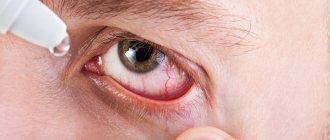
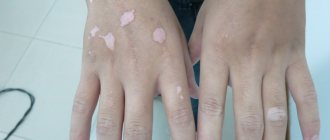
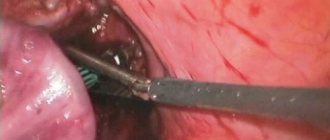
Seborrheic keratosis - includes a whole group of skin diseases that are united by a single factor - thickening of the stratum corneum of the skin. It is noteworthy that the main risk group is people over forty years of age. Currently, the causes of this pathology are not fully understood, and clinicians identify a rather narrow range of predisposing factors, which are based on chemical and mechanical damage to the skin.
Online consultation on the disease “Seborrheic keratosis”. Ask a question to the experts for free: Dermatologist.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention and prognosis
The clinical picture will differ slightly depending on the form of the disease. The most specific symptom is the formation of spots on any part of the body except the palms and feet.
Establishing the correct diagnosis will not be a problem for an experienced dermatologist, which is why diagnosis is based only on a thorough physical examination, which is carried out personally by the clinician.
Treatment of seborrheic keratosis in the vast majority of cases is performed with minimally invasive surgical operations, but sometimes traditional medicine can be used.
The International Classification of Diseases has given special significance to such benign skin pathology. The ICD-10 code is L82.
Seborrheic keratosis: what is it?
Keratosis is a pathology of the epidermis, characterized by the appearance of a neoplasm on the epidermis, which is benign in nature. There are several types of the disease and one of them is seborrheic keratosis.
As the disease progresses, a seborrheic keratoma appears. Locations: face, lower and upper limbs, neck and epidermis of the head. Usually formation does not occur singly, but in groups. At the first stage of development, the keratome is a brownish or yellow spot.
Over time, the formation increases in size, a characteristic crust and dark brown color appear. The surface of the wart cracks. When the formation grows, pain occurs. Often, an increase in size is accompanied by bleeding and itching.
With seborrheic keratosis, senile keratoma can also appear, which occurs after 30 years. Localization sites are the upper limbs, face and neck, less often - the abdomen, chest or back.
Externally, a keratoma is similar to a mole, but has a grayish-yellow or white tint. The formation increases in size over time and is sometimes accompanied by inflammation. The wart is benign in nature and rarely becomes malignant.
Reasons for appearance
Causes of seborrheic keratosis:
- Regular exposure to the sun for long periods of time. As a result, the epidermis does not have time to absorb ultraviolet radiation. This leads to disruption of cell formation, which causes skin growth and keratinization of the skin;
- Genetic predisposition. If the grandmother and mother had seborrheic keratoma, then there is every reason to believe that it will appear in the daughter;
- Deficiency of nutrients in the body. Excessive consumption of fatty foods is also a provoking factor;
- Predisposition to pathologies of the epidermis. If a person has constantly had the need to deal with dry or oily seborrhea throughout his life, then there is a high probability of developing seborrheic keratosis in adulthood;
- Age-related changes. The disease develops after 30 years of age. At this age, the epidermis loses some of its protective properties, which leads to complex adaptation of the skin to sunlight and cold.
Why is it dangerous?
The main danger is that seborrheic keratomas can develop into malignant formations at any time. This happens suddenly and the appearance of the wart may not change.
The most dangerous condition is when malignant oncology develops on the epidermis directly under the keratoma. At the same time, the appearance of the wart does not change in any way. It is extremely difficult to diagnose seborrheic keratosis in the early stages of development, since the patient is not bothered by anything and does not observe external changes.
As a result, the patient receives untimely medical care. Sometimes this leads to the fact that the pathology is detected in the later stages, when the tumor has metastasized, which poses a danger not to the health, but to the life of the patient.
If multiple keratomas appear on the epidermis, this may indicate an oncological pathology of some internal organ. In this case, experts recommend performing a study not only of the formation, but also of the body as a whole.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
A distinctive feature of keratomas among most skin tumors in humans is that not every tumor requires mandatory medical intervention and removal. Typically, doctors recommend that if a patient has neoplasms of any kind on the body, periodically visiting a dermatologist for preventive purposes, for example, once or twice a year. This measure is enough to prevent the transformation of benign tumors into malignant ones, or, if the process has already begun, to detect it in time.
As for the indications for laser removal of keratomas, the main one among them is keratoma, which is dangerous, that is, it has the likelihood of degenerating into a cancerous tumor. The main symptoms that should alert a person:
- peeling;
- itching;
- pain in the keratome;
- darkening of its surface;
- falling off of the keratoma, leaving a bleeding wound.
In such cases, you should immediately contact a dermatologist or oncologist.
It should be noted that laser removal, along with surgical and radio wave, is the most preferred method of treating malignant keratomas, in contrast to cryodestruction or electrocoagulation, since the latter do not provide adequate efficiency in removing cancer cells.
In addition, laser destruction can also be carried out in cases where the keratoma does not pose any threat to the patient’s health, but at the same time represents an obvious cosmetic defect, that is, removal can be prescribed at the request of the patient.
Contraindications to the procedure may be:
- pregnancy;
- general serious condition of the patient;
- acute infectious or inflammatory processes in the body;
- some psychiatric diseases.
If a person has an acute inflammatory or infectious lesion, it is necessary to first remove the aggravation, after which it will be possible to perform an operation to remove the keratoma.
Pregnant women are traditionally advised to avoid any interference with the body while they are carrying their baby. Of course, if the situation is critical and cannot be delayed, the procedure for removing a tumor with a laser can be prescribed as an exception, however, if possible, it is better to postpone it until the child is born.
Classification and characteristics of forms
There are several types of keratosis:
- Follicular pathology. Symptoms of the disease are the appearance of yellow or pink nodules on the epidermis. The skin around the formations becomes red and inflamed;
- Actinic pathology. The disease affects people over 45 years of age with a light-colored epidermis. Localization sites are uncovered areas of the skin. The pathology is characterized by small rashes of a gray or yellow hue, on the surface of which there are scales;
- Horny keratosis or cutaneous horn. Externally, it is a conical formation with a dark or light shade. The pathology got its name due to its external resemblance to animal horns. Most often, the formation from a benign growth turns into a malignant form;
- Seborrheic wart. Outwardly it resembles a mole, but with cracks on the surface. Such a formation rarely develops into a malignant tumor.
There are also several forms of seborrheic dermatitis:
- reticular formation, on the surface of which there are horny brushes;
- flat form, in which spots of bright dark shades are observed on the epidermis, which do not rise above the epidermis or rise, but only slightly;
- inflammatory type - characteristic features are swelling of the soft tissues, redness of the epidermis near the formation;
- irritable form - blood and mucus accumulate in the growth.
When does a keratoma become dangerous?
Keratosis begins as a small, raised, brown or grayish patch on the skin that may peel. Gradually, the size of the tumor increases, and a crust appears on top. If it comes off, minor bleeding may occur, causing some discomfort to the person. Keratomas can appear in several places at once, usually in areas of the body exposed to sunlight. In themselves, they are not dangerous, and a person can live with such a growth all his life. The danger arises when it degenerates into a malignant tumor, and the spots can grow and transform into squamous cell carcinoma. It is impossible to predict such a transition, so doctors recommend immediately removing such tumors.
They are suitable for those who have a lot of skin damaged by photography and chronoformation, which means that the wrinkles and furrows are quite deep and scattered. They require a period of hospitalization at home during which the exfoliation of the skin is completed, which is much more noticeable than a superficial peel.
Results depend on the type of deep peel. Effective treatment, for example, has a definitive result and only one treatment is sufficient, while medium and superficial peels are less invasive, but they provide less long-lasting results and require repetition with regularity.
Symptoms of the disease
At the initial stage of development, seborrheic keratosis practically does not manifest itself at all. Colorless spots appear on the epidermis, which can only be detected with a thorough examination of the skin. Over time, the formation changes its shade to a darker one, rises above the epidermis, a crust and cracks appear on the surface.
The formations have different colors. The palette of shades includes yellow, brown, black, burgundy and gray. Seborrheic warts have a diameter of 1 mm to 10 cm. Keratoma is sometimes accompanied by itching, burning and bleeding.
The pathology has pronounced manifestations; if the first signs and clear symptoms are detected in adults, it is recommended to consult a doctor and a specialist, after conducting appropriate research, will prescribe treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
Seborrheic keratosis manifests itself as single or multiple elements, which are most often localized on the anterior surface of the chest and back, in rare cases - on the face, neck, scalp, posterior surface of the forearm, dorsum of the hand, and external genitalia. Very rarely, the disease affects the palms and plantar surfaces of the feet.
The shape of the tumor is most often oval or round, sizes - from 2 mm to 6 cm. The formations have clear boundaries and are often accompanied by itching.
Tumors are pink, yellow, dark cherry, dark brown, black. The surface of the neoplasms looks like a large number of flaky warts, covered with an easily removable thin crust, which begins to bleed at the slightest mechanical damage. Over time, the crust gradually thickens and can reach 2 cm, and black dotted inclusions form in it.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of keratosis consists of conducting an external examination and prescribing appropriate studies:
- Cytological analysis. To conduct the study, a piece of the growth is taken from the patient;
- Ultrasound of the soft tissues on which the keratoma is located.
Seborrheic keratoma of the skin is diagnosed during an external examination. An experienced doctor will not confuse the pathology with other formations. Additional studies are carried out only to determine the benign or malignant nature of the pathology.
Treatment
If seborrheic keratoma is diagnosed, only a doctor can prescribe treatment. You should not try to remove the growth yourself. Any such manipulation can lead to unpredictable consequences. Injury to the keratoma threatens to accelerate the growth of the formation, the rapid proliferation of warts and the transition of the growth to a malignant tumor.
In most cases, keratoma does not require removal or therapy. Surgeon intervention is required in the following cases:
- if the formation experiences regular mechanical stress;
- if itching, burning, inflammation and bleeding occur;
- if the growth grows and multiplies quickly;
- when pain occurs in the area of the affected epidermis.
Keratomas are also removed if they cause aesthetic discomfort. This is true if growths appear on the face and open areas of the body.
Advantages of laser surgery over other keratoma treatment methods
Doctors who work with skin tumors and reduce them note that laser destruction has a number of undeniable advantages over other methods of treating keratomas. It is performed non-contactly, so the risk of wound infection during tumor removal is extremely low. Controlled exposure of biological tissues with a laser beam leaves small and unnoticeable scars in most cases. If you follow all the rules for caring for the affected area of the skin, recovery after the procedure is quick and without discomfort. The process itself is almost painless for the patient.
The likelihood of developing complications after surgery is also extremely low. Relapses occur only in 8-10% of all cases of keratoma removal.
Laser removal of skin tumors, including keratomas, is prescribed by doctors almost as often as surgical removal. Its high efficiency, coupled with low morbidity for humans, makes the procedure permitted not only for adults, but also for children. In order to receive a referral for the procedure, you need to visit a doctor - a dermatologist or oncologist, and possibly undergo some tests. Laser removal of keratoma occurs in an outpatient clinic, as well as in private medical institutions - by dermatologists and cosmetologists.
Keratosis of the scalp is one of the most unpleasant diseases. It is also called hyperkeratosis due to the fact that there is excessive growth of the stratum corneum of the skin. The disease can be localized only in the scalp area or spread throughout the body.
When compactions and dry growths occur, the hair follicles become clogged. In this case, pointed bumps like goose bumps form on the surface.
Preparations for seborrheic keratosis
At the initial stage of the pathology, treatment of seborrheic keratosis is recommended with special medications. The doctor prescribes the use of gels, creams, ointments and other similar products, which contain cytostatics and active acids.
Such components destroy keratosis cells. The products are used only as prescribed by a doctor and under his supervision. The specialist must understand how the selected drug affects the formation, correctly calculate the dose and evaluate the effectiveness of the chosen therapy.
Traditional medicine treatment at home
Folk remedy therapy can only be used as prescribed by a doctor, since any independent treatment at home poses a danger to the health and life of the patient.
To treat seborrheic keratosis, you cannot use aggressive traditional medicine, as they injure the growth, which can lead to cancer.
To get rid of pathology, it is recommended to use the following recipes:
- Propolis is softened and fixed with a plaster on the problem area of the epidermis. The compress is renewed once a day. The bandage is worn continuously until the formation disappears;
- Small beets are peeled and grated into a fine grater. The resulting slurry is fixed on the affected area of the epidermis using a bandage and adhesive tape. The product is kept for four hours. The procedure is carried out daily;
- Pork fat is melted and mixed with crushed celandine. The resulting ointment is used to treat the problem area several times a day. The product is stored in the refrigerator.
In this video, you can see effective methods of treatment with folk remedies:
Surgical removal
There are several ways to surgically remove a keratoma. The choice of technique depends on the individual characteristics of the patient, his financial capabilities and the stage of development of the pathology. Methods for removing formation:
- Surgical intervention. The essence of the procedure is cutting out all damaged soft tissues with a scalpel;
- Laser removal of tumors. One of the most popular methods of treating seborrheic keratosis. The essence of the procedure is burning out the growth using a laser;
- Treating the build-up with liquid nitrogen. The procedure is safe and painless.
What is the essence of the laser method for treating skin diseases?
The appearance of the laser as a physical phenomenon became possible after Albert Einstein developed the theory of interaction between matter and radiation at the beginning of the 20th century. It traced ideas for the possible creation of quantum radiation amplifiers and generators of electromagnetic waves.
The first ruby laser device was designed by the American scientist Theodore Maiman in 1960. The laser wavelength was 0.69 μm. At the same time, for the first time, the properties of laser were used to destroy human hair follicles. This event became the starting point in the history of laser surgery, medicine, and cosmetology.
Laser removal of keratomas refers to both medical and cosmetic procedures. Not only hospitals and private medical institutions, but also the offices of cosmetologists and dermatologists are equipped with special devices with an attachment that generates a directed laser beam.
The medical device used in the process, using the properties of light rays and a special system of mirrors, generates a laser beam. By directing it to the affected area, the doctor ensures that the cells of the neoplasm burn from its top to the deepest layers. At the same time, coagulation of the blood vessels damaged in the process occurs, which eliminates the risk of bleeding.
After treating the tumor in this way, a barely noticeable scar remains in its place. The duration of the wound healing period is rarely more than 3-4 weeks. There is virtually no risk of wound infection during the procedure.
In the laser surgery industry, lasers with high radiation power are used, due to which they can cause significant heating of biological tissue, which contributes to its evaporation or cutting. Such an intervention, although considered surgical, is minimally invasive.
Thanks to modern laser devices and systems, during the operation it is possible to ensure:
- dry work area;
- effective contactless and contact vaporization and destruction of biological tissue;
- minor damage to surrounding tissue;
- stopping lymphatic and blood vessels;
- effective hemostasis;
- high sterility of the process;
- the possibility of combining the procedure with laparoscopic and endoscopic measures.
Preventive measures
To reduce the risk of seborrheic keratosis, doctors recommend the following preventive measures:
- sunbathe less often and visit the solarium;
- before going outside, treat the epidermis with protective agents;
- normalize unstable emotional background;
- adhere to the principles of proper nutrition;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- to live an active lifestyle.
Seborrheic keratosis is a pathology of the epidermis that can trigger the development of cancer. To avoid this, you should consult a doctor immediately after the onset of the disease.
Types of destructive techniques
The choice of removal method depends on the type, shape, and size of the tumor. Each method has contraindications and consequences of the postoperative period.
The clinic to which the patient applies initially conducts a differential examination of the tumor by visual examination, including dermatoscopy - examination using a microscope allows you to examine the skin without trauma. When a tumor or suspicion of malignancy is removed, a histological examination of its tissue is performed.
Laser
Laser is effective in removing malignant tumors. Signs for which removal of keratomas is indicated:
- Severe itching;
- Sharp darkening;
- Peeling;
- Falling off of the keratoma, formation of a bleeding wound.
Contraindications limiting laser removal are noted:
- Pregnancy;
- The patient's serious condition;
- Inflammatory processes in the body;
- The presence of certain psychiatric diseases.
Laser removal of keratoma is not carried out in the summer; two weeks before the procedure, you should not stay in the sun for a long time or visit solariums. Before removal, the surface is treated with antiseptic alcohol-free solutions. The duration of the process is 15 minutes. A single time is enough to completely remove the tumor - relapses are possible in 8% of cases.
After removal, a scar is formed - small or large, depending on the size of the tumor. Dangerous symptoms may appear:
- There is redness around, the wound itches;
- The ulcer bleeds and does not heal;
- After removal of the tumor, an allergic reaction developed;
- The wound festered.
Care proceeds as follows:
- Washing with water.
- Treatment with potassium permanganate and restorative ointment.
- Apply a sterile bandage to the surface.
Complete healing of the skin occurs after 6 weeks. Ultraviolet radiation is undesirable in the coming year to avoid a relapse.
Nitrogen
Cryodestruction is an innovative method. During the operation, the tumor is cooled to the lowest temperatures, as a result, it is destroyed and falls off on its own. The procedure is carried out using a special apparatus. Sometimes a cotton swab is simply soaked in liquid nitrogen and then applied to the affected skin. The process takes a few minutes.
2-3 procedures are required for the complete disappearance of the tumor. Nitrogen removal on the facial surface is not applicable.
Painful discomfort after the procedure is a natural phenomenon. Initially, a bubble forms at the site of the wound. It is filled with white or scarlet liquid, depending on the depth of exposure.
- Until complete healing, the bladder should not be injured.
- Apply only a gauze pad to the bubble.
- Allowed to come into contact with water.
- It is permissible to bandage the affected area.
The bubble takes longer to heal under the bandage; air baths are necessary, then a crust forms faster. If it gets wet and does not heal, use a healing ointment. If the crust falls off and a red spot remains, it means that the skin will soon be renewed. After complete healing, no traces of damage remain.
Radio wave method
The radio wave procedure is non-contact. It is easy to remove a tumor with a radio knife. When damaged by a powerful stream of radiation, the cells evaporate. The process is painless. There is no risk of infection after using a radioknife.
This method is indispensable for removing hard-to-reach keratomas, and only small formations need to be removed using this method.
- Presence of diabetes mellitus.
- Diseases of the heart and vascular system.
- The radio wave procedure is carried out after complete recovery of patients with respiratory diseases.
When removed using the radio wave method, healing proceeds in stages. At first, a slight sore appears, which will disappear on its own over time. It is necessary to protect it from mechanical influence. If a rough crust appears within 6 days, do not wet the healing area of skin with water.
It is not recommended to use decorative and other cosmetics based on alcohol or ethanol analogues for several months. Also, you should not overuse sunbathing or visit a solarium.
There are no complications from removal with surgitron. It is recommended to inspect the surgical site daily. If a lump has formed and the wound is swollen, consult a doctor.
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is a process using high-frequency current, as a result of which high temperature cauterizes the tumor. After cauterization, it is completely eliminated. Skin renewal occurs after a week and a half.
This method is used to combat small tumors, since after healing there are no scars. It is better not to use the method on the face and visible surfaces of the body. Despite its safety, treatment with electrocoagulation is contraindicated for arrhythmia, hypertension, and angina.
Pain and swelling that occur after electrocoagulation do not require treatment or additional observation and go away on their own after a couple of days. If the skin turns red after interacting with the electrocoagulator, this will quickly go away.
Rough crusts that form after removal will come off on their own after 10 days. To prevent the removal site from becoming inflamed, avoid contact with water. Be sure to treat with a weak solution of 5% potassium permanganate and a solution of furatsilin. It is prohibited to use cosmetics around the treated wound.
Surgical intervention
This method is applicable for large growths, because, in essence, an operation is performed where the doctor uses a scalpel to remove the keratoma and the skin in contact with it, then stitches are applied. A specialist can remove very large formations by grinding using a special brush.
The surgical operation involves extensive local damage to the skin, so local anesthesia is typically used. The operation is effective; the tumor is completely removed in one go. However, the wound takes longer to heal compared to other removal methods. A visible scar remains at the site of the lesion.