No heartbeat at 8 weeks
The cardiovascular system and organs develop functionally in infants. Between 5 and 6 weeks of pregnancy, the baby's heart begins to function and beats at a speed of 80 to 85 BPM (beats per minute). From this point on, the fetal heart rate increases by 3 RPB every day that1st month. But in some cases, there is no pulse to be detected at 8 weeks or later, which often makes parents more worried.
No heartbeat at 8 weeks, why?
Around 6 weeks of pregnancy, the fetal heartbeat can be detected through ultrasound, which, however, can vary greatly in real situations. Doctors usually do not recommend an ultrasound at 6 weeks because it can usually show nothing or very little image of the fetus, even in a completely normal pregnancy. But you may have much clearer findings on the ultrasound if you wait another week or more than 10 days. In most cases, a fetal heartbeat can be heard at 8 weeks, but there are many factors:
Questions Device Test
With different types of ultrasound, results may vary. Common handheld fetal devices that are used during prenatal visits sometimes cannot detect a heartbeat until 12 weeks. But a transvaginal ultrasound can find the baby's heartbeat quite early at 6 to 7 weeks. An abdominal ultrasound takes more than one week (7-8 weeks) to find a heartbeat.
Gestational Age Must Be Accurate
The gestational age is usually counted from the last day of the period. Some women report that poor gestational age makes them worry about having no heartbeat at 8 weeks. Perhaps you remember the wrong date of your last period, which is important for gestational age, or your doctor gives the wrong gestational age. A properly performed transvaginal ultrasound will never miss the fetal heartbeat. The scan also provides reliable and accurate results only if the rhythm is present. Just wait and see for further exams and confirmation.
Miscarriage Possible
If a transvaginal ultrasound shows no heartbeat at 8 weeks, pregnancy loss is possible. But this only means a transvaginal ultrasound, which can detect even the slightest heartbeat. If a heartbeat is noticed immediately and later the ultrasound does not find confirmation, then a miscarriage can be suspected. Also, if there has been enough time for pregnancy, but the ultrasound does not show any heartbeat, then the possibility of miscarriage should be considered.
Normal Fetal Heartbeat
By knowing the possible reasons why your baby may not be able to hear your heartbeat at 8 weeks, a normal heartbeat can help you better monitor your entire pregnancy. The normal fetal heart rate varies with the weeks of pregnancy and increases over time. Here we have listed the numbers you can find, heartbeat by week.
- Beginning of the 5th week: The normal fetal heart rate is between 80 and 85 beats per minute.
- Later Jan 5 weeks: The normal fetal heart rate starts at 103 and ends at 126 BPM.
- At 6 weeks: ranging from 103 to 126 BPM from start to finish.
- At 7 weeks: Range from 126 to 149 beats per minute from start to finish.
- At 8 weeks: Ranges from 149 to 172BPM from start to finish.
- At 9 weeks: ranging from 155 to 195 BPM from start to finish. Average heart rate can be 175BPM. At week 9, the fetal heart rate will accelerate to a normal fetal BPM of 120-180 beats per minute.
- At 12 weeks: Range from 120 to 180 beats per minute from start to finish. The average heart rate can reach 150 beats per minute.
No heartbeat at 8 weeks, could it be a miscarriage?
Some statistics have shown that out of 7 pregnancies, miscarriages occur in at least one. The cause of miscarriage varies, but most are due to genetic problems. This may be a sign of miscarriage, and other signs include severe bleeding, clotting, and cramping. Normal pregnancy symptoms also disappear with miscarriage. Threatened miscarriage is a condition in which cramps and bleeding stop, but the pregnancy continues.
If you are pregnant and your vagina is bleeding, contact your gynecologist right away. Heavy bleeding and severe cramping require a medical visit, and too much bleeding and pain may be due to a tubal pregnancy. However, if you have a history of miscarriage, you don’t have to go straight to another one, and you can simply carry the child in the future.
Contraction frequency by week is normal
Using modern sensitive equipment, the first beats can be heard already in the second month of pregnancy. There are certain norms for fetal heart rate:
- at week 5, the heart of the unborn child contracts at a frequency of 80–103 beats per minute;
- at 6 - the heart already beats 103-126 times within one minute;
- at 7 weeks of pregnancy, the contraction frequency ranges from 126–149 beats per minute;
- in 8 - heart rate reaches 149–172 times per minute;
- in 9 - the heart contracts approximately 155–195 times per minute;
- by 10 - the SS frequency reaches 161–179 times.
Then the number of beats over 1 minute gradually decreases and by the end of the 14th week it is already 146–168 beats.
The baby's heartbeat can be heard for the first time at approximately 6 weeks. At this time, the length of the fetus reaches about 6 mm. At this stage it has already been formed, but it is not yet fully developed.
At this stage, it is still impossible to see the baby’s heart on an ultrasound examination, since it is still too small. But you can listen to how it knocks for the first time.
Despite this, it is already directly involved in pumping blood and oxygen throughout the small body, ensuring its normal development and functioning.
Only at 8 weeks the baby’s heart is already fully formed. Throughout the rest of the woman's pregnancy, it will grow and increase in size.
Formation time
As a rule, fetal heartbeat appears within 30 days after successful implantation. The fact is that of all organs, the heart is one of the first to form. Its formation occurs already from 21 days after conception. At 3-4 weeks, the heart muscle is a small hollow tube, which, however, is already capable of contraction. It becomes a full-fledged four-chamber organ at the 8th week of pregnancy.
To hear the heartbeat, a woman needs to visit an ultrasound specialist.
Starting from the third month of pregnancy, examinations can already be performed abdominally.
The number of contractions during normal childbearing should be at least 80-100
and no more than 200 in one minute.
The time when the fetal heart begins to beat is usually the same for all women.
However, if at the first ultrasound it was not possible to hear it, but the fertilized egg in the uterus is visualized, you should not get upset prematurely.
The fact is that the period of conception may be set incorrectly and the heart muscle has not yet had time to fully form
.
The doctor will definitely prescribe a repeat test in 7-14 days. When the fetal heartbeat is heard on an ultrasound, we can confidently say that the pregnancy is not frozen.
It is worth noting that during the first ultrasound examination, the doctor may not hear what kind of heartbeat the embryo has if the study is performed on an old device. Therefore, it is best for a woman to go to a good clinic with high-quality medical equipment and experienced specialists.
At what hCG level can you hear a heartbeat? As a rule, in the middle of the second month after implantation, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin reaches 7200 IU/l. With this indicator, you can already see the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity, and distinguish the beating of the heart muscle that is not yet fully formed. Knowing at what hCG the heartbeat is heard, you can choose the right day to visit a doctor who, using modern equipment, will confirm pregnancy.
It is important to measure heart rate during the first trimester
. The fact is that it is in the first three months that congenital defects can occur in the embryo. As a rule, pathology appears due to the bad habits of the expectant mother, taking antibiotics, hereditary predisposition, severe stress and infectious diseases.
To try to prevent abnormal heart development in a child, it is recommended to plan conception
in advance. A few months before pregnancy, you should completely get rid of bad habits, stop taking medications that can be toxic to the baby, eliminate coffee and tea from your diet, and try not to be nervous or worry about anything.
There is no fetal heartbeat at 6 weeks of pregnancy
The fact that the heart is the most important organ of the human body is no secret to anyone.
The health of the unborn baby depends on how correctly its formation and development occurs throughout the entire period of a woman’s pregnancy.
Some parents have many questions when the fetal heartbeat cannot be heard in the early stages of its development.
Using modern sensitive equipment, the first beats can be heard already in the second month of pregnancy. There are certain norms for fetal heart rate:
- at week 5, the heart of the unborn child contracts at a frequency of 80–103 beats per minute;
- at 6 - the heart already beats 103-126 times within one minute;
- at 7 weeks of pregnancy, the contraction frequency ranges from 126–149 beats per minute;
- in 8 - heart rate reaches 149–172 times per minute;
- in 9 - the heart contracts approximately 155–195 times per minute;
- by 10 - the SS frequency reaches 161–179 times.
Then the number of beats over 1 minute gradually decreases and by the end of the 14th week it is already 146–168 beats.
The baby's heartbeat can be heard for the first time at approximately 6 weeks. At this time, the length of the fetus reaches about 6 mm. At this stage it has already been formed, but it is not yet fully developed.
At this stage, it is still impossible to see the baby’s heart on an ultrasound examination, since it is still too small. But you can listen to how it knocks for the first time.
Despite this, it is already directly involved in pumping blood and oxygen throughout the small body, ensuring its normal development and functioning.
Only at 8 weeks the baby’s heart is already fully formed. Throughout the rest of the woman's pregnancy, it will grow and increase in size.
In modern medicine, there are several methods that allow you to listen to the baby’s heartbeat. Each of them gives positive results at different periods of pregnancy:
- Auscultation. In this case, the gynecologist uses a special gynecological stethoscope, which is applied to the woman's abdomen. This method can be used at approximately 27–28 weeks of pregnancy.
- Ultrasonography. This technique allows you not only to hear how the child’s heart beats, but also to record these sounds. Its peculiarity is that ultrasound is performed only three times (10–12, 21–23, 31–32 weeks). It is possible to perform ultrasound more times, but only if the need arises.
- Cardiotocography. This is one of the types of ultrasound, which makes it possible not only to listen to the heartbeat, but also to record its graphic image.
Each of the above methods has its own positive and negative aspects, but at the same time, without their use it is impossible to determine the presence of pathologies in the development of the fetal cardiovascular system or even hear the heartbeat.
There are often cases when a baby’s heart beats faster or slower than the generally accepted norm. There may be several reasons for this. For example, if at a period of 6–8 embryonic weeks the heart rate is 200, this may indicate the development of hypoxia in the child - oxygen starvation.
In this case, various pathologies of the development of the cardiovascular system or physiological disorders may occur.
In the same case, when the beat is heard less frequently than the established norm (80 times per minute), this may signal the development of bradycardia in the fetus.
The reasons for the absence of a heartbeat may include factors such as the mother’s smoking or drinking alcoholic beverages, her development of anemia, severe toxicosis, etc.
There are often cases when in the initial stages of pregnancy the heartbeat is not heard at all or is heard very faintly. There are several main reasons:
- old equipment - in this case, the woman can be advised to go to another clinic, where the equipment is more sensitive, which will allow the fetal heartbeat to be heard;
- too much or insufficient amount of amniotic fluid - this situation simply does not make it possible to hear the baby’s heart beat. In this case, it is recommended to wait a while and repeat the examination;
- multiple births - during an ultrasound examination, the specialist cannot listen to the mixed sound of beating several hearts;
- the woman’s pregnancy period is incorrectly determined - since heartbeats can be heard for the first time only after six weeks, if the period is incorrectly determined (too short), this is simply impossible to do;
- fetal position - if the baby lies pressed against the opposite abdominal wall, during an ultrasound examination the contractions of his heart are simply not audible.
These indicators cannot be considered borderline. In each individual case there may be slight deviations from the above standards. But this is not a reason to panic.
The doctor may also recommend that the woman take another hCG test.
At different stages of pregnancy, the amount of this hormone changes.
Repeating the test will help confirm once again that the woman is indeed pregnant.
The woman must also independently take certain measures that will contribute to the normal development and functioning of the child’s heart, as well as the baby’s health.
Dear future mothers! I want to write my story for everyone who in Russia, at the 6th, 7th or 8th week of pregnancy, is already advised to go for a cleanse, because... The ultrasound does not show the embryo or its heartbeat. I finally saw my little baby yesterday for the first time during my eighth obstetric week. He is already more than 1 cm and his heart is beating fast! How happy I was! Having learned about the positive test, I went for an ultrasound to rule out an ectopic one. My fertilized egg was half a cm, which fully corresponded to 5+0 obstetric weeks (3 weeks from conception), of course, I didn’t think about any embryo or heartbeat at that time. After 5 days, my stomach hurt very much at night, I got scared and we went to the hospital, where the doctor gave me an ultrasound and said that the fertilized egg was 0.4-0.5 cm, again there was no embryo. I began to get very worried, because it turned out that it had not grown at all in almost a week. And then I started reading horror stories from the Internet about the fact that by the 6th week there should definitely be a heartbeat and about how in Russia almost from the fifth obstetric week you are sent for cleaning. I was shocked. I live in Germany and German sources do not have such strictness in terms. In general, after sitting on pins and needles for another week, I went back to the hospital for an ultrasound, there was not much hope that everything was fine. There the doctor said that the fertilized egg was completely empty (the period was already 6 + 4 obstetric weeks), but did not raise any panic, saying that everything was ok. But I had no time for peace anymore. How can this be, I thought, because other mothers already have everything in the fifth and sixth weeks, but in my seventh week it’s empty. In general, I had already lost all hope, relying on information from the Internet))) And yesterday, after waiting another five days, I went for an ultrasound again, and lo and behold! Here he is my baby in full glory and his tiny heart! Yesterday I was 7 weeks and 2 days. The doctor asked who told you such nonsense that it is not normal if the heart is not heard before the eighth obstetric week? German doctors apparently trust nature more. By the way, I didn’t do hCG. In general, girls, don’t you dare go under the knife early! wait until at least the 9th week for your miracle to appear on the screen with a small pulsating heart! Everything will be fine!
Oh, this Internet! What does he not bring into our heads? My internet friend diagnosed herself with uterine prolapse! I was 100% sure, I even remembered the reason for the loss (in the summer I carried heavy bags of apples at the dacha). She walked to G as if she were on a scaffold and she herself voiced this diagnosis and reason to him. The doctor rolled his eyes out in surprise, looked into her, took a smear and diagnosed it as some kind of thrush (without discharge). She walked, thinking that they were going to cut her, and then they gave her a pack of suppositories and the “loss” fell into place.
Agree. The Internet is a terrible thing! If you read it, you won’t want to live! I used to read and believe everything. Now I understand that this is stupid! You can find a lot of fictitious diseases. although there are none))
I did an ultrasound at 6 weeks from the moment of conception, they said that there was no heartbeat, that the baby froze, there was an area of detachment on the back wall of 20*5.5mm, hCG was growing, I took it again, the Doctor said to do an ultrasound on Monday, if a heartbeat does not appear, then interrupt the medication. There is no pain, no bleeding, just nausea. I only take folic and L-thyroxine. Please write, is it too early to terminate the pregnancy, maybe the heartbeat will appear later, has anyone encountered this?
Only group members can comment.
Hello! My hCG decreased, and the ultrasound confirmed that my pregnancy was not developing at 6 weeks. , no heartbeat, placental abruption 60%, the doctor said that the fetus was floating, I understood that it was floating in the blood, that is why it did not develop. Please write, who knows that first there is placental abruption and its fading or fetal fading, and then placental abruption? The doctor said that I should have taken duphaston to avoid detachment as soon as I found out about pregnancy. But my progesterone was -77 nmol/l in the first weeks of pregnancy, and after studying everything about duphaston here, I found that this was a good number and didn’t drink it, so I decided to try what it would be like without it.
3 years ago I had a spontaneous miscarriage at 12 weeks, I took Kagocel against the background of an acute respiratory infection, without knowing about the pregnancy, and then I took Duphaston for tone, but it didn’t help, apparently Kagocel led to incorrect implantation. and have a miscarriage. I was examined for everything after. Now they had a medical abortion, a control ultrasound will be on Monday, but it seems that I have not seen the release of the fertilized egg yet, it is bleeding, but moderately for the 3rd day. Please write who experienced this medical abortion, otherwise I’m scared, I’ll have to go to a vacuum, if that happens.
Measurement methods
Fetal heart rate is measured using modern hardware methods
, which include
- Ultrasound is one of the most common ways to determine the duration of pregnancy, the size of the baby, examine the heart muscle and listen to its tones. You can listen to the frequency of contractions on an ultrasound examination as early as 5-7 obstetric weeks
. When the fetal heartbeat is heard on an ultrasound for the first time, the woman feels true happiness, since she is now sure that the baby is developing normally. - A stethoscope is a medical device that can be used not only by specialists, but also by people without medical education. A stereoscope can be used closer to the third trimester.
- Cardiography to determine whether the heart muscle is working properly. With high accuracy, this method can detect oxygen starvation, thanks to which the doctor has the opportunity to take the necessary measures in a timely manner. The first time CTG is performed in the middle of the third trimester .
Cardiography may be prescribed earlier.
This is done if other hardware examination methods have given questionable results. - Echocardiography is one of the highly informative methods of ultrasound examination. Echocardiography is prescribed at 18-28 weeks
if the doctor suspects that the embryo has developed a heart muscle defect.
Each of the above methods is informative and highly accurate. Hardware research methods not only make it possible to calculate the fetal heartbeat by week, but also to promptly identify abnormalities in the development of the embryo.
Methods for listening to the fetal heartbeat
Many people are interested in what week the fetal heartbeat appears. There are many ways to hear the heartbeat.
- Ultrasound. Experts advise every pregnant woman to undergo an ultrasound examination both during registration and for further monitoring of fetal development. Nowadays, with the help of ultrasound, you can not only examine in detail the development of the baby in the womb, but also hear the work of the heart. This method helps to study the condition of the placenta and the fetus as a whole, and with its help you can see all deviations (if any) and begin to eliminate them in a timely manner. When does fetal heartbeat appear on ultrasound? It can be heard from the sixth week.
- Auscultation. The examination is carried out by a specialist with a special medical device - a stethoscope; this method is used only after the 18th week of pregnancy at each examination by a gynecologist.
- Cardiotocography. This technique is very effective, it allows you to study the baby’s heartbeat in detail, as well as identify deviations even in the early stages of pregnancy. This method is mainly used after 32 weeks or before childbirth.
- Echocardiography. This method is used when there is a suspicion of a heart defect in the fetus. It is used at 18-28 weeks of pregnancy.
- for overweight pregnant women
- when the placenta is located on the anterior wall of the uterus (then vascular noise interferes with auscultation)
- with too little or too much amniotic fluid
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytaboutru
Timely research helps to avoid abnormal development, as well as identify all heart rate deviations and immediately begin their treatment.
This is the very first method used during pregnancy. When conducting a study, along with determining the heart rate, the doctor evaluates the size of the fetus, the condition of the placenta and gives a comprehensive conclusion. Listen especially carefully to heart sounds and study the structure of the heart in case of developmental defects in a pregnant woman and the birth of children with defects of the cardiovascular system in the past. It is very important to identify abnormalities in the structure and functioning of the heart in cases of infections suffered by the mother during pregnancy.
Auscultation
This is listening to heart sounds using a special obstetric stethoscope. You can determine your heartbeat in this way starting from 18-20 weeks of pregnancy. An experienced doctor can use a tube to determine the approximate heart rate, clarity of tones, and the best place to hear them. But even a person without medical education is able to detect heart sounds and count their number per minute using a stopwatch.
In some cases, auscultation with a stethoscope is difficult or impossible:
A very informative method that allows you to assess the baby’s heartbeat. Using this procedure, it is possible to identify oxygen starvation of the fetus in the early stages and take appropriate measures (see interpretation of fetal CTG during pregnancy).
The CTG machine is an ultrasound sensor that sends and receives reflected signals from the fetal heart. All changes in heart rate are recorded on film. Together with the main sensor, a uterine contraction sensor is also installed. It shows the activity of the uterus, which is especially important during childbirth.
In recent years, devices have special sensors for fetal movements; sometimes, using a separate button, a pregnant woman can record them independently. All information coming from the sensors is displayed on the tape. The duration of the CTG procedure is 50-60 minutes. This time is usually enough to catch the baby’s moments of activity and sleep. In special cases, sensors are attached to the pregnant woman’s belly and left for a day.
For fetal heartbeat analysis, gestational age plays a very important role. The first CTG study is carried out after 32 weeks, since before this period the data will be uninformative. It is after 31-32 weeks that the connection between motor activity and cardiac activity of the fetus is formed. Typically, a woman undergoes CTG twice during pregnancy (at 32 weeks and immediately before birth). According to indications, CTG can be performed an unlimited number of times, since the procedure is harmless.
The CTG tape is deciphered by a doctor who compares the results of this study with the data of ultrasound and tests. Cardiotocography itself is not a source of definitive diagnosis.
- The normal fetal heart rate is on average 120 to 160 beats per minute.
- in response to movements, the heart rate increases
- There are no decreases in heart rate or they are present in minimal quantities
The device independently analyzes all these parameters and produces the result in the form of a special bandwidth index. Normally it does not exceed one. But the functioning of the baby’s heart is influenced by many other factors, which only a doctor can evaluate.
- Hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the fetus is the most common cause of changes on CTG.
If the baby experiences a lack of air, then his heart begins to work harder and the frequency of contractions increases. In response to a contraction or his own movement, the baby may react by slowing down the heartbeat, which is also not the norm.
- Pressing the umbilical cord against the fetal head or bones causes short-term changes in the band. They look the same as during oxygen starvation, but the child feels good and does not lack oxygen.
- Incorrectly attached sensors
If, when listening to the fetal heartbeat, hypoxia is detected, confirmed by other methods, then the doctor prescribes treatment or performs an emergency delivery (depending on the period and condition of the fetus).
Echocardiography
Echocardiography is used at 18-28 weeks of pregnancy only if the development of heart defects in the child is suspected. This is an ultrasound method that studies the characteristics of blood flow and the structure of the heart. It is indicated if:
- the woman already has children with heart defects
- the mother herself has congenital heart defects
- past infectious diseases during this pregnancy, especially in the 1st trimester
- woman over 38 years old
- pregnant woman has diabetes mellitus
- intrauterine growth restriction
- detected malformations in the fetus in other organs and there is a suspicion of congenital heart defects
The echocardiography method is also used as two-dimensional ultrasound, and other modes of the ultrasound scanner are used: one-dimensional ultrasound and Doppler mode. This combination of techniques helps to thoroughly study both the structure of the heart and the nature of blood flow in large vessels.
Can you feel the beat through your stomach?
Regardless of the stage of pregnancy, a woman cannot feel
the heartbeat of the unborn baby.
What she mistakes for heartbeats is only the pulsation of her own aorta, which occurs as a result of increased pressure in this vessel.
A surge in blood pressure occurs due to serious hormonal changes occurring in the female body.
If a woman feels through her stomach
something similar to a heartbeat, it is imperative to contact a gynecologist, who, after a thorough examination, can refer her for a consultation with an experienced cardiologist.
Is it possible to hear the fetal heartbeat yourself at home? It is quite difficult to do this without the help of specialized medical equipment. Fortunately, today you can purchase devices that will allow you to hear the heartbeat of your long-awaited and already beloved baby already in the third trimester.
How can you listen to the beat yourself?
If you are interested in how to listen to the fetal heartbeat at home, you should know that in the early stages it is impossible to do this on your own.
In the first and second trimesters, this can only be done by a specialist using special equipment.
Popular methods for listening to the fetal heartbeat at home:
- Fetal Doppler, which can be used from the second trimester. This ultrasonic detector provides fairly accurate results. However, the cost of such a device is high.
- Starting from the third trimester, the expectant mother can independently listen to the baby’s heartbeat using a stethoscope.
However, in some cases this cannot be done. For example, hearing the beat frequency may be difficult due to the mother's thick abdominal fat or large volume of amniotic fluid.
All of the above devices are absolutely harmless to the embryo. However, the baby often feels the radiation emanating from the device and always tries to move away from its rays. If a woman feels the baby is restless, it is best to postpone the measurement until the baby calms down. The measurement time should not exceed 10 minutes.
Longer use of the device causes stress in the child.
The frequency of the rhythms directly depends on the period of gestation of the child. Modern doctors have established the normal heart rate
fetus by week, which allows you to control the development of the embryo.
The fetal heart rate by week is presented in the following table.
Is it possible to hear the fetal heartbeat on your own?
If the expectant mother has a desire to listen to the heart of her baby, then it is not necessary to make an extraordinary visit to the antenatal clinic. There are several ways to listen to the sound of life developing.
Stethoscope
Auscultation with an obstetric stethoscope is accessible to absolutely everyone. This requires an obstetric tube (which costs very little) and an attentive and patient assistant. If he is not a doctor, then it is unlikely that he will be able to hear the heart before the 25th week of pregnancy.
The main thing is daily training. Then one fine day a husband, mother or other owner of a stethoscope will be able to hear the long-awaited sounds of a heartbeat. It is important to learn to distinguish them from the sounds of fetal movement, pulse or peristalsis of the mother.
If you don’t have time to train in auscultation, you can purchase a portable ultrasound detector - a fetal doppler. This device works on the principle of a conventional CTG machine, but does not write a graphic image on film. Often, headphones are included with the device for comfortable listening.
| Pros of a portable doppler: | Disadvantages of a portable doppler: | |
|
Despite the safety of Doppler, you need to observe moderation in everything and not use the device often and for a long time |
When can you hear the fetal heartbeat in your ear? In late pregnancy (after 30 weeks), you can make sure that the fetal heartbeat is normal by simply placing your ear to the pregnant woman’s stomach, but it depends on the woman’s fat layer. You need to listen to the baby's heart in a certain place in the abdomen, depending on the location of the fetus in the uterus.
Cases of serious pathologies causing heartbeat disturbances are quite rare. Nature has decreed that the vast majority of pregnancies end in the birth of an absolutely healthy and full-fledged child. Therefore, in parallel with observation by a doctor, you need to listen to the life emerging inside and rejoice in future motherhood.
Fetal heartbeat during pregnancy
There is nothing more touching, gentler and more important than the beating of a little heart in the womb of a future mother. This is the main signal of human life within us. It is by the heartbeat that you can determine what state the baby is in: whether he is healthy, nervous, worried or happy. That is why during pregnancy both doctors and mothers pay such close attention to this.
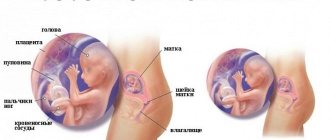
The frequency and nature of the unborn baby’s heartbeats are actually a mirror of his condition. The heart develops more complexly and longer than other human organs. Its embryo is formed in the fourth week of pregnancy and looks like a hollow tube. Somewhere in the 5th week, the first contractions appear, and by 8-9 weeks the heart of a little person in the womb becomes the same in structure as that of an adult: four-chambered, consisting of two atria and two ventricles. However, the fetal heart in the mother’s womb is still different: it has an oval window (an opening between the right and left atria) and
the ductus arteriosus (the vessel that connects the aorta and the pulmonary artery), since the baby is not yet breathing on its own, and this structure of the heart allows the mother’s oxygen to access all its organs. The oval window closes and the ductus arteriosus collapses immediately after the baby is born.
The baby's heartbeat is the main indicator of his vitality. If it is less than 85-100 beats per minute or more than 200 beats, this is a serious reason to worry. If the baby, when it has reached its embryonic length of up to 8 mm, does not hear a heartbeat at all, then the pregnancy is most likely frozen.
Cardiac contractions may be rare due to fetoplacental insufficiency and intrauterine fetal hypoxia. This can also happen with a breech presentation of the fetus. It’s bad if the baby has no more than 70 beats per minute for no more than a minute.
The longer the pregnancy, the better the heart can be heard. The doctor must, at every examination, listen to these tappings. The doctor listens to him
by auscultation. By the way, this is the easiest way. The doctor listens to the baby with an obstetric stethoscope. This is a small tube with a wide funnel.
Can't see heartbeat at 7 weeks
I’ve been very nervous since Thursday: I had an ultrasound at the end of the 7th week (I don’t know why, but they did it) and didn’t see a heartbeat. They put it in frozen. I read that symptoms may not appear (this is my case, nothing has changed).
In general, I just can’t believe it. I decided to wait a week until the full 8 weeks.
HCG was normal. It’s confusing that the size of the embryo is smaller than the ultrasound term + I have late ovulation.
One G sent for surgery, the other G said we can wait. I was completely exhausted in ignorance.
No heartbeat.
Well, nothing, two weeks of bed rest at home + doctor’s appointments, and I’m now the mother of a strong 2.5 year old boy
Everything will be fine.
On the pages of the Mail.Ru Children project, comments that violate the legislation of the Russian Federation, as well as propaganda and anti-scientific statements, advertising, and insults to the authors of publications, other discussion participants and moderators are not allowed. All messages with hyperlinks are also deleted.
The accounts of users who systematically violate the rules will be blocked, and all messages left will be deleted.
You can contact the project editors using the feedback form.
Signs of an undeveloped pregnancy
The absence of a fetal heartbeat at 8 weeks is not the only sign of an undeveloped pregnancy. To diagnose it, it is important to have other signs, which include: lack of physical activity (this was discussed above); discrepancy between the coccygeal-parietal size and the size of the ovum with the expected gestational age; the presence of an empty fertilized egg, that is, there is no embryo (anembryony).
The fetal heartbeat, which is heard using an ultrasound examination at 8 weeks of pregnancy, does not mean that it can be heard by a woman or a doctor using a stethoscope.
Pregnant women mistakenly mistake the pulsation of the abdominal aorta for the fetal heartbeat, which coincides with the pulse detected on the radial artery. If at 8 weeks of pregnancy the fetal heartbeat is not recorded, then additional research methods are necessary to either confirm or refute the diagnosis of a frozen pregnancy.
If the heartbeat of the embryo is not heard, then the following examinations are prescribed: determination of the level of human chorionic gonadotropin over time; ultrasound examination in dynamics, etc.
If all of the above studies confirm the diagnosis of a non-developing pregnancy, then instrumental evacuation of the uterine cavity is performed.
If at 8 weeks of pregnancy the fetal heartbeat is normally recorded and its indicators correspond to the norm, then we can say that at this stage everything is normal with the pregnancy.
Such a pregnancy only needs to be monitored; it does not require any treatment. Therefore, it is clear that the fetal heartbeat at 8 weeks is an important prognostic sign. Ultrasound opens up new possibilities for diagnosing the state of pregnancy, since previously, with the help of a stethoscope, the heartbeat became audible only after 20-22 weeks.
Thus, the fetal heartbeat, which is determined at 8 weeks of pregnancy, is an important indicator by which one can judge how the pregnancy is progressing. Identification of certain deviations is an indication for carrying out certain diagnostic procedures with the development of a further plan for managing this pregnancy.
Is there a possibility of error?
Despite the many advantages of this method of monitoring the baby’s heartbeat, there is a certain likelihood of errors during ultrasound due to imperfect equipment. Thus, an outdated sensor can distort heart sounds and make them dull. In extreme cases, faulty equipment can lead to the most terrible diagnosis - lack of heartbeat in the fetus.
The patient can always undergo such an examination in another clinic to ensure the reliability of the results obtained, or monitor the heart rhythm using other methods and diagnostic tools, if time permits.
Determining the heartbeat using ultrasound is one of the most basic methods for recognizing the heart rhythm of an unborn child. This diagnostic has a wide list of undeniable advantages over other types of monitoring the state of the baby’s cardiovascular system: wide availability, convenience, low cost, high information content, objective accuracy, speed and simple procedure algorithm.
Ultrasound is the only diagnostic method that allows you to track the baby’s heartbeat at the earliest stage of pregnancy (4-6 weeks), which other methods cannot boast of. Ultrasound allows you to detect many pathologies, including because the heart is also visible on the screen during the examination. Every woman should note this method for herself as a priority for determining the heartbeat of her unborn baby.
Fetal heartbeat during pregnancy
There is nothing more touching, gentler and more important than the beating of a little heart in the womb of a future mother. This is the main signal of human life within us. It is by the heartbeat that you can determine what state the baby is in: whether he is healthy, nervous, worried or happy. That is why during pregnancy both doctors and mothers pay such close attention to this.
The frequency and nature of the unborn baby’s heartbeats are actually a mirror of his condition. The heart develops more complexly and longer than other human organs. Its embryo is formed in the fourth week of pregnancy and looks like a hollow tube. Somewhere in the 5th week, the first contractions appear, and by 8-9 weeks the heart of a little person in the womb becomes the same in structure as that of an adult: four-chambered, consisting of two atria and two ventricles. However, the fetal heart in the mother’s womb is still different: it has an oval window (an opening between the right and left atria) and
the ductus arteriosus (the vessel that connects the aorta and the pulmonary artery), since the baby is not yet breathing on its own, and this structure of the heart allows the mother’s oxygen to access all its organs. The oval window closes and the ductus arteriosus collapses immediately after the baby is born.
The baby's heartbeat is the main indicator of his vitality. If it is less than 85-100 beats per minute or more than 200 beats, this is a serious reason to worry. If the baby, when it has reached its embryonic length of up to 8 mm, does not hear a heartbeat at all, then the pregnancy is most likely frozen.
Cardiac contractions may be rare due to fetoplacental insufficiency and intrauterine fetal hypoxia. This can also happen with a breech presentation of the fetus. It’s bad if the baby has no more than 70 beats per minute for no more than a minute.
The longer the pregnancy, the better the heart can be heard. The doctor must, at every examination, listen to these tappings. The doctor listens to him
by auscultation. By the way, this is the easiest way. The doctor listens to the baby with an obstetric stethoscope. This is a small tube with a wide funnel.
Poor fetal heartbeat
A muffled fetal heartbeat can occur as a result of prolonged hypoxia. It replaces tachycardia and is characterized by a reduction in the number of beats per minute. A slow heartbeat is considered if the beat rate is less than 120 beats; this deviation is also called bradycardia. The appearance of bragycordia during childbirth is the main reason for surgical intervention. The occurrence of a slow heartbeat in the fetus is the main reason for additional examinations and, if necessary, treatment.
At what stage does an ultrasound determine the baby’s heartbeat?
The fetal heartbeat is considered a significant indicator of the normal development of pregnancy. Its frequency, as well as its nature, can reflect the general condition of the fetus. This is why doctors need to periodically monitor the baby's heartbeat through ultrasound. Expectant mothers are also interested in the question: “When can you hear their baby’s heartbeat? How long does it take for the heart to start beating?
The most important indicator of the viability of the expected baby is its heartbeat. Thanks to it, specialists can determine the condition of the fetus and see any changes that occur in situations unfavorable for the child. For this reason, doctors monitor the functioning of the fetal heart throughout pregnancy using ultrasound and some other diagnostic methods. At the time of birth, control of the heartbeat is also necessary.
Fetal heart development
The expectant mother eagerly awaits her baby's heartbeat. She is waiting for an ultrasound and asks the specialist when her baby’s first heartbeat will be heard. At what stage of development can a child’s heartbeat be heard clearly?
The formation and development of a baby’s heart is a very complex process that takes place in the fetus’s body. The rudiment of this organ appears in the 4th week of pregnancy. It looks like a hollow tube that entangles the small body of the embryo. It is already clearly visible and is considered the primary circulation. In the future, this blood circulation will become an independent organ - the baby’s heart.
The first contraction occurs on a curved section of the vascular tube when the formation of the fetus reaches the 4th week. It is not yet controlled by the fetal nervous system. In the sixth (obstetric) week of pregnancy, the pulsation of the small heart becomes clearer and more intense. The first pulsation of an already single-chamber heart appears by the 26th day (5 weeks) of a child’s life. This organ is capable of independently pumping blood flow through the child’s body at a set rhythm.
The baby's heart becomes four-chambered by the end of the 9th week. At this time, you can hear the clear work of a full-fledged heart. By the 9th week the fetus has already formed:
- 2 atria;
- 2 ventricles;
- Valves for their separation;
- Vessels for moving blood in two directions.
The formation of all heart structures ends around the 22nd week of fetal development in the womb . Over the next period, his muscle mass only increases, and the network of blood vessels throughout the child’s body, as well as his heart, grows.
There are significant differences in the structure of a child’s heart from that of an adult:
- Presence of an oval window. It is represented by an opening that is located between the left and right atrium;
- Presence of ductus arteriosus. This ductus ductus is necessary to connect the pulmonary artery with the aorta.
These structural features are necessary for the fetus to receive the oxygen it needs from the mother (when it is in the womb of a woman). It is this structure of all organs and systems of the child that contributes to its saturation with oxygen. Closing of the oval window occurs only after the birth of the baby. The ductus arteriosus also collapses and is no longer needed.
Diagnosis of heart function is carried out using the following methods:
- Ultrasound;
- CTG – cardiotocography;
- Auscultation - listening;
- EchoCG – echocardiography.
Monitoring cardiac activity using ultrasound
Ultrasound can detect the beating of the fetal heart. Transvaginal ultrasound can detect fetal heart contraction earlier than transabdominal ultrasound. Using a special sensor inserted into a woman’s vagina, the heartbeat is detected at 5-6 weeks, and when examined with a sensor on the abdomen - at 6-7 weeks.
How many beats/minute is considered normal for a developing fetus? – this is also a very important question. Heart rate changes at different stages of pregnancy:
- 6-8 weeks – 110-130 beats/minute;
- 9-10 weeks – 170-190 beats/minute;
- 11-40th – 140-160 beats/minute.
This difference in numbers is explained by the formation of the autonomic nervous system. She is responsible for controlling the functioning of the baby's internal organs.
The deterioration of the child’s condition can be seen by a significant deviation of the heartbeat from the norm:
- Reduction to 85-100 beats;
- Increase in frequency above 200 beats;
- No heartbeat.
When no heartbeats are observed in a fetus larger than 8 mm, the examining specialist assumes a diagnosis of a non-developing pregnancy. In this case, it is necessary to conduct a repeat ultrasound so that this diagnosis can be confirmed/refuted. A repeat ultrasound examination should be performed after approximately 5-7 days.
Ultrasound is necessary to determine the following indicators:
- Location of the heart. This organ should be on the left and occupy about 13 of the chest;
- Heart rate. 140-160 beats at this stage are considered normal;
- The nature of the abbreviations. Rhythmicity/irrhythmicity is determined.
In late pregnancy, heart rate can vary depending on many factors:
- Fetal mobility;
- The level of physical activity of the mother;
- Presence of diseases in the pregnant woman;
- Impact of ambient temperature on the mother.
Timing of detection and fetal heart rate
The baby's heartbeat can be detected early. Using a conventional abdominal ultrasound sensor, the doctor will detect heart beats at 5 weeks of pregnancy, and a vaginal sensor will allow you to do this already at 3-4 weeks, that is, almost immediately after the first beat of a small heart (see calculating the gestational age - calculator).
The fetal heart rate varies not only depending on its activity, but also changes with the duration of pregnancy.
- At 6-8 weeks, the beat frequency is 110-130 per minute
- from 8 to 11 weeks it can increase to 190 beats
- starting from 11 weeks it stays in the range of 140-160 beats, with slight deviations in one direction or another.
| gestational age | number of strokes/min. | |
| 4-6 weeks | 80-85 | |
| 6 weeks | 100-130 | |
| 7 weeks | 130-150 | |
| 8 weeks | 150-170 | |
| 9 weeks | 170-190 | |
| 10 weeks | 170-190 | |
| 11 weeks | 140-160 | |
| 12-40 week | 140-160 |
The doctor evaluates not only what the fetal heartbeat is like by week, but also takes into account additional factors (illnesses of the mother and child, listening time and the baby’s activity phase).
Although the baby’s blood supply is entirely dependent on the mother, the blood coming from the placenta throughout the body is “dispersed” by his own heart. Therefore, the fetal heart rate is different from the mother’s; “two hearts beat in unison” is a poetic metaphor, nothing more.
As the fetus grows, its heart rhythm can be heard more and more clearly - starting from the sixth week it can be recorded on an ultrasound machine, and from the 20th week the doctor literally hears it - for this it is enough to attach a stethoscope, or more often, a special auditory tube to the belly of the expectant mother.
Starting from the third trimester, if the doctor is concerned about the condition of the fetus, the baby’s heartbeat can be monitored using cardiotocography or CTG. It is this method that is used to monitor the baby’s condition during prenatal contractions, so we can safely say that most mothers are familiar with these three methods of measuring the baby’s heartbeat - ultrasound, auscultation, CTG.
What do doctors measure? First of all, the baby’s heart rate. It is much higher than that of the mother and depends on the stage of pregnancy.
| Gestational age | Fetal heart rate |
| 6-8 weeks | 110 – 130 beats per minute |
| 9-10 weeks | 170 – 190 beats per minute |
| 11-12 weeks | 140 – 170 beats per minute |
| 13 weeks until birth | 130 to 160 beats per minute |
Many mothers are worried when they discover that their baby's pulse is outside the normal range. But in a fetus, as in an adult, the heartbeat depends on many factors: whether he is active or resting, what medications his mother is taking, whether she is calm or excited, and finally, what method is used to calculate the pulse, where the placenta is located (on the front wall of the uterus it “ screens the baby from the doctor).
At what age does the fetal heartbeat begin to be heard?
The intrauterine period of child development consists of:
- Embryonic. It covers the first 2 months of embryo formation;
- Fetal. Includes 3-9 months of pregnancy.
When can you hear the fetal heartbeat on an ultrasound? The heartbeat can be heard even in the embryo. On the 22nd day after fertilization, the heart begins to beat and then its beats can already be clearly heard. Self-circulation of blood, which occurs through one’s own circulatory system, appears 26 days from the moment of conception.
Thanks to ultrasound, the fetal heartbeat can be detected already at the 5-6th obstetric week of pregnancy. Fetal development is good if the heartbeat is audible and within normal limits. If it is not detected, you can conduct a re-examination in about a week or use other diagnostic methods.
When viewing a four-chamber section of a child’s heart on an ultrasound, a specialist can see the presence/absence of disturbances in the development of this organ. In this section, the doctor can clearly see both atria and ventricles of the fetus. This examination is necessary to identify heart defects that act as the cause of a decrease or increase in the child’s heart rate.
When a specialist determines on an ultrasound that the number of heartbeats does not correspond to the norm, the doctor may prescribe additional methods for further examination of the pregnant woman.
At 7 weeks no heartbeat can be heard
I’m in the hospital for conservation, 6 weeks with a penny per month, an ultrasound 2 days ago said 4 weeks, but there’s no heartbeat yet, the doctor said it’s on the next day. We'll look for it for a week, but I'm afraid, because...
Table of contents:
- At 7 weeks no heartbeat can be heard
- Can't see heartbeat at 7 weeks
- at seventh week there is no fetal heartbeat
- 7 weeks and still no heartbeat
- ultrasound 7 weeks - no heart heard
- Heartbeat can't be heard
- The fetal heartbeat cannot be heard.
- The heartbeat cannot be heard ((( Term 6-7 weeks.
- The ultrasound said that at 6 the baby’s heartbeat could not be heard.
- No heartbeat can be heard.
- threat and no heartbeat can be heard
- The fetal heartbeat cannot be heard.
- The child's heartbeat is difficult to hear
- For those who are already desperate to hear their baby's heartbeat
- For those who are already desperate to hear their baby's heartbeat
- Heart cannot be heard on ultrasound
- Comments
- At 7 weeks no heartbeat can be heard
- Can't see heartbeat at 7 weeks
a year ago there was a ZB. When you have palpitations, how can you avoid going crazy?
tune in for the best. everything will be fine, try not to lose hope.
At 5-6 weeks, according to ultrasound, I was taken to the gynecology department at Krestovsky for preservation; according to the obstetrics, it was already 6 full weeks. We didn’t hear a heartbeat, I thought I was going crazy, and I pestered the doctor to do it again every day. Before discharge (7-8 weeks) I persuaded her. We watched for a VERY long time, it seemed like an eternity to me. From the expression on the doctor’s face I understood that apparently everything was not very good. nothing through the abdominal wall. intervaginally. I looked at it for a long time, almost turned me inside out and was already in despair. but this is happiness. the little heart began to beat.
Don't lose hope. If the embryo is growing, let them look for the heart, it will soon start beating. But if according to ultrasound the period is only 4 weeks, then definitely don’t worry - it’s still too early. quite a little girl.
Heart palpitations at the time of childbirth
The fetal heartbeat, as the most important indicator of its healthy development, is listened to throughout pregnancy. The moment when a child is born is no exception. Usually the heart rate is measured before birth, but if the pregnancy is considered high risk, then the baby's heart rate is monitored during labor. Monitoring can be done by listening with a special tube or using sensors specially designed for this purpose.
Continuous measurement of the baby's heart rate is necessary in the following cases:
- Use of epidural anesthesia;
- The presence of developmental delay in the fetus;
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Premature or delayed birth;
- Presence of hypoxia;
- Use of any stimulants for labor;
- Presence of gestosis;
- Presence of chronic diseases in a pregnant woman.