Lumbar lordosis - what is it?
Lumbar lordosis is a natural curve in the lower part of the spine, concave inward. Lordosis of the lumbar spine is considered normal only within certain limits, determined by the angle of curvature. Some were unlucky to be born with such a pathology, and some acquired it as a result of an unhealthy lifestyle, excessive stress, illness, etc. Excessive bending in the lower back can cause pain and spinal diseases.
Lordosis often affects the fair sex in adulthood (from about 30 years old) and is a consequence of bearing a child.
There are some parameters that characterize lumbar lordosis. With their help, make a conditional division into types.
Depending on the root cause of the pathology:
- Primary lumbar lordosis - when the unnatural curve is caused by benign or malignant formations inside the body, congenital pathologies of the vertebrae;
- Secondary – when the disorder is caused by mechanical damage to the spinal column.
Depending on when the disease appeared:
- Congenital lordosis - the disorder manifests itself in childhood, but it is believed that abnormal changes were already present at birth;
- Acquired lordosis - pathology develops under the influence of any factors (trauma, tumor, disease).
Depending on the type of deviation:
- Hypolordosis - the lumbar curve is either absent or much less than normal;
- Hyperlordosis - the lower back is bent inward at too great an angle.
What are lordosis and kyphosis
These 2 concepts are similar and often have the same causes. The difference is that with lordosis there is a forward bend, and with kyphosis - backward .
Most often, kyphosis develops in the thoracic region. Pathology can occur in both children and adults. Excessive backward curvature contributes to changes in the remains, and over time leads to irreversible pathologies in the spinal column, causing the development of characteristic symptoms (pain in the affected area, limited mobility).
The disease often develops in childhood . In this case, the child has a bending forward, not backward, as with kyphosis .
The cause of the development of curvature is considered to be incorrect posture, when the child has a stoop, but at the same time the baby holds his head straight. This situation contributes to the development of a disease that initially does not manifest itself. Therefore, many parents often do not notice warning signs, however, the disease continues to develop, turning into a more complex form. We recommend that you read articles about cervical and lumbar lordosis.
Causes
Since lumbar lordosis can be either congenital or acquired, there are many reasons for its appearance. Factors should be divided into two groups: for congenital pathology and acquired. If lumbar lordosis has bothered a person since birth, the following factors contribute to this:
- The pathology bothered the parents or one of them;
- There were any malnutrition of the fetus in the womb;
- Injuries to the pregnant mother;
- Incorrect delivery, which led to injury to the baby.
If the pathology appeared in adulthood or adolescence:
- In pregnant women, the curve in the lower back increases; this pathological process is associated with increased load. After childbirth, after a certain time, the disease goes away on its own;
- A complication of flat feet is an increased bend in the lower back;
- Osteochondrosis and all its complications, including Schmorl's hernia (a vertebra may collapse) can lead to lumbar hyperlordosis;
- Mechanical damage to the structure of the spinal column;
- Severe sprains or tears along the spinal extensor muscles;
- Various types of inflammation of the spine;
- Radiculitis and its complications;
- Sedentary lifestyle, constant sitting;
- Overload from heavy sports with spasms of the lower back muscles;
- Impaired metabolism;
- Abuse of nicotine and alcohol.
Reasons for the development of lordosis
Physiological lordosis does not have a negative effect on the human body, but the pathological variety has many unpleasant consequences.
Among them, it is especially worth highlighting the displacement of organs and poor protection of bone tissue and joints. It is important to know what factors can provoke the development of this pathological process and try to avoid them.
The disease is hereditary in nature; the risks of hyperlordosis increase significantly if the mother suffered a spinal column injury while carrying a child.
The acquired pathology begins to manifest itself when the patient reaches 30 years of age . Medical experts explain this by weakness of muscle tissue and the fact that during this period of life people spend most of their time in a sitting position.
The training period also has an impact. These factors provoke further development of the disease.
To understand what lordosis is, you need to know the reasons for its development:
- weakened muscle tissue of the lumbar region;
- disturbances in the functioning of the hip joints;
- hernia of the spinal column and other pathologies of a chronic nature;
- mechanical damage to the spine;
- malignant tumors of the spinal column or cancerous tumors in nearby areas;
- The risk of developing lumbar hyperlordosis increases during pregnancy.
Expectant mothers often experience an increase in prolapse of the spinal column, which is explained by a shift in the center of gravity as the fetus increases in weight and height.
It is increasingly difficult for the muscle tissues of the lumbar region to hold the spine in the correct position. After the birth of a child, as weight decreases, the spine recovers on its own.
Symptoms
Symptoms for this pathology vary. It all depends on the patient’s lifestyle, the degree of progression of the pathology, the cause that caused it, etc. The lower back bends excessively or is excessively leveled. Manifestations of a minor violation will be minimal; the person may not even understand what it is. There may be almost no discomfort, except perhaps fatigue. The pathology will manifest itself a little later.
As the angle of bending increases, pain occurs, which intensifies with voluntary and involuntary arching of the back. A person’s gait changes, his posture deteriorates, his stomach goes forward, and his buttocks go back.
With hypolordosis, the picture is somewhat different: the lower back becomes flat, the back is rounded, and the pain is concentrated in the lower back itself.
In both cases, the pathology is dangerous and you need to see a doctor to get quality treatment. In addition to the fact that a person is overcome by pain, the risk of many diseases increases. Here are some manifestations:
- Pain radiating to the buttocks;
- Loss of sensation in the legs, numbness;
- It is difficult for a person to walk for a long time, pain quickly arises when moving;
- Disruption of the pelvic organs;
- Women experience increased pain during menstruation;
- In men, potency may be impaired;
- Disturbances in the digestive system.
Classification
Lordosis can be lumbar and cervical. Lumbar lordosis is caused by pathologies and diseases of the spine, hip joints, hip dislocation, rickets, thoracic or cruciate kyphosis, osteochondrosis, coxarthrosis, diseases of the muscles and nerves of the spinal column.
Lordosis is divided into:
- Physiological – lordosis that occurs during normal growth and development of the body.
- Pathological – deep curvature of the spinal column at the site of physiological lordosis due to the action of predisposing factors and causes stimulating the disease.
According to the causes of occurrence, they distinguish:
- Primary, which occurs as a result of a disease of the spinal column.
- Secondary, which occurs as a consequence of any disease of the body as a whole.
According to the timing of occurrence, lumbar lordosis is divided into:
- Congenital.
- Acquired.
According to the degree of curvature of the spine, there are:
- Hyperlordosis is an excessive forward curvature of the spine in the lumbar region;
- Hypolordosis is a flattening of an existing physiological lordosis in the lumbar region.
With lordosis, some physiological postures are inaccessible to a person.
For example, hyperlordosis of the cervical spine is accompanied by limited flexion and extension of the head, as well as difficulties when trying to tilt it towards the shoulder girdle. Pathological lordosis negatively affects the work of all internal organs - the stomach, intestines, kidneys, liver and other organs, affects the mobility of the spine, and complicates the work of the chest and abdominal cavity.
Lordosis has characteristic areas of localization:
- Lordosis in the lumbosacral spine is located in the region of 3–4 vertebrae.
- In the cervical region, lordosis occurs at the level of 5–6 vertebrae.
Depending on the causative factor, the disease is classified into:
- Primary.
- Secondary.
Primary hyperlordosis is an independent disease associated with damage to the vertebrae.
With it, the anatomical shape of the cervical vertebrae is disturbed, which on the radiograph look like a parallelogram with the apices directed downward.
Secondary pathology occurs against the background of damage to the spine in other parts, as a compensatory reaction to reduce the shock-absorbing load on the spinal column. In older people, the disease is often combined with osteochondrosis (reduction of intervertebral spaces) and spondylosis (fusion of vertebral segments with each other).
Diagnostics
Knowing what lordosis in the lower back is, you can understand for yourself whether you have it or not. This method of self-diagnosis can only be applied to hyperlordosis - when the lower back is too concave.
You can simply stand point-blank against the wall, straighten your back and check whether your hand can fit between your lower back and the wall. If so, you should contact a traumatologist.
The traumatologist conducts an initial examination, probes some problem areas, and does a full interview of the patient. It is important to independently notice all manifestations of pathology; this will be very important for making a diagnosis and future course of treatment.
As with many spinal pathologies, there are several types of diagnostics for low back pain:
- Radiography is a simple and accessible examination method that provides general information about the pathology, but sometimes it is not enough;
- Computed tomography is an excellent examination method; it provides a very detailed image of bone tissue, but does not affect soft tissue lesions and is contraindicated for pregnant women;
- Magnetic resonance imaging is the most effective diagnostic method, allowing you to find out everything about the disturbing pathology, find out all the little things and details without harm to health or pain.
Treatment of pathological curvature of the spine
Treatment depends on what caused the change in the physiological curve of the spine. The treatment regimen includes several types of therapy and a combination of different drugs. Basics of treatment of physiological curvatures:
- drug treatment;
- Wellness treatments: swimming, massages;
- manual therapy;
- use of auxiliary dietary supplements;
- physiotherapy;
- surgical solution.
Surgery is used only in cases where it has been proven that other therapy is pointless. This happens when nerve endings are pinched or when pathology develops in the internal organs. In other cases, specialists are in no hurry to intervene with neurosurgeons. Every effort is made to force the spine to return to its usual curve on its own. It is safer for health and much more effective.
Treatment
Proper treatment of lumbar lordosis should be diverse; it is necessary to influence the pathology from all sides. Any disease of the spine requires complex treatment to achieve a therapeutic effect.
In case of lumbar lordosis, treatment should be carried out by a highly qualified specialist. Since osteochondrosis often occurs with this pathology, the specialist may be a vertebrologist or neurologist. If the cause of the pathology is not defects of the spine itself, but other dangerous diseases, such as disorders of the digestive tract, the help of a gastroenterologist is necessary.
If there are metastases, the help of an oncologist is needed; here it is necessary to act very quickly. This pathology is incredibly dangerous.
The most common option is osteochondrosis and its complications. Let's consider treatment under such circumstances
Drug treatment
The doctor, based on an individual examination and examination, may prescribe a course of the following medications:
- Chondroprotectors. They help speed up the regeneration of cartilage tissue and stop the processes of destruction of the integrity of the structure of the intervertebral discs. Without such drugs, treatment may be ineffective.
- Muscle relaxants. Relieve muscle spasms and help improve blood circulation in the affected area.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They help relieve swelling, reduce inflammation, and slightly reduce pain.
- Painkillers. Designed to return a person to their usual way of life. Eases pain.
- Antidepressants. Potent drugs that are used very rarely for severe pain.
- Vitamin and mineral complex. Serves to strengthen immunity, strengthen bone and cartilage tissue.
All medications must be prescribed by a doctor; unauthorized use can lead to severe complications.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment is used to eliminate pain, strengthen muscles and speed up recovery. This includes: massages, treatments, exercises. If you correctly combine all the components, recovery will not take long to arrive.
The following procedures have a good therapeutic effect:
- Electrophoresis with painkillers;
- Acupuncture - acupressure;
- Leeches - as a way to restore impaired blood circulation;
- Stimulation of nerve endings with low current;
- Traction of the spinal column under water or on special devices in a hospital;
- Exposure to magnetic field.
Such procedures, if carried out correctly, can greatly improve the situation and speed up recovery.
Massage
Massage procedures must be carried out by a qualified massage therapist who knows his business. It is necessary to massage the area of the lumbosacral region and buttocks.
To effectively treat the disease, you should not put pressure on the spine itself, this can increase pain and lead to pinching of the spinal nerves. It is important not to make sudden movements, only smooth and soft ones.
Physiotherapy
There are many different exercises that will tell you how to correct your posture, get rid of hyperlordosis pain and strengthen your muscle corset. Here are some examples:
- Lying on your back, you need to straighten your back and pull in your stomach, reducing the lumbar curve, stretching tight muscles and easing the load on the compressed intervertebral disc.
- Feet shoulder width apart. We bend: you must try to round your back at the lower back, but without pressure, smoothly.
- You can lie down or on the horizontal bar to tighten your legs, rounding your lower back, relieving the load.
- You can try to do squats without abducting your lower back, keeping your back straight.
A set of these or similar exercises is simply necessary to eliminate excessive bending in the lower back. Any correction of spinal pathologies should include kneading and stretching exercises. This will help not only make your back stronger and more stable, but also fix the spine in the desired position.
It is important to always warm up before any exercise and not make sudden movements. It is better for a specialist to observe you and not make mistakes in the technique. If everything is done correctly, the pathology will recede.
Operation
In some cases, when a pathological change has bothered a person since birth, the doctor gives a referral for surgery. Of course, any surgical intervention, especially in the structure of the spinal column, is fraught with dangerous consequences. A person may remain disabled or introduce an infection into the body.
If lordosis cannot be corrected using conservative methods, then the person is operated on: the damaged vertebra is removed and replaced with an artificial one; The option of metal elements is possible.
Treatment to eliminate lordosis
If you discover the first symptoms of pathology on your own, you must immediately seek medical help. It cannot be treated at home without doctor's recommendations. The doctor, first of all, determines the cause that contributed to the appearance of the defect, since without its elimination, the effectiveness of therapy will be lower. For example, cure bone injury, osteochondrosis, relieve inflammation in soft tissues, prescribe a diet to reduce excess body weight.
Modern medicine offers a comprehensive approach to the treatment of lordosis. It includes the following techniques.
Lordosis can only be treated comprehensively
Drug therapy
When a disease such as lordosis is diagnosed, a person is referred to an orthopedist or vertebrologist. These specialists are engaged in restoring the normal position of the spinal column in adults and children. In the course of therapy, the main goals will be to eliminate the root cause of the development of pathology, return the physiologically correct location of the ridge, and strengthen the muscle frame. Drug treatment includes taking the following medications:
- Painkiller. It comes in the form of tablets or ointments aimed at relieving pain at the site of pathology development. To prevent overdose, you should use the prescribed product as prescribed by your doctor or as recommended in the instructions for use.
- Anti-inflammatory. To stop the process in soft tissues near the vertebrae and improve the general condition of the patient.
- Antispasmodics. They are taken in a course, most often the doctor prescribes “Sirdalud” or “Mydocalm”.
Each medicine is selected individually, based on the patient’s condition and the severity of symptoms. Some medications can negatively affect the digestive system, so people with stomach problems are additionally prescribed medications to protect it.
Physiotherapy
Drug treatment can be enhanced through physiotherapy. Before prescribing them, the doctor assesses the general condition of the patient, the absence of contraindications and the dynamics of the pathological process in the back. Curvatures are removed as follows:
- Thermal impact.
- Electrophoresis.
- Balneotherapy.
- Acupuncture.
- Acupuncture.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Swimming.
Sessions are conducted against the backdrop of physical therapy (physical therapy) and taking a course of medications. Their constant implementation allows you to reduce recovery time, reduce pain, strengthen the muscle corset, and improve the patient’s well-being.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy sessions can be added during the treatment process. They will relieve the discs between the vertebrae, eliminate spasms and normalize natural blood flow. But you should not trust all the specialists who offer their services in this area. Before contacting a chiropractor, you need to familiarize yourself with his qualifications (supporting documents) and read reviews of people who have already received treatment from him.
Sessions are carried out only during the period of remission; if the patient experiences acute pain, visiting a manual specialist is strictly prohibited. A person can be offered several methods of influencing the problem: lymphatic drainage, acupressure or classic massage. In each specific case, it will be of varying strength and duration to restore the normal position of the vertebrae.
Exercise therapy is one of the components of the treatment of lordosis
Physiotherapy
During the rehabilitation period, the orthopedic doctor selects for the patient a set of exercises aimed at warming up the spine and improving the condition of the muscles that support it. Exercise therapy is carried out in a medical institution under the strict supervision of specialists so that the patient gets used to the correct performance of gymnastic actions.
Lordosis is an unpleasant pathology that develops under the influence of negative factors and is difficult to treat. Therefore it is easier to prevent. To do this, experts recommend watching your diet, not overloading your back, playing sports and walking more often, doing light exercises every day, and maintaining your posture. This will keep your back healthy and prevent curvature of the ridge in one direction or another.
Prevention
The best preventative measure for pathological processes in the spine will be a healthy and active lifestyle. It is necessary to exclude heavy strength sports from life, because it increases the risk of spinal pathologies many times over. When working out in the gym, you need to select moderate weights, follow the technique and consult with a trainer.
It is necessary to do exercises in the morning. When working sedentarily, you need to maintain correct posture, periodically stand up and warm up.
Sometimes you can hang on the horizontal bar, this relaxes the spine.
It is necessary to give up bad habits, follow a daily routine, and go to bed on time. It is better to buy an orthopedic, semi-rigid mattress. You can choose a special pillow for it.
Prevention of spinal curvature
It is best to prevent lordosis in childhood, when the child’s bone skeleton is developing. It is also very necessary for people who suffer from various diseases of the musculoskeletal system or sit at work all day.
To protect yourself from the development of lordosis, you should follow the following rules:
- Watch your posture. Keep your back straight while walking and sitting.
- Swimming, gymnastics, yoga, Pilates.
- For those who have a sedentary job, take breaks by doing the following exercises: rotational movements of the pelvis, turning the spine in both directions.
- The complex of morning exercises should include exercises that strengthen the abdominal muscles. These muscles are of great importance for the formation of correct posture.
If, nevertheless, a person is found to have lumbar lordosis, then, by following all the recommendations of specialists, one can count on a positive treatment result.
Author: Petr Vladimirovich Nikolaev
Chiropractor, traumatologist-orthopedist, ozone therapist. Methods of influence: osteopathy, post-isometric relaxation, intra-articular injections, soft manual technique, deep tissue massage, analgesic technique, craniotherapy, acupuncture, intra-articular administration of drugs.
Does physical therapy help with stage 1 scoliosis?
How to do exercises for spinal kyphosis?
source
Symptoms of lordic curvature
At first, lordosis is detected through a visible violation of posture:
- A relatively rare cervical deformity of this type is manifested in a strong protrusion of the head anteriorly and its low position.
- External signs of lordic curvature become clearly visible when a person tries to straighten his back by standing against a straight wall.
The most common lumbar pathology changes a person’s figure as follows:
- the head and shoulders move forward somewhat;
- the chest flattens;
- the stomach protrudes greatly;
- knees diverge in different directions.
Lordosis, especially localized in the lumbar region, begins to create problems earlier than other types of incorrect posture - kyphosis or scoliosis.
The curvature in the lower part of the spine significantly redistributes the load on it. The back experiences constant increased tension, and the stomach, on the contrary, turns out to be too relaxed. The result of this is:
- increased fatigue;
- change in gait;
- sprains of muscles and ligaments leading to pain;
- disruption of the transmission of nerve impulses, fraught with the sensation of goosebumps, numbness, and pain.
Increased stress can lead to an inflammatory process. Inflammation of the iliopsoas muscle has its own name - psoitis.
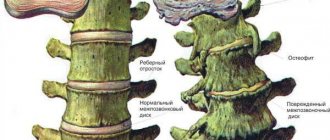
An advanced curvature can cause further disorders of the structure of the spine:
- vertebral displacements,
- formation of bone osteophytes (compensatory outgrowths),
- arthrosis,
- formation of intervertebral hernia.
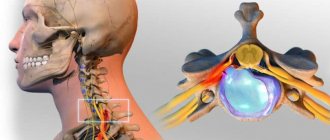
Cervical curvature, like lumbar curvature, gives rise to pain, and the latter can radiate to the arms.
Complications of lordosis on internal organs:
- Pushing the shoulders forward lowers the diaphragm, and changing its position adversely affects the functioning of the lungs.
- All organs located under the diaphragm are constrained. Their blood supply deteriorates.
- The main organ of the circulatory system, by the way, also suffers. Lordosis sometimes precedes heart failure.
- Against the background of the mentioned pathological changes, some patients develop chronic diseases of the respiratory, digestive, and excretory systems.
Lordosis is most often found in the lumbar spine. With such a curvature of posture:
- the stomach protrudes strongly forward;
- shoulders move forward;
- the chest becomes flatter than necessary;
- the pelvis moves back.
- In order to maintain balance, a person has to change his gait.
- Gradually his legs become deformed - his knees move apart.
Symptoms of lumbar lordosis:
- Significant deformation in the form of an enlarged anterior arch almost always leads to overstrain of the muscle corset and frequent back pain.
- They can be so severe that normal mobility becomes difficult. The nature of the pain is usually described as burning and sharp.
- The more a person moves, the harder the work falls on the back muscles and ligaments.
- Accordingly, an active lifestyle and lack of rest periods during the day greatly worsen the condition.
- Some people, knowing about this acquired feature of their body, begin to beware of physical labor and long walks.
- Overload of the muscular-ligamentous system is expressed not only in a burning sensation, but also in a feeling of general severe fatigue and depression that occurs at the end of the day.
Symptoms of cervical lordosis:
- With cervical lordosis, the head moves forward sharply and is slightly below the normal level. The stronger the unnatural deflection of the neck, the more problems this pathology causes to the patient.
- Patients with lordic curvature of the neck usually complain of increased fatigue, burning pain in the area of the curvature and below it, in the back.
- The pain is especially severe if it is caused not only by overstrain of muscles and ligaments, but also by compression of nerve endings.
- If neurological symptoms are detected, as well as pressure on blood vessels, treatment must be approached especially responsibly.
- Otherwise, there will be a likelihood of movement disorders and complications caused by deterioration of blood supply - migraines, changes in intracranial pressure, weakened vision and hearing.
About the spine
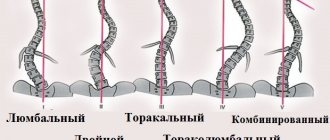
The vertebral column is not a straight chord, as in lower vertebrates. The ability of a person to sit and walk on two legs led to the formation of 4 bends here:
- 2 curves - cervical and lumbar - are convexly directed forward, that is, these are lordoses;
- 2 bends - thoracic and sacral - bend backwards. They are called kyphosis.
This curved position allows the spinal column to better withstand loads, which include upright walking: when loaded, the spine is compressed like a spring, as a result the pressure decreases.
A child is born with a straight spinal column, and only when he begins to learn to sit does a curve in the lumbar region first appear, and then, for balance, all the other “concavities” appear. This curvature of the lumbar region, as long as it is within 150-170° (according to an x-ray, CT or MRI in a lateral projection) is physiological lumbar lordosis. As soon as this angle decreases or increases, lordosis is called pathological.
Pathological lordosis leads to the fact that the vertical load, first on the lumbar region, and then on the entire spine, increases. Compressed vertebrae change their shape (deform) and can easily move relative to each other even when performing normal work. Changes in several vertebrae at once lead to pinching of the nerves leaving the spinal cord, and this causes pain and dysfunction of internal organs.
The sacrum is 5 large fused vertebrae, convexly facing forward. Only the first, upper vertebra can separate from this structure, but all of them cannot bend in the other direction. Therefore, the term “lumbosacral lordosis” does not exist.
How to sleep with this pathology
If the curvature of the spine is quite pronounced, it is recommended to purchase a special orthopedic mattress. It must be designed to support the patient's weight. Otherwise, the disease will worsen even more.
While there is no mattress yet, it is best to lie on your stomach while sleeping, but at the same time you need to place a bolster under it. Its thickness should correspond to the degree of curvature of the spine. You cannot use a roller if a person has an aggravated disease of the internal organs (chronic) or when the disease is in an acute phase, and, of course, it is contraindicated for pregnant women.
Types of lumbar lordosis
We have already considered that lumbar lordosis can be physiological (normal) and pathological (formed as a result of disease). Below we present classifications that relate only to its pathological type.
Depending on the type of reasons, lordosis of the lumbar spine can be:
- Primary. There are two subspecies. The first is vertebrogenic, when the bending is caused by diseases or anomalies in the development of the vertebrae themselves, their displacement relative to each other. The second is paralytic, developing as a result of weakness of the muscles that hold the spine. The causes of muscle weakness can be inflammatory, metabolic or oncological processes.
- Secondary. In this case, the curvature in the lumbar spine may increase or decrease due to diseases of one or both hip joints associated with the bones of the pelvis, which connects to the sacrum.
Depending on the angle at which the spine now curves in the lumbar region, pathological lordosis may be called:
- hypolordosis, when the angle formed by the vertebral bodies at the point of bending is 171° or more. This condition is said to be that the lumbar lordosis is smoothed;
- hyperlordosis: the angle between the vertebrae is less than 150°, usually 140-150°. The vertebral bodies are no longer adjacent to each other, but fan out. This is said to be increased lumbar lordosis.
When they write “lumbar lordosis is preserved,” this means that the angle of curvature of the spine is within 150-170°, and its apex is at the level of 3-4 lumbar vertebrae (or L3-L4 in medical terms).
There is another classification that takes into account the ability to bring the vertebrae into the proper position. According to it, the method of treatment is chosen. So, hypo- or hyperlordosis can be:
- unfixed, when a person can return the spine to its normal state with certain movements;
- fixed: the spine is not brought into the proper position by any voluntary movements;
- partially fixed: the angle of bending can only be partially changed by movements of the back.
Lordosis: normal or pathological?
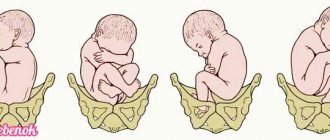
A child is born with a straight spine, but as they grow and mature, the vertebrae move forward relative to each other, resulting in characteristic curves. In the first year of life, when the baby learns to hold his head up, cervical lordosis appears, and at the moment when he learns to crawl, the spinal column bends in the lower back. Each age is characterized by a certain bend, which is measured when assessing the correct development of the child. The final formation of the spinal column ends by the age of 16-18, when the closure of bone growth zones occurs.
Life cycle of the human spine
For reference: natural lordosis is a small convexity (in adults it is 150-170 degrees), which is located at the level of the 3-4th lumbar vertebrae and is almost invisible to the prying eye.
Curves of the spine
Prices for orthopedic corsets and posture correctors
Causes of excessive or flattened curve in the lumbar region
Pathological lumbar lordosis of the spine in childhood and adulthood is caused by various reasons.
Thus, excessive or, conversely, a smoothed curve in the lower back in adults occurs due to:
- osteochondrosis;
- fracture or dislocation of the vertebrae;
- osteoporosis;
- Bekhterev's disease;
- flat feet;
- obesity, when a large load is placed on the lower back;
- spondylolisthesis;
- pregnancy, especially multiple pregnancy or occurring with polyhydramnios. Pathological lordosis occurs by 16-20 weeks and is usually transient (disappears 0.5-1 year after birth). If a woman already had spinal diseases before pregnancy (osteochondrosis, ankylosing spondylitis and others), then the lordosis that arose during pregnancy may not go away on its own;
- intervertebral disc herniation;
- Schmorl's hernia;
- dislocation or ankylosis (immobility) of one of the hip joints;
- inflammatory or degenerative diseases of the muscles that support the spine;
- cicatricial changes in the muscles that fix the spine;
- ruptures of the ligamentous apparatus that holds the lumbar spine;
- vertebral lesions in systemic diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, lupus erythematosus;
- achondroplasia;
- infectious lesions of the vertebrae (this is only possible with syphilis, tuberculosis or brucellosis);
- tumors growing from the vertebrae, or metastases of any cancer to the lumbar vertebrae;
- diseases in which metabolism and, accordingly, the nutrition of the structures that fix the spine, as well as the vertebrae themselves, are disrupted. These are diabetes mellitus, thyroid diseases;
- oncological diseases of internal organs lying directly next to the lumbar spine: kidneys, uterus, prostate, ovaries, intestines.
Some of these diseases can “bend” the spine in a certain direction. So, a person who received (or received) a “whiplash” injury while traveling in a car - when they first drove with great acceleration and then had to brake sharply - experiences a smoothed lordosis of the lumbar region. Pregnancy, tumors and inflammation of internal organs located in the retroperitoneal space are characterized by increased bending.
When lumbar lordosis is detected in children, the cause is one of the following conditions:
- hereditary metabolic disorder in the vertebrae or the apparatus that fixes them;
- spinal injury during childbirth;
- vertebral developmental anomalies;
- cerebral palsy;
- rickets, which results in softening of bone tissue;
- hip dysplasia and congenital hip dislocation, which is the last stage of dysplasia;
- poor posture;
- a sudden growth spurt that occurs during childhood or adolescence. It is more likely to provoke hyper- or hypolordosis if the child has weak back muscles;
- Kashin-Beck disease.
If in childhood and adolescence hyperlordosis did not arise as a result of a hereditary change in the spine or its ligamentous apparatus, then if all efforts are directed towards eliminating the cause, the curvature of the spine can be returned to normal. If the vertebrae are located at a distance from each other for a long time (like a fan) in an adult, it is very difficult to completely eliminate this condition using conservative methods.
Massotherapy
A procedure such as massage helps to relax muscles, relieve pain and normalize blood circulation. In the case of lordosis, among other things, it also helps the spine prepare for straightening.
For patients diagnosed with lumbar lordosis, the following types of massage are recommended: acupressure, classical therapeutic and lymphatic drainage. If you massage and simultaneously do physical therapy, you can achieve good results.
How to recognize pathological lordosis in yourself
Depending on whether the angle of curvature of the spine increases or decreases, the disease manifests itself in various symptoms. The following signs will be common to both conditions:
- aching back pain that intensifies when doing physical activity, lifting heavy objects, or staying in an uncomfortable position;
- in women, pain increases during menstruation;
- men may experience erectile dysfunction;
- characteristic appearance: drooping shoulders, protruding belly (even in the absence of excess weight), tilted pelvis back, spread legs with fully extended knees;
- change in gait: the upper body (up to the stomach) leans back, and the stomach forward, the legs are apart and the person “rolls” from one leg to the other;
- increased fatigue;
- pain in the legs, which intensifies after a long walk;
- problems with the digestive system: constipation, bloating, intestinal cramps;
- sleep problems;
- deterioration of temperature sensitivity in the pelvic area and lower extremities.
When lumbar lordosis is smoothed, the following are added:
- a feeling of not only pain, but also numbness in the lower back;
- fatigue when standing and sitting;
- appearance: shoulder blades protrude and the lower half of the abdomen protrudes.
If hyperlordosis develops, it is noted:
- severe tension in the lumbar muscles;
- lying on your stomach is impossible due to severe pain;
- when lying on your back, you can see a large distance between your back in the lumbar region and the horizontal surface;
- bending can only be done by bending the legs at the hip joints;
- when standing, it is clear that the legs are either hyperextended at the knees or slightly bent at them;
- the head drops slightly and moves forward.
In addition to these manifestations, symptoms are observed that indicate a possible cause of hypo- or hyperlordosis. This:
- Increased temperature, decreased appetite, weakness - due to infectious processes;
- Gradual development of symptoms of lordosis plus a sliding gait. This combination suggests that the cause of changes in the angle of bending in the lumbar spine are tumors or inflammatory processes in the area of the spinal nerve roots. This may be radiculitis, arachnoiditis of the spinal cord or other pathologies, which causes contracture in the area of the gluteal or lumbar muscles, which lordosis tries to compensate for;
- The appearance of symptoms of lordosis in middle age indicates the presence of lumbar osteochondrosis. It can be gradual and even acute (if the nucleus pulposus suddenly breaks through). Osteochondrosis is indicated by pain in the hip joints, which occurs when trying to place the back and buttocks in a normal position.
What signs and symptoms of pathology exist? ↑
Lumbar lordosis is considered physiological only within a certain angle.
Deviation in one direction or another is considered a pathology. If the spine is slightly straightened in the lower back, this condition is called hypolordosis; if the angle, on the contrary, is too large, this is hyperlordosis.
The symptoms of these two conditions are different.
Common symptoms will be:
- backache;
- bulging belly;
- metabolic disease;
- chronic fatigue;
- disruption of the abdominal organs;
- leg pain;
- difficulty getting proper sleep.
Fig.: severity of lumbar lordosis
Symptoms of a condition where lordosis is increased:
- buttocks stick out;
- the stomach protrudes forward;
- legs spread;
- the pelvis is tilted back;
- the lower back muscles are very tense;
- the inability to sleep on the stomach, since in this position the spine is aligned, and this causes pain;
- you can bend over only by working in the hip joints;
- if a person lies on his back, a fairly large distance appears between the lower back and the floor.
Signs of smoothed lumbar lordosis (hypolordosis):
- lower back pain;
- flattening of the back;
- fatigue in sitting or standing positions;
- change in gait;
- a feeling of numbness in the area of smoothed lordosis.
Complications of lordosis
If lumbar lordosis is not treated, no matter what it is - hyperlordosis or hypolordosis - this leads to severe stress on individual vertebrae and the discs between them. When this condition exists for a long time, it leads to complications such as:
- intervertebral hernia;
- pathological (excessive) mobility of individual vertebrae;
- decreased stability of discs between several vertebrae (multiple scalene pseudospondylolisthesis);
- disc loss;
- inflammation of the iliopsoas muscle;
- deforming arthrosis of the joints between the articular processes of the lumbar vertebrae;
- compression of the spinal cord, which leads to disruption of independent urination and defecation, infertility, immobilization (partial or complete) of the lower extremities.
Causes of spinal lordosis
For any form of lordosis, if it is not physiological, the causes are the same. Lordosis can be congenital and caused by abnormalities in the structure of the spine. These are congenital or acquired pathologies of the spine, which can be caused by the following reasons:
- rickets;
- hyperactive growth against the background of formation in the presence of muscle weakness;
- dysplasia;
- cerebral palsy disease;
- Kashin-Beck disease;
- trauma during birth.
The reasons for acquired lordosis of any form and type are the same. The main source is osteochondrosis, especially if untreated. Osteochondrosis progresses rapidly, destroys bone and joint tissue, and causes severe and often irreversible complications. In case of pathological lordosis, the “first violin” is the osteochondrosis of the spine. Most of the following causes are also caused by this disease:
- vertebral displacement;
- spondylosis;
- disc hernias.
More often, a neglected chain leads to primary lordosis: osteochondrosis – spondylosis – hernia. The reasons can be combined in any order. Additional causes of lordosis:
- spinal tuberculosis;
- osteoporosis;
- the presence of cysts and other formations;
- inflammations like myopathies;
- rheumatism, arthritis, arthrosis.
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis is not made at home. Even a traumatologist does not have the right to do this based on examination alone: radiography, CT or MRI is required to see the pathological lordosis and assess the angle of bending. And if radiography only helps to establish a diagnosis and determine the type of lordosis, then tomographic methods can help find the cause of this condition.
The doctor can only suspect this disease. To do this, he asks the patient to stand with his back to the wall, pressing his buttocks and shoulder blades against it. If there is a lot of free space left in the lumbar region (more than 5 cm at the deepest point of the bend), this indicates pathological lordosis.
In addition to determining the lordosis itself and its type, studies are carried out (tests and instrumental diagnostics), the purpose of which is to determine the cause of this condition.
How is pathology detected?
The doctor identifies spinal deformity based on a visual examination of the patient and an x-ray examination (frontal and lateral projection). At the initial appointment, the peculiarities of posture are determined, tests are carried out to determine the nature of lordosis, and there are concomitant neurological disorders. To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo standard blood and urine tests, as well as rheumatoid factor. In addition, instrumental research methods are also used:
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- X-rays of light.
- ECG.
- CT scan.
- Ultrasound of the pelvis.
They allow you to determine the degree of development of lordosis, choose the appropriate treatment tactics, as well as the appearance of other disorders of the internal organs against the background of the disease.
X-ray is the most effective and fastest way to diagnose lordosis
Treatment
Treatment of lumbar lordosis begins with conservative measures, which are carried out in combination. If this does not lead to the desired effect and, moreover, there are signs of compression of the spinal cord, surgery is performed.
Conservative therapy
It consists of a complex consisting of:
- measures aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease;
- drug correction;
- exercise therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- diets;
- additional methods.
Eliminating the cause of the disease
This is only possible if the cause of hyper- or hypolordosis is identified:
- if it is osteochondrosis, deforming spondylarthrosis or deforming disease of the hip joints, chondroprotective drugs (Dona, Arthra or others) are prescribed;
- when the cause of pathological lordosis is infectious processes, treatment is prescribed by an infectious disease doctor. Usually these are antibiotics that take into account the sensitivity of the microorganism. The course may include immunomodulators and vitamins;
- if it is determined that the cause is a systemic disease, a rheumatologist is involved in treatment. She prescribes drugs that affect the immune system and stop its attack on its own cells;
- for spondylolisthesis, intervertebral hernias and Schmorl's hernias, treatment is carried out with medications and manual therapy;
- in case of obesity, an endocrinologist is involved in therapy, who helps to find the cause of this condition, and a nutritionist, who selects an effective diet.
Drug treatment
It includes the prescription of medications that should relax the tense muscles of the lumbar region and allow the spine to move into the desired position through exercise, physical therapy and additional methods. These are medications such as:
- anti-inflammatory drugs. For severe or persistent back pain, they are taken in tablets or injections (Diclofenac, Celebrex). If the pain is tolerable, it is better to use local remedies: Olfen patch, Diclofenac ointment, Voltaren, Fastum gels and others;
- muscle relaxants (directly relaxing muscles): “Mydocalm”, “Sirdalud”;
- B vitamins: “Milgamma”, “Neurorubin”.
Exercises for lumbar lordosis should be prescribed by a doctor, who will take into account the type and degree of pathological curvature and the condition of your spine. Here are some general exercises that are used in most cases:
| Initial position | Performance |
| Lying on the floor, legs bent at the knees on a chair, forming a 90° angle between the knees and hips | Place one hand in the “gap” under your lower back. At the same time, pull in your stomach and move your pelvis forward so that this distance decreases as much as possible. |
| Lying on your back, arms to the sides, legs straight | Raise your straight legs and very smoothly try to throw them behind your head or at least place the knees of your half-bent legs on your forehead |
| Lying on your stomach, with a cushion under its lower part (just above the pubis) | Put your hands behind your head, close them in a “lock”. Inhale: lift your upper body, spreading your elbows to the sides, pause. Exhale: lie on your stomach. |
| Lying on your back | Get into a sitting position without helping yourself with your hands. Repeat the movement 5 times |
| Same | Try to flatten your lower back on the floor as much as possible; hands-free and hands-free |
| On all fours, supported on your knees and palms, which are shoulder-width apart | Inhale: arch your pelvis with your tailbone up and your shoulders back. Exhale: lower your head and hunch your back |
| Standing, feet shoulder-width apart | Exhale: bend over, try to reach your feet with your hands. Inhalation: rise |
| Standing near a wall, pressing your heels, buttocks and shoulder blades against it | Try to bring your lower back as close to the wall as possible, without moving your shoulder blades and pelvis away from it |
| Standing, feet shoulder-width apart | As you exhale, do squats |
| Same | Lean forward, hug your legs and slowly and carefully try to bring your face closer to your knees |
| Same | Place your palms on the sides of your chest, fixing it. Rock your pelvis and lower back from side to side without moving your upper body |
When performing exercises, follow these rules:
- Exercise regularly.
- Before performing a set of exercises, warm up, massage your spine and joints.
- Start with minimal load and gradually increase it.
- There should be no pain in the lower back, as well as other unpleasant sensations, when performing. If you feel dizzy, have pain, or have palpitations, stop doing the exercise.
- The emotional mood should be positive.
- After classes you should feel slightly tired, not a feeling of exhaustion.
- Wear loose clothing and orthopedic shoes. The lower back should be covered and insulated.
Physiotherapy
It includes a therapeutic massage, which should improve blood circulation in the affected lower back and improve blood flow from it, relax “tight” muscles and tone overly relaxed muscles. In addition to massage, one or more of the following procedures are performed:
- underwater (in a therapeutic bath) traction;
- electrophoresis on the lumbar region, with novocaine and hydrocortisone;
- ultrasonic influence on the spine area;
- magnetic therapy on the buttocks and lower back;
- mud applications on the lumbar region.
After such procedures, you need to put an orthopedic bandage on your lower back to fix the spine and prevent it from “resetting” the changes that were achieved by the treatment. You need to wear the bandage all the time, removing it only for the duration of local treatment and before going to bed. You need to sleep on an orthopedic mattress. While he is away, temporarily sleep on your stomach, under which you place a cushion.
Additional methods of conservative treatment
These are methods that not all doctors include in the course of treatment. At the same time, the methods themselves demonstrate high efficiency. These include:
- acupuncture – exposure of bioactive points with needles, which helps direct the body’s necessary energy to a specific place – in this case, to the lumbar spine;
- hirudotherapy is a method when leeches are placed on biologically active points. They stimulate the points themselves, directing energy to the lumbar region, and inject substances into the blood that thin it. As a result of the latter effect, blood circulates better throughout the body without forming stagnation;
- manual therapy is the use of hands on the area of pathological bending, the purpose of which is to bring it to a normal angle.
Diet
Compliance with the following nutritional rules will not cure pathological lordosis, but will help food pass through the compromised gastrointestinal tract, being absorbed and without stagnation. This will help prevent constipation and therefore intoxication:
- drink at least 30 ml/kg of liquid weight, more is possible if there is no heart or kidney failure;
- eat fresh vegetables that are high in fiber;
- eat less sweets and starchy foods;
- completely eliminate fatty, fried and spicy foods, alcohol, and smoked foods.
Surgical treatment
It is used mainly for severe congenital conditions, as well as in cases where compression of the spinal cord occurs due to lordosis. The operations are traumatic and are performed under general anesthesia. After them, long-term and competent rehabilitation is needed. There are 2 types of them:
- fixation of vertebrae in the area of pathological lordosis using plates, rods or other metal structures;
- replacement of affected vertebrae with titanium implants, from which a structure with a normal bending angle can be assembled.
Unfortunately, the second type of operation is practically not performed in the CIS countries.
Physiotherapy
A specially selected set of exercises for lumbar lordosis is one of the main methods of treating this disease. Just remember that all exercises must be approved by a specialist and should be performed systematically and over a long period of time.
Recommended exercises:
- Starting position – lying on your back. Place your feet on some elevated surface, such as a chair or sofa. In this case, the hips and knees should be at right angles to each other. Place your hand under your lower back and use it to control forward movements of your pelvis. At the same time, pull your stomach inward so that the free space under your lower back decreases.
- Lie on your back, spread your arms to the sides, stretch your legs. Raise your legs and try to put them behind your head.
- Press your back against the wall; your shoulder blades, pelvis and heels should touch its surface all the time during the exercise. Place your hand under the lower back and try to touch the surface of the wall with this place.
- This exercise should be performed lying on your stomach. Hands are behind the head. At the level of the pelvic bones, place a cushion under the stomach. Inhale and raise your chest, spreading your elbows to the sides. Stay in this pose for a few seconds and return to the starting position.
In addition to therapeutic exercises, you can resort to yoga:
- Fix your chest with your palms and make rocking movements with your lower back and pelvis.
- Lie on your back, bend your knees, put your hands behind your head, place your feet hip-width apart. Straighten your arms, do not lift your lower back off the floor, do the exercise while exhaling. Then return to the starting position.
- Starting position as in the previous exercise. Straighten your leg, lift it up and try to reach it with your hand.
- Exercise "Bridge". Starting position - lying on your back, arms extended along the body, legs bent, shoulder-width apart. Lift your body off the floor so that your hips and torso form one line. Hold for a few seconds and return to the starting position.
How lordosis becomes a pathology
A person normally has two lordosis. One of them is the cervical one. The second is lumbar. Located, respectively, below, in the lumbar region, it represents a deflection of the vertebral arch inward. Pathological lordosis is not such a rare phenomenon, occurring either congenital or acquired as a result of lifestyle, overload, or disease.
Lordosis
If the lower back bends excessively, taking lordosis beyond the norm, this becomes the cause of pain and leads to various diseases of the spine.
By the way. Very often, lumbar lordosis begins in women around the age of thirty, during pregnancy. When they are pregnant, their posture changes, the center of gravity shifts, and the spinal deflection increases to lighten the weight of the heavy belly.