There are open and closed traumatic brain injuries (TBI)
Open traumatic brain injuries include head wounds and open fractures of the skull.
- brain concussion;
- compression of the brain;
- closed fractures - fractures of the bones of the vault and base of the skull.
A concussion is a serious blunt force injury that occurs due to closed skull injuries. In this case, swelling and swelling of the brain is observed.
– loss of consciousness from a few seconds, so that the person does not even have time to fall (knockdown in boxing) and up to several days or more;
– retrograde amnesia – the victim cannot remember the events that preceded the injury.
Bruises and concussions are characterized by general cerebral symptoms: dizziness, headache, nausea and vomiting, slow pulse, etc.
With bruise and compression of the brain, there is also partial destruction of brain tissue, as a result of which focal symptoms of brain damage appear: impaired vision, speech, facial expressions, and limb movements (paralysis).
The final diagnosis can only be made by a doctor based on the results of special studies.
In case of fractures of the skull bones, brain damage occurs not only from the blow, but also from the introduction of bone fragments and spilled blood (compression of the brain by a hematoma).
Open fractures of the skull bones are dangerous due to the possibility of infection of the brain tissue with subsequent complications: meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscess, etc.
Fractures of the bones of the calvarium occur in the form of cracks or in the form of a violation of the integrity of one or more bones. In comminuted fractures, bone fragments compress the brain, disrupt its integrity and damage cerebral blood vessels. The resulting internal bleeding causes swelling of the brain.
Signs of a calvarial fracture:
- complaints of pain and tenderness at the site of injury;
- external swelling or wound;
- When palpated, an indentation is possible.
In case of damage to the brain, membranes and blood vessels, additional general cerebral and focal signs are present.
Fracture of the bones of the base of the skull is a serious and dangerous injury to the brain, meninges and cranial nerves. The fracture leaves the brain cavity open to infection through the ear, nose and mouth.
Signs of a skull base fracture:
- severe general condition, loss of consciousness; leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid), blood from the nose, external auditory canals, along the back wall of the pharynx (an absolute sign of a fracture of the bones of the base of the skull);
- the appearance of a “symptom of glasses” - bruises around the eyes on the second day after the injury;
- paralysis of the olfactory, optic, oculomotor, facial nerves.
First aid for traumatic brain injuries:
1. Create complete rest, lying on your side; the victim’s attempts to get up, sudden changes in body position, and body shaking during transportation are unacceptable;
2. Prevent possible blockage of the respiratory tract with blood and vomit. If the victim is unconscious, it is necessary to clear the oral cavity of vomit by inserting a finger wrapped in gauze or a handkerchief. To do this, the patient's head is turned to the side. If you suspect a fracture of the spine in the cervical region, you should not turn your head due to the risk of damage to the spinal cord.
3. With a concomitant fracture of the spine in the cervical region, a fixed position of the head. The victim’s head is fixed using available means, by creating a cushion around the head; 4. For fractures of the cranial vault, apply a dry aseptic bandage.
4. Cold to the head (ice pack, cold compresses).
5. Urgent delivery of the victim to a medical facility, transportation in a supine position. If the victim is unconscious, he is placed on his side or just turned his head.
Didn't find what you were looking for? Use the search:
Best sayings:
Learn to learn without studying!
10404 — | 7899 - or read all.
The number of road accidents is steadily growing every year - such a sad price to pay for the “blessings of civilization.” Head injuries occupy one of the leading places among other peacetime injuries. An average of 700 people die every year, and this figure is not yet the limit. The tragedy of the situation lies in the fact that the best people die very early: these are children (the frequency of traumatic brain injuries (TBI) in them is much higher than in adults) and young people, the so-called “color of the nation.”
Traumatic brain injury is mechanical damage to the skull and its contents, which is manifested by certain neurological symptoms. In case of head injuries, it is extremely important to provide first aid in a timely and competent manner so as not to waste precious time, which is why it is important for every person to know its basics.
Head Injury Clinic
Brain concussion. This is the most common head injury, occurring in 80% of cases. No macrostructural pathology is detected, and damage is observed only at the cellular level; therefore, concussion is a functionally reversible form. The patient is unconscious for several seconds or minutes with amnesia, and is also characterized by nausea and vomiting. After the patient regained consciousness, he complained of dizziness, diffuse headache, double vision, and sweating. Vital functions are not impaired. Minor neurological disorders manifest themselves in the form of asymmetry of tendon reflexes, small-scale nystagmus, which disappear after a week. The patients' condition improves significantly during the first week, and CT and MRI do not reveal any pathology.
Brain contusion. With this pathology, unlike a concussion, there is gross macrostructural damage to the brain substance in the form of hemorrhage and destruction. Subarachnoid hemorrhage is a “companion” of such injuries. Fractures of the skull bones are also no exception for them, and the severity of the patient’s condition directly depends on the severity of these manifestations. One of the main symptoms is edema-swelling of the brain substance. The following types of damage are distinguished:
- mild severity. Patients may be unconscious for about 20 minutes. Complaints typical for head injuries are nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and diffuse headache. Retro- and anterograde amnesia is noted. Vital functions are not significantly impaired; changes in the cardiovascular system appear in the form of bradycardia and hypertension. Neurological symptoms manifest themselves in the form of pyramidal insufficiency, mild anisocoria, clonic nystagmus.
- moderate severity. The patient is unconscious for several hours. After the patient regains consciousness, repeated vomiting, severe amnesia, and mental disturbances appear. Violations of vital functions manifest themselves in the form of persistent bradycardia, hypertension, tachypnea without obstruction of the airway. The neurological status includes nystagmus, asymmetry of muscle tone and tendon reflexes, meningeal symptoms and pathological signs. Focal symptoms are presented in the form of pupillary and oculomotor disorders, paresis of the limbs, and speech impairment.
- severe severity. The patient remains in a coma for a long time (if he does not die) - several weeks. Vital functions are grossly impaired and pose a significant threat to life. Stem symptoms come to the fore in the form of floating movements of the eyeballs, disturbances in the rhythm and frequency of breathing, bilateral mydriasis or miosis, divergence of the eyeballs vertically or horizontally, hormotonia, pathological foot signs, paresis of the limbs, convulsive seizures are possible. Such patients are in a deep coma and the prognosis for life is very often unfavorable. With such brain contusions, fractures of the skull bones and massive subarachnoid hemorrhages are noted.
Compression by intracranial hematomas. Hematomas form above or below the dura mater as a result of depressed fractures of the skull bones. Clinically, they manifest themselves as a brain contusion, but have their own characteristics. After the patient regains consciousness, a so-called “bright period” is possible, when he feels better for a while, but as cerebral edema progresses and its dislocation, the patient again plunges into a coma.
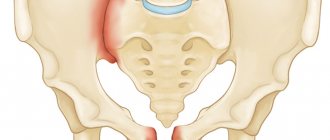
Back injury
Damage to the back, or more precisely, to the spinal column, is dangerous and serious. Such injuries can leave a person disabled, cutting off the sensitivity of the limbs, immobilizing the patient completely, or lead to death.
Classification
If a spinal fracture occurs, complete paralysis is often observed. When the cervical region is injured, this is fraught with respiratory arrest, circulatory disorders, which often ends in death. A large number of cases of such injuries occur as a result of diving or falls from great heights, car accidents, or taking a strong blow to the spine
Types of spinal injuries:
- Quadriplegia. This is the result of severe bruising of the neck and upper thoracic vertebrae.
- Paraplegia. The result of damage to the lower thoracic spinal column.
- Dislocation accompanied by severe sprain or rupture of ligaments. Causes injuries to the spinal cord, which are formed due to the fact that the vertebrae close together.
- Cervical spine fracture. Severe injury, often leading to the death of the victim.
Features of manifestation
Symptoms of spinal injury:
- intense pain in the neck, lumbar region or chest;
- inability to move limbs, complete paralysis of arms and legs;
- urinary incontinence, a person is unable to control urination;
- severe weakness;
- signs of brain damage;
- feeling of numbness in the arms and legs.
A bruise of the spinal column is different from injuries, since the bone tissue remains intact.
The consequences of such an injury can be quite dangerous, although the injury itself is not considered complex. Against the background of such a defect, hematomas and abrasions may occur, disrupting the movement of cerebrospinal fluid, and this leads to necrotic tissue damage in the area of \u200b\u200bthe inflammatory process. The first signs of a spinal bruise are often very unclear to the victim. If spinal shock has developed, the person usually does not feel the area below the injury site. The patient’s coordination of movements is disrupted, and habitual reflex movements change.
If, after receiving such an injury, the victim is able to independently bend his legs and feel the process of urination, then this greatly increases his chances of complete restoration of the spine. Of course, to improve the condition, it is important to undergo a special rehabilitation course of gymnastics.
Injury to the cervical vertebrae causes more severe symptoms. The limbs become numb, and complete paralysis may occur. After receiving such a wound, a person often experiences a painful shock, which is accompanied by loss of consciousness.
First aid for traumatic brain injury
Not only recovery, but also life largely depends on the quality of first aid and the prompt delivery of the victim to a medical facility. In this regard, any person providing assistance should first call an ambulance.
First aid algorithm:
- determine the presence of consciousness in the victim (try to wake him up, evaluate the reaction to painful stimulation);
- examination of the type of injury (open or closed; presence of bleeding, liquorrhea, or leakage of cerebrospinal fluid);
- determine the nature of breathing and heartbeat (tachypnea or bradypnea, presence of aspiration; bradycardia or tachycardia; presence of pulse in the central and peripheral arteries);
- If the examination reveals an open craniocerebral injury, then it is necessary to apply an aseptic bandage. If bone fragments protrude from the wound or brain tissue is visible, then the bandage should be applied in a circle in the form of a ring;
- if the patient is unconscious, then it is necessary to check the patency of the airways (remove foreign bodies from the nasopharynx - blood clots, fragments of teeth; if there is no breathing, it is necessary to begin artificial respiration from mouth to mouth);
- if there is no pulse in the main arteries, begin chest compressions;
- in the presence of liquorrhea, the nasal passages and external auditory canal are tamponed with gauze turundas;
- if the victim is unconscious, he is placed on his side to prevent aspiration and asphyxia. If there is a suspicion of a spinal fracture and the patient is conscious, then he is placed on his back, fixing the cervical spine;
- apply cold to the injury site;
- wait for the ambulance to arrive. If such a patient has to be transported by passing transport, then on the road breathing and pulse are monitored every 10 minutes and the airway is maintained.
Severity of injury
In order for the provision of assistance to the victim to really have the desired effect, experts recommend conducting at least a cursory initial examination before starting pre-medical procedures. This will allow you to determine the approximate severity of the head injury.
The easiest way to cope is with a mild degree of the disease, which is more typical of accidental household injuries such as hitting your head on the edge of a cabinet. The deviation is not accompanied by any heavy bleeding and does not bring any particular discomfort during recovery. Typically, such mild bruises are limited to the formation of a small swelling, which is popularly called a “bump.”
It goes away on its own, but sometimes, to speed up the process, it is allowed to apply cold immediately after the blow. This will somewhat reduce pain and also limit the spread of swelling.
The situation with damage to the integrity of the skin is a little more complicated. The category includes not only extensive wounds that occur when a large area of skin along with hair is combed. Even ordinary abrasions provoke an outflow of blood. But only in the first case the patient has to deal with a large amount of blood, and in the second case only capillary bleeding is stopped.
If emergency measures are taken, it will be possible to block capillary breaks to stop bleeding within 5-10 minutes.
Three other categories are considered separately:
- jaw damage;
- traumatic brain injury;
- combined options.
Complex pathologies are more suitable for describing polytrauma, when, in addition to deformation of the head, destabilization of the spine or any other part of the body is simultaneously recorded. This format is most often found in road accidents, fights and industrial injuries, when there is damage to the chest and limbs.
A particularly serious development of events is a related deviation in the issue of the integrity of the neck systems. We are talking about the rupture of nerve endings and large vessels designed to nourish the brain.
Almost always, a head blow is accompanied by minor, but still skin injuries. In addition to the immediate top layer, the natural integrity of the fatty tissue is disrupted. Because of this, blood flow through the affected vessels is obstructed. The clinical picture ends with the collection of blood at the site of localization, which externally transforms into a hematoma of various sizes.
Depending on the severity and duration of the blow, the color of the hematoma changes. If initially it turns purple due to fresh blood stains under the skin, then later the tone changes. The transformation is due to the launch of the process of hemoglobin breakdown and increased activity of leukocytes. Externally, such manifestations are expressed in a change in color to blue-green with yellowness.
The swampy tint is provided by biliverdin, and bilirubin is responsible for imparting yellowness.
If there is strong external pressure during a mechanical injury, it is often accompanied by destabilization of the tendon helmet. Doctors recognize such a deviation due to a hematoma, which seems to be spreading across the face.
When a victim falls on their face, they have to deal with soft tissue damage. There is one pitfall here that ordinary people do not know about. Some people unknowingly confuse the outer rim of a hemorrhage with a depressed cranial fracture.
Types of World Cup injuries
Signs
First aid for traumatic brain injury mainly involves determining the patient's neurological clinical picture and externally noticeable damage.
TBI has symptoms that require special attention and mandatory medical assistance:
- intense bleeding;
- blood flow from the ears and nose;
- acute pain in the head;
- irregularities in rhythm or weakness of breathing;
- disturbance of consciousness;
- long-term loss of consciousness;
- malfunctions of the vestibular apparatus, loss of balance, unbalanced movements;
- complete loss of mobility of some skeletal limbs or weakness in muscle tissue;
- convulsions;
- vomit;
- lack of clarity of words;
- lack of a reflex reaction of the pupil to a beam of light, etc.
In case of a traumatic brain injury, the patient must be taken to a medical facility. Even with externally absent damage, it requires additional examination and an accurate diagnosis.
The human head contains many nerve endings responsible for smell, swallowing, maintaining balance, hearing, vision, etc. Failures in the functioning of one of the internal organs should be the reason for a doctor to prescribe treatment and provide emergency care for a traumatic brain injury.
First aid
Providing first aid for a traumatic brain injury is a person’s first priority. It is important, before the doctors arrive, to take all necessary measures and provide urgent support to the victim. When injured, the patient often loses consciousness and memory, which, as a rule, is restored over time.
Click to enlarge
It is very important to wait for the doctors to arrive and explain to them the causes and circumstances of the injury. This will help them initiate precise and immediate resuscitation and treatment efforts for the patient. During first aid the following measures must be taken:
- it is necessary to place the injured person on his back without placing pillows or bolsters under his head, the surface should be smooth and hard;
- An unconscious patient should turn their head to the side. This is necessary to avoid asphyxia by vomit and prevent the sunken tongue from blocking the flow of air into the respiratory tract;
- transportation of the patient occurs when the head and neck are immobilized;
- When the injured person’s body is pinched between objects, there is no need to try to remove it yourself. This may result in additional injury;
- in the presence of an open head injury, it is necessary to use a sterile dressing to prevent infections and pathogenic bacteria from entering the wound. To do this, bandages soaked in saline are applied along the edge of the wound, and then a bandage is placed on top. She bandages tightly. This helps stop blood loss and protect the wound. It is important, however, to try to injure the damaged tissues to a minimum;
- finger pressure on the open wound will help stop bleeding;
- You can immobilize the patient’s neck and head using a special pharmaceutical collar.
Understanding the seriousness of the injury, when providing assistance for TBI, one should not forget about the accuracy of all actions. This will prevent the patient from experiencing severe pain and prevent possible complications after injury.
Dislocation of the lower jaw
This injury is very common because it can happen when laughing, yawning too widely, when hitting, and in older people the usual dislocation of the jaw occurs.
Signs of the condition in question:
- open mouth;
- severe drooling;
- there is no speech (the victim makes mooing sounds);
- jaw movements are difficult.
Help is to reduce the dislocation. To do this, the person providing assistance needs to stand in front of the victim sitting on a chair. The thumbs are inserted into the mouth along the lower molars. Then the jaw is forced back and down. If the manipulation was carried out correctly, the victim’s jaw movements and speech are immediately restored.
Please note: when realigning, the victim’s jaw spontaneously closes with great amplitude and force.
Therefore, before carrying out the procedure, you need to wrap your fingers with any cloth and try to immediately pull your hands out of the victim’s mouth immediately after the characteristic click appears (this is the joint snapping into place). Otherwise, injury may be caused to the person providing assistance. We recommend reading: Dislocation of the lower jaw: symptoms, treatment, methods of reduction
Any injuries and wounds to the head should be under medical supervision. Even a simple blow can lead to a concussion, which will certainly affect your overall health.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical observer, therapist of the highest qualification category
15, total, today
( 166 votes, average: 4.58 out of 5)
Loss of consciousness: causes and first aid for fainting
Transient ischemic attack: symptoms, treatment and prevention
Related Posts
Errors
First medical aid requires coordinated actions of all participants at all stages of treatment. But often the inexperience and confusion of the person who finds himself next to the victim leads to some mistakes. It is forbidden:
- seat the injured person;
- resort to sudden and rough movements;
- lift and stand;
- leave him without supervision.
In this case, the patient is in dire need of anesthesia and pain relief, but it is not recommended to give them, as this leads to difficulties in diagnosing and determining signs of injury, and hiding the full picture of symptoms.
In this case, the breathing, pulse, and heartbeat of the injured person must be closely monitored. In the absence of vital signs, they resort to artificial respiration or cardiac muscle massage. If visible bone fragments are found through an open wound, you should not remove them. This can lead to heavy bleeding. It is worth remembering that TBI victims are in a state of shock and their requests are often harmful to their health. Therefore, taking into account the severity of the injury, it is necessary to follow only the rules for providing primary care for TBI.