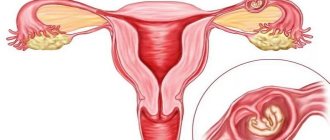
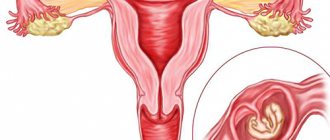
To accurately confirm an ectopic pregnancy and perform the appropriate surgery, laparoscopy is used. This is a progressive treatment and diagnostic method that avoids traditional surgery.
Laparoscopy for ectopic pregnancy is performed only if the fertilized egg is in the fallopian tube (tubal ectopic pregnancy). In this case, laparoscopy is performed using two methods:
- Tubotomy is a laparoscopy method in which the fallopian tube is opened and the fertilized egg is removed, after which the entire abdominal cavity is cleared of egg remnants and blood clots. The main advantage of tubotomy is the preservation of the fallopian tube as a fully functioning organ.
- Tubectomy is a laparoscopy method that is used in case of severe damage to the fallopian tube and requires its mandatory removal. In case of irreversible damage to the fallopian tube, this organ can no longer perform its functions, and the risk of recurrent ectopic pregnancy after laparoscopy is very high. With this diagnosis, as a rule, doctors insist on removing the damaged organ to avoid further complications.
It should be remembered that the sooner a woman consults a doctor, the more successful laparoscopy will be during ectopic pregnancy, which reduces the risk of complications after surgery.
Laparoscopy after an ectopic pregnancy may be required in case of formation. In this case, the operation is performed in order to separate the adhesions and restore the patency and basic functions of the fallopian tubes.
Recovery after laparoscopy for ectopic pregnancy
The postoperative period for laparoscopy for ectopic pregnancy is about 5-7 days. On the seventh day after surgery, the sutures are removed. In the first two weeks after laparoscopy, it is recommended to take only a shower and treat the wounds with iodine. For 1-2 weeks, it is recommended to adhere to a gentle diet, not to load the stomach with fatty, hot and spicy foods.
Sex after laparoscopy for ectopic pregnancy is permitted after the menstrual cycle has been restored, that is, after the end of the first menstruation that began after the operation.
You can plan after 3-4 months, if there are no contraindications from your doctor. Although in some cases the possibility of pregnancy occurs within 1-2 months after surgery. In any case, consultation and observation by a doctor is mandatory for a woman who has undergone laparoscopy.
Laparoscopy is a type of surgical intervention that is performed under general anesthesia using special instruments inserted through small punctures in the anterior abdominal wall. Due to the fact that laparoscopic surgery does not require cutting into the anterior abdominal wall, it is a gentle and minimally invasive technique. In addition, there is minimal blood loss during laparoscopy. Thus, laparoscopy is the optimal surgical technique for the treatment of ectopic pregnancy, since it has the following advantages:
- No scars on the skin of the abdomen, since instruments are inserted through small punctures;
- Minor blood loss;
- Minimal intervention in organ structures during surgery;
- Minimal risk of developing adhesions in the pelvis after surgery.
Laparoscopic surgery is performed under general anesthesia.
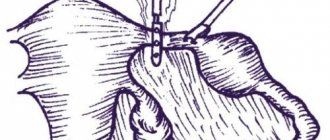
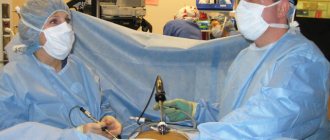
To insert instruments, three punctures with a diameter of about 10 mm are made on the anterior abdominal wall. Through punctures, a small amount of inert gas is first introduced into the abdominal cavity, which is necessary to ensure that the organs diverge as much as possible in different directions. When the abdominal organs are separated from each other at the maximum distance, it is convenient for the surgeon to perform manipulations. Then a lighting device, a camera and a holder for a surgical scalpel, needle, etc. are inserted into three punctures. The lighting device and camera capture the entire picture in the abdominal cavity and display the image on the screen. It is by looking at the screen that the doctor sees everything that is in the abdominal cavity. Then, controlling his own movements according to the picture on the screen, the doctor takes the third manipulator, in which the scalpel is clamped, and performs the necessary manipulations with the fallopian tube. After removing the fertilized egg and the remains of inflamed and destroyed tissue, the doctor replaces the scalpel with a needle and sutures the organs. Then the instruments from the three punctures are removed, and one or two cosmetic stitches are applied to the punctures. As a result, the wounds heal well, leaving virtually no scars on the skin. During laparoscopy, the doctor assesses the condition and degree of damage to the fallopian tubes, on the basis of which a decision is made on the required amount of surgical intervention. For an ectopic pregnancy, two types of intervention are possible during laparoscopy: tubectomy or tubotomy. Tubotomy is the removal of the fertilized egg through an incision in the fallopian tube, which is sutured after the manipulation. A tubectomy is the removal of the entire fallopian tube in which an ectopic pregnancy has developed.
During a tubotomy, the doctor cuts the wall of the fallopian tube, removes the fertilized egg through the incision and sutures the wound. Tubotomy is an organ-preserving operation, since it allows you to leave the fallopian tube in which the fertilized egg is located. However, a tubotomy cannot always be performed. As a rule, a tubotomy is performed if there are no irreversible changes in the tube that disrupt its normal structure. Tubotomy is possible when an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed before the tube ruptures. If an ectopic pregnancy was detected when the tube had already ruptured, then a tubotomy would not be possible because the tissue structure was too damaged.
Tubectomy is performed when the tube has irreversible changes, for example, after a rupture. A tubectomy is also performed if an ectopic pregnancy develops again in a tube that has previously undergone a tubotomy. If there is a strong adhesive process in the pelvis, then a tubectomy is also indicated. During a tubectomy, the ligaments adjacent to the tube are excised, and then the organ itself with the fertilized egg located in it is removed.
Technologies actively used in modern surgery have not bypassed obstetrics and gynecology - one of them is laparoscopy. Since the internal genital organs are located in the pelvic area, which freely communicates with the abdominal cavity, access to them is carried out in this way. But traditional incisions were too large and traumatic, so doctors resorted to them only in emergency situations.
During laparoscopy, all manipulations are carried out under the control of endoscopic equipment using special instruments passed through probes. This requires only a few small punctures on the abdominal wall, which are performed using a trocar. Therefore, this technology has become widespread not only as a method of surgical treatment, but also as an effective diagnostic procedure.
Laparoscopy is used especially effectively for ectopic pregnancy - although it is the equivalent of surgery, there is no more informative method besides it. The growth in popularity is due to its combined nature - if pathological changes are confirmed, parallel treatment measures are possible. Therefore, elimination of ectopic pregnancy and correction of its complications is currently performed primarily through laparoscopic access.
Concept of method
Patients do not always correctly imagine the technology of the upcoming intervention, as a result of which an appropriate attitude towards it develops. Laparoscopy is considered a surgical option, so preparation for it is carried out in a standard way. A full examination of the patient is carried out in advance to eliminate the risk of possible complications from the procedure.
Depending on how the ectopic pregnancy proceeds, the intervention can be performed in two variations. Each of them has a different volume of manipulations, as well as its own indications for implementation:
- Regardless of the type, anesthesia is first performed - usually combined general anesthesia is used. In this case, a rapid induction of anesthesia is carried out using drugs administered intravenously, after which this state is maintained by inhalational anesthetics.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy for ectopic pregnancy is performed quite rarely - it is a last resort when it is not possible to confirm the diagnosis by other means. In this case, only two probes are inserted into the abdominal cavity - with an endoscopic camera and a clamp for moving organs.
- Therapeutic laparoscopy is used to surgically eliminate a progressive pregnancy, as well as correct complications that have arisen - tubal abortion or rupture of the fallopian tube. In this case, four ports are used - through them an endoscopic camera, a clamp and a pair of working instruments are inserted.
The diagnostic option of the procedure can be immediately expanded to a therapeutic option if, during the examination, complications of an ectopic pregnancy requiring emergency care were discovered.
And grandmothers also say...
Everything that is not harmful to the body is considered beneficial. This is what our grandmothers said and they treated themselves with what Mother Nature provided us. Of course, in those days, ectopic pregnancy was a terrible diagnosis, but adhesions and obstruction of the fallopian tubes were treated with herbs.
Possible consequences after surgery for an ectopic pregnancy will depend on how exactly the pregnancy was terminated: the woman had a simple operation and there was minimal damage to the reproductive organs, or her fallopian tube was removed along with the fertilized egg. If doctors remove the tube completely, it will be difficult to conceive a child in the future. But if a woman is in good health and is young, then there is a chance that she will become pregnant with one tube.
Planning your next pregnancy is best done under the supervision of a doctor. After surgery for an ectopic pregnancy, the specialist will be able to select drug treatment and special physiotherapeutic procedures that will minimize the risk of recurrence of this condition.
Salpingoscopy helps to make a decision in favor of tubotomy or tubectomy during laparoscopy - a detailed examination of another unchanged fallopian tube, which allows you to assess its functionality (pipe patency, presence or absence of adhesions, etc.).
For diagnostic purposes
According to the examination protocol for women in whom an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, laparoscopy is allowed to be performed only at the fourth stage. Previously, the patient must undergo a survey and examination by an obstetrician and a transvaginal ultrasound, after which she should be sent for diagnostic hysteroscopy or determination of the level of hCG in the blood. If these studies do not confirm the diagnosis, then indications for laparoscopy are determined:
- If the results of endometrial scraping obtained during hysteroscopy and histological description show signs of ectopic (outside the uterine cavity) implantation of the fertilized egg. These include structures of reverse development of three stages, Overbeck's light glands, the Arias-Stella phenomenon, as well as plexuses of spiral vessels.
- An increase in the level of hCG in the blood to 10 mIU/ml (but not higher than 2000) with the simultaneous absence of ultrasound signs of a normal “uterine” pregnancy.
In obstetric practice, the second indication is used much more often - the analysis gives a quick and reliable result, which allows you to timely decide on further tactics.
Progressive pregnancy
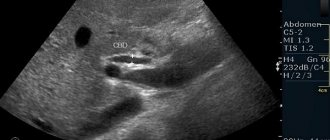
Since the technique is visualizing, doctors focus on direct signs characteristic of pathology in typical cases. Typically, an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed between 7 and 9 weeks, when changes visible through the endoscope camera already appear:
- An indirect manifestation of the disease is an increase in the vascular pattern and dilation of the veins in the area of the broad ligament of the uterus, as well as the mesentery of the fallopian tube and ovary. Moreover, the changes are always one-sided, indicating the side of the lesion.
- In the area of one of the uterine segments, a local thickening is visualized - most often in the widest and most voluminous ampullary section. It has a round or oval shape, and a bluish-pink color that stands out in contrast against the background color of normal tissue.
- The size of the formation can be varied, depending on the stage of pregnancy.
Of greatest interest is the localization of the process in the intramural region, which is located in the thickness of the uterine wall. In the early stages, the characteristic thickening can be almost invisible, plus it can be masked by the apparently healthy tissue of the pipe.
Interrupt
The outcome of an ectopic pregnancy is almost always spontaneous abortion, which can occur in several ways. The development of each of them is accompanied by a vivid clinical picture of an “acute abdomen.” This allows laparoscopy to be used urgently to determine the cause of the symptoms:
- Incomplete tubal abortion is characterized by the identification of a typical thickening in shape, color and size in any part of the fallopian tube. The appearance of the latter also changes - against the background of the pink and shiny peritoneum, its bluish color is noted. And from the opening of the tube, dark blood is released into the abdominal cavity, which is also found in the rectal-uterine cavity and the lateral recesses of the small pelvis.
- With a complete tubal abortion, there is a decrease in the size of the fallopian tube while maintaining its pale bluish color. No active bleeding is detected from its opening. Near it or a little lower on the peritoneum of the small pelvis, a fertilized egg is found - a dense round clot with a purplish-blue color.
- The most unfavorable scenario is a rupture of the fallopian tube. Laparoscopy reveals a defect in its wall with uneven edges, and there are signs of active bleeding.
If signs of complications are detected during the diagnostic procedure, the intervention immediately takes on a therapeutic nature. Depending on the conditions, radical or gentle surgical techniques are performed.
Authorized products
Nutrition after an ectopic pregnancy should be aimed at restoring the functioning of the entire body, namely normalizing hormonal levels, normalizing metabolic processes, promoting scar healing and strengthening the immune system.
What can you eat after ectopic pregnancy surgery:
- milk soup, if milk is allowed;
- broths with pureed chicken meat;
- light soups with cereals and vegetables;
- semi-liquid porridge with water or milk;
- biscuits;
- cottage cheese and other natural fermented milk products;
- vegetables except cabbage;
- berries and fruits;
- a piece of rye, dried bread. White and fresh bread provokes gas formation.
Strawberries and citrus fruits are prohibited. Butter is allowed with restrictions and only in fresh form.
All legumes, cabbage, baked goods and white bread cause bloating. It causes pain to a woman because it acts on an unhealed scar. Doctors recommend drinking plain water, highly diluted juice, fruit juice, jelly, and green tea. Alcohol, soda, coffee and black tea are prohibited.
By following all the doctors’ recommendations and following a diet, a woman will quickly restore her vitality and return to her lifestyle.
After surgery, doctors allow mild patients to eat liquid food, such as soups and cereals in a liquid consistency. The rule here is that there is a small amount of food, but often.
For the purpose of treatment
With the development of surgical techniques, the use of laparoscopy now has virtually no restrictions. The only absolute contraindication to it is hemorrhagic shock in a woman, which requires full intervention. The adhesive process in the pelvic cavity is only a relative limitation - with sufficient experience of the doctor, it is not a serious obstacle.
Previously, open access surgeries were widely used to treat complications of ectopic pregnancy. Thanks to a number of advantages that completely cover the disadvantages, the laparoscopy method is gradually replacing it from practice:
- Small incisions and a shortened duration of intervention determine a parallel reduction in the incidence of early and late complications. This allows for effective surgical treatment in women without fear of life-threatening consequences.
- Laparoscopy makes it possible to carry out sparing operations much more often, as a result of which it is possible to preserve the function of the fallopian tube.
- A small amount of intervention reduces the body’s recovery time, ensuring faster physical and social rehabilitation. Consequently, early activation of the patient in combination with careful manipulations reduces the likelihood of the formation of adhesive disease.
According to the expected outcome of the operation, there are two options for laparoscopy - radical, implying complete or partial removal of the altered tube, or organ-preserving.
Types of operations
The expected extent of intervention is usually determined in advance, although in some cases it may change during a diagnostic examination of the changes. Therefore, even before the start of manipulations, the doctor already assumes what therapeutic actions he will perform:
- “Conservative” operations include squeezing out the fertilized egg (only when it is located in the ampoule), and tubotomy - cutting the fallopian tube and removing the pathological formation. They are carried out only if possible contraindications have been excluded, as well as the absence of complications confirmed during examination.
- Radical operations involve either resection of a section of the fallopian tube or tubectomy—its complete removal. Their implementation is indicated for repeated tubal pregnancy, detected scar changes, rupture of the tube, the size of the ovum is more than 3 centimeters, as well as its location in the intramural region.
A relative indication for radical intervention is the woman’s personal desire - if she does not plan a pregnancy in the future, and provided she has children. In this case, to reduce the likelihood of complications, the affected fallopian tube is immediately removed.
Collapse
Therapy for ectopic pregnancy involves removing the embryo that has implanted in the ovary, oviduct or abdominal cavity. Depending on the period, this can be done either medicinally or surgically. Laparoscopy for ectopic pregnancy is most often performed.
Advantages and disadvantages
Laparoscopy is a modern, low-traumatic surgical treatment method. Its essence lies in the fact that the operation is performed through 3 small holes on the front wall of the abdomen. A laparoscope is inserted into one hole, which is equipped with a backlight and a camera that transmits an image of the internal organs to the monitor.
Operation scheme
Various surgical instruments are inserted into the remaining holes. The abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide, as a result of which its front wall is raised above the organs and a space is formed between them, allowing the doctor to perform surgery.
The advantages of the method include the following:
- the surgeon sees the internal organs more clearly, since the surgical intervention is performed under multiple magnification;
- internal organs are less injured than during abdominal surgery, since their contact with the doctor’s hands, air and cotton-gauze swabs is excluded;
- minimal blood loss;
- short hospital stay;
- there is almost no pain (except for the feeling of abdominal distension, which is observed within 24-48 hours after surgical treatment, as soon as carbon dioxide is absorbed, the discomfort will go away);
- absence of large scars, on the front wall of the abdomen, only three small scars remain, which are barely noticeable;
- short rehabilitation period;
- minimal risk of developing postoperative adhesions;
- the procedure can be carried out simultaneously for the purpose of treatment and prevention.
The disadvantages of laparoscopy include the following:
- surgery is performed under general anesthesia;
- Not all removal of ectopic pregnancies is possible using this method.
Laparoscopy for ectopic pregnancy is indicated if the embryo is localized in the ampulla or isthmic section of the oviduct, and the size of the pathological tube is maximum 5 cm.
If the diameter is larger, then there is a high probability of bleeding and getting the tube through a small incision in the abdomen is problematic. Also, due to the risk of blood loss, laparoscopy is not performed when the embryo is located in the rudimentary uterine horn.
Pregnancy after surgery
While for some women the issue of planning a pregnancy is not at all difficult, for others it presents a whole dilemma. The second group includes women who have certain health problems, as well as those who had to undergo surgery on internal organs. They are the ones who are interested in whether pregnancy is possible, and if so, whether it will be dangerous and whether it will take place at all.
Of course, the operation of the operation is discord. However, we can safely say that after the vast majority of existing surgical interventions, you can become pregnant three months after complete recovery. Remember, we are not talking about the operation itself, but about recovery, which, in special cases, can take six months or a year. In addition, it must be taken into account that the nature of the operation undergone and the place where it was carried out are of particular importance. If we are talking about abdominal surgery, in which the surgeon cuts the tissue, then it will take much more time than after performing the operation using the laparoscopic method, which involves puncturing the body in a certain place.
As for the organ on which the operation was performed, this plays one of the leading roles. For example, during surgery to remove varicose veins, you can become pregnant quite quickly: in a month or two. In this case, it is necessary to take into account that as the tummy grows, the load on the lower limbs increases, which can cause expansion of other veins. This fact has no effect on the baby himself.
cleaning is painful pregnancy has stopped All rights to the materials posted on the site are protected by copyright and related rights legislation and cannot be reproduced or used in any way without the written permission of the copyright holder
But after undergoing ovarian surgery, you can plan a pregnancy no earlier than 3-6 months later. If a woman has undergone surgery to remove the tube as a result of an ectopic pregnancy, it can be quite difficult to get pregnant. However, in many cases this is possible, and therefore you should not give up. You can't plan
Source
Types of laparoscopy
Laparoscopy for ectopic pregnancy happens:
- diagnostic;
- operational.
Diagnostic laparoscopy helps to examine the internal organs, determine whether the oviduct is ruptured or not, assess its condition, and determine where the embryo is located.
Surgical laparoscopy, depending on the implantation of the fertilized egg and the severity of the development of an abnormal pregnancy, can be performed in combination with such surgical interventions as:
- (Tubotomy) - dissection of the wall of the oviduct to remove the embryo. Such laparoscopy for ectopic pregnancy with preservation of the tube allows you to restore its function.
- (Tubectomy) - complete removal of the tube, performed when the oviduct is severely damaged and its function cannot be restored.
- Resection of a section of the fallopian tube is a segmental or partial removal of the tube, which allows plastic surgery of the oviduct.
- or extrusion - such an intervention is carried out when the trophoblast is detached, it is squeezed out of the oviduct, while the fallopian tube is preserved.
- - amputation of the ovary, performed when an ovarian pregnancy develops.
- — the ovary and fallopian tube are removed at the same time.
- Hysterotomy is a dissection of the uterine wall; this operation is performed if the embryo is very deeply implanted.
- Hysterectomy is the amputation of the uterus; it is used in severe cases when the fertilized egg is localized in the cervical canal.
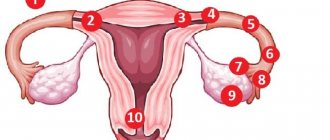
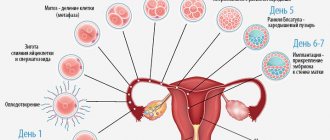
What is ectopic pregnancy and what are the causes of its occurrence?
Ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy is the development of a fertilized egg when its location is incorrect. Normally, the fertilized egg moves through the fallopian tubes into the uterus and attaches to the mucous membrane there. But if a woman has anatomical abnormalities or diseases, the egg may be localized in other places:
- cervix;
- abdominal cavity;
- fallopian tubes;
- ovaries.
The method of terminating an ectopic pregnancy will depend on where the fertilized egg is located. In the vast majority of cases, surgical intervention is used for this.
If an embryo is detected in the cervix, the entire uterine cavity is scraped. In other cases, laparotomy and removal of the fertilized egg will be required. In modern gynecology, instead of laparotomy (gastric section), laparoscopy is increasingly used - a low-traumatic operation that uses miniature instruments. They are inserted into the abdominal cavity through a small hole in the peritoneum.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation after an abnormal pregnancy is a very important period; how it goes depends on whether the woman will be able to have children in the future. It allows you to prevent the development of adhesions, eliminate hormonal imbalances, and restore reproductive function.
In the postoperative period, antibiotic therapy is prescribed to avoid infection. If pain is observed after surgery, it is possible to take analgesics.
After surgery, a special diet is indicated. You need to eat little and often. Porridge, broth, and cutlets are allowed.
A week after surgery, physical therapy may be prescribed to speed up the recovery process. The doctor may prescribe:
- laser treatment;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetotherapy.
After completion of the postoperative period, the patient is discharged on sick leave.
Recovery from surgery varies from woman to woman.
Menstruation after ectopic pregnancy and laparoscopy begins on day 25-30. If bleeding is observed earlier, this indicates that bleeding has begun after surgery. When menstruation is absent for more than a month, this indicates a hormonal imbalance. In this case, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. You should also visit a specialist if there is abnormal discharge from the genital tract after laparoscopy of an ectopic pregnancy that has an unpleasant odor, as this may indicate an infection.
Sex after laparoscopy is allowed after a month, during which time the woman’s body will recover. If a woman experiences pain during intimacy, this may indicate the development of inflammation or postoperative complications.
In addition, after laparoscopy for a month it is not recommended:
- visiting the bathhouse and sauna, showering is allowed;
- sunbathe;
- lift weights (you are allowed to lift objects up to a maximum of 3 kg);
- do physical education.
How to prevent another ectopic pregnancy
A woman must do everything in her power to ensure that the pregnancy proceeds normally. One of the causes of ectopic pregnancy is sexually transmitted diseases.
If a woman is not married, then in order to protect herself from sexually transmitted infections, she needs to use a condom. In addition, it is recommended to be tested for infectious diseases transmitted through sexual contact 1-2 times a year, and also to stop smoking.
If you take care of your health yourself, you can expect a pregnancy without pathologies.