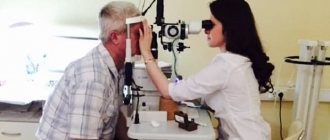
Deterioration of vision, eye diseases of various types - an ophthalmologist is involved in the diagnosis and elimination of all these problems; a doctor’s office can be found in any district or city hospital. To accurately establish the diagnosis and select adequate conservative therapy or surgical intervention, the specialist prescribes a comprehensive examination.
Diseases related to the eyes are treated by an ophthalmologist, popularly called an ophthalmologist.
What does an ophthalmologist treat?
The responsibilities of an ophthalmologist are diagnosis, therapy, monitoring the effectiveness of treatment and prevention of eye diseases. An ophthalmologist-surgeon identifies diseases that require surgical intervention, eliminates injuries to the visual organs and their consequences, prescribes examinations and prepares the patient for surgery, and gives recommendations for speedy rehabilitation.
To become an ophthalmologist, a person must graduate from a higher medical school, then study for 2 years in residency.
What diseases does an eye doctor treat:
- glaucoma is a disease in which intraocular pressure increases;
- cataract – clouding of the lens, more common in older people and diabetics;
- strabismus – incorrect position of the visual axis, a person cannot focus his gaze on an object, the disease occurs in one or both eyes at the same time;
- myopia – with myopia, the image is fixed in front of the retina, all objects in the distance look blurry;
- farsightedness - with hypermetropia, objects close up look blurry, a person cannot read without glasses, but sees well into the distance;
- spasm of accommodation - the ciliary muscle is constantly in a contracted form, the lens is fixed in a convex state, it is difficult for a person to examine objects, the pathology most often develops against the background of severe eye fatigue;
- astigmatism – curvature, deformation of the surface of the cornea, lens, rays are refracted incorrectly, an object at any distance has unclear contours;
- angiopathy - damage to the ocular vessels, due to which the nerve cells of the eyes suffer from oxygen deficiency, photosensitivity worsens, the disease develops against the background of diabetes, hypotension, hypertension, after injuries;
- stye is a bacterial infection that affects the eyelash follicle or nearby tissues, characterized by swelling, redness, and pain in the area of the affected eyelid;
- chalazion is a chronic inflammation of the sebaceous glands of the eyes, it looks like a small round lump, the skin around it turns red, and it hurts when pressed;
- demodicosis is a parasitic pathology, acne mites live and reproduce in eyelash follicles and sebaceous glands;
- conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes of the organs of vision of viral, bacterial, allergic origin, characterized by redness, lacrimation, burning, and pus accumulating in the corners of the eyes.
The task of a pediatric ophthalmologist is to establish the causes of eye problems and understand whether they are chronic
A pediatric ophthalmologist deals with the treatment and diagnosis of congenital and acquired ophthalmological pathologies in children.
An ophthalmologist is no different from an ophthalmologist - these are different names for the same specialist.
What diseases does an ophthalmologist treat?
The competence of an ophthalmologist has a fairly broad profile. An ophthalmologist deals with the correction of visual impairments manifested in the form of farsightedness, myopia, strabismus, and amblyopia.
An ophthalmologist also specializes in diagnosing and treating the following diseases of the visual system:
- conjunctivitis - inflammatory processes affecting the mucous membranes of the eyes;
- barley;
- chalazion - inflammatory lesion of the upper edge of the eyelids;
- clouding of the eye lens - cataract;
- trachoma - inflammation of the conjunctiva, occurring in a chronic form;
- blepharitis - pathologies of the eyelid margins;
- astigmatism - disruption of the shape of the eye cornea, deformation of the lens;
- retinal detachment;
- night blindness;
- ptosis - drooping eyelids;
- lacrimation;
- glaucoma - increased intraocular pressure with concomitant damage to the optic nerve;
- thorn;
- vitreous opacification;
- allergic diseases of the visual apparatus;
- keratitis - infectious lesion of the cornea;
- iridocyclitis - inflammatory disease of the iris;
- traumatic damage to the visual organs.
The task of the ophthalmologist also includes identifying other pathologies with accompanying pathological changes in the area of the eyeball. These include diabetes mellitus, nephropathy, traumatic lesions of the head and neck, hypertension, and genetic predisposition.
When to contact an ophthalmologist?
The eyes experience heavy stress every day, suffer from the negative impact of external factors, poor-quality cosmetics, which negatively affects the condition of the visual organs, therefore, in order to timely detect pathologies, it is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist at least once a year.
For what symptoms should you visit an ophthalmologist:
- deterioration in the acuity of central or peripheral vision - objects near or far look blurry;
- double vision, flashing flashes, flies, multi-colored spots;
- the eyes get tired quickly, dryness, burning, and a feeling of sand occur;
- excessive lacrimation and photophobia;
- redness of the proteins, mucous membranes of the organs of vision;
- cataract.
If you have double vision, be sure to visit an ophthalmologist - this is one of the symptoms of serious illnesses
You should immediately consult a doctor after an injury or if a foreign body gets into the eye.
When is a doctor needed: a pediatric ophthalmologist?
The difference between an adult and a pediatric ophthalmologist is great; a pediatrician specializes in the organ of a growing body. Monitoring the development of children's eyes is an important task, because by noticing deviations at an early stage, you can save the child from problems in adulthood.
Children in the first year of life need to visit an ophthalmologist every 3 months. After a year, it is recommended to visit a doctor at least once every 6 months, but this is only if no pathologies were found.
If an older child complains of a burning sensation in the eyes, constantly rubs them until they become red, and squints when looking into the distance, then he urgently needs a pediatric ophthalmologist to rule out serious diseases or diagnose them on time. If your baby’s eyes are constantly watering and you can see pus in the corners, you should not self-medicate, as such symptoms may indicate the presence of a serious illness, in which case a pediatrician is also needed.
The child’s vision must be treated with great attention, and if you have complaints, you should go to the doctor just in case to make sure everything is fine.
Where does he receive it?
There is a doctor’s office who treats eyes in district or city municipal medical institutions; appointments, consultations, some types of diagnostics in such clinics are free, you must first make an appointment at the reception desk.
You can undergo diagnostics and treatment for a fee in private clinics and centers, the cost of the examination depends on many factors, the average price of a consultation is 1.2–1.5 thousand rubles, therapy – from 5 thousand rubles. Reviews on the forums will help you avoid making a mistake in choosing a good specialist.
Specialization – ophthalmology
Ophthalmologist - who is this? A doctor who diagnoses, treats and corrects vision. This is a narrow direction in medicine, the main subject of study of which is the human eye. This specialist knows everything about how the eye works, how it functions and receives images of the surrounding world. In simpler terms, an ophthalmologist is an ophthalmologist (from the old name for the eye - eye) or, quite simply, an eye doctor, an ophthalmologist.
It is extremely difficult to underestimate the role of the eyes in life. It is through the visual channel that a person receives most of the information (about 70%). Thanks to vision, we can move freely, observe, read and write, drive a car and perform a wide variety of activities. And although our vision is imperfect compared to some other representatives of our planet, its importance is very great. Therefore, maintaining the health of our eyes is a significant task for everyone. And if any suspicions arise, an ophthalmologist can check your vision and identify problems in the early stages, when it is not too late to do something.
What does an ophthalmologist do during an appointment?
An appointment with a doctor for the eyes begins with an examination - the doctor assesses the condition of various structures and parts of the visual organs, listens to complaints, and makes a preliminary diagnosis.
Primary diagnostic methods:
- checking visual acuity using special tables to identify myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism;
- assessment of the refractive system of the eye;
- visual field examination;
- examination of the fundus using an ophthalmoscope – helps to identify glaucoma, angiopathy, retinal detachment;
- measurement of intraocular pressure using a special tonometer-weight - normally the readings should be in the range of 9–20 mm Hg. Art.;
- color perception test – carried out if color blindness is suspected;
- biomicroscopy of the eye - a narrow strip of light is directed into the eye to accurately assess the condition of the lens, cornea, and eyeball;
- identifying the degree of sensitivity of the cornea - a thin hair is carried through the organ.
One of the main diagnostic methods is the use of an ophthalmoscope to assess the condition of the eye.
Assessment of binocular vision using the Sokolov technique - the patient brings a sheet of paper rolled into a tube to one eye, both eyes should be open. The doctor puts his hand on the side of the tube and swings a sheet of paper with its edge. If there are no problems, then the effect of a hole in the palm occurs - it is as if the person sees the image not through a paper tube, but through a hole in the palm.
After completing the examination, the ophthalmologist can refer the patient for a consultation with an ophthalmologist-surgeon, endocrinologist, oncologist, ENT specialist, allergist, neurologist or cardiologist, since eye pathologies often occur against the background of other diseases. If visual acuity is impaired, the ophthalmologist selects lenses for correction; for people who have to work a lot at the computer, the doctor recommends special anti-glare glasses.
Important! In order to correctly diagnose some pathologies, the doctor puts special drops into the eyes that prevent pupillary constriction. For several days after such a procedure, a person sees practically nothing up close and his eyes water.
Why are preventive examinations by an ophthalmologist necessary?
Even if you feel absolutely healthy, it is still advisable to undergo an annual examination by an ophthalmologist. It will once again confirm the normal functioning of the visual system or identify eye pathologies at an early stage, which is important for effective treatment.
Both children and adults should undergo preventive examinations by an ophthalmologist. In a young child, the visual system is still developing, and if the disorder is identified at an early stage, there is a high probability of restoring normal vision functions. The capabilities of modern ophthalmology make it possible to effectively treat childhood strabismus, binocular vision disorders, myopia and other pathologies. They can be identified during preventive examinations.
For adult patients, prevention of eye diseases is also important. With age, certain changes occur in the eyes, which can lead to a decrease in visual acuity, the development of macular degeneration, and pathological changes in the lens and retina. Monitoring by an ophthalmologist will help to detect in time and, with the help of well-chosen therapy, slow down the pathological processes that lead to age-related vision loss.
Prevention of eye diseases during pregnancy is of particular importance. The period of bearing a child changes a woman’s hormonal levels, increases stress on the eyes, and can lead to a decrease in visual acuity and exacerbation of chronic diseases. An ophthalmologist for pregnant women is one of the most important specialists, because together with the gynecologist, he decides whether a woman can give birth on her own or whether a cesarean section will be required. With some eye pathologies, retinal detachment may occur during childbirth, so in some cases natural childbirth is contraindicated.
When should you contact an ophthalmologist during pregnancy? Typically, routine preventive examinations are provided every trimester. However, if the doctor detects a risk of retinal detachment, progressive myopia, or other pathologies that may threaten a woman's vision, he may schedule more frequent visits for the pregnant patient.
What diagnostic methods does it use?
Laboratory tests and complex types of diagnostics are rarely used in ophthalmology; usually the doctor has enough data obtained during examination and standard examination to make a diagnosis.
To determine eye pathologies, a routine examination by a doctor is often sufficient.
The doctor prescribes a general and biochemical blood test, microscopic and microbiological examination before surgical interventions.
Additional diagnostics
To conduct additional diagnostics aimed at identifying diseases that provoke vision problems, the patient may be prescribed the following procedures:
- immunogram;
- laboratory tests of urine and blood;
- laboratory analysis to identify certain infectious pathogens;
- taking bacteriological cultures from the eyes;
- blood tests for hormones and sugar levels;
- demodex scraper.
Based on the results obtained, the ophthalmologist makes a diagnosis for the patient and prescribes appropriate treatment. If it is necessary to correct visual function, suitable glasses or contact lenses are selected.
For diseases of an inflammatory infectious nature, a course of antibiotic therapy, eye drops, systemic medications, and rinses are prescribed. In some particularly severe clinical cases, for example, with cataracts, glaucoma, strabismus and other pathologies, it may be necessary to perform surgical intervention.
Ophthalmologists emphasize that regular preventive examinations and contacting a specialist when the first warning signs appear significantly increases the chances of early diagnosis, successful treatment and restoration of visual function.
What is the difference between an ophthalmologist and an ophthalmologist?
Many people know that an ophthalmologist is a doctor who treats various diseases of the visual organs. But medical and preventive examinations are often performed by an ophthalmologist. The question arises: an ophthalmologist and an ophthalmologist - are there differences in competence between these doctors?
If we summarize the differences between doctors of these specializations, then medicine will claim that an ophthalmologist and an ophthalmologist are identical concepts. Both terms are synonymous with each other, and in translation from Greek, both ophthalmologist and ophthalmologist mean the concept of “eye”.
To completely dispel doubts about the competence of these doctors, you can refer to the medical documentation. 30 years ago, the staffing schedule of medical institutions included a specialty with the name - ophthalmologist. But in 1981, the position of a doctor who deals with various problems of visual function was abolished, and the specialty of ophthalmologist appeared in the official medical records, which replaced the specialty of an ophthalmologist.
Elderly patients, out of habit, call an “eye doctor” an ophthalmologist, but modern youth prefers to call such a doctor an ophthalmologist.