the injured pelvic bones. For this purpose, a special fixative is used, which helps reduce bleeding and does not interfere with the operation (during surgery).
If profuse bleeding occurs, in which blood loss reaches 30% of the total volume of circulating blood, the wound is filled with large sterile napkins soaked in a sodium chloride solution. If necessary, compensation for blood loss is provided.
Therapeutic immobilization
The patient is immobilized to prevent displacement of bone fragments and injury to organs, blood vessels, muscles, and nerves. To do this, he is placed on a special bed equipped with a shield, and all body movements are reduced to a minimum. At the same time, place a pillow or a small cushion under the knees.
Surgical intervention
Quite often, when the pubic bone is fractured, internal organs are injured: the vagina, bladder, urethra and rectum, the integrity of which is restored exclusively by surgery.
Surgical intervention is also required when the symphysis is ruptured or when fragments of the pubic bone are displaced. During the operation, damaged bones are fixed using knitting needles, screws, plates with screws, etc. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia.
Rehabilitation
After healing of a fracture of the pubic pelvic bone, rehabilitation takes a lot of time and includes:
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- cryomassage;
- water procedures;
- wearing a special medical corset or bandage;
- the use of various gels, ointments, warming effects;
- physical therapy;
- therapeutic traction;
- a rich diet that involves the consumption of foods rich in calcium: dairy products; legumes, fresh herbs, nuts, rose hips, persimmons, fresh vegetables, etc.;
- taking medications to help restore bones.
The recovery period lasts about a year
During the recovery period, walking with the help of devices such as crutches or walkers is allowed. They are usually used for 3 months or more.
Even after minor injuries, the recovery period lasts about a year. In this case, a return to the usual rhythm of life usually occurs after two years. Therefore, the issue of restoration should be approached with all seriousness and responsibility.
Consequences
The consequences of a fracture of the pubic bone can be quite serious.
Despite the high level of medical care, when treating this type of injury, the risk of complications remains quite high.
Possible consequences of injury:
- removal of lower limbs;
- stiffness of the hip and knee joints;
- deformation of the pelvic ring and depression in the area of the ilium;
- damage to the pelvic organs;
- reduction in the length of one leg;
- damage to nerve endings, muscle tissue and tendons;
- inability to give birth to children naturally (for women).
How to make a diagnosis?
The main diagnostic method is x-ray in two or three projections. Using this study, you can find out about the number of fractures, their location, the integrity of the pelvic ring, and the presence of fragments.
If additional information is needed about the condition of ligaments, joints, and the presence of small cracks, modern methods are used: computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
An ultrasound examination of the abdominal and pelvic organs is mandatory. Free fluid in the abdominal cavity, blurred, distorted contours of organs are alarming.
If internal bleeding, rupture of the spleen or bladder is suspected, diagnostic laparoscopy is necessary. The surgeon uses a special device to examine the condition of the internal organs through incisions in the anterior abdominal wall. If damage is detected, non-viable tissue is removed, bleeding is stopped, and ruptures are sutured. Thus, laparoscopy is used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Additionally, special symptoms are used, which consist of the application of an axial load that causes pain. However, such symptoms are checked carefully so as not to aggravate the fracture or cause injury to organs.
Diagnosis of pathology
When visiting a clinic, the primary diagnosis is made by a doctor after interviewing and examining the victim. Additional examinations include:
- radiography;
- computed tomography;
- MRI;
- urethrography;
- Ultrasound of the organs of the excretory system.
In difficult cases (if there are signs of an “acute abdomen”), diagnostic laparotomy and laparoscopy are performed.
A treatment regimen, including medications, a set of surgical procedures and physiotherapeutic procedures, is prescribed by the attending physician upon completion of all necessary studies.
First aid
If you suspect a pelvic fracture, you should call emergency services. The sooner the patient is taken to the hospital, the greater the chance of a successful recovery.
If external bleeding occurs, you need to stop it; only a doctor can handle internal bleeding in a hospital setting. To do this, use available materials: a belt, a scarf, clothes twisted into a rope. The main task is to save a person’s life by preventing him from bleeding to death before the ambulance arrives.
Remember! You cannot move the patient yourself. This can lead to damage to organs from bone fragments and increased bleeding.
After the doctor arrives, it is necessary to administer anesthesia, give the patient the correct position, and transport him to the hospital as quickly as possible.
Rules for first aid for hip fractures
In case of injuries to the pelvic bones, it is extremely important to rush to provide correct and timely assistance to the victim. At the same time, everything needs to be done clearly and consistently, without unnecessary fuss and excitement. The main stages of first aid include:
- Immediately call a team of medical workers who will competently provide all the necessary measures in this situation.
- Reducing the level of pain. To do this, the injured person must be given or injected with some kind of anesthetic. However, it is not always possible to give an injection, so if the victim is not unconscious, then he needs to be given the drug analgin or aspirin with diphenhydramine, as well as strong coffee.
- Stop bleeding. If the patient experiences heavy bleeding or an open wound, it should be stopped immediately by applying a tight bandage, and the edges of the open wound should be treated with an antiseptic. Applying ice to the injury site and drinking salty drinks will also help stop bleeding.
- Fixing the correct position of the victim’s body, the so-called “Volkovich” (or “frog”) position, is the main stage of helping a patient with this type of injury. A prerequisite is that the victim is positioned on a flat surface; folded clothing or a towel must be placed under the head, back and knee joints.
When providing first aid to a victim, you should not carry him or try to take him to the hospital yourself, as this can accidentally cause even greater injuries to the patient. Especially if the injured person has impaired not only the integrity of the pelvic bones, but also the correct location and functioning of the internal organs of the pelvic cavity.
Treatment
In the hospital, first of all, you need to stabilize the person’s condition: stop the bleeding, administer pain relief.
The issue of anesthesia (pain relief) is decided individually. Intraosseous or intrapelvic administration of novocaine and lidocaine is used. In severe cases, general anesthesia and urgent surgery are indicated, the purpose of which is to stabilize the fracture, eliminate organ damage, if this occurs, and stop bleeding.
It is necessary to replenish the volume of blood loss with the help of intravenous administration of plasma, saline, and blood substitutes. It is worth remembering that the volume of blood loss can range from 3 to 5 liters, and it increases with instability of the pelvic ring.
After stabilizing all vital functions in an uncomplicated fracture, the surgeon begins direct treatment of pelvic fractures. The choice of patient management tactics for fractures depends on the severity of the condition and the presence of complications.
- Immobilization of simple fractures without displacement is carried out on a backboard or in a special hammock. The state of the immune system, the presence of concomitant diseases, and age affect how long it takes for a fracture to heal. On average, this period is 3 months, but it can be longer.
- Displaced fractures are a direct indication for skeletal traction. Knitting needles are passed through the bone and fixed externally on a special frame. This procedure allows you to pull the bone fragments away from each other. As a rule, surgery follows.
- The operation consists of fixing all parts of the pelvis using pins, metal plates, screws, and rods in an external fixation apparatus. After osteosynthesis, immobilization is indicated for 3-4 months.
Features of treatment for pelvic injuries
Patient management tactics depend on the type of injury and the presence of concomitant disorders of internal organs. If there is no change in the configuration of the pelvic ring and the function of other systems is preserved, the orthopedist recommends a protective regime in the supine position with legs apart and bent at the knee joints. The duration of treatment with positioning takes 5-6 weeks.
Displacement of the fragments requires the application of a plaster cast or fixation using special devices. In this case, the period is extended to 8-12 weeks. If necessary, reconstructive operations of the pelvic organs are performed in order to restore their function.
To increase bone tissue regeneration and improve metabolism, a proper diet is an important factor. At the initial stages of the rehabilitation period, food should be easily digestible. This is necessary to normalize digestion.
Later, the diet is expanded to include foods that are enriched with calcium and phosphorus.
Useful components are found in sufficient quantities in dairy products, fish, nuts, legumes, herbs, sesame and poppy seeds. In some cases, the doctor prescribes complex medications with minerals and vitamins that speed up the healing process.
Complications
Despite all efforts, 20% of patients develop unpleasant consequences of a pelvic fracture. Multiple injuries, improper fusion of fragments, massive blood loss affect future health . The most common complications include:
- chronic pain syndrome occurs when the bones are not aligned correctly or the nerve endings are damaged;
- lameness, change in gait;
- muscle atrophy and immobility of the hip joint occur as a result of prolonged immobility. To avoid complications, it is recommended to gradually load the lower limbs and perform exercises after the doctor’s permission;
- Severe complications include disorders of the internal organs: urinary incontinence, sexual dysfunction, decreased sensitivity in the lower extremities.
Unfortunately, treating the long-term consequences of a pelvic fracture is a complex process. With the help of painkillers, vitamins, and therapeutic exercises, it is only possible to reduce the symptoms. It is impossible to completely restore all functions.
Anatomical features
The pelvis is a skeletal support system located in the lower part (base) of the spine, protecting the internal organs (urinary, reproductive, rectum) and acting as a connecting link between the torso and legs.
The structure of the complex includes:
- sacrum;
- motionless, connected by bone sutures, 3 paired bones (ischium, pubis, ilium).
The latter, fastened in the outer lateral part, form the acetabulum (AC) - an integral element of the hip joint.
The pubic bones meet in front to form the pubic symphysis.
The continuity of the system is ensured by the sacroiliac joints, through which the iliac bones articulate with the sacrum.
Recovery
How long it will take for a pelvic fracture to heal depends not only on the type of injury, but also on the implementation of all the doctor’s recommendations and the patient’s diligence in implementing them. Rehabilitation for fractures is carried out only under the supervision of a specialist.
Standing up on your own, making sudden movements, or exercising is prohibited! The bones may not have fused together at the time of such “amateur activity,” which will lead to complications.
- Physical therapy is the main method of preventing muscle atrophy (weakness) and stiffness in joints. Recovery begins immediately after stabilization or surgery. The early recovery period should begin with breathing exercises, contracting individual muscle groups and holding them in this position for several minutes. When the bones begin to heal and the doctor allows light warm-up, physical activity must be increased. At first, the exercises are performed in a supine position, and closer to recovery - in a standing position. Rehabilitation after a pelvic fracture is aimed at restoring muscle strength and the full range of active movements.
- Swimming or simply walking in the water is shown.
- Massage improves blood circulation in the damaged area, removes stagnation of lymph and venous blood. Light massage movements lead to an increase in muscle tone.
- With food, building material for bone tissue restoration enters the body. It is necessary to eat foods rich in calcium: green vegetables, cabbage, parsley, cottage cheese, cheese, nuts, sea fish, legumes.
- If nutrition alone is not enough, the doctor prescribes special calcium supplements.
- Chondroprotectors and collagen are necessary to prevent bone destruction and restore cartilage tissue.
- Rehabilitation for fractures includes physiotherapeutic procedures. There is a large selection of them, which is determined by the attending physician.
- Patients are recommended to wear a bandage, corsets, crutches, and walkers for a long time in order to reduce the load on the pelvis.
It is impossible to predict how long rehabilitation will take. It all depends on the efforts made, the body’s internal reserves, and the severity of the damage received. As a rule, healing of pelvic fractures takes from 5-6 months to a year.
Rehabilitation after a pelvic fracture
Rehabilitation is part of the system of treatment measures for damage to the pelvic bones; it begins early and is carried out in stages. Prolonged bed rest carries the risk of complications. During this period, methods aimed at preventing trophic changes and congestion in the lungs and pelvic organs are applicable.
Carrying out rehabilitation therapy is a necessary condition for complete recovery and return to work. Rehabilitation methods include:
- physical therapy;
- massage;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- balanced diet;
- taking medications to strengthen bones.
The plan for the rehabilitation period is individual for each victim and is drawn up by a rehabilitation doctor. Efforts are aimed at eliminating dysfunction, preventing complications and returning to an active life.