Staphylococcal infection
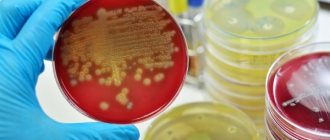
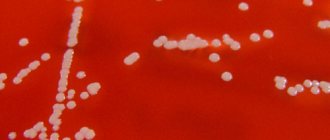
Staphylococcus is a microorganism belonging to the group of gram-positive bacteria. In a microscopic specimen it looks like regular balls, grouped into one pile, or stretched out in the form of a chain.
Bacteria are not equipped with a capsule or flagella; the structure of the cell wall contains peptidoglycan and teichoic acid.
The staphylococcal family includes 27 representatives, 14 of which “parasitize” the mucous membranes and skin of humans.
Three representatives of a large bacterial group pose a threat to the life and health of citizens of all age categories:
- golden;
- epidermal;
- saprophytic.
The pathogens are opportunistic in nature, as they are present in small quantities on the surface, inside the body and in the surrounding air.
Staphylococcal infection takes a leading position in the development of food poisoning and purulent-septic pathologies.
The detection of bacteria in the mouth leads to the development of purulent sore throat. When it enters the bloodstream, bacteremia develops.
The infection is dangerous due to an increased risk of death.
In fact, staphylococcus is the basis of the purulent process.
Types of staphylococcus dangerous for pregnant women
Pregnant women should be extremely careful about staphylococcus and the infection it causes.
Microbes are opportunistic, which determines their presence in the body without a pathological process.
If unfavorable conditions develop for the host organism, staphylococcus becomes active, begins an active mitotic process, and the pregnant woman’s body attacks its own flora.
- Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus) poses a particular danger during pregnancy. This is one of the types of bacteria that is the most dangerous not only for pregnant women, but also for newborn children. During the gestational period, the microbe can be localized anywhere in the mother’s body: this includes the genitourinary system, the gastrointestinal tract and even the circulatory system. Purulent processes caused by the microbe provoke a deterioration in the condition of the pregnant woman and can cause spontaneous miscarriage. It is important that the entry of staphylococcus into the blood provokes the development of sepsis.
- Epidermal or cutaneous staphylococcus does not cause harm to the pregnant patient. To a greater extent, it settles in the epidermis, causing acne. However, in the presence of open wounds, it can cause long-term non-healing wound processes.
- The saprophytic type of microbe differs from previous representatives in that it absorbs dead cells of the body, however, if it enters an organism weakened by pregnancy, it can cause urogenital inflammatory processes.
Detection of staphylococcus during gestation is not uncommon.
The risk of fetal infection remains even with a slight increase in the number of bacteria.
How can you become infected with staphylococcus during pregnancy
? Since the microbe is present in the human body in a “sleepy” state, there are factors that influence its activation during the gestational period:
- weakened immunity;
- chronic diseases;
- depression and stress during pregnancy;
- taking immunosuppressants and other drugs in excessive dosages.
Routes of transmission and causes of pathology:
- airborne, for example, when a carrier coughs or sneezes - a sick person;
- food - entry through food where the microbe was localized (butter cream, cakes, stale protein products);
- household - through non-sterile medical instruments, the hands of medical staff and during manipulations associated with the introduction of instruments into the mucous layers;
- fecal-oral – the microbe enters the female body if hygiene rules are not followed.
Penetration of a microbe does not appear immediately. Quite often, the clinical picture of the pathology develops after several hours or even days.
A pregnant woman can become infected with the infection when visiting public catering places, at a doctor’s appointment, or from a work colleague who has had symptoms of a respiratory virus for a long time.
Risk group for the development of a pathological process, where the main pathogen is staphylococcus:
- patients with diseases of the endocrine system, in particular diabetes mellitus;
- women receiving antibiotics for a long time;
- infected with the immunodeficiency virus.
In all cases, a persistent decrease in immunity develops. A weakened body is not able to resist the infectious process.
How to recognize the disease?
As it has already turned out, Staphylococcus aureus in pregnant women is a rather serious disease. The sooner it is detected and the sooner measures are taken to eliminate it from the body, the more chances a woman has to save her health and her baby. It can be recognized by several characteristic features:
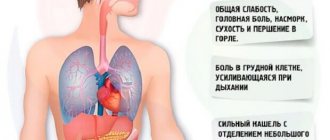
- Changes in the appearance of the skin: the appearance of acne, eczema, redness, dermatitis and other lesions.
- A prolonged runny nose is a characteristic symptom of the formation of staphylococcus in the nose of a pregnant woman.
- Severe pain in the throat and difficulty swallowing. In the early stages of bacterial growth, only mild discomfort is felt: dryness and itching.
- Long-term lack of appetite.
- Severe discomfort when urinating. The appearance of sharp pain in the lower abdomen and back is a characteristic symptom of the formation of staphylococcus; this bacterium can be found in the urine of pregnant women.
A woman planning to become a mother should listen to her body. You should inform your gynecologist about the appearance of new suspicious symptoms.
Diagnosis of staphylococcus in a pregnant woman
According to statistics, in patients with staphylococcal infection, in 70% of cases, children were infected in utero and were born with a developing process.
In 20%, primary symptoms appeared after 48 hours from birth.
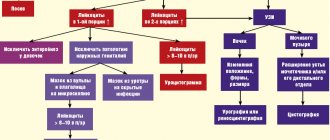
Diagnosis of pathology is carried out only by laboratory methods:
- venous blood examination to study general indicators;
- collection of vaginal secretions discharged during a gynecological examination;
- examination of gynecological smear for flora;
- collection of material from the nasal cavity and larynx;
- urine test for sterility;
- sowing biological material on nutrient media to grow a pathogenic culture.
An infection can be suspected if local signs are present, such as: chronic vulvovaginitis, conjunctivitis, sore throat, non-healing wounds and scratches.
The symptoms of the disease depend on the location of the bacterium.
Diagnostic measures
To differentiate staphylococcal infection from other bacterial and viral diseases, the following must be done:
- collection of mucous discharge from the throat and nose;
- smear from the cervical canal and vagina;
- bacteriological culture of urine.
The study of the obtained material in laboratory conditions is carried out in a short time, and with high accuracy of the result.
Sinus and throat swab
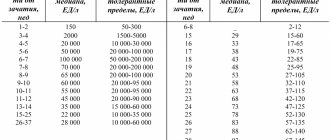
The analysis is taken after removing mucus from the nasal passages and treating them with an alcohol solution. When counting bacteria, the content of opportunistic microbes in the nasopharynx should not exceed 103 - 104 CFU/ml. Otherwise, the test is positive and the woman needs special treatment.
How dangerous is staphylococcus for mother and child?
Microbial infection has a detrimental effect on both the mother’s body and the fragile body of the unborn child.
Consequences for the mother:
- purulent-septic local lesions;
- inflammation of the upper and lower tracts of the respiratory system;
- infectious endocarditis;
- inflammation of ENT organs.
Possible development of peritonitis, which can cause sepsis or septic shock. - a condition in which microorganisms enter the blood and “poison” it with producing poisons.
Septic shock is fatal.
Consequences for the baby
During intrauterine development, bacteria can enter the baby’s body through the bloodstream and cause various infectious processes:
- congenital eye damage, up to complete loss of vision;
- pneumonia;
- violation of the structure of the hearing organs;
- dysbacteriosis;
- dermatitis;
- infection of the umbilical wound;
- enterocolitis.
During the rehabilitation period, the baby has an increased risk of blood poisoning, depending on the type of obstetric care and the period at which the child was born. The possibility of nosocomial infection cannot be ruled out.
To prevent this phenomenon, pediatric intensive care and physiology departments undergo frequent monitoring to detect the microbe. Swabs are taken from the hands of employees, instruments and room air.
When is a throat swab for staphylococcus prescribed?
A throat swab is prescribed to diagnose a bacterial infection.
During pregnancy, any woman seen by a gynecologist undergoes a whole range of diagnostic procedures. Testing for staphylococcal infections and other unfavorable microorganisms is also available.
As a rule, they are planned, but under special circumstances (for example, a high susceptibility to staphylococcal infection during an epidemic), additional examinations may be carried out.
Determining a staphylococcal infection in the body of an expectant mother is a complex event. In a typical case, the presence of this microflora is checked in:
- urine
- genital smear
- throat swab
Since today’s article will mainly focus on “throat” staphylococcus, we will pay more attention to the examination of a throat smear than to other diagnostic methods.
First of all, it should be noted that a throat smear is performed no more than 2 times in pregnant women as a routine examination. If no danger regarding staphylococcal infection is observed, diagnostics of this kind are not repeated, giving preference only to checking the genitourinary system for risks of infection.
In situations where staphylococcus is found in the throat of a pregnant woman, monitoring its condition for the entire period of pregnancy is mandatory.
Often, specialists monitoring pregnant women at risk of developing staphylococcal infections prescribe monthly testing for bacteria in the throat. In other cases, the need for such a diagnosis is quite naturally eliminated, of course, if the corresponding pathological condition with suspicion of staphylococcus is also absent.
The diagnostic procedure and its possible results
A few days before taking a smear, you need to stop using medications.
The procedure for performing a throat smear aimed at identifying staphylococcus in pregnant women is completely identical to the procedure that is carried out for ordinary people who are not pregnant. This type of diagnosis does not have any significant specificity.
To properly prepare for a smear, a woman being examined needs only:
- 2-3 days before the examination, stop using throat sprays, mouth rinses, nasal ointments and similar antimicrobial products
- 2-3 hours before taking a smear, do not drink, eat, brush your teeth or in any other way change the state of the throat microflora
The procedure itself is carried out as follows:
- A pregnant woman sits on a medical chair and throws her head back.
- The diagnostician, using previously prepared and completely sterile equipment, takes a smear.
- After this, the stick with which the biomaterial was collected from the throat is placed in a special container and sent to the laboratory for research.
Based on the results of manipulations carried out by laboratory technicians, the final results of the examination are formed. Often, the diagnostic sheet for a throat smear contains the following information:
- confirmation of the presence or absence of staphylococcus, as well as other dangerous or potentially dangerous microorganisms
- general state of local immunity
- if there is an infection, its severity
Naturally, a pregnant woman should not draw any independent conclusions based on the results of a throat smear. Do not forget that monitoring a woman’s condition is the task of the doctor observing her, so the first thing you should do after receiving the test results is to visit him.
A professional doctor who has all the necessary information about the pregnant woman will certainly be able to determine the degree of normality of the results obtained and the need to take any measures.
Treatment of staphylococcus during pregnancy
Due to increased resistance to external provoking factors, it is extremely difficult to cure a bacterial infection caused by staphylococcus.
Treatment is aimed at reducing the activity of the microbe and stimulating the immune system. Antibiotic therapy is carried out after establishing the resistance of the strain to the type of active drug.
It is not safe to treat with antibiotics during pregnancy and there is a possible risk of side effects. Once bacteria enter the bloodstream, there is no other way for a complete cure.
The development of staphylococcal infection can be stopped with the correct selection of immunomodulators and vitamins.
Therapeutic measures can be local in nature: if there is pathology in the mouth - irrigation or inhalation, genitals and urinary system - douching.
Treatment methods
When deciding whether to prescribe treatment for a pregnant woman, the doctor follows the rule under which such treatment is justified. In this case, drugs with the least side effects are selected, which include bacteriophage.
To treat nasopharyngeal infections, a solution of Chlorophyllipt, Furacilin, alcohol and oil treatment is used.
If a woman is infected with the golden type of bacillus, then complex treatment is prescribed. It consists of local treatment and taking medications that increase the mother’s immunity without affecting the fetus - Activin, Timalin, vitamins.
If there is a threat of infection spreading, antimicrobial therapy is carried out, taking into account all possible consequences for the baby. Recently, these are expensive drugs to which these microbes are not yet resistant.
Treatment is best done at home, since hospital strains of staphylococcus are the most toxic.
Most often, various antibiotics are used for treatment, unless the disease is caused by microbial toxins, as happens with food poisoning. In addition, to select medications, a test is carried out to determine the sensitivity of microbes found in a woman to a particular drug. It makes no sense to treat staphylococcus with an antibiotic to which it has developed resistance.
Prevention of staphylococcus during pregnancy
Compliance with preventive measures during the gestational period helps reduce the risk of infection with staphylococcus or another type of similar microorganism.
To do this you should:
- Do not neglect personal hygiene measures. Use a personal towel and liquid soap.
- Wash fruits, vegetables and hands thoroughly before eating, as well as after visiting the toilet (especially public).
- Ventilate the room, take the necessary vitamins and be in the fresh air.
- In case of epidemic season, use personal protective equipment - a mask.
- Gargle with saline solution or Furacilin.