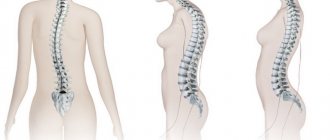
Today, medicine knows a lot of diseases affecting various parts of the spine. However, one of the most common and dangerous pathological processes is considered to be the formation of an intervertebral hernia.
A hernia can form in any part of the spinal column, and despite the fact that the formation rarely appears in the cervical spine, it is the one that poses the greatest danger. For this reason, it is important to understand what this pathology is, the reasons for its occurrence, what are the symptoms and treatment in the case of a herniated cervical spine.
Mechanism of development of intervertebral hernia of the neck
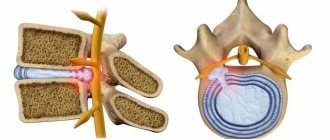
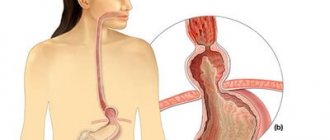
Between the human vertebrae there is a specific layer - the intervertebral disc. Its central part, the nucleus pulposus, is filled with a jelly-like substance and plays the role of a shock absorber.
Outside, along the perimeter, the nucleus pulposus is surrounded by a fibrous ring, which consists of a substance resembling a muscle tendon in density. When this ring weakens in some place, the principle “where it is thin, it breaks” comes into force: the jelly-like core immediately flows into the place of rupture, tries to break out and put pressure on the spinal cord or the nerves extending from it. A protrusion of the nucleus that appears outside the vertebrae is an intervertebral hernia.
The cervical (cervical) region is the most dangerous localization for the formation of a hernia. It is in this area that the centers of the spinal cord are located, which give rise to the nerves going to the respiratory muscles (to the main one - the diaphragm, and to the additional ones - the intercostal respiratory muscles). Paralysis of this muscle means stopping the flow of air into the lungs. If help arrives in time, the person can still be saved by connecting him to an artificial respiration apparatus.
The spinal cord (in its cervical region) also contains other important centers that give commands to the heart, esophagus and hands. The vertebrae of this area are in close contact with the carotid arteries, jugular veins and their branches, which provide nutrition to the organs of the neck, head, and most importantly, the brain. If a hernia in the cervical spine “shoots” between these vertebrae, an ischemic stroke may develop.
What are the features of a C5-C6 disc herniation? Why is it especially dangerous?
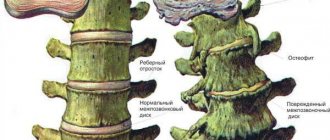
Doctors call ruptures of the fibrous rings in the discs between the 5th and 6th vertebrae of the neck “C5-C6 disc herniation.” This is one of the most common locations for a neck hernia, which is often combined with protrusion, instability, segmental insufficiency, and arthrosis in the C4-C5, C6-C7 vertebrae.
This disease is often preceded by chronic pain, osteochondrosis, limited neck mobility, and disc protrusion at the initial stage, most often circular.
Uncovertebral arthrosis in the C6-C7 vertebrae indicates the existence of osteochondrosis with complications: osteophytosis and the formation of pathological joints.
In medical practice, only the posterior (also called dorsal) type of hernia plays an important role, which can contribute to the narrowing of the intervertebral canals and canals of the spinal cord.
If a nerve root is pinched, vertebrogenic radiculopathy of vertebrae 5-6 may occur.
Before this disease appears, it is preceded by osteochondrosis of the neck in the area of vertebrae 4-5, 5-6. Due to the fragility of the intervertebral disc, microtrauma occurs and protrusions form. After some time, a protrusion appears.
Causes of cervical hernia
An intervertebral hernia in the cervical region is found in every thousand people; Men get sick more often. The “favorite” age is over 60 years old.
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
| Three causes of pathology | Factors that increase the chances of developing a hernia |
| 1. Age-related disruption of the blood supply to the intervertebral discs, due to which the fibrous ring becomes more “dry” and brittle. | Neck injuries |
| 2. Osteochondrosis, in which the intervertebral disc is destroyed due to metabolic disorders in it. | Disturbed general metabolism (caused by diseases of the endocrine organs) |
| 3. Frequent injuries to the cervical spine: professional activities in which a person’s neck is often forced to take an unnatural position, move jerkily, and turn sharply. Example - athletes: boxers, wrestlers, racers, basketball players. | The habit of drinking little fluid (less than 30 ml per day per kg of body weight) |
| Smoking | |
| Prolonged neck immobility during the day due to sedentary work | |
| Spinal diseases (Bechterew's disease, infection of the vertebrae) | |
| Congenital anomalies of the structure or relative position of the cervical vertebrae |
What types are there and their associated symptoms?
Depending on which segment of the cervical vertebra is damaged, the following types of hernia of the cervical spine are distinguished:
- Intervertebral hernia C2-C3 can provoke disturbances in visual functions, heart function and respiratory organs. A person also feels that his tongue often goes numb, his throat hurts, and the timbre of his voice may change. Other symptoms are also concerning: dizziness;
- decreased appetite;
- lump in the throat;
- frequent headaches.
- frequent headaches;
- change in voice, it becomes rough, hoarse;
- dyspnea;
Symptoms of the disease
Initial manifestations of a cervical hernia:
- neck discomfort;
- periodic crunching when turning the head (especially if you turn sharply);
- When turning and tilting the head, pain occurs in the neck.
Later symptoms of pathology depend on which disc is damaged by the herniation.
Symptoms of a herniated disc depend on its location. The diagram shows which areas of the spinal cord in the cervical region are responsible for which functions, and what problems arise when they are damaged. Click on photo to enlarge
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
| Localization of the hernia | Symptoms |
| If the disc is affected between 1 and 2, between 2 and 3 or 3 and 4 vertebrae | In the worst case, a hernia manifests itself as breathing problems and surges in blood pressure. At best: impaired sensitivity on the face; “lumbago” simulating electric ones, which can “go” from the neck to the shoulder or to the head |
| Between 4th and 5th vertebrae | Pain in one shoulder, weakness when flexing and extending the shoulder, as well as abducting it to the side |
| Between 5th and 6th vertebrae | It is difficult to bend the arm at the elbow and wrist joints. Even without movement, pain appears in the arm, which spreads from the shoulder joint to the thumb. In addition to this pain, the patient feels tingling, burning, numbness on the outer side of the forearm |
| Between 6th and 7th vertebrae | It is difficult to straighten the forearm and fingers. Burning and tingling extends from the back of the shoulder to the middle finger |
| Between 7 cervical and 1 thoracic | A feeling of “cottoniness” in the brush, which causes the handshake to become “sluggish”, and it is difficult to write, sew, and perform small movements with the brush. The patient feels pain accompanied by numbness, tingling of the entire shoulder and forearm to the little finger |
If the ruptured nucleus pulposus of the hernia compresses the vessels supplying the brain, the following symptoms are noted:
- noise in ears;
- unsteadiness of gait;
- imbalance: a person may describe it as “the head swam with a completely clear consciousness”;
- headache;
- decreased visual acuity;
- “flies” before the eyes;
- difficulty concentrating on a task, decreased attention.
Prevention
It is impossible to completely prevent intervertebral hernia of the cervical spine in the presence of organic skeletal diseases, but if you reduce external risk factors to a minimum, you will be able to significantly reduce the risk of its occurrence.
In order not to look for an answer to the question of how to treat a cervical hernia, it is better to constantly follow certain rules.
Necessary:
- try to keep your back straight;
- avoid significant overload of the spine;
- constantly stretch your neck, especially if it is often in a static position;
- avoid uncomfortable positions;
- replace the pillow with a small one and choose an orthopedic mattress.
Intervertebral hernia of the cervical spine only at first glance seems like a minor disease, but it can lead to many negative consequences.
If you experience any symptoms that indicate the development of pathology, immediately go to the doctors.
It is possible to successfully get rid of pain and complications only if you seek medical help in a timely manner.
Diagnostic methods
To make a correct diagnosis, you need to undergo examination by a neurologist.
The symptoms we talked about above also occur in other diseases:
- spinal cord tumors;
- metastases in the spine (tumor cells brought by blood from a cancerous tumor);
- damage to the spinal cord in diabetes mellitus,
In addition to examining and determining reflexes, the neurologist will prescribe:
- radiography of the spine;
- electromyography (study of electrical activity of muscles);
- myelogram (x-ray of the spinal cord, when a contrast agent is injected into the space above it using a lumbar puncture);
- magnetic resonance imaging (it better “sees” the substance of the spinal cord itself) or computed tomography (it better visualizes the bones).
What's the diagnosis, doctor?
Trying to diagnose yourself is not a good idea.
The symptoms listed above, even in their minimal manifestation, are a reason to visit a neurologist. The doctor will check reflexes and sensitivity in the shoulders and arms, then find out the location of the hernia and prescribe an in-depth examination. There are four methods for detecting a hernia:
- Radiography.
- CT (Computed tomography).
- MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging).
- Myelogram.
Let's take a closer look at each of them.
Radiography
Radiography is a method of studying internal organs using x-rays. The final image is projected onto a special film or paper.
X-ray
Pros: fast, inexpensive, accessible.
Cons: indicates only indirect signs of pathology.
CT (computed tomography)
Computed tomography, like radiography, is a method of examining the patient’s internal organs using x-rays. The difference is that X-rays provide a two-dimensional image, while CT provides a three-dimensional image. Thanks to the special structure of the CT machine, which consists of a ring-shaped contour, many images are obtained from different angles. The images are processed by computer.
CT scan
Pros: CT allows you to accurately assess the condition of the cervical spine.
Disadvantages: this research method is contraindicated for pregnant and breastfeeding women.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
Magnetic resonance imaging, like computed tomography, processes a lot of images and ultimately produces a three-dimensional image of the imaged area. However, MRI uses electromagnetic waves rather than X-rays. Images are obtained by reflected pulses emanating from the area under study. They are captured by equipment, processed by a computer, and then a 3D image is created.
Magnetic resonance imaging
Pros: accuracy and information content of the analysis due to good visibility of soft tissues.
Cons: MRI cannot be performed on patients with a pacemaker or those who have ferromagnetic, metal or electronic implants.
Myelogram
A myelogram is a research method in which a special contrast agent containing iodine is injected into the spinal canal through a special needle. Then the necessary photographs are taken. They show how bulging the intervertebral disc is and whether a pinched nerve has occurred.
Myelogram
Pros: thanks to the introduction of a contrast agent, the degree of narrowing of the spinal canal is clearly visible. This allows you to determine how advanced the disease is.
Cons: carried out only according to strict indications.
Conservative and surgical treatment
The intervertebral disc does not heal quickly and completely, like cut skin or broken bones. It is also constantly subject to the load of the overlying areas of the body (in the case of the cervical vertebrae, this is the head), which also complicates recovery.
Treatment goals:
- temporarily immobilize the area of the spine with the “sick” disc;
- improve nutrition and eliminate inflammation with medications;
- strengthen the muscles that are involved in supporting the spine so that after the period of immobilization the situation does not worsen even more (it is necessary to prevent the problem vertebra from “sliding” towards the weakest muscles).
A herniated disc in the cervical spine is treated conservatively and surgically. In the absence of signs of respiratory and circulatory disorders, conservative therapy is carried out.
Conservative therapy
For severe pain in the neck, back, dizziness, or visual or hearing impairment caused by a herniated disc, the patient is prescribed bed rest for 5–7 days. The neck is secured with a Shants collar.
The patient is prescribed:
- medicines,
- physiotherapy,
- exercise therapy,
- additional types of therapy.
The Shants collar is used during exacerbation of the disease
Drug treatment
For intervertebral hernia, 4 groups of medications are used:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: ibuprofen, diclofenac, celecoxib and others. They are used in the form of tablets or injections into a muscle or vein. These medications eliminate inflammation and swelling of the nerve compressed by the herniation.
- Muscle relaxants relax the muscles that are “clinging”, trying to fix the cervical spine affected by a hernia.
- Chondroprotectors prevent further destruction of the fibrous ring in the affected intervertebral disc.
- A blockade - the introduction of anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs directly into the affected area - is carried out in case of severe pain in rare cases.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment must be used in conjunction with medication. The following methods are used:
- magnetic therapy;
- stimulation of certain muscles with weak current;
- paraffin and ozokerite applications (paraffin and ozokerite are petroleum distillation products that are hard when cold, but when heated they soften and emit heat for a long time);
- electrophoresis with novocaine.
Exercise therapy
Treatment with exercises begins when the person is on strict bed rest (in the first 5–7 days of treatment). Classes during this period consist of periodic sessions of diaphragmatic breathing.
After about a week (a neurologist will indicate the exact timing in your case), movements in the elbow and wrist joints begin (circular, shaking, squeezing expanders). You can't move your neck.
When the doctor allows you to remove the Shants collar, physical activity increases. The exercise therapy complex includes 7 exercises:
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
| Initial position | Exercise |
| Lying on your back | Press the back of your head onto the couch |
| Same | Press the assistant's hand with your forehead |
| Lying on your stomach | Press your forehead on the couch |
| Same | Press the back of your head into the assistant’s palm |
| Sitting | Press the assistant’s palm first with your forehead, then with the back of your head. As you heal, increase the resistance force of the other person's hand. |
| Sitting, brushes lie on the table | Raise and lower your shoulder girdle |
| Sitting | Very carefully, at a slight angle, turn your head first to the left, then to the right. This exercise should not hurt. If you feel dizziness, pain or other unpleasant symptoms, stop turning your head. |
How to treat a spinal hernia surgically?
Treatment should be started only after the diagnosis has been accurately confirmed by a doctor. To do this, the doctor needs to do a lot of research; he must accurately indicate the location and size of the intervertebral hernia. Only after this treatment methods are selected. Doctors often resort to surgical treatment, but you can do without it.
If you do not want to undergo surgery, you can choose from many other methods that are most effective and acceptable to the patient.
Then treatment is aimed at relieving pain, stopping the development and complication of the disease, and preventing the appearance of new hernias.
The very first stage of treatment will be relief of pain symptoms. The patient must remain in bed for some time and take medications that prevent inflammation and have an analgesic effect. They do everything to relieve the pain.
Painkillers do not relieve pain, they only temporarily mask it; at this time, anti-inflammatory drugs act, which relieve inflammation, which, in turn, reduces the pressure on the nerve endings or removes it altogether.
The second stage consists of direct action on the disease, prevention and prevention of disease progression. Here, most often, you can do without medications. It is enough to regularly visit a massage therapist and do preventive exercises at home. Then the intervertebral hernia will no longer bother the patient.
- Acupuncture – relieves tension and pain well, has a good effect on joints, strengthens them and tones them. Prevents the occurrence of inflammatory processes.
- Manual procedures. In a short time, the doctor painlessly returns the discs to their places.
It is better not to delay the treatment of a hernia, then the patient will be able to do without surgery. If you use only pills, then you should not forget that they only relieve pain without eliminating the cause, while the disease continues to progress, the consequences are disappointing. And you will need more than one operation, which is very common. And even if the patient still resorts to surgical treatment, he will need a restorative course.
It is possible to cure an intervertebral hernia of the cervical spine without surgery; this treatment option is considered the most extreme. But the choice remains with the patient.
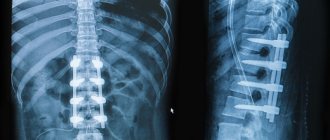
A hernia is operated on when conservative methods are ineffective. And this happens, depending on the characteristics of the body and the condition of the hernia. If the combat symptom does not go away or the hernia becomes larger and causes disruption to the functioning of other organs, then it is operated on.
- The front surface of the spine - an incision is made in the problem area and the part interfering with the nerve is removed, then a substance is injected that helps accelerate tissue regeneration, the vertebrae are fused and its mobility is lost.
- The back surface is the same as the front one, only on the other side.
- Cervical disc replacement is practiced. The damaged disc is removed and an artificial one is installed in its place. This method helps maintain vertebral mobility.
- Micro endoscopic discectomy is a special method of spinal surgery. The incisions are made minimal to allow the device to enter, the growths are carefully and one by one removed, and the canals of the vertebrae are cleaned. This operation lasts about an hour, depending on the complexity.
If the disease is uncomplicated, the patient is prescribed a number of medications.
A herniated disc in the cervical spine can be treated without complications using medications prescribed by a neurologist.
During the therapy period, the patient is monitored and the effectiveness of the treatment is assessed. If the condition does not return to normal and the size of the protrusion is more than 3 mm, a decision is made on surgical intervention.
What are the most common signs of a C5-C6 hernia?
When a hernia occurs in this area, infringement of the sixth nerve root or stenosis of the spinal cord canals occurs (this depends on the type of hernia).
With a disease such as a herniated cervical vertebrae, completely different symptoms can occur. We are talking specifically about a C5-C6 hernia.
Firstly, there is pain and numbness in the thumbs and index fingers, the sides of the arms, hands, neck, and headache. Secondly, this is a decrease in the reflex of the biceps muscle, the possible appearance of weakness when abducting and turning the arms inward. Thirdly, slight weakening when extending the hands and decreased mobility in the neck.