Location
The cervical canal is the internal portion of the cervix, which connects the cavity of the reproductive organ and the vagina. In medicine, it is usually called the pharynx, since it is an opening. During menstruation, menstrual blood is discharged into the vagina through this pharynx, and during unprotected sexual intercourse, the male sex cells - sperm - penetrate into it.
The diameter of the external and internal pharynx, located in the cervical canal, averages 2-3 mm. During a gynecological examination, the external pharynx of a nulliparous woman looks like a point. After childbirth and abortion, the pharynx looks like a specific gap.
The length of the cervical canal is approximately 4 cm for nulliparous women and 7-8 cm for those who have a history of childbirth or abortion. The mucous membrane lining the walls of the pharynx of the cervix is called the endocervix.
How the cervical canal changes during pregnancy
When pregnancy occurs, the cervical canal acquires a characteristic bluish tint instead of the usual pink. Often, it is precisely by this sign that the doctor determines that a woman is pregnant.
After conception, a dense mucous plug forms inside the cervical canal, which becomes protection for the baby for the next 9 months. Mucus is actively produced by the endocervix. The cork becomes a reliable barrier to pathogenic bacteria and viruses that threaten from the outside.
Shortly before labor begins, the plug comes off, thereby freeing the birth canal. This event can occur either 2 hours before birth or 2 weeks - the exact timing is difficult to predict. The detached plug looks like yellow or transparent mucus streaked with blood. Not all women notice its departure, since most often it leaves the womb of the expectant mother in parts, in the form of small mucous discharge. Read more about how the mucus plug comes off during pregnancy →
Video
Often, women in the report received after an examination by a gynecologist see a note that the cervical canal is dilated, but they do not know what this means. Let's try to understand this issue.
What should the cervical canal be like normally?
It is worth noting that the norm is considered to be a condition in which only part of it is open or closed, the length of which does not exceed 3 cm. Usually it has the same diameter along its entire length. Its length is about 3.5-4 cm.
A change in the cervical canal is noted before ovulation, when it is somewhat dilated. This is necessary for better penetration of sperm into the uterine cavity and further conception.
What are the reasons that the cervical canal is dilated?
As a rule, an increase in this parameter is observed with the development of sexually transmitted diseases. In order to accurately identify them, a vaginal smear is prescribed.
Separately, it is necessary to say about the situation when the cervical canal is dilated. During this period, such a phenomenon is caused by excess pressure of the fetus itself on the cervix. As a result, the development of isthmic-cervical insufficiency occurs. This disorder leads to spontaneous abortion. When diagnosing it, the condition of the cervical canal is monitored over time using ultrasound diagnostic data.
Is it possible to narrow the dilated cervical canal?
Such a need arises only if the woman is pregnant. Correction of the canal lumen can occur in 3 ways: hormone therapy, installation of a pessary, surgery. It is worth noting that the latter is resorted to quite rarely when previously taken measures did not bring the expected result.
Sometimes the cervical canal may become partially or completely closed. Bougienage of the cervical canal is the expansion of the area of the internal genital organs using surgical instruments. The operation is performed under anesthesia, so the patient does not feel pain. After surgery, there is a high recovery rate.
Normal cervical canal during pregnancy
Normally, the external os of the cervical canal and the cervix itself are closed into a tight ring during pregnancy. This allows the woman's body to keep the fetus inside the uterus throughout the entire gestation period.
When the female body begins to prepare for childbirth, a gradual softening and smoothing of the cervix occurs, aimed at facilitating the passage of the baby through the birth canal. At the same time, the expansion of the cervical canal begins, which remained tightly closed during pregnancy. With the onset of contractions, the cervical canal opens gradually from 1-2 to 10 cm. Read more about how the cervix opens before childbirth→
Depending on the degree of opening of the cervical canal, doctors determine the expected time of labor and the woman’s anatomical readiness for it. When the width of the cervical canal reaches 10 cm, a single birth canal is formed, consisting of the uterus, cervical canal and vagina.
What happens to the cervix before childbirth
The cervix begins to prepare for the birth of a child from 32 to 34 weeks of pregnancy. First, its edges soften, leaving a dense area of tissue along the cervical canal. Closer to childbirth, the uterus more often comes to tone, due to which its lower segment softens and becomes thinner. The upper myometrium, on the contrary, becomes denser.
Due to this, the fetus begins to gradually descend and put its weight on the neck, provoking its further opening.
Dilatation of the cervix before childbirth does not occur equally in women who give birth for the first time and in multiparous women. In the first, it begins with the opening of the internal pharynx.
In the latter, the process of opening the internal and external pharynx occurs simultaneously, since by the end of pregnancy their external pharynx usually already allows one finger through. As it opens, the neck thus becomes shorter. A couple of days before the onset of labor itself, the process of its maturation accelerates significantly. Gradually it completely smoothes out and easily lets through 2 fingers or more.
Based on the Bishop scale above, on the eve of childbirth the cervix should meet certain parameters.
A soft cervix is ideal for childbirth. Her softness is evidenced by the fact that she freely passes 2 or more fingers of the doctor. During this period, a woman may notice the release of the mucus plug. This is one of the harbingers of the upcoming birth, indicating the imminent onset of contractions. As for the length of the cervix, during pregnancy a length of 3 cm is considered normal for it. In this case, both ends of the cervical canal must be closed. Closer to childbirth, it shortens. The length of the cervix before childbirth should not exceed 1 cm, gradually smoothing out completely.
As for its location, it was tilted back throughout the entire pregnancy. This further helps keep the fetus inside. Gradually, due to the softening of the lower segment of the uterus, it begins to unfold forward. When the time comes for childbirth, it should be located exactly in the center of the small pelvis.
If the cervical canal is dilated
An ultrasound of the cervical canal during pregnancy may reveal that it is expanding ahead of schedule. Sometimes pathology is discovered during a routine visit to an antenatal clinic.
During an examination on the chair, the gynecologist may notice that the pregnant woman has a slit-like cervical canal and has begun to dilate (the cervix allows the doctor’s finger to pass through). This means that preterm labor can begin at any time. Usually this situation occurs after the 20th week.
Why does this condition occur? Firstly, the reason may be a hormonal imbalance - the presence in the body of an increased level of male sex hormones, which stimulate the ripening of the cervix.
Secondly, we may be talking about a multiple pregnancy, which creates serious pressure on the cervix of the reproductive organ. Thirdly, the causes may be injuries and pathologies of the development of the cervical canal itself.
If you do not see a doctor, you may lose your pregnancy. Treatment is carried out in a hospital. If timely assistance is provided, the prognosis for carrying the fetus to term remains favorable.
Postoperative period and healing of the cervix
After bougienage of the cervix, the patient can return to normal life in about 2 weeks. During this time, all pain completely disappears.
If the pain intensifies within 14 days, you should urgently visit a doctor. A woman may experience a recurrence of infection. For this purpose, it is possible to install an alloplastic channel.
During postoperative treatment, the patient should take anti-inflammatory drugs and suppositories to speed up the wound healing process. They are prescribed only by a gynecologist, focusing on the woman’s health condition and the presence of individual intolerance to certain medications.
You should immediately consult a doctor if the following symptoms appear:
- discharge of blood and mucus from the genitals;
- persistent pain in the lower abdomen;
- increase in body temperature.
To prevent the development of negative consequences of bougienage of the cervical canal, the patient should take antibacterial drugs.
Depending on the severity of the clinical case, tablet or injection forms are used. To prevent the development of thrush, you need to take antifungal agents (most often they are prescribed in the form of suppositories).
To prevent infection, the following measures must be taken:
- promptly treat inflammatory processes in the uterus and cervical canal;
- undergo regular medical examinations to detect inflammatory pathologies and malignant neoplasms (such examinations should be carried out starting from adolescence);
- abortions should be performed only in a hospital setting and only by qualified personnel;
- do not use douching without control and the need, do not use aggressive solutions;
- from childhood you need to adhere to the rules of a healthy lifestyle and exercise regularly;
- do not use chemical contraceptives without supervision;
- avoid infection with infectious pathologies;
- During pregnancy
, do not take medications that have a toxic effect on the baby.
Pathologies
The main function of the cervical canal is to maintain pregnancy. If for some reason the body does not cope with the set goal, pathologies may arise that threaten the expectant mother with a premature onset of labor.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency
If the cervical os is dilated, and there is still a lot of time before the expected birth, we are talking about isthmic-cervical insufficiency. In this case, the reproductive organ cannot perform its functions and hold the fetus. Many women encounter this diagnosis at 18-20 weeks of pregnancy, it is at this time that the child begins to rapidly gain weight.
Normally, the length of the cervical canal during pregnancy at 20 weeks is 5-7 cm, and the diameter is no more than 6 mm. If these indicators do not meet normal criteria, for example, the cervical canal is shortened to 2-3 cm, the doctor threatens miscarriage or premature birth. Read more about the norms for cervical length by week →
The causes of the pathology are hormonal disorders, multiple pregnancies, and abnormalities of the cervical canal. To prevent miscarriage, the woman is prescribed medications aimed at strengthening the cervix and an obstetric pessary is installed. If these methods are ineffective, the doctor will place surgical sutures around the cervical canal. Removal of sutures is practiced before labor begins.
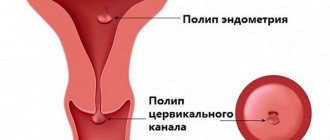
Pharynx polyp
A polyp of the cervical canal during pregnancy, discovered during an examination, can frighten the expectant mother. But first you need to find out the nature of the disease in order to find out which polyp we are talking about - true or decidual. To do this, the gynecologist prescribes a colposcopy for the expectant mother, as well as histological and cytological examinations.
A decidual polyp, in fact, is a pseudopolyp or polyp-like formation that appears exclusively during pregnancy and disappears on its own after childbirth.
Decidual pseudopolyp becomes the result of a hormonal imbalance in the body. It does not require surgical removal, they try not to touch it at all, only treatment with antiseptics is possible. The pseudopolyp itself disappears after the birth of the child or begins the reverse process of development in the first days after birth.
Less common is a true polyp of the cervical canal during pregnancy. Typically, such a pathology appears even before conception, and it actively prevents it. If a woman wants to become pregnant, surgical removal of the true polyp is recommended, as well as the necessary course of medication. Only after this can you plan for a child.
But sometimes a true polyp of the cervical canal develops after conception, already during pregnancy. In this case, they try not to touch him until the baby is born. At the same time, throughout the entire period, careful monitoring is carried out for any changes in the formation to prevent complications.
Why is this dangerous?
If the cervical canal is dilated in the absence of pregnancy, this does not pose an immediate danger to the woman’s life. But such dilatation is a symptom of various pathological processes in the cervix or body of the uterus, which requires adequate diagnosis and timely, comprehensive treatment.
Enlargement of the cervical canal during pregnancy is clearly a pathological sign. It may be a manifestation of:
- Threatened spontaneous abortion in early pregnancy. At the same time, in addition to the expansion of the cervical canal on ultrasound, there are signs of pathological hypertonicity of the uterus. Incipient detachment of the ovum with a retrochorial hematoma can also be detected, while maintaining the viability of the embryo.
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency, which is diagnosed from the 2nd trimmeter of pregnancy. Additional diagnostic ultrasound signs of this condition are a funnel-shaped expansion of the internal os, a decrease in the length of the cervix at less than 20 weeks to 3 cm, a decrease in the ratio of the length of the cervix to its diameter (at the level of the internal os) to less than 1.5. Isthmic-cervical insufficiency is the cause of recurrent miscarriage.
- Abortion in progress or incomplete spontaneous abortion (in early pregnancy), premature birth (after 26 weeks of gestation).
Therefore, if dilation of the cervical canal is diagnosed during pregnancy, the doctor needs to decide on treatment tactics as soon as possible and assess the advisability of urgent hospitalization of the patient.
Prevention
To avoid unnecessary worries, it is important for the expectant mother to monitor her well-being and not ignore timely medical examinations at the antenatal clinic. Preparation for pregnancy is of great importance, during which any gynecological and endocrine pathologies are excluded, and, if necessary, they are treated.
A woman must also maintain intimate hygiene - wash herself daily and change her underwear frequently. It is prohibited to use the douching method during pregnancy, since external influence on the cervical canal can cause infection or injury to the mucous membrane. This also applies to too active sexual relationships - violent sexual intercourse can lead to the same consequences. Read more about dangerous and safe sex positions during pregnancy →
The condition of the cervical canal during pregnancy is an important indicator on which the birth of a baby at term depends. To prevent possible problems, it is recommended to visit a doctor on time, take tests and undergo an ultrasound. Monitoring your health and the course of pregnancy can fight back any complication.
Author: Olga Rogozhkina, obstetrician-gynecologist, especially for Mama66.ru
Useful video about the first symptoms of premature birth
There is no doubt about the uniqueness of the female body. Mother Nature has provided everything in the smallest detail. The structure of a woman’s body allows the formation of a fetus, which begins its journey with a set of cells, subsequently turning into an embryo, and by the beginning of the third trimester already resembles a person. After fertilization of the egg, the body enters a new phase, the purpose of which is the development of a new life. The length of the cervical canal plays an important role in this process.
It is not for nothing that doctors pay close attention to this parameter at an appointment at a antenatal clinic. Fixing the length of the cervix allows you to timely detect the presence of a particular pathology, as well as take all necessary measures to avoid serious complications. But what length is considered normal, and in what cases is this a sign of deviation? Actually, this is the topic of this article.
General information
First, let's reveal the essence of the concept of the cervical canal - what is it even? Essentially, this is a segment that connects the vagina to the cavity of the reproductive organ. In the language of doctors, it is called the pharynx. It is through it that seminal fluid passes to fertilize the egg, as well as discharge during menstruation.
The size of the canal is directly dependent on whether the girl gave birth or not. The standard throat diameter is no more than 3 mm. Moreover, if the girl has not yet become a mother, then during a gynecological examination the doctor will see a point, and for women who have already given birth, a gap. As for the length of the cervical canal, here are the following dimensions:
- for nulliparous girls – 40 mm;
- in mothers - up to 80 mm.
During the second pregnancy, it can be considered normal if during the examination the pharynx allows a finger to pass through. At the same time, the length of the neck should not be less than 20 mm. Otherwise, this clearly indicates isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI).
The role of the cervical canal during pregnancy
The main functions of the pharynx are as follows:
- This lumen connects the vagina and the uterine cavity; menstrual flow passes through it, which indicates the absence of pregnancy. But if the girl does not have her first menstrual bleeding (menarche), therefore, the problem lies in the obstruction of the cervical canal.
- Formation of a mucus plug along the entire length of the cervical canal during pregnancy. This substance assists in the promotion of male germ cells into the cavity of the reproductive organ. Mucus provides protection against infection because it has bactericidal properties. During pregnancy, it hardens and a plug forms, finally closing the passage into the uterus. This forms a physical barrier that prevents the penetration of any pathogenic microorganisms into the organ cavity.
- At the stage of enlargement of the reproductive organ, the canal becomes smaller (this is not a pathology) and denser. This measure allows you to avoid premature rupture of amniotic fluid.
- During childbirth, the canal can stretch to allow the baby to pass through.
As for the cork, it remains for the entire 9 months while the woman is carrying a child under her heart. And together with the opening of the pharynx, it moves away on its own. But how is the length of the cervical canal determined by weeks of pregnancy and in normal physiological conditions?
Cervicometry
This term should be understood as a technique for ultrasound examination of the cervical canal. It allows doctors to find out not only its length, but also other parameters. In addition, ultrasound helps determine the size of the internal and external pharynx.
The examination itself is carried out using a transvaginal sensor, with the help of which all parameters of the canal are determined. This procedure does not cause pain in women and is easily tolerated by them.
The technique is based on the principle of reflection of outgoing ultrasonic waves from biological structures of various types. Typically, ultrasound can be performed not only in a hospital setting, but also during a clinic visit.
In addition, the length of the cervix along the cervical canal can be determined during a routine visit by pregnant women to the doctor for a gynecological examination. The specialist determines its size by touch. Moreover, in this way, not only the length is determined, but also the density, localization, and expansion.
What is cervical dilatation?
This is a surgical operation performed as a result of narrowing or complete atresia (fusion) of the cervical canal. Pathology occurs in women of reproductive age for various reasons.
But often narrowing or fusion of the cervical canal occurs due to curettage or age-related changes. These actions have a negative impact on the condition of the cervix.
The patency of the cervical canal is restored using a simple surgical operation. It is carried out using a special instrument - a bougie (hence the name of the procedure).
Bougienage is the only way out for treating serious pathologies that limit a woman’s ability to have children. This type of intervention is also performed for women during menopause.
Some patients describe this procedure as scary. This is not true, because the woman does not feel pain during the cervical canal dilatation operation due to the action of anesthesia. Medical centers use equipment that can reduce the time a patient spends in a hospital.
Women who do not know what cervical bougienage is sometimes refuse to undergo the intervention. By doing this, they expose themselves to danger, because in this case the development of inflammatory and oncological pathologies is possible. In addition, a blockage of the cervical canal can lead to infertility.
Normal indicators
Normally, the cervical canal is in a closed state, which allows the fetus to be kept in the cavity of the reproductive organ throughout the entire pregnancy. Typically, the condition of the pharynx is recorded during a standard diagnostic procedure. But if there are any suspicions, the doctor prescribes an additional study for the patient, which will confirm the diagnosis or refute it.
Women will also have to undergo all necessary tests. This will allow doctors to create an objective clinical picture of the current situation both in relation to the woman herself and her child.
The length of the cervical canal begins to change from the 20th week of pregnancy and, starting from this period, doctors already record this parameter every seven days. This is done with the aim of timely detection of deviations from the norm, if they occur.
Change in canal length by week of pregnancy
With the onset of the first trimester of pregnancy, the length of the canal is 40 mm, which is within normal limits. In the second period of gestation, the canal begins to shorten and the pharynx itself begins to expand. At this time, a length of 35 mm is considered the norm. Before birth, at 36-37 weeks, the length of the canal becomes even shorter - up to 30 mm, which is also not a pathology. A week before delivery, this value becomes even slightly smaller, while the pharynx is expanded to 100 mm. The table below will provide a more accurate idea of the change in channel length.
Table of changes in the length of the cervical canal by week of pregnancy is normal.
| Gestational age (by week) | Channel length (in mm) |
| From 10 to 14 | 34-36 |
| From 15 to 19 | 38-39 |
| From 20 to 25 | 40 |
| From 25 to 29 | 41 |
| From 30 to 32 | 30-33 |
| From 32 to 36 | 33-36 |
| From 36 to 40 | 29-30 |
Cervix during pregnancy norm by week
To successfully carry a pregnancy, women must regularly go for examinations with gynecologists. Specialists can determine the size of the cervix in the following ways:
- Manual. The patient sits on the gynecological chair. The doctor assesses the structure of the organ and its length through palpation. Normally, the following results should be observed: the external pharynx is closed, dense structure, length 3.5 cm.
- Hardware. The cervix is measured and its condition is assessed during an ultrasound examination with a vaginal probe. The doctor, thanks to highly sensitive equipment, is able to determine the size with an accuracy of a millimeter. From the 20th week, this data can be obtained by undergoing an ultrasound with a transabdomial sensor.
Gynecologists take into account the approved standards:
- 16-20 weeks - from 4.0 cm to 4.5 cm;
- 25-28 weeks - from 3.5 cm to 4.0 cm;
- 32-36 weeks - from 3.0 cm to 3.5 cm.
Pregnancy is the most important period in the life of every woman. The instinct of motherhood is inherent in the fairer sex by nature itself.
But despite this, bearing a fetus is still stressful for the body. All organs and systems undergo various physiological changes during pregnancy. The cervix plays a key role in the development and preservation of the health of the unborn baby. It is part of the internal reproductive system.
The condition of the cervix can tell a lot about the timing of pregnancy and the readiness of the female body for childbirth. The size, length and walls of the canal that leads into the uterus are examined by ultrasound.
The gynecologist necessarily recommends that the patient undergo this procedure regularly in order to monitor the formation of the child and the progress of pregnancy.
Transvaginal ultrasound is the best method for diagnosing the length of the cervix
From the twentieth week, the length of the cervix is recorded weekly, since it is at the 20th week that this parameter begins to change. It is necessary to study what is the normal length of the cervix during pregnancy. Sizes of the cervix during different periods of pregnancy
The normal length of the cervix during pregnancy in numerical terms depends on the period of gestation. The period after 20 weeks is more important (the length of the cervix at 20 weeks is 40 mm), but in the early stages of pregnancy it is also advisable to determine the value of the parameter. The weekly norm for different periods is disclosed in the tabular format below.
Table of norms for cervical length by week of pregnancy
- during an examination by a gynecologist, density, size and location are assessed;
- Using ultrasound, more accurate indicators are determined, because this method is more informative.
If measuring the length with ultrasound shows the parameters are significantly lower than acceptable, then an additional study is prescribed using transvaginal ultrasound (through the vagina).
The critical length of the closed part indicates the risk of miscarriage. With such a pathology, sutures or a gynecological pessary will be required to prevent the death of the child.
The normal length varies from 3.5 to 4.5 centimeters, and the condition should be tight and closed. A decrease in this indicator is possible only in the last months, which is explained by the body’s preparation for childbirth.
When studying the length of the cervix, you should first understand what it is and why it is required. Many processes occurring in the female body can depend on the parameters of this organ. First of all, normal pregnancy and childbirth.
The cervix is an organ with a muscular structure that looks like a tube. It ensures the connection between the uterus and the vagina. Inside the cervix there is a cervical canal, which ensures the removal of congestion during menstruation.
The area connecting the uterine cavity with the cervical canal is the internal os, and the cervical canal with the vagina is the external os.
Important! During the examination, if everything is normal and there are no deviations, then the cervical canal should be in a closed state and blocked by a plug with a mucous structure. This will protect the child from exposure to various harmful substances.
The structure of the uterus of women may have distinctive congenital features. But normally, the length of the cervix should be from 3.5 to 4 cm. This length indicator will ensure normal stretching and will allow it to withstand the loads that the fetus exerts during pregnancy. However, it will not open.
Over a long period of pregnancy, the cervix should have a dense structure, and the internal and external pharynx should be closed. It is worth considering that the length of the cervix when carrying a child may depend on the period.
The table shows length norms in accordance with the duration of pregnancy.
| Week of pregnancy | Length, mm |
| 16, 17, 18, 19, 20 weeks | 40-45 |
| 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28 weeks | 35-40 |
| 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35 weeks | 30-35 |
| 36, 37, 38, 39, 40 weeks | 25-30 |
Attention! If a woman has injuries to the cervix during surgery, and premature shortening of the length of the cervix is observed, then diagnosing the length of this organ begins after 4 months.
| Gestational age in weeks | Cervical length in mm |
| 1-31 | 45-35 |
| 32-36 | 34-24 |
| 37-40 | 25-20 |
The cervix of a non-pregnant woman is lined with a muscle layer, but during gestation, normally starting from 20-23 weeks, it is transformed into connective tissue, due to which the cervix becomes very elastic (see also: short cervix at 20 weeks of pregnancy). Changes in the cervix cause the uterus to stretch, so the connecting tube itself becomes shorter.
Starting from about 12 weeks, the connecting canal between the uterus and vagina gradually shortens. Just before childbirth, the cervix normally changes greatly, shrinking to a length of two centimeters.
These changes are physiological and indicate a normal rate of cervical ripening. The norms of size indicators for primiparous and multiparous women may be different. In the case when the connecting canal does not change in size or rapidly shortens, doctors note a pathology that is dangerous to the health and life of the expectant mother and her baby.
An examination of the canal connecting the vagina and uterus is performed during each examination of a pregnant woman in a gynecological chair. There are two methods for measuring it:
- Determining the length of the canal using a finger. The doctor inserts his fingers into the lumen of the canal that leads from the vagina to the uterus and records its approximate length. When palpating the cervix, not only its size is determined, but also the condition of the internal walls. A good cervix just before childbirth becomes soft and elastic, greatly shortens and widens significantly. When dilated to 6 fingers, labor begins.
- Examination of the cervix using ultrasound. An ultrasound machine can measure the cervical canal with millimeter precision. With this study, it is also possible to record the degree of maturity of the channel.
The most important indicator of the condition of the uterine cervix is the Bishop scale. She evaluates the cervix according to the following criteria:
- Disclosure. If the ball is closed, it is scored 0 points, the maximum opening width is 6 cm (4 points). Dilation up to 2 cm is assessed as 2 points, up to 4 - three points.
- Smoothness. This indicator is measured as a percentage: the higher the percentage of smoothing, that is, ripening, the more points the neck receives. Three points are given when the cervix is fully mature, when all the muscle fibers in it are replaced by connective tissue, soft and elastic, capable of easily stretching.
- The position of the ball relative to the wire axis of the pelvis. The most convenient position for childbirth is parallel to the pelvic wire line. If the cervical canal acquires this position, the doctor gives two or three points for this.
- Position relative to the ischial spines. The closer to them the canal connecting the uterus and vagina is located, the higher the score.
- Length. This indicator depends on the period. In the early stages, up to 17-21 weeks, this parameter changes slightly. Later the CMM becomes shorter.
| Gestation period by week | Normal cervical length for primigravidas | Normal cervical length for multiparous women |
| 10-14 | 35.3 mm | 35.6 mm |
| 15-19 | 36.5 mm | 36.7 mm |
| 20-24 | 40.4 mm | 40.1 mm |
| 25-29 | 40.9 mm | 42.3 mm |
| 30-34 | 35.8 mm | 36.3 mm |
| 35-40 | 28.1 mm | 28.4 mm |
In some cases, indicators may deviate slightly from normal values, depending on the individual characteristics of the expectant mother’s body. For a gynecologist, the most important information is the length of the cervix at 24 weeks. If significant abnormalities are detected during this period - the cervical mass will be about 28-29 mm - there will be a possibility of miscarriage or premature birth.
The cervix performs an important function. It closes the entrance, securely holds the baby in the womb, and prevents the penetration of vaginal secretions and pathogenic microflora.
A short cervix is a serious threat
The length of the cervix during pregnancy is an important indicator for assessing the condition of the pregnant woman. It is not permanent. Closer to childbirth, the cervix becomes smaller and this is normal, since the tissues stretch. But in the early stages, the length of the canal should be within normal limits; this is the key to a pregnancy without complications.
Pregnant women may not even be aware of the measurements taken, because if there are no deviations, the woman is not notified. This examination is called cervicometry.
It is an ultrasound of the reproductive system and is carried out at 20-24 weeks.
If the first routine ultrasound examination showed abnormalities, the length of the cervical canal can be measured at an earlier date with a break of 1-2 weeks.
External ultrasound to measure the length of the cervix during pregnancy, preferably in later stages
No special preparation is required for the ultrasound; you should empty your bladder before the procedure. This is necessary for greater comfort for the pregnant woman herself. The examination is painless, there is no need to worry.
Channel extension
Over the course of 9 months of bearing a child, the length of the cervical canal during pregnancy normally first increases and then decreases, and this is not a pathology. But what if the channel size does not correspond to the average value during a certain period? Is this the norm or can this phenomenon already be regarded as a pathology? First, let's look at the reasons for lengthening the cervical canal:
- anatomical structure of a congenital nature;
- frequent inflammatory processes of the female reproductive system;
- getting injured;
- surgical intervention.
Due to the elongated dimensions of the canal, disruption of the process of fertilization and fetal development, including subsequent delivery, may occur. In addition, the uterine os undergoes undesirable changes, and the placenta itself may not attach correctly to the wall of the uterus. At the same time, there are often cases of post-term pregnancy due to the fact that the reproductive system is not yet ready for childbirth.
In addition, when the length of the cervical canal deviates from the norm, it has a solid structure. Consequently, it does not stretch well and therefore does not ripen at the required time. In addition, the duration of contractions increases, which leads to a weakening of the female body and a complication of delivery. As a rule, in such situations they resort to stimulation of labor.
A canal that is too long should be considered pathological. This condition does not lead to anything good, and therefore requires the intervention of specialists. For this reason, research is carried out in antenatal clinics.
How is cervical maturity assessed?
Starting from 38 weeks of pregnancy, during an examination with a gynecologist at a antenatal clinic or in a maternity hospital, the doctor conducts a vaginal examination to assess the condition of the cervix. It is also mandatory to examine the cervix before childbirth, as well as during labor. This is necessary to understand how quickly the process of maturation occurs.
There are four main parameters, by assessing which an obstetrician-gynecologist can conclude that the cervix is ready for childbirth. Its maturity is determined by a special Bishop scale, according to which each of the parameters is assessed on a three-point system (from 0 to 2 points). If this scale is rated 5, then we can talk about readiness for natural childbirth.
- The first parameter that the gynecologist evaluates during a vaginal examination is consistency. The maximum number of points is 2 for a soft neck; if it is softened, but a little denser near the internal pharynx, then its condition is assessed as 1 point; a hard cervix is not ready for childbirth and is scored 0 points.
- The second important parameter is length. On the Bishop scale, a smoothed neck, the length of which does not exceed 1 cm, is scored 2 points. A neck 1–2 cm long receives 1 point. If the length is more than 2 cm, then it is not ready for childbirth and is scored 0 points.
- The third parameter that matters is location. The Bishop score suggests a score of 0 for a cervix that is deviated posteriorly; 1 point for anterior deviation and 2 points for midline position.
- The fourth important parameter is the patency of the cervical canal. It is usually measured by the number of fingers that can pass beyond the outer and inner pharynx. If the external pharynx is closed or allows only the tip of the finger to pass through, the neck is considered not ready (0 points). If the outer pharynx has opened, but the internal pharynx remains closed, then this is scored 1 point. If the channel freely passes 2 fingers through the internal os, then 2 points are given.
Provoking factors
The length of the cervical canal changes throughout the 9 months of pregnancy. However, this process is normally influenced by hormones and a number of other reasons.
However, one cannot exclude provoking factors that contribute to the deviation of the length of the cervical canal at 12 weeks from the norm (or at any other time). Some of them do not bode well:
- Hormonal imbalance. Biologically active substances provide control over pregnancy. They also ensure the preparation of the reproductive system of the female body for labor. For this reason, the occurrence of an imbalance inevitably causes a deviation in the length of the cervical canal from normal limits.
- Trauma to the cervix during surgery. In particular, we are talking about abortions or previous births. In this case, the cervix may become shorter or longer.
- Diseases of the reproductive system of an infectious nature.
- Features of the anatomical structure.
- Stress. It is not without reason that experts recommend that pregnant women avoid severe anxiety. It is important for any expectant mother to ensure peace, since a stable state helps maintain hormonal levels within normal limits. Stressful situations (especially strong ones) can provoke various pathologies in the development of the fetus.
For this reason, it is necessary to constantly monitor the length of the cervical canal during pregnancy. This will allow appropriate measures to be taken in a timely manner.
Complications after surgery
- inflammatory lesions of the pelvic organs;
- bleeding;
- violation of the integrity of the cervix.
Attention! The listed conditions provoke repeated narrowing and obstruction and are indications for repeated surgery.
A rather rare but dangerous complication of bougienage is hematometra. At the same time, menstrual blood accumulates in the uterine cavity. This condition is dangerous and, without treatment, can be fatal. Against the background of hematometra, the woman develops severe pain, pale skin and decreased blood pressure. Treatment is always surgical. In severe cases, the uterus is completely removed.
If bougienage is carried out in compliance with the standards and strictly as directed, the risk of complications is low. A woman needs to monitor her own health and promptly consult a doctor when the first symptoms of gynecological diseases appear.
If the cervical canal is completely closed, the woman experiences menstrual irregularities. With significant narrowing, the amount of bleeding decreases, but the number of days of menstruation increases. Gynecologists consider such conditions as dangerous, the ability to conceive and bear fruit is reduced, and childbirth is complicated. Drug treatment is not able to provide expansion of the uterine canal, so patients are recommended to have surgery.
Channel expansion
In cases where patients are found to have an enlarged cervical canal, they are sent to the hospital. The need for this decision is largely due to the fact that this sign indicates ICN. That is, the cervix itself is already dilated ahead of schedule. The fruit, increasing in size, puts even more pressure on it. And if we are talking about multiple pregnancies, then this phenomenon is almost always observed due to the specifics of this situation.
To eliminate the pathology, drug therapy or surgery are used. With the help of medications, it is possible to bring hormonal levels back to normal, as well as eliminate hypertonicity of the reproductive organ.
Indications and features of the procedure
Bougienage is prescribed for the following conditions:
- infectious pathologies (herpes, syphilis, chlamydial infection, toxoplasmosis);
- taking medications for a long time;
- exposure to ionizing radiation on the body;
- carrying out the procedure of curettage of the uterus;
- cauterization of the uterine epithelial layers using electrocoagulation or the use of silver nitrate;
- cancer of the cervix and uterine body;
- abortion;
- endometritis or endocervicitis;
- stenosis or atresia of the cervix;
- hypertrophic scarring.
The procedure is performed in a hospital setting using general anesthesia. Local anesthesia is not prescribed because it is ineffective. The type of anesthesia is determined by the doctor after a thorough examination of the patient’s body.
The operation implies that a special instrument, a bougie, will be inserted into the cervical canal. Without anesthesia, the patient would be in pain ,
because it leads to traumatization of the mucous membranes. The bougies increase gradually, otherwise the neck is likely to rupture.
Trauma to the tissue always leads to re-closure of the cervical canal. Correctly performed dilation of the cervical canal guarantees the absence of complications.
Bougienage is not done if it has developed as a result of a malignant process. In this case, more radical operations are necessary. Bougienage is prohibited if the duration of false amenorrhea in a woman is more than six months. In this case, recanalization of the cervix is performed.
Inflammatory pathology
The impact of pathogenic microorganisms on the cervical canal contributes to the development of the inflammatory process. This condition is called endocervicitis. As a rule, inflammation is caused by the presence of a wound (along the entire length of the cervical canal or in a certain part of it). Microorganisms such as chlamydia and staphylococcus can cause a similar reaction, even if the canal is not injured.
The danger of endocervicitis is as follows:
- hypertonicity of the uterus;
- insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus;
- loosening of the membranes;
- premature onset of labor.
During a gynecological examination of the patient, based on the above signs, the specialist diagnoses endocervicitis. To determine the course of treatment, a smear is taken and examined in a laboratory. First, you need to find out the type of causative agent of the disease and only then determine the drug to combat it.
Since not all medications are approved for use by pregnant women, preference is given to topical medications: suppositories, capsules. Only a highly qualified doctor should prescribe this or that external drug. In addition, not only the type of pathogen should be taken into account, but also the duration of pregnancy.
Frightening diagnosis
In some cases, when determining whether the length of the cervical canal is normal during the week of pregnancy or not, doctors can identify the presence of a polyp. Many girls are scared by this diagnosis.
However, in this case there are two ways of development:
- True polyp. Often its presence causes problems with conception. For this reason, when planning a pregnancy, it should definitely be removed. After this, the woman must undergo drug therapy to avoid relapses.
- Pseudopolyp develops only in expectant mothers. At the same time, the growth itself does not have any effect on the health and well-being of the woman and her child. And after childbirth, it resolves on its own. The reason for the appearance of this neoplasm is a change in hormonal levels in the female body. Since it is eliminated on its own, there is no need to resort to surgery; it is enough to treat it with any antiseptic.
At the same time, a true polyp can also be found in pregnant women. Only in this case should he not be disturbed before the birth of the child, only vigilant monitoring of his condition should be carried out during routine examinations of the length of the cervical canal. This will allow you to prevent any complications in a timely manner. Only in the most severe cases, despite the special situation of the woman, is surgery prescribed when there is a threat to the mother’s life.
Anatomy of the cervical canal
The lumen of the cervix can have a different shape and length in different women. On average, the length of the cervical canal in an adult nulliparous woman is 35–40 mm. The shape of the canal depends on race, the structure of the pelvis and genital organs.
Along its length, the cervix has two narrowings, called the internal (closer to the uterus) and external (closer to the vagina) pharynx. The internal os canal communicates with the uterine cavity, the external os with the vagina and the external environment. During each trimester, the obstetrician-gynecologist evaluates the size and lumen of the external pharynx and, based on these data, determines the duration of pregnancy and the presence of a threat of premature birth.
The inside walls of the cervical canal cavity are covered with a special columnar epithelium. The cells of this epithelium produce a mucous secretion, the quantity and quality of which depend on hormonal levels.
Hormone levels vary on different days of the menstrual cycle. Accordingly, the onset of ovulation and the phase of the menstrual cycle can be determined by the quality of mucus. Also, assessing the quality of mucus allows us to identify various pathologies of the menstrual cycle and changes in the hormonal levels of the female body.
Interesting! The symptom of mucus tension is used by the gynecologist to determine the saturation of a woman’s body with estrogen. Between the legs of the forceps, the mucus obtained when taking a smear from the cervical canal is stretched - the longer the thread, the more estrogen in the body.
Cervical mucus has bactericidal properties, which helps maintain sterility inside the uterine cavity. Mucus fills the cervical canal throughout pregnancy. During this period it is thicker and denser. Forms a mucus plug that performs a protective function. The cork protects the fetus from infection. Just before birth, the mucus plug comes off.
The mucus reaction is different in different phases of the menstrual cycle. During ovulation, when conception is most likely, the mucus becomes alkaline. For sperm, the alkaline reaction of the environment is most favorable. In addition, under the influence of estrogen, the mucus thins, and sperm are able to move faster.
Before and after ovulation, the mucus in the lumen of the cervix is thicker, and its reaction is acidic. This helps slow down the movement of sperm.
Interesting! It is on this property of mucus that the action of hormonal contraceptives is based. Hormones change the state of cervical mucus, and it does not allow sperm to enter the uterine cavity.
Pregnancy
If the cervical canal is dilated during pregnancy, then premature labor can begin at any time. The reason for such a deviation may be:
- increased levels of male hormones in the body that stimulate cervical ripening;
- multiple pregnancy;
- trauma and pathology.
The most common pathologies due to which the cervical canal becomes dilated during pregnancy include:
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- pharynx polyp;
- endocervicitis.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency
This pathology is one of the common reasons why the cervical canal becomes enlarged. The uterus is unable to support a baby that is gaining weight.
Ultrasound helps to detect dilation of the cervical canal in a pregnant woman.
Violations can be caused by:
- abnormalities in hormonal levels;
- polyhydramnios;
- scar deformities.
If the canal is dilated, then the woman is prescribed drugs that strengthen the cervix.
Polyp
Polyps can be true or decidual (pseudopolyp that forms exclusively during gestation). To find out the type of tumor, the pregnant woman is prescribed a colposcopy of the cervix.
Decidual polyp develops against the background of hormonal imbalance and does not require removal. A true polyp is rarely diagnosed during pregnancy. It is removed after the baby is born.
Endocervicitis
The cervical canal can be dilated as a result of inflammation involving its inner surface. The pathology is caused by microorganisms of both pathogenic and opportunistic classes.
The choice of drugs depends on the type of pathogen. Preference is given to local remedies - vaginal suppositories or tablets.
If it turns out that the cervical canal is dilated, this does not always mean the presence of any pathology. The expansion may be physiological, but in any case, the woman will be prescribed an examination.
Cervical canal
- a spindle-shaped hollow area that connects the uterine cavity and vagina. Normally, this area is tightly closed. It performs a protective function - the infection should not penetrate the uterus. The inner layer of cells produces mucus, which creates a kind of plug in the cervix.
During pregnancy, a mucous seal forms in the canal, which tightly closes the cervix and protects the embryo.
For manipulations in the uterine cavity and diagnostic procedures, the doctor must expand the cervical canal.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
Dilatation of the cervical canal is prescribed in the following cases:
The procedure is not performed if:
- suspected ectopic pregnancy;
- established ectopic pregnancy;
- inflammatory process in the acute period of any localization - gynecological and other organs;
- infectious diseases
Other cases are discussed individually with each patient.
How does the procedure work?
Manipulations are carried out only in a medical facility
. Observance of asepsis rules and practical skills by medical personnel is mandatory.
1
.
the patient is on the gynecological chair; 2
.
external genitalia and vagina are treated with disinfectants; 3
.
The gynecologist conducts a manual examination of the patient - both intravaginal and rectal; 4
.
Speculums are inserted into the vagina and the cervix is exposed; 5
.
the anterior lip of the cervix is grabbed with forceps; 6
.
the uterine cavity is examined, the direction of insertion of instruments is determined; 7
.
expand the cervical canal to 8 mm. For this purpose, special dilators are used; 8
. Then the required manipulations are carried out in the uterine cavity - examination, surgery, termination of pregnancy.
After the procedure, the gynecologist examines the lips of the cervix. If there are signs of bleeding, appropriate treatment is carried out.
Complications after the dilation procedure
The procedure for expanding the cervical canal is an invasive procedure. Therefore, after the procedure, the following complications may arise:
- bleeding;
- rupture or perforation of the walls of the cervical canal;
- infection of internal organs;
- allergic reactions to anesthesia materials, medications;
- psychological problems in the patient.
If gynecological manipulation is carried out in a medical institution, then the risk of complications is minimized.
What determines the length of the cervical canal
The length of the cervical canal changes in each period of a woman’s life. In an adult nulliparous woman, the length of the cervical lumen does not exceed 40 mm, its width on average is 8 mm.
During pregnancy, the cervical cavity decreases in size - both in length and width. This is necessary in order to form a compacted muscle barrier for the growing fetus. Under the influence of gravity, the fetus, increasing in size, tends downward, towards the exit from the uterine cavity. The thickened and decreased lumen of the cervix does not allow the fetus to leave the uterine cavity and keeps it there until the time of physiological labor.
At the same time, the walls of the canal are so extensible that it can allow the baby’s head to pass through during childbirth. The mucous membrane of the cervical cavity is much thicker than the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity. In addition, on the front and rear walls of the canal it is collected in numerous folds. This folding contributes to the expansion of the cervical canal during childbirth and the passage of the fetus through it.
The muscular layer of the cervix is also slightly different from the muscular layer of the uterus. It has an increased content of elastic fibers, which also contributes to the greater extensibility of the canal.
The length of the cervix depends on a variety of external and internal environmental conditions. It can change under various pathological and physiological conditions.
- With congenital pathology of the development of the genitals, for example, atresia of the cervical canal. In this case, the lumen of the cervix is partially or completely closed, and its length may decrease.
- Expansion of the cervical canal is observed during various inflammatory processes in it.
- The length of the cervical lumen can be affected by such a pathological condition as its stenosis.
- A polyp of the cervical canal in most cases leads to its expansion. The length of the channel, as a rule, does not change. The polyp can be located in any part of the cervical canal mucosa.
- The length of the cervical canal often changes due to various injuries - childbirth with a large fetus, surgery, abortion.
- During pregnancy, throughout its entire length, the length of the cervical canal should not be less than 35 mm. A decrease in this length indicates the development of cervical incompetence—isthmic-cervical insufficiency. This condition threatens premature birth.
If the length of the cervical canal during pregnancy decreases to 22 mm, this indicates a possible risk of premature birth. The length of the cervical canal is considered critical if it is less than 15 mm. This is an indication for suturing the uterine isthmus.
A pregnant woman is prescribed several ultrasound examinations throughout her pregnancy. This is done precisely in order to monitor the condition of the cervical canal and timely notice the developing signs of isthmic-cervical insufficiency. Ultrasound allows you to accurately determine the length of the isthmus.
Important! If signs of isthmic-cervical insufficiency appear, the woman is hospitalized in the hospital to maintain the pregnancy. If conservative treatment fails, several stitches are placed on the cervix. These sutures hold the opening external os in the desired position and prevent the development of premature birth. The sutures are removed at the time when physiological labor is possible.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, the physiological length of the cervical canal is 40 mm. In the second trimester, the canal is shortened to 35 mm. At 36 weeks of pregnancy, the length of the canal is 30 mm. In the last week before childbirth, the cervix ripens. The channel reaches a length of 10 mm. There is an expansion of the canal and opening of the uterine pharynx. In the first stage of labor, the cervix smoothes and the external and then internal os gradually open. At this time, every half hour the obstetrician assesses the condition of the cervix and the woman’s readiness for childbirth.
If labor is weak, prostaglandins can be injected into the cervical canal - substances that enhance the contractility of the uterus.
When giving birth to a large fetus or with a narrow pelvis, a rupture of both the perineum and the cervix may occur. In this case, the lumen of the cervical canal increases and bleeding develops. To restore the integrity of the cervix, the obstetrician-gynecologist applies stitches. Within a month after the rupture, sexual rest is prescribed for complete healing. But even under such conditions, the shape and length of the cervical canal may change.
Cervical canal: what is it, what is the normal length during pregnancy, what are the causes of deviations?
Women have an idea about the structure of the female reproductive system, the process of conceiving a child and pregnancy from adolescence.
This is generally covered in school biology classes. However, women sometimes do not realize the most important details that allow them to carry a baby for 9 months until they become pregnant. Only during this period will expectant mothers learn what the purpose of the cervical canal is and why it is important to monitor its condition during pregnancy. Obstetricians monitor the size of the cervix in pregnant patients to prevent deviations that could affect pregnancy and delivery.
The concept of the cervical canal and its role in the female body
The outer pharynx, like the internal pharynx, has a diameter of no more than 2-3 mm, and reaches 40 mm in length. In a woman who does not have children, the opening has the shape of a point; after childbirth or abortion, the pharynx becomes slit-like and lengthens to 70-80 mm. The walls of the pharynx are lined with a mucous layer - the endocervix, which performs the following functions:
- Formation of a barrier. The mucus in the cervical passage is an obstacle to pathogenic microflora. Thanks to this mucous fluid, viruses and bacteria do not penetrate the uterine cavity.
- Removal of uterine secretions. During menstruation, as well as after the birth of the baby, blood, mucus and placenta are removed through the cervical dilatation.
- Creating conditions for sperm penetration during ovulation. Under the influence of hormones, the acidity of the mucous plug of the cervix changes, and its expansion occurs. Thanks to these temporary changes, male cells are able to reach their target.
- Participation in the birth process. When the cervical canal expands at the time of birth, the baby is able to safely leave the uterine cavity. Full dilatation of the cervix can be seen in the photo.
How does the endocervix change during pregnancy?
After fertilization and throughout pregnancy, the shade of the cervix structures changes, it becomes bluish. Changes also occur inside the cervix; from the moment of conception, a mucus plug begins to form in it, which is designed to protect the embryo and fetus from the external environment. Mucus production is carried out by the endocervix.
The width of the cervical lumen in women is 7-8 mm, regardless of pregnancy. However, in expectant mothers, the shape of the pharynx may have distinctive features. The shape is also influenced by the number of births, the health of the hormonal system, and diseases of the reproductive organs.
When a woman wants to make sure that pregnancy has occurred, she turns to a gynecologist, who first examines her and then sends her for an ultrasound.
This method allows you to see the embryo attached to the wall of the uterus and its size.
In addition, using an ultrasound examination, a specialist evaluates the parameters and condition of the cervix to identify possible risks of miscarriage or premature birth.
In the normal position, the ends of the pharynx should close tightly. The length of the cervical canal during pregnancy is in the range of 35-40 mm. The obstetrician can also judge the imminent onset of labor by the condition of the pharynx.
Norms for the length and width of the cervical canal at different stages of pregnancy
In the early stages of pregnancy, the length of the cervix, as well as the canal, does not differ from the same parameter in an ordinary woman. Changes become noticeable starting at 16 weeks. So, by the 19th week of gestation, the length of the cervix can reach 39 mm; at 21 weeks, the length increases to 40 mm. The maximum length of the cervical canal is observed at 29 weeks.
Then the reverse process gradually occurs, and until about 32 weeks the clearance decreases slightly. At 30-33 weeks, its normal value is from 30 to 33 mm. From 33 to 36 weeks of pregnancy, the cervix lengthens again. The range of normal length values at this stage is 33-36 mm.
Then, until the end of gestation, the length of the cervix will decrease. This means that the body is preparing for the arrival of the baby. The closed ends of the pharynx open, and the tissues of the cervix soften. Before the baby is born, the pharynx opens a certain amount, and the baby gets the opportunity to pass through the birth canal.
To ensure that delivery does not occur prematurely, gynecologists often conduct examinations of the cervix. Data on its length are of particular importance in the period preceding childbirth.
Diagnostic methods
When pathologies of the cervical canal are identified, the cervix is examined; this examination is performed comprehensively, which allows for a differentiated approach to making a diagnosis and choosing the optimal list of therapeutic measures. Conducting a visual examination using mirrors allows the obstetrician to see the external pharynx. As a rule, if the presence of polyps is recorded in the vaginal area, then they are also present in the cervical cavity.
During the examination, the doctor takes smears from the patient to assess the presence of pathological bacterial microflora and identify existing diseases, which often include:
- inflammatory processes;
- benign changes in the mucous membrane;
- mild metaplasia of the cervix, if the changed cells are present only in the superficial layer of the epithelium;
- moderate degree of metaplasia with deeper penetration into the epithelial layer of dysplastic formations;
- deep metaplasia with damage to the epithelial cover without penetration of cells into the basement membrane;
- precancerous conditions;
- malignant tumors.
During pregnancy, expectant mothers are diagnosed several times using ultrasound. A special feature of ultrasound examination of pregnant women is cervicometry. The specialist measures the thickness and length of the cervix. If deviations from the norm are detected, the obstetrician decides which methods of correcting the condition to use.
Possible deviations from the norm and their causes
The cervical canal of the cervix is one of the objects of careful observation by gynecologists when working with pregnant women. This is explained by the fact that not only the birth of a baby depends on his condition, but also the ability to bear a child, because disorders of the cervical canal are often factors that provoke miscarriages and premature births.
The most common pathologies of the canal:
- endocervicitis;
- pathological narrowing of the canal lumen;
- cyst;
- tumor formations;
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- expansion of the internal pharynx, which must be closed.
Endocervix expansion
If the cervical canal is dilated in a patient who is not carrying a baby, then she needs to undergo an examination to identify diseases of the uterine cavity.
The reasons for the expansion of the cervical canal are often pathological conditions such as uterine fibroids, endometriosis, cystic ovarian lesions, chronic cervicitis, and adenomyosis.
The lumen of the cervix can be enlarged due to the use of hormonal drugs and smoking.
Closed channel
When a doctor determines during diagnosis that the cervical canal is closed, he can assume that the lumen of the cervix is closed. In this case, conceiving a child is almost impossible, since the narrow lumen completely blocks the sperm’s path to the egg.
Canal closure can be either complete or partial. The reasons are:
- operations with curettage of the uterine cavity;
- unprofessional treatment of cervical erosions;
- presence of polyps;
- oncological neoplasms;
- diseases of the mucous membrane of the canal.
Signs of cervical canal infection:
- too little discharge during menstruation;
- pain during menstrual bleeding;
- pain in the groin area;
- heaviness in the vagina;
- pain in the bladder area.
Pathological processes in the female body
The functions of the cervical canal may be disrupted for other reasons. The state of the channel is influenced by both external and internal factors. Common diseases of the cervical canal:
- Inflammatory processes. The mucous membrane of the canal becomes inflamed due to the penetration of sexually transmitted infections, and a disease such as endocervicitis occurs. It can occur under the influence of fungi, viruses or bacterial microorganisms.
- Polyps. These formations are benign, but are often the cause of female infertility. Expectant mothers are sometimes diagnosed with a false decidual polyp. Its appearance is the result of a hormonal deviation from the norm. When the balance of hormones is normalized, such a polyp goes away on its own.
- Cervical tumor formations: fibromyoma, hemangioma, myoma, fibroma. These benign tumors are treated surgically.
What to do if violations are detected?
If irregularities in the shape or size of the cervical canal are detected, the gynecologist, after examination, should refer the patient for additional examinations. A woman must undergo tests for sexually transmitted infections, diseases of the urinary system, and a smear to determine malignant neoplasms in the early stages of their development. In addition, colposcopy and biopsy are performed.
If during the examination the doctor discovers any formations in the cervical cavity, he will scrape the mucous layer of the cervical canal in the area where the tumor is detected. Next, the obtained cells from the cervix will undergo a thorough histological examination, which will allow us to draw a conclusion about the nature of the formation and its danger to the patient’s health.
Preventive measures
When preparing to conceive a child, you should undergo a comprehensive examination to identify existing disorders and take measures to eliminate them. This will make it possible to avoid complications during pregnancy and bear a healthy baby.
The expectant mother should constantly monitor the hygiene of the intimate area, not neglect washing and change her underwear in a timely manner. Doctors advise pregnant women to avoid douching for therapeutic or prophylactic purposes, because... this method has a negative effect on the cervical canal, increasing the risk of injury and infection.
Source: //www.OldLekar.ru/beremennost/jenskoe-zdorove/cervikalnyj-kanal.html