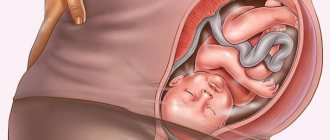
In order for a child to develop normally in the womb, many conditions are necessary. The condition of the umbilical cord, chorion, and then the placenta affects how the embryo feels. He must receive oxygen and nutrition from the woman’s body. Only under such conditions is a normal pregnancy possible. In the article we will talk about what localization of the chorion is and what it is like.
When a new life is born in a woman’s body, a period of major restructuring begins. First of all, hormonal levels change. Then the womb responds to such a significant event, because it will become that very womb.
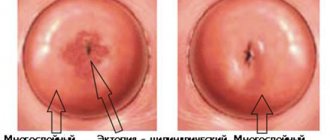
Chorion on the posterior wall what does this mean?
Not all women, during an ultrasound during pregnancy, when they are told that the chorion is formed along the back wall of the uterus, understand what this means.
Let us consider this phenomenon in more detail and tell you what types of chorion presentation generally exist. What is chorion?
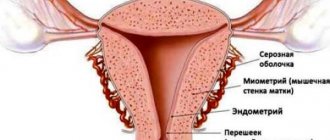
Before talking about the localization of this anatomical formation, let us clarify what is meant by the term “chorion” - this is a membrane that is part of the so-called placental complex, which plays a critical role for the development of the fetus and pregnancy in general. As the chorion develops, one might say “grows” into the placenta, which attaches to the wall of the uterus directly in the area of its fundus or body.
Is it normal for the chorion to be localized along the posterior wall of the uterus?
It is worth noting that this type of chorion attachment to the uterine wall is a classic option and is the most common. In this case, the placenta is attached in such a way that it partially captures the side walls of the reproductive organ from the inside.
The location of the chorion along the posterior wall of the uterus is normal and does not cause any concern among doctors. It must be said that it is the place of attachment of this anatomical formation to the uterine wall that has a direct impact on such a parameter as the growth of the size of the abdomen in pregnant women.
So, if the attachment of the chorion occurs along the posterior wall, the increase in the size of the abdomen occurs at a slow pace. It is in such cases that those around and close to a pregnant woman may not even suspect her situation if she herself does not report it.
Can the position of the placenta change during pregnancy?
It is worth noting that in obstetrics there is such a thing as “placental migration”. So, if it is located along the front wall, then normally, after 1-2 weeks, its upward displacement is observed. This is normal.
Doctors are concerned about the phenomenon when the chorion moves to the lower part of the uterus and is located in it in such a way that it partially or completely blocks the entrance to the uterine cervix, the so-called internal os. This location of the placenta is dangerous because it can lead to bleeding and termination of pregnancy altogether. To prevent this, such pregnant women are usually admitted to a hospital. Such measures allow you to avoid negative consequences, respond in time to the changed condition of the pregnant woman, and thereby prevent spontaneous abortion.
What is hypertonicity of the anterior wall of the uterus during pregnancy and why is it dangerous?
Hypertonicity is excessive muscle contraction. If the muscle bundles are contracted only in a certain area of the uterus, then they speak of local hypertonicity. Hypertonicity of the posterior and anterior walls of the uterus is more often noted.
With hypertonicity of the anterior wall of the uterus muscles, a woman feels pain and a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen. The pain symptom is similar to that during menstruation. Naturally, during the normal course of pregnancy, this should not happen.
Hypertonicity is dangerous because it can cause miscarriage in the early stages or placental abruption in the future.
Hypertonicity is diagnosed during an ultrasound. An expectant mother with uterine hypertonicity should maintain peace of mind and limit physical activity. The need for drug treatment is determined by the doctor.
What it is
The chorion is a temporary organ that performs the functions of a pharmacist. It is formed from the moment the fertilized egg is implanted from the fallopian tube, where the egg and sperm meet, into the uterine cavity. As soon as the blastocyst (which is what the fertilized egg turns into by 8-9 days after ovulation) reaches the uterine cavity, it strives to gain a foothold in it. It is this process that is called implantation.
At the site of attachment of the blastocyst shell, special enzymes are secreted that make the mucous membranes of the uterus more pliable and allow the fertilized egg to “grow.” A chorion is formed at the site of attachment. It is necessary to supply the fertilized egg with useful substances from the mother’s blood. A little later, the placenta appears in its place. But until the 12-13th week we are talking specifically about the chorion, since the placenta is still forming and does not function.
If implantation is successful, the fertilized egg is fixed in the fundus of the uterus (this is its upper part). If, for some pathological reason, the blastocyst fails to implant in the upper or middle part of the uterus, it may descend into the lower uterine segment. And then the chorion will form low.
Chorionic presentation refers to its location relative to the cervical canal, a thin passage inside the cervix that connects the uterine cavity and vagina. There is no talk of presentation only if the chorion has formed in the area of the fundus of the uterus or in its middle part (in the body of the uterus).
If the chorion is low, there are several types of presentation.
Varieties of presentation
Chorion presentation can be complete or partial. When complete, the chorion completely covers the internal os of the cervix - this is considered the most dangerous condition. Accordingly, with partial, only part of the pharynx is blocked. There is also a low location of the chorion - when the chorion is attached less than 3 cm from the internal pharynx, without blocking it, but creating a certain threat of blocking.
Symptoms of previa
Chorionic presentation is detected during the first ultrasound, and in the absence of any complaints from the woman. Sometimes improper attachment of the chorion is manifested by bleeding of varying intensity - spotting or heavy blood. At the same time, a woman can feel great. The occurrence of bleeding can be triggered by external influences - physical activity, taking a bath that is too hot, or sexual intercourse.
Possible complications
Complications of the current situation are equally possible for the mother and the fetus. What are the most common complications?
There is no treatment as such for presentation, since it is simply impossible to change the attachment of the chorion artificially. And all therapeutic measures in this situation are aimed at maintaining pregnancy and preventing, and subsequently treating, complications
It is important to remember here that the chorion migrates upward during pregnancy, as a result of which the threat of complications can be eliminated by itself
Features of pregnancy
The anterior position itself does not cause any trouble to the woman and does not worsen her well-being. Being simply a feature of pregnancy, it does not require treatment. In addition, there is no treatment for it, since it is impossible to influence the location of the placenta, as well as change its position and move it to the back wall.
However, this feature of pregnancy requires constant and close monitoring so as not to miss the possible onset of complications, which are still more likely with an anterior location than with a normal one.
To reduce the risk, pregnant women with this placement are advised to rest more, completely avoid lifting weights (even if it seems that the objects are not heavy at all), and avoid worries, stress, and physical exertion.
This is especially important in the later stages.
It is important to visit the doctor on time so as not to miss changes in the placenta and its location. This approach will allow you to notice in time that the child’s seat tends to move downwards.
Diagnosis
The most appropriate time for an ultrasound examination of the chorionic villus is the 13th week of pregnancy. At this stage, the formed villi are clearly visible; the doctor can accurately determine the position of the future placenta - the connecting link between the mother and the fetus.
According to statistics, in 90% of cases the chorion is visualized in a physiological place - at the bottom of the uterus. But sometimes this structure is located lower, which is a deviation and causes complications. However, when diagnosing chorionic presentation, the expectant mother should not worry too much, since the placenta can change its position after the 1st trimester of pregnancy. This phenomenon is due to the fact that over time the uterus increases in size and pulls up the fetal membrane.
Usually, the incorrect position of the placenta does not show itself in any way; the expectant mother does not have any symptoms. But sometimes, in the presence of chorionic previa, a woman may experience brown discharge on her underwear or sanitary pad. In very rare cases, the abnormal location of the membranes manifests itself as uterine bleeding. The listed symptoms occur against the background of irritants - fitness classes, during stress, etc.
Symptoms and diagnosis
There are no signs that would directly indicate an abnormal location of the future placenta (marginal, partial, complete, low). The pathological course of gestation can be determined only by a number of indirect manifestations:
- bleeding;
- occasional spotting;
- weakness;
- attacks of dizziness;
- clouding of consciousness;
- pulling or cramping pain in the lower abdomen.
This pathology can be detected only after 12 weeks of gestation. In modern medicine, chorionic presentation at 13 weeks can be diagnosed exclusively using ultrasound.
Consequences of chorionic presentation
The most common complication of chorionic presentation is bleeding. Its abundance depends on the degree of presentation. During complete presentation, bleeding can occur as early as 2-3 months; lateral bleeding can cause bleeding after 6 months, during childbirth.
Blood effusion occurs outward. In this way, the appearance of hematomas between the uterus and chorion can be avoided, but the danger for mother and child does not decrease.
The peculiarity of such bleeding is suddenness, but the pregnant woman does not experience pain at this time. This distinctive feature makes it possible not to confuse bleeding with.
Against the background of presentation, the embryo often finds itself in a transverse or breech position. Then it is recommended to do so to avoid all risks.
Expectant mothers should remember that chorion presentation is not a death sentence. By following your doctor's recommendations, you can carry and give birth to a healthy baby. Believe that this will be the case!
Especially for
Elena TOLOCHIK
The first weeks of an expectant mother are the most difficult in her new status. The daily routine, nutrition and usual life are completely restructured. The happiest and most carefree time of bearing a new life does not always go smoothly. Problems and complications arise. At the direction of the gynecologist, the expectant mother undergoes an ultrasound examination of the condition of the fetus. An important procedure takes place at the end of the first trimester, when specialists identify pathologies.
The name chorion is used by gynecologists. This concept refers to the placenta during the first three months of pregnancy. Expectant mothers do not understand the name “chorion presentation”, which they read on the exchange card.
The chorion is a special organ that creates a connection between mother and baby. One part of it is attached to the uterus, and the other to the fetus.
The placenta is the connection between the baby and the mother. With its help, the baby in the womb eats, breathes, and develops. The correct development of pregnancy, as well as the future life of the child, depends on its condition.
It is important to suspect deviations from the norm early in order to provide timely assistance and deliver a healthy baby.
The chorion (placenta) attaches normally to the uterus and does not block the cervical canal. There are situations when it is located low, does not completely or completely covers the internal pharynx. This is where chorion presentation occurs.
Is placenta migration possible?
Migration is a change in the original location of the placenta. Experts believe that a change in the localization of placental tissue during presentation along the anterior wall is possible. Pregnant women and doctors are usually warned about this when consulting them.
If placenta previa is detected to the anterior wall in the early stages of pregnancy, the expectant mother should not panic first of all. There is still quite a long way to go before birth occurs. During this time, the placental tissue can shift and even significantly change its position.
Such changes are assessed through ultrasound. As a rule, to track dynamics, doctors prescribe several sequential ultrasound examinations. When placental tissue previa is present, vaginal examinations should often not be performed. The lower the placenta is, the higher the likelihood of damage. Tracking the dynamics of the location of placental tissue during presentation is very important. It helps doctors timely identify developing complications and take the necessary measures to improve the situation.
It should be noted that in most cases the placental tissue changes its position rather slowly. It is optimal if this process occurs in the female body within 6-10 weeks. In this case, the likelihood that the expectant mother will experience any significant discomfort symptoms is quite low. Typically, migration of placental tissue is completely completed by the middle of the 3rd trimester of pregnancy.
If the placental tissue shifts too quickly for some reason, adverse symptoms may occur. The most dangerous of them are the development of bleeding and detachment of placental tissue from the uterine wall. As a rule, adverse symptoms develop if the placenta migrates within 1-2 weeks. The speed of placental migration depends on many factors and reasons, including how high the placental tissue was originally located.
Chorionic presentation therapy and delivery
Currently, medicine is not able to rid a woman of this condition. In hospital settings, careful monitoring is required. Reducing physical activity, stress, and treating neuroses and depressive states are mandatory. Regular examination by a gynecologist and ultrasound are required. Under the supervision of doctors, the condition can be monitored and complications managed.
The expectant mother should eat properly and regularly and include vitamins in her diet. Proper functioning of the stomach and intestines will prevent constipation. And this will eliminate tension in the pelvic organs, which can cause severe bleeding. In the hospital, iron-containing and antispasmodic drugs are prescribed according to indications. Lifting heavy objects, walking up stairs and running are prohibited. It is advisable to avoid high mental stress.
When placenta previa occurs, sexual intercourse is prohibited. They can cause severe bleeding.
Treatment for atypical presentation depends on the following:
- gestational age
- general condition of the expectant mother
- readiness of the birth canal.
If a woman at 16 weeks of pregnancy, when she came to the antenatal clinic, did not complain of symptoms, but the gynecologist determined the presentation, she is simply observed once a week or every two weeks. Starting from the 24th week, they are treated in a hospital.
Delivery is considered an important issue. If a lateral or marginal presentation is detected without bleeding, doctors expect a natural birth
When the cervix is dilated by 3 cm, there is bleeding before contractions, when the cervix is soft and stretchable, an amniotomy is performed for prevention. The baby's head, pressing against the pelvis, compresses the bleeding.
Presentation from 8-14 weeks can move to the natural location of the placenta or persist in the form of low placentation. If the problem does not improve, but turns into an anomaly in the location of the placenta, then by the time of birth the baby may be transverse in the uterus or with the buttocks downwards.
To reduce the risk to the baby's health, it is recommended to give birth through cesarean section. It is prescribed to those pregnant women who have a complete presentation or pathologies: unnatural position of the fetus, a scar on the uterus. The surgical technique depends on the location of the placenta. If along the front wall, the corporal method is used.
Treatment
With placenta previa, only symptomatic treatment is possible; at the moment, doctors cannot change the abnormal position of the fetal membranes.
Low and marginal presentation of the chorion at week 13 does not require any measures; in most cases, the organ will independently take the correct position. If after a few weeks the position of the placenta does not change, but the woman does not have bleeding, she is advised to avoid physical and emotional stress, refuse intimacy, sleep more than 8 hours a day, and get plenty of rest. Also, the expectant mother should follow a diet rich in vitamins and microelements, especially iron. It is recommended to include more fresh vegetables and fruits, lean meat, fish, and cereals in your diet.
In case of central placenta previa, as well as in the presence of bleeding, hospital treatment is recommended for the woman. In addition to bed rest and a balanced diet, the expectant mother is prescribed medications to support pregnancy.
To prevent placental abruption, progestin drugs are used - Duphaston, Utrozhestan. Their therapeutic effect is based on reducing the tone of the uterus. The woman is prescribed iron supplements that reduce the loss of hemoglobin - Ferrum-Lek. If bleeding develops, the expectant mother is given hemostatic agents - sodium etamsylate.
Also, the expectant mother is prescribed multivitamin complexes aimed at improving metabolism. If there are mental disorders, doctors recommend taking sedatives - Valerian, Motherwort. In case of persistent bleeding that is not amenable to drug treatment, the question of emergency delivery is raised.
What is chorionic presentation and why does it occur?
Until the placenta is formed, the embryo is surrounded by a villous membrane, which grows into the lining of the uterus. Until the 16th week of gestation, this is the chorion (from the 17th week - the placenta), which performs the following main functions:
- Nutrition of the embryo;
- Respiration – delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide;
- Isolation of metabolic products;
- Embryo protection.
During the normal course of pregnancy, the chorion attaches to the fundus of the uterus and grows along the anterior, posterior and lateral walls, but this does not always happen.
Chorion presentation is its incorrect location, in which there is complete or partial overlap of the internal os of the cervical canal.
Why this condition occurs is not completely clear. But a connection has been established with some factors:
- chronic inflammation of the uterus;
- previous operations;
- fibroids;
- abnormal development of the uterus;
- a large number of pregnancies and births;
- low attachment of the placenta in the previous pregnancy.
The position of the chorion during pregnancy, what threatens incomplete chorion presentation
Ultrasound examination helps diagnose certain pathologies associated with an unfavorable pregnancy. Already during the very first planned ultrasound, incomplete chorion presentation can be detected.
Many women would like to know why incomplete chorion presentation occurs, what it is and why it is dangerous. Only narrow specialists can answer this question. The chorion is the outer shell of the embryo. It is covered with numerous villi. Over time, the chorion turns into the placenta. In the early stages of pregnancy, it is the villous membrane that transports nutrients to the embryo, protects the embryo, and also performs excretory and respiratory functions.
If pregnancy proceeds without pathologies, the chorion develops in the area of the uterine fundus. Usually this is exactly what happens, with the placenta subsequently attaching predominantly to the back or front wall. When presenting, the chorion is located in the lower part of the uterus. The internal pharynx is partially blocked.
There are many reasons why this pathology develops. These include:
- presence of inflammatory diseases of the genital area;
- abnormal structure of the uterus;
- a large number of births in the anamnesis.
How dangerous is partial presentation? Doctors consider this a rather serious pathology, but it all depends on how severe it is. In this situation, the chorion covers only the area of the internal os of the uterus. With marginal presentation, there is a chance that in the future the placenta will begin to form a little higher and the pregnancy will proceed without complications.
Central incomplete chorionic presentation usually leads to complete placenta previa. This pathology serves as an indication for cesarean section. When the internal uterine os is blocked, natural childbirth is simply impossible.
Incomplete chorion presentation not only leads to improper formation of the placenta. A woman may encounter a number of complications not only during childbirth, but also at different stages of pregnancy. The most common and very dangerous complications include:
- spontaneous termination of pregnancy;
- intrauterine fetal death;
Often, it is during partial presentation that a woman notices a scarlet discharge from the genital tract. Sexual intercourse or taking a hot bath can provoke the development of bleeding.
This diagnosis can be established only after the woman undergoes ultrasound diagnostics. Unfortunately, this pathology cannot be treated. It is simply impossible to move the chorion to another part of the uterus. After diagnosing incomplete presentation, all efforts of doctors and the patient herself should be aimed at maintaining the pregnancy. If pain or bleeding occurs, gynecologists usually offer the expectant mother hospital treatment
In such a situation, it is very important to strictly observe bed rest and be under medical supervision around the clock. Iron supplements may be prescribed to prevent anemia.
In case of incomplete chorion presentation, sexual intercourse is strictly prohibited, as well as performing heavy loads, heavy lifting and overwork. This can lead to very sad consequences.
If a woman has already had pregnancies with incomplete chorionic presentation, the risk of pathology occurring during repeated pregnancies increases. Unfortunately, it is very difficult to prevent such developments, but it is possible with a competent approach to conception planning.
Incomplete chorion presentation is a rather serious and dangerous pathology.
It is very important to diagnose it on time and take all measures aimed at preserving such a pregnancy. The best results are achieved with inpatient treatment
Complications
Expectant mothers with this feature are concerned about whether the location of the placenta along the anterior wall is dangerous. Experts do not give a definite answer. Pregnancy with such attachment of the fetus can proceed normally and be resolved by natural birth. But there are certain risks of complications. All of them are due to the fact that the placental walls are highly dense. When the embryo attaches to the anterior part of the embryonic organ, the process of excessively active stretching of the latter begins. Possible complications include:
- Insufficient functioning of the “baby place”, disruption of the process of transporting oxygen and nutrients to the fetus.
- Preeclampsia.
- Placental insufficiency.
- Movement of the “children’s place” downwards. When the distance to the uterine os is reduced to 4 cm, anterior placenta previa is diagnosed, which entails the threat of miscarriage and bleeding.
- Low presentation (rare cases when the “baby spot” can completely close the uterine os). In this case, natural childbirth is excluded.
- Partial or complete placental abruption (develops against the background of presentation along the anterior wall and placental insufficiency).
- Internal or external bleeding, hypoxia, fetal death. Such complications develop if, when the embryo is located along the anterior wall in the later stages, intense movements of the baby lead to an increase in the tone of the uterus and the “baby place” moving away from it.
- Placenta accreta occurs when the baby's place is placed in front and is attached too strongly to the uterus. The risk of such a complication increases sharply in women who have had abortions, cesarean sections, or inflammatory diseases in the past.
The main causes of chorion presentation
The main cause of this disorder is considered to be pathology of the internal walls of the uterus, due to which the embryo cannot attach to them. Often, these pathologies arise as a result of abortion or due to sexually transmitted infections. Presentation can also develop with uterine deformation, which occurs as a result of myomectomy.
Women with severe forms of heart, kidney or liver disease are at increased risk. This is due to congestion in the uterine cavity. Chorion presentation often affects second-bearing women, especially those over 35 years of age.
This deviation may be associated with pathology of the fertilized egg, as a result of which full attachment of the latter is impossible. It also happens that the placenta is attached too tightly and cannot separate on its own during childbirth.
It would be appropriate to note that chorionic presentation, excluding the central variant, can only be definitively diagnosed at the end of pregnancy, since the position of the placenta can always change.
Features of this location
Attachment of placental tissue along the anterior wall is less physiological. This arrangement of placental tissue has both disadvantages and advantages. There are far fewer pros than cons.
It should also be noted that such a clinical situation requires a certain medical approach. A pregnant woman who has such a location of the placenta requires quite close monitoring by doctors.
pros
The advantages of anterior placenta previa include the possibility of migration. During the several months of waiting for the baby to be born, the placental tissue may change its position. Doctors note that the placental tissue with anterior placenta previa moves much more easily than with a posterior one.
Minuses
It is noted that the placenta is extremely rarely attached to the anterior wall of the uterus. This feature has important biological significance. This is explained quite simply. Placental tissue is very delicate. It can be easily damaged due to various external traumatic influences.
Causes of presentation
Why exactly the developing placenta is attached in such dangerous proximity to the pharynx of the cervical canal is completely unknown. However, several main factors have been noted that contribute to a greater likelihood of developing this pregnancy complication. Especially often, various variants of chorionic presentation develop in women who have had in the past or currently have the following diseases and conditions:
Inflammatory lesions of the uterus, abortions, especially using the curettage method, surgical interventions for fibroids or cesarean section.
All these factors are united by one consequence - after this, scars and adhesions can be left on the inner surface of the uterus, which make it difficult for the chorion to attach to the “right” place.
Diseases of the liver, kidneys or heart.
It would seem, how can these conditions affect the position of the fetus and its placenta in the uterus? But with pathologies of these organs, blood stagnation may occur in the pelvic area, which contributes to lower attachment of the chorion.
Multiple births in the past.
If you are pregnant not for the first time, then your chances of improper attachment of the chorion significantly increase. Most physiologists see the reasons for this phenomenon in the fact that after each pregnancy, in the area of the uterus where the placenta was attached, the structure of the endometrium changes. Therefore, at the next conception, the chorion can no longer attach there. Over time, such places on the inner surface of the uterus become less and less, which leads to the attachment of the placenta in the danger zone.
Uterine deformities
, acquired (for example, after surgical interventions) or congenital in nature, can also lead to chorion presentation.
How is childbirth?
The choice of obstetric care tactics for placenta previa is, as a rule, quite responsible. The life and health of the expectant mother and her baby depend on this.
It should be noted that nowadays, more and more often, obstetricians-gynecologists give their preference to the surgical method of childbirth, choosing a caesarean section. In this situation, the risk of developing birth injuries and damage is much lower. Of course, a caesarean section has certain disadvantages, since it is essentially a surgical operation.
However, with placenta previa, preserving the baby’s life is important. Reviews from many women who have placenta previa on the anterior wall of the uterus and have already become mothers confirm that they had a caesarean section.
The presence of a burdened obstetric and gynecological history in a pregnant woman is also an additional condition for a caesarean section to be performed. In this case, independent natural childbirth can be dangerous not only by the development of a number of pathologies for the baby, but also by a significant deterioration in the health of the expectant mother.
The tactics of obstetric care are chosen individually. To do this, the specialist evaluates several factors at once. Obstetricians-gynecologists necessarily take into account the woman’s age, the presence of concomitant diseases, clinical indicators of intrauterine development of the fetus, the presence of formed pathologies during pregnancy, and much more.
It is important to remember that during pregnancy, which occurs with the development of placenta previa along the anterior wall of the uterus, the expectant mother should very carefully monitor her well-being from the first days after such a diagnosis is established.
If adverse symptoms occur, it is extremely important not to delay visiting your obstetrician-gynecologist to clarify the situation.
To learn what placenta previa means, watch the following video.
The placenta is formed in the first weeks of pregnancy and acts as a conductor of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus and removal of waste products, and also serves as a barrier to infections.
There are several options for its attachment in the uterus. One of them is the location on the front wall. Having heard such a verdict from a doctor, it is important for a woman to know how this threatens the normal course of pregnancy and the development of the child.
Chorionic presentation causes and types, complications, treatment, prevention
During the mandatory ultrasound after 12 weeks, the location of the chorion is assessed, among other things.
Sometimes an ultrasound specialist diagnoses chorionic presentation. What does this mean and how dangerous is it?
Until the placenta is formed, the embryo is surrounded by a villous membrane, which grows into the lining of the uterus.
Until the 16th week of gestation, this is the chorion (from the 17th week - the placenta), which performs the following main functions:
- Nutrition of the embryo;
- Respiration – delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide;
- Isolation of metabolic products;
- Embryo protection.
During the normal course of pregnancy, the chorion attaches to the fundus of the uterus and grows along the anterior, posterior and lateral walls, but this does not always happen.
Chorion presentation is its incorrect location, in which there is complete or partial overlap of the internal os of the cervical canal.
Why this condition occurs is not completely clear. But a connection has been established with some factors:
- chronic inflammation of the uterus;
- previous operations;
- fibroids;
- abnormal development of the uterus;
- a large number of pregnancies and births;
- low attachment of the placenta in the previous pregnancy.
Types of chorion location
Based on the attachment of the chorion relative to the internal os, presentation occurs:
- Complete – a condition in which the chorion completely covers the internal os. This will subsequently develop into placenta previa.
- Incomplete – characterized by overlap of part of the uterine os. If the villous membrane comes out up to a third, then this is called marginal presentation.
- Low - the chorion is located at a distance of 3 cm or less from the pharynx, but does not overlap it.
Chorionic presentation at 12 weeks is not the final verdict. As the uterus and fetus grow, migration may occur, and the condition will return to normal. A more favorable prognosis is noted for the posterior location of the chorion and presentation along the anterior wall.
Complete blocking of the uterine pharynx by the chorion is a dangerous type of pathology that threatens massive bleeding.
How is chorionic presentation manifested?
Most often, pathology is detected during ultrasound.
Bloody discharge can also be caused by presentation, especially if a hot bath, sauna, or sexual intercourse took place shortly before. In this case, you need to urgently consult a doctor.
Treatment of chorionic presentation
Partial chorionic presentation without bleeding does not require hospitalization. Isolation of any amount of blood is an indication for treatment in the hospital.
It is impossible to artificially change the location of the villous membrane, so the main task facing doctors is maintaining pregnancy. A protective treatment regime is created in the hospital:
- The woman is in a calm environment, on bed rest;
- Physical activity is limited;
- A balanced diet is provided with the exception of foods that strengthen or relax the stool.
Drug treatment is as follows:
- Suppositories with Papaverine, Drotaverine tablets to relieve uterine tone;
- Vitamins;
- Iron preparations, for example, Totema, Maltofer - for the prevention or treatment of anemia.
In the presence of bleeding, the hemostatic drug sodium etamsylate is additionally used. At the beginning of therapy, it is administered intravenously or intramuscularly. Then you can switch to tablets.
Massive bleeding that cannot be treated with conservative methods is an indication for termination of pregnancy.
After discharge from the hospital, at home it is necessary to adhere to a measured lifestyle, eliminate stress and increased workload. It is forbidden to have sex, because this may cause new bleeding and miscarriage.
What is the prognosis for the pathology?
Chorionic presentation at 8-14 weeks can transform into a normal location of the placenta or persist in the form of low placentation.
If the presentation does not disappear, but turns into an anomaly in the location of the placenta, then by the time of birth the baby may be transverse in the uterus or with the buttocks down. In such cases, to reduce the risk, it is recommended to deliver by caesarean section.
Treatment with medications
It should be said that often with incomplete marginal presentation of the chorion (placenta), uterine bleeding is insignificant. In such cases, the pregnant woman is prescribed bed rest, as well as a course of drugs that reduce uterine contractions:
- rectal suppositories containing papaverine;
- Magnesium sulfate with Novocaine (drugs are administered intramuscularly).
In addition, the following hemostatic agents are prescribed:
- aminocaproic acid intravenously;
- Dicynone (intramuscular injections).
In case of reduced blood clotting, a pregnant woman is usually prescribed intravenous administration of plasma and Dicinone.
After the bleeding stops, the expectant mother should remain in the hospital under the supervision of a doctor, since bleeding may resume. In addition, with any form of chorion previa (placenta), there is a high probability of bleeding in the first stage of labor due to intense contractions of the uterus.
It should be noted that any form of chorion previa (placenta) is one of the prerequisites for a planned cesarean section.
In addition, if the pregnant woman’s condition worsens and there is heavy bleeding, a cesarean section is performed regardless of the stage of pregnancy, since here we are talking about preserving the woman’s life.
As for general precautions for marginal chorion presentation, such a diagnosis requires the pregnant woman to be in a state of physical rest: bed rest, lack of physical and emotional stress. It is necessary to exclude all factors that can provoke uterine contractions.
The chorion is a structure that includes the outer membrane of the embryo called the serosa. It is the precursor of the placenta, which is formed by 12-14 weeks of pregnancy. The chorion consists of many villi that perform nutritional, respiratory, excretory and protective functions.
Initially, the villi completely cover the chorion, but from the 5th week of gestation they begin to grow on the side of the fetus and die off on the opposite side. Normally, the outer membrane of the fetus develops at the bottom of the uterus and extends onto its anterior, posterior and side walls. Chorionic presentation is a pathology in which this structure is not located in a physiological place.