Blood pressure is an individual physiological indicator that determines the force of blood compression on the walls of blood vessels.
In many ways, blood pressure depends on how a person’s heart works and how many beats per minute it can make.
A person’s normal blood pressure is an indicator that can vary depending on the physical load on the body.
Thus, during active training or strong emotional experiences, a person’s normal blood pressure can increase and go beyond the norm.
For this reason, it is recommended to measure blood pressure in the morning, when the person is not worried or physically overexerted.
The ideal blood pressure reading at rest is 110/70. Low blood pressure starts at 100/60. Increased (hypertension) - from 140\90.
The critical (maximum) indicator is 200/100 or more.
A person's normal blood pressure can also change after physical activity. If the heart copes with its functions, then the change in blood pressure is not a deviation. Thus, after sports activities, a person’s blood pressure may increase to 130/85.
There are factors that have a significant impact on the normal pressure (including intraocular, intra-abdominal, etc.) of a person:
- The person's age and general health. It is important to know that existing diseases (especially chronic pathologies of the kidneys, heart, sexually transmitted or viral diseases) can significantly increase blood pressure.
- The presence of diseases that can thicken the blood (diabetes mellitus).
- The presence of progressive abnormalities in pressure (hypertension, hypotension).
- The condition of the heart and the presence of diseases in it.
- Atmosphere pressure.
- Thyroid hormone levels and menopause in women.
- Hormonal disruptions in the body that narrow arteries and blood vessels.
- General elasticity of vascular walls. In older people, blood vessels wear out and become brittle.
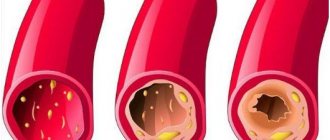
- Presence of atherosclerosis.
- Bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
- The emotional state of a person (frequent stress and experiences negatively affect a person’s normal blood pressure).
Normal blood pressure varies somewhat among women, adult men, and children.
If a person experiences disruptions in this indicator and problems with blood pressure surges, he requires urgent medical attention and medical treatment.
In addition, the pulse rate also plays a significant role, since the blood pulse is inextricably linked with venous pressure.
What is blood pressure?
Blood pressure is the level of pressure of blood on the walls of the body's arteries. This is an individual indicator; its changes may be influenced by:
- person's age;
- stressful situations;
- the presence of chronic pathologies;
- Times of Day;
- exercise stress.
There is an average blood pressure of 120/80 mm Hg. Art., which doctors rely on in the process of diagnosing a patient. Pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury and shows two numbers - upper and lower pressure.
Blood pressure is one of the most important indicators of human health
- Upper (systolic) is the pressure exerted by the blood at the moment of maximum contraction of the heart.
- Lower (diastolic) – blood pressure at the moment of maximum relaxation of the heart muscle.
Deviations of 20-30 mm Hg. Art. above or below the average 120/80 mmHg. Art. in an adult indicates possible diseases. Timely treatment will protect against the disease becoming chronic and from severe complications.
Every person should know about blood pressure and what it is to prevent possible diseases.
What the hell is this in medicine?
Blood pressure - what is it? This is the effect of blood on the walls of blood vessels. In other words, an increase in fluid pressure in the circulatory system compared to atmospheric indicators.
It is believed that systolic is cardiac pressure, and diastolic is vascular pressure. Systolic blood pressure - what is it? It is produced by contraction of the heart muscle. The aorta, which acts as a buffer, is partially involved in its formation. Therefore, to say that this is heart pressure is not entirely correct.
Diastolic blood pressure is lower, what does this mean? After the heart contracts, the aortic valve closes and blood does not flow into the heart. At this point, it is enriched with oxygen before subsequent contraction. At this stage, blood moves through the vessels passively. This is an indicator of diastolic pressure.
Increased systolic pressure poses a danger to life and the condition of internal organs, since the diastolic pressure is significantly lower even during a hypertensive crisis. The only thing that increased diastolic pressure indicates is that the person has persistent hypertension. It should be noted that pulse pressure is also released. Blood pressure readings should have a difference in mmHg.
A higher or lower indicator is undesirable, however, it is not decisive in the diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
As a rule, men are more susceptible to the disease. How does blood pressure manifest itself in this case? This is a disease characterized by a slight increase in systolic reading up to mmHg. Blood pressure readings are unstable. After rest, they may return to normal, but this does not mean that the disease has passed. At this stage, there is no hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart, the ECG is within normal limits. The structure of the fundus does not undergo any changes, the functionality of the kidneys is not impaired.
In this case, blood pressure becomes higher. High blood pressure in adults is accompanied by migraines and ischemic heart pain. At this stage, hypertensive crises are observed. The moderate degree differs from the mild degree by the presence of target organ damage, hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart, a decrease in the level of blood circulation in the kidneys and changes in the structure of blood vessels. From the nervous system, vegetative-vascular dystonia is manifested; transient ischemic attacks and strokes are also possible.
Exudates and hemorrhages are observed in the fundus. What does severe blood pressure mean? With this form, serious vascular damage often occurs, which is caused by a persistent increase in blood pressure. The functioning of the heart, kidneys, and brain is disrupted. However, many patients do not develop severe changes in the structure of blood vessels for many years. The reasons for increased blood pressure lie in nervous overload and constant worry.
Hypertension can also develop in a person with a genetic predisposition to the disease. The environment also plays an important role. The more stress a person endures, the higher the likelihood of developing an illness. With timely treatment of hypertension, complications can be avoided. But, as a rule, people do not notice its signs and do not carry out treatment at the initial stage. Even a healthy person may experience increased blood pressure.
But they do not reach a critical level and do not pose a health threat. An increase in levels can be caused by a high level of saturated acids in food. They are found in palm and coconut oils, and are also present in animal fat.
For example, in products such as sour cream, butter, cheese, sausage, various snacks, chocolate, and sweets. All of these foods contain a lot of calories, although at first glance they seem low-fat. Another risk factor is considered to be high salt content in food. Many foods contain hidden salt. From a preventive point of view, you should eat only fresh foods and not overuse processed foods.
Avoiding foods containing salt would bring undeniable benefits to human health. Its increased consumption contributes to the thinning of blood vessels and their fragility. Blood pressure can also increase from excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages. In moderate doses, alcohol has no effect on the condition of the heart, but in increased quantities it contributes to the development of tachycardia.
Blood pressure directly depends on heart rate. If it is possible to establish the exact cause of the increase in pressure, then doctors deal with secondary symptomatic arterial hypertension, which can occur under the following conditions: In addition, the cause of the disease may be the use of certain medications. For example, such as corticosteroids, tricyclic antidepressants, bronchodilators, anabolic steroids, lithium preparations, etc.
After a careful interview and history, the doctor may recommend the following examinations: How is high blood pressure treated? You should take medications only as prescribed by your doctor. The specialist will be able to assess all risk factors, select the necessary medications and medical measures. Invaluable health benefits will come from reducing salt intake, quitting tobacco products and drinking alcohol. Increasing physical activity and relaxation are also recommended.
Usually, drugs are prescribed that help reduce blood viscosity, normalize cholesterol, glucose and water-electrolyte balance. High blood pressure is a condition that can be treated with surgery. These are relatively new therapies. They have a fairly high level of effectiveness in treating vasoconstriction of the kidneys.
The procedure is carried out during angiographic examination. For this purpose, catheters are inserted through small punctures into the arteries in the kidneys. There is a small balloon at the end of the catheter. When it swells, the atherosclerotic plaque is crushed and pressed against the artery wall. So the narrowed area undergoes expansion. This procedure is called balloon angioplasty. Often, to ensure long-lasting effect and keep the lumen enlarged, angioplasty is supplemented with stenting.
The method involves installing a special metal device, a stent, into a narrowed artery. The effect of blood pressure if it increases is negative. Doctors indicate that people affected by hypertension are at risk of developing atherosclerosis. Therefore, such patients often have a heart attack or stroke.
Hypertension can also cause lameness because the normal flow of blood to the legs is disrupted. What does high blood pressure affect? The blood vessels and heart are affected first. The heart works in an increased mode, which causes a change in blood circulation in the small and large circles. This causes shortness of breath, coughing up blood, and swelling. Such manifestations can cause death.
Very dangerous complications are changes in the brain. If high blood pressure torments a person for a long time, then tiny hemorrhages and cholesterol deposits appear in the retinal vessels.
This leads to poor circulation, which causes retinopathy. With this disease, vision is obscured. In some cases, a person may lose the ability to see altogether.
To establish accurate indicators, a blood pressure tonometer is used. It can be of mechanical and automatic configuration.
The disadvantage of the first model is that there is a human factor when working with it. It is difficult for people with hearing loss and the elderly to operate such a device. An automatic tonometer is more accurate, but on the recommendation of specialists, when using the device you should strictly adhere to all the rules set out in the passport.
The method helps to identify a hidden threat. During the procedure, the patient wears a special device on his body for two days, which records pressure readings in natural conditions. Daily blood pressure gives the doctor a clear picture of a person’s condition and helps to identify whether the patient has hypertension or hypertension caused by diseases of the internal organs. For the purpose of prevention, it is recommended to normalize the work and rest schedule.
Mechanism of arterial regulation
In the human body, all processes are interconnected. The mechanism of arterial regulation is very complex, it is influenced by such things as the central and autonomic nervous system, and the human endocrine system.
Blood pressure fluctuates within its normal range due to the following factors:
- Movement of blood through vessels (hemodynamics). Responsible for blood pressure levels.
- Neurohumoral regulation. Nervous and humoral regulation constitute a common system that has a regulatory effect on blood pressure levels.
Blood pressure (BP) is the force of blood pressure on the walls of the arteries.
The nervous system reacts with lightning speed to changes in the body. During physical activity, under mental stress and stress, the sympathetic nervous system activates the stimulation of cardiac activity and affects the speed of the heartbeat, which causes a change in pressure.
How to treat blood pressure
Knowing the principle of the development of such cardiac pathology, it is important to correctly and timely select intensive therapy, which can be carried out at home. Taking medications depends on the level of blood pressure, chronic diseases of the body, and the age of the patient. Regulation of blood in the vessels is achieved through medication, but the patient will additionally have to reconsider their usual lifestyle and give up bad habits forever. The list of effective medications is detailed below.
Increased
A systematically elevated blood pressure level means that the patient is a chronic hypertensive patient and is under systematic monitoring by a cardiologist. In such a clinical picture, a course of treatment with representatives of the following pharmacological groups is necessary to prolong the period of remission of the underlying disease, reduce blood pressure and get rid of unpleasant symptoms:
- ACE inhibitors that dilate vascular walls: Fosinopril, Captopril, Ramipril, Enalapril, Lisinopril, Perindopril;
- beta blockers that reduce the minute volume of systemic blood flow: Bisoprolol, Atenolol, Nebivolol, Metoprolol;
- diuretics to reduce portions of fluid in the systemic circulation: Furosemide, Chlorthalidone, Torasemide, Indapamide;
- sartans, also known as angiotensin receptor blockers: Losartan, Valsartan, Losartan, Valsartan, Telmisartan;
- calcium channel blockers that expand the lumen in peripheral vessels: Amlodipine, Verapamil, Nifedipine, Diltiazem.
Decreased
If there are obvious signs of hypotension, it is recommended to consume caffeine and vitamin C, while completely eliminating bad habits, leading an active lifestyle, and eating more sweets. Among medications, the medical drug Etimizol is particularly effective. However, doctors also prescribe biological phytostimulants, represented by infusion of Chinese lemongrass or aralia, extracts of eleutherococcus, ginseng, echinacea, and radiola. If arterial pressure has pathologically decreased, the natural drug Pantocrine is recommended to reduce the risk of collapse.
Methods and rules for measuring indicators
Pressure can be measured by direct and indirect methods. The direct (invasive) method of measuring pressure is used during inpatient treatment of a patient, when constant monitoring of the indicator is needed. It is performed using a catheter, the needle of which is inserted into the patient’s lumen of the radial artery. The catheter itself is connected to a pressure gauge to obtain pressure readings.
To measure blood pressure, classic tonometers with a phonendoscope are used
The indirect (non-invasive) method of measuring pressure does not require direct contact with the bloodstream:
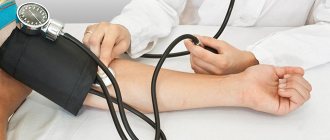
- Auscultatory or auditory method. It is performed using a mechanical tonometer with a phonendoscope. The cuff compresses the artery with the help of inflated air and the readings are heard in the form of noise, which is emitted as blood passes inside the artery.
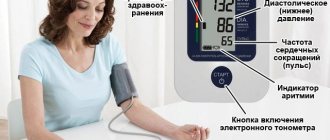
- Oscillometric method. Does not require noise listening and the readings are displayed on the digital tonometer display. The most common measurement method, which requires minimal effort and is convenient for daily use at home in the form of an electronic tonometer.
To get the correct tonometer readings when measuring pressure, you must follow these rules:
- Blood pressure is measured while sitting or lying down.
- The patient should be in a relaxed state and not talk.
- One hour before the measurement, you need to avoid food intake, two hours - alcohol and cigarettes.
- The cuff placed on the arm is secured at the level of the heart.
- If the tonometer is semi-automatic, air injection is carried out smoothly and without sudden movements.
- The rolled up sleeve of clothing should not squeeze your hand during the measurement process.
The normal blood pressure of a person directly depends on his age and lifestyle
It is better to take the first home pressure measurements on both hands. The hand on which the indicators are higher is used for constant measurements. It is believed that the pressure in right-handed people will be higher on the left hand, and in left-handed people - on the right hand.
How to measure blood flow strength
Measuring it with a tonometer helps to visually understand what blood pressure is. A manual tonometer is considered the most accurate. It consists of a cuff for inflating air, a bulb that works like a pump, and a device with a scale of digital pressure values. All these elements communicate with each other through tubes. A phonendoscope for listening to tones is included separately.
Step-by-step guide to measuring blood pressure:
- Release excess air from the cuff by pressing on it with your hands.
- Place the cuff on your arm just above the elbow joint.
- Place the phonendoscope on the area of the brachial artery in the bend of the elbow.
- Inflate the cuff with air.
- Begin to release the air smoothly, listening to the sounds that appear and marking the corresponding values on the scale.
- The first knock will indicate upper pressure, and the last knock will indicate lower pressure.
Some features of the procedure:
- Measure your blood pressure at the same time, preferably in the morning and at night.
- To accurately determine the indicators, you need to measure your blood pressure for several days in a row.
- Indicators are measured in different body positions and on different arms in order to have a complete picture of the patient’s condition.
- The bladder must be emptied before the procedure.
- Manipulations with the tonometer are carried out no earlier than 30 minutes after eating or smoking a cigarette.
- First, a person must come to a calm state.
- Do not subject the body to physical stress before measuring blood pressure.
- When measuring, it is necessary to make allowances for general well-being, the presence of diseases, pain syndrome, and the use of medications.
Arterial hypotension: symptoms and treatment
Systematic pressure below 100/60 mmHg. Art. called arterial hypotension.
Teenagers and young girls are most prone to it. The main symptoms of hypotension include:
- dizziness;
- fatigue;
- lethargy;
- nausea;
- insomnia;
- cardiopalmus.
During the treatment process, the specialist must establish the root cause affecting the decrease in blood pressure.
Although low blood pressure is not fraught with such dangerous complications as high blood pressure, it is uncomfortable for a person to live with it
Along with the treatment of the underlying disease, drug treatment is prescribed:
- Psychomotor stimulants. Such medications activate the nervous system, they stimulate performance and relieve lethargy, increase heart rate and increase blood pressure (Sindocarb, Mesocarb).
- Analeptic drugs. They increase blood circulation in the process of excitation of the vasomotor center of the posterior part of the brain. These drugs increase a person’s performance and mood (“Cordiamin”).
- Alpha adrenergic agonists. They increase vascular tone and cause constriction of arterioles (Gutron, Midodrin).
Each of the medications described has its own number of side effects, and therefore should be prescribed under strict medical supervision. Hypotonic patients should devote time to physical activity and long sleep, and a contrast shower is also recommended.
Products that increase blood pressure and improve the condition of the hypotensive body:
- coffee;
- strong tea;
- nuts;
- cheeses.
A cup of coffee helps, but you should remember that the drink is addictive
Inhibition is in medicine
Today, the population of our country is increasingly susceptible to hypertension. This occurs due to the influence of many factors, such as stress, heredity, sedentary lifestyle and more. The disease causes lethargy, drowsiness, and a dull headache in a person, which significantly reduces performance. Many hypertensive patients have purchased a tonometer in their first aid kits, which allows them to measure blood pressure if necessary and take the right medicine. However, you should not self-medicate, as it can lead to complications, and the disease will only progress. Our readers successfully use ReCardio to treat hypertension.
Hypertension: manifestations and principles of treatment
Increased constant blood pressure 139/89 mm Hg. Art. is one of the most common diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Older people with heart and vascular diseases are most prone to hypertension. But it is possible that high blood pressure may occur in people over 30 years of age.
Risk factors for developing arterial hypertension include:
- systematic stress;
- excess weight;
- heredity;
- age over 55 years;
- diabetes;
- elevated cholesterol levels;
- renal failure;
- constant smoking and drinking alcohol.
Normal by age
In adulthood, indicators differ not only by year, but also by the gender of the patient. Each person simply must know what acceptable blood pressure levels exist in their case, so that after measuring with the device, they can reduce the likelihood of recurrence of dangerous pathologies more often in the cardiac system. Below is a table that shows what ideally blood pressure should be in adult women and men, according to age category.
| Patient age | Women | Men |
| Up to 20 years | 110 – 120/70 – 75 | 120 – 125/70 – 80 |
| Up to 30 years old | 115 – 120/70 – 80 | 120 – 127/75 – 80 |
| Up to 40 years old | 120 – 130/80 – 85 | 125 – 130/80 – 85 |
| Up to 50 years | 135 – 140/80 – 85 | 130 – 135/80 – 85 |
| Up to 60 years old | 140 – 145/85 – 90 | 135 – 145/85 – 90 |
| From 60 years old | 145 – 155/85 – 90 | 135 – 145/80 – 85 |
During pregnancy, there is a high probability of mild hypertension, which is an acceptable normal limit. This deviation is explained by a doubling of systemic blood flow due to the presence of new life in the womb. Getting rid of such a disorder is a matter of time, so there is no need to take medications with synthetic active ingredients in vain - they will not help the pregnant woman, and they may harm the child.
Causes and risk factors for high blood pressure
Based on its origin, hypertension is divided into two different types:
- Primary hypertension, if no other pathology can be found that leads to increased blood pressure.
- Secondary hypertension, when the increase in blood pressure is caused by another disease.
In the case of primary hypertension, the exact causes of the disease are not determined, but it seems that it may be associated with an inherited genetic abnormality of arterial vasoconstriction.
Also considered risk factors are:
- Alcoholism.
- Poor nutrition.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Obesity. Obesity plays a very significant role. Obese people are three times more likely to develop hypertension than thin people. On the other hand, not all obese people suffer from arterial hypertension.
- Stress.
Secondary hypertension can be determined by the following factors:
- Kidney disease, including renal artery stenosis (narrowing of the artery that supplies blood to the kidneys), glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the glomeruli of the kidneys), trauma, tumors, which may affect the ability to eliminate excess sodium and water, thereby increasing blood volume and pressure.
- Hormonal disorders such as hyperthyroidism (hyperfunction of the thyroid gland), Cushing's syndrome (characterized by high levels of cortisol), hyperaldosteronism (hypersecretion of the hormone aldosterone).
- Atherosclerosis, which stiffens the arteries, preventing them from expanding.
- Some substances such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, contraceptives, cortisone.
What to do if you are diagnosed with hypertension
Before going on clinical trials, you should make sure that hypertension was not caused by another pathology.
In cases of moderate hypertension, before resorting to any kind of medication, you should simply change your lifestyle, then the pressure parameters, as a rule, return to normal:
- To exclude alcohol, you can only drink half a glass of wine with meals, preferably red.
- Stop smoking.
- Eat a low-fat, low-sodium diet (halve your salt intake). Typically a person consumes about 5-6 grams of sodium per day: this should be reduced to 2 (including preservatives and glutamates).
- In case of obesity, return to normal weight parameters as quickly as possible (a weight loss of 10 kg is equivalent to a decrease in blood pressure of 15 mmHg).
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Practice moderate aerobic activity: one and a half hours every day is recommended (a simple walk, no stopping, no running).
- Consume plenty of fruits and vegetables that are high in potassium, which is a sodium antagonist.
- Eliminate stress.
- Measure your blood pressure regularly and record the results.
Drug therapy for hypertension
If previous measures have not brought results, then, on the recommendation of a doctor, they resort to antihypertensive drugs.
There are several mechanisms and therefore different active ingredients that help lower blood pressure.
Here are some of them:
- Diuretics: Help eliminate excess sodium and water, reduce blood volume and also cause dilation of blood vessels. Often, diuretics, however, also increase potassium loss. Diuretics are especially useful in older adults, obese individuals, and those with heart failure or chronic renal failure.
- Adrenolytics, which include alpha blockers and beta blockers: these block the effects of the sympathetic system. They act on the production of adrenaline and on the contraction of smooth muscles, which determines the increase in pressure.
- Antiserotonergic agents: Reduce the production of serotonin, which increases blood pressure.
- Short-acting or long-acting calcium antagonists: cause dilation of the arteries.
Often, many medications combine several active ingredients to make life easier for the patient.
If it is necessary to quickly reduce blood pressure, an adrenergic blocker - Clonidine - administered orally is used.
Natural remedies to normalize blood pressure
Many plants contain active components that help lower blood pressure, but they should be chosen not only based on personal preferences, but, above all, in consultation with a doctor.
Among them we list:
- Garlic: Due to its thiocyanine derivatives and catecholamine inhibition, garlic has diuretic and hypotensive effects. Its extract can, in fact, be used as a medicine against high blood pressure.
Decoction: crush 4 cloves of garlic, boil in a glass of milk, let cool and strain. Drink 2 glasses of decoction per day between meals.
- Hawthorn: Due to its tannins and essential oils, it is recommended for lowering blood pressure in the form of a decoction or water infusion taken three times a day.
- Mistletoe: Rich in choline and vitamin J, it is a vasodilator and is used as an infusion for hypertension and atherosclerosis.
Consequences of hypertension
If left untreated, high blood pressure increases your risk of developing:
- heart diseases such as heart failure, angina and heart attack, because it causes thickening of the walls of the heart muscle;
- vascular diseases such as thrombosis, aneurysm, stroke, because high pressure puts pressure on the walls of blood vessels and can lead to injury, loss of elasticity, fragility and the formation of cracks;
- renal failure due to accumulation or excessive excretion of substances in the urine;
- brain disorders such as memory loss, dementia due to decreased oxygen supply;
- eye diseases such as hypertensive retinopathy, which is associated with narrowing of the retinal blood vessels, which may also include bleeding and swelling.