Late autumn and winter is the time of mass epidemics of colds, sore throats, acute respiratory viral infections and influenza. The latter disease poses the greatest danger, is extremely difficult and often leads to death.
In many cases, recognizing the symptoms of a disease in a timely manner is extremely important for maintaining health, avoiding complications to internal organs and, in some cases, for life.
However, the main attention should be paid not to recognizing the disease and its symptoms in the early stages, but to preventing influenza. By getting vaccinated in time against the most common strains of influenza viruses, leading a healthy lifestyle and taking vitamins and other health-improving medications, you can avoid seasonal flu and maintain your health.
In this article we will talk about what the flu is, what the main symptoms of the disease are, how to properly prevent the disease and answer other popular questions from Ukrainians.
Flu: source: germania.one
Popular articles now
“Servant of the People” came to the Rada with Prada: how much does this handbag cost in your monthly salary?
Coronavirus outbreak leads to production of realistic face masks, photo
The network showed a secret scheme of how Vodafone despicably cheats pensioners out of money
Ukrainians will have their pension payments automatically closed in just a few minutes: details of the innovation
show more
The influenza virus is...
Influenza belongs to the class of acute, highly contagious ( infectious ) respiratory viral infections with an aerosol mechanism of infection.
The causative agent of the infection belongs to the Orthomyxoviridae of the genus Influenzavirus .
The virus is widespread. In any geographical location it can infect people of all age groups. The first flu epidemic was recorded 850 years ago.
There are different strains of the influenza virus. Viral strain “A” is capable of infecting animals and humans, and replication (multiplication) of influenza viruses “B” and “C” occurs only in human cells.
The high ability to mutate , especially of the “A” strain, leads to frequent epidemics and multiple infections of humans within one season.
At the same time, viral virions are unstable and easily die when exposed to elevated (up to 60 °C) temperatures and chemical disinfection (how is that?), but survive and remain viable for up to 3 weeks at low air temperatures (4 °C), retain high contagiousness at minus 70°C.
Influenza infection is characterized by a short incubation period and a rapid cyclical course with signs of catarrhal and intoxication syndromes.
The predominant lesion is the mucous epithelium of the upper respiratory tract. The severe clinical picture of the disease is accompanied by infection of the lower respiratory tract with the frequent development of bacterial complications.
If treatment is not started on time, irreversible processes occur in the lungs in the first five days of the disease.
Flu shot, consequences?
Answers:
Maria
We recently did this in our garden. There are NO consequences!!! And the fact that you have a runny nose, there are two options - the body’s reaction and thereby instills immunity for a year; or the infection appeared before the vaccination and made itself felt in this way. Monitor your temperature for two days; if you have an acute respiratory infection, treat it! Good luck. Do not be ill!
Natalia V.
and also aches and spinning in the joints, lethargy...
Galina Shkil
Vaccinated with a weakened virus, it is possible that he suffers a mild form of influenza and develops good immunity to this strain of influenza.
Nikolay Dendeberya
This is exactly what the reaction is. The vaccine is a weakened flu virus. But where is the guarantee that this year will be exactly like this, and not “B” or “C” or something else?
Tatyana Pajitnova
If there have been cases of allergy to chicken eggs, then vaccination is contraindicated (it can cause a severe allergic reaction with complications); vaccination should not be done after a serious long-term illness, during an illness (acute respiratory infection, cold, etc.). And if there are no contraindications, then do it.
Fairy Winged
yes whatever. In principle, you waited for them, the reaction can be expressed this way.
Just LANA
Yes, these are consequences of vaccination. Viruses mutate, and the vaccine is the same year after year, so I don’t see the point in doing it, although I am not an opponent of vaccination. My son received this vaccination once in the garden and now I will never agree to it again (I fell ill on the same day with a critical temperature). Good luck!
*** just me
easily. I never get my flu shot. I often hear that children get even sicker after it. My husband, though not a child, got vaccinated last year and was very sick. three days 39 and not lower. I didn’t get vaccinated and my temperature didn’t rise above 37.7. I also heard that the vaccine is standard, but the flu virus is different every time. This opinion is my personal and does not have any propaganda character
Mechanism of infection
The main mechanism of infection is airborne transmission or household contact. The infectious agent virus is released from the nasopharynx with saliva, mucus, or sputum when a patient or carrier of the infection talks, coughs, or sneezes.
Penetrating into the human respiratory tract, the virus, with the help of surface proteins (neuraminidase and hemagglutinin), attaches to the cell, and, destroying the membrane, penetrates inside, disrupting the processes of cellular vital activity.
Using its own resources, the cell begins independent synthesis of viral proteins, replication of viral RNA molecules and assembly of the virus itself. New virions, when released, destroy the cell and invade others.
The exceptionally high rate of viral replication explains the very short incubation period. The replication cycle of the pathogen does not exceed 6 hours.
Viral shedding in an infected patient begins a couple of days before the first signs of the disease appear. The peak of viral shedding is observed in the first 6 days of the disease, and stops a week after the cessation of clinical symptoms of the disease.
Complications from the nervous system
Influenza exacerbates neurological diseases that were previously asymptomatic. Therefore, against its background, the first hypertensive or hypotensive crisis may develop, radiculitis or neuropsychic disorders may manifest themselves for the first time.
Since the influenza virus is able to penetrate the blood-brain barrier, it can infect the walls of blood vessels in the brain and meninges. People who have previously suffered a concussion or traumatic brain injury, as well as those who abuse alcohol, are especially susceptible to this. As a result, meningitis, encephalitis, and arachnoiditis may develop.
Symptoms of influenza in an adult
The clinical course of influenza is characterized by the manifestation of three main symptom complexes - intoxication, catarrhal symptoms and hemorrhage.
Intoxication syndrome manifests itself at the very beginning of the disease. The patient's temperature reaches critical levels, the following are noted :
- dizziness;
- headache;
- chills and weakness;
- moderate joint and muscle pain;
- involuntary convulsions and loss of consciousness.
The severity of the clinical picture of uncomplicated influenza determines the intensity of intoxication , which can manifest itself in both moderate and intense forms, accompanied by :
- vomiting;
- high fever and delirium;
- hyperemia (blood filling) of the face and dry skin;
- tachycardia and decreased blood pressure.
The fever usually subsides by the end of the week Intoxication may be accompanied (although not always) by catarrhal symptoms, in the form of :
- dry or strained cough, increasing in intensity;
- discomfort and pain in the nasopharynx and throat;
- runny nose and hoarseness;
- chest pain, tachypnea (difficulty breathing).
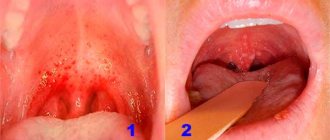
In 15% of cases with influenza infection, hemorrhagic symptoms develop in the form of:
- hyperemia (blood filling) of the tissues of the pharynx and pharyngeal wall;
- minor hemorrhages in the mucous tissue of the oropharynx;
- nosebleeds;
- alveolar pulmonary edema, as a result of severe hemorrhage.
Influenza in adults is not accompanied by disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract or dysfunction in the pelvic organs. If negative symptoms appear, this is most likely due to an exacerbation of chronic pathologies, or due to a neurogenic nature.
The average duration of the disease is 5-7 days .
In medicine, variants of atypical, mild and erased influenza clinical manifestations, as well as its combination with other viral infections, have been noted.
How to prevent flu complications
Flu is not a cold! It is one of those diseases that cannot be cured on your own; you need to call a doctor as soon as possible. It is better not to leave the house, because a cold with the flu increases the risk of complications. So, if the doctor gives you a release from work and forces you to lie in bed, then you need to do so.
The body needs rest and time to overcome the disease. Get into bed and cover yourself with a blanket - raising your body temperature blocks the ability of viruses to reproduce.
Home remedies will also help: fruit teas, milk with butter and honey, hot chicken soup - they warm up the body and mobilize the immune system to action, prevent dehydration and eliminate discomfort.
Anyone who is at high risk of contracting the flu should get vaccinated! Vaccines significantly reduce the risk of contracting influenza, and in case of illness, they alleviate the course of the disease and protect against complications.
Flu symptoms in children
In addition to the general symptoms characteristic of influenza, the clinical picture of influenza infection in children may be accompanied by toxic damage to the central nervous system, disorders of the cardiovascular and urinary systems, manifesting itself:
- neurotoxicosis and encephalopathy;
- convulsive and delirious states;
- auditory hallucinations;
- tachycardia;
- disturbance of cardiac auscultation (heart tone);
- signs of nephropathy;
- the presence of blood in the urine;
- decrease in the volume of urine excreted.
The severity of the clinical course of influenza in children and its form (mild, moderate, severe and hypertoxic) is determined by the severity of catarrhal and intoxication symptoms.
With mild to moderate influenza symptoms, the child’s condition improves after 4 days, but inflammatory processes of a catarrhal nature can persist for up to 2 weeks. During the recovery period, sweating, weakness, and a feeling of fatigue persist.
The hypertoxic form of influenza is dangerous for children , as there is a high risk of mortality, which can be caused by:
- acute alveolar swelling of the lung tissue;
- rapid development of pneumonia;
- DIC syndrome (disturbances in the blood coagulation system);
- acute renal, cardiovascular or respiratory failure.
Children under 2 years of age .
Influenza is often more complicated before the age of 5:
- secondary and bacterial pneumonia,
- bronchiolitis,
- acute obstructive laryngitis;
- sinusitis and otitis media;
- inflammatory processes in the brain, skeletal and cardiac muscles;
- "white liver disease" (Reye's syndrome).
Flu can be complicated not only in young children, but also in adults. Especially if there is a whole “bouquet” of concomitant diseases (DM, congenital heart pathologies, asthma, kidney disease, immunodeficiency conditions, etc.).
Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible and begin treatment.
Remember that treating influenza with home or folk remedies, as we all treat colds and acute respiratory viral infections, is not effective.
Only antiviral drugs can prevent complications by stopping viral replication (reproduction) at an early stage of the disease.
Reasons for the development of complications
The following are the most common causes that lead to the development of complications in humans:
- The practice of self-medication, when a patient takes medications without a doctor’s prescription. This is especially true for antibiotic therapy. It should be said right away that these drugs are not effective against the flu, since it is caused by a virus, and antibiotics are aimed at suppressing the activity of bacteria. Such medications can only be used for advanced viral colds, when there is a risk of pneumonia and bacterial infection.
- Cases when a person does not pay attention to the fact that he is sick and suffers from the flu “on his feet”. At the same time, the patient can go to work and lead a normal life, believing that the virus will go away on its own.
In fact, this is a very big mistake, because the virus can really seem to disappear after a week, but after another 10-14 days it can easily recur with renewed vigor, causing dangerous consequences of the disease in a person in the form of sinusitis, rhinitis, otitis and other complications.
- Cases when the patient does not completely cure the flu. In this condition, he may have a cough for a long time, which will ultimately lead to the most common complication - pneumonia. The same can be observed with a runny nose, which can easily cause inflammation of the sinuses.
- High fever can cause acute liver and kidney damage. In children, this symptom can provoke Reye's syndrome. This usually happens when bringing down the temperature is practiced using drugs based on acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin).
- If a person already suffers from heart and vascular diseases, then the flu can easily cause a deterioration in the patient’s condition and exacerbation of existing cardiac pathologies.
Treatment of influenza (therapy methods)
Influenza treatment tactics are based on indications of clinical signs of the disease and the results of rapid diagnostics - detection of viral antigen in nasal swabs (RNIF, or ELISA diagnostics).
A typical mistake made by all patients with suspected influenza is the use of vasoconstrictor nasal drops. Drying the mucous membrane in the nasal cavity deprives the patient of a natural barrier and provides the virus with open access to the body.
You should also not rely on immune protection, because at the initial stage of the disease its capabilities are determined only by the period during which the virus overcomes the phagocytic defense.
The basis of the fight against the virus is direct-acting antiviral drugs. Moreover, it is necessary to start taking them in the first two days after the development of initial symptoms.
At the onset of the disease , to combat the influenza virus, drugs are selected that can resist the introduction of the virus and its replication, inhibiting the synthesis of enzymes that promote the formation of infectious virions. It is useless to prescribe such drugs later.
Treatment is complex and step-by-step , including: detoxification, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antibacterial and antiviral therapy, selected individually, depending on the complexity of the clinical course.
- With the development of initial signs of influenza - in the first three days of the disease - arbidol, oseltamivir, zanamivir, aerus, ingavirin, drugs - COX inhibitors and antioxidants, detoxification drugs are prescribed.
- From the third to the sixth day , at the stage of acute development of infection, the drug contrical is added to the above drugs (to prevent hemostasis disorders).
- From the 6th to the 14th day , during the development of complications, antibiotic therapy, drugs of the interferon group, various methods of enriching the blood with oxygen (oxygenation) can be added as respiratory support.
If necessary, in each specific case, symptomatic therapy drugs are selected to alleviate the clinical course of influenza.
Can antibiotics prevent complications?
Everyone should know that treating influenza with antibacterial drugs is prohibited. This group of products does not have any effect on viruses and their destruction. Drugs are prescribed in case of bacterial diseases.
Some people want to use antibiotics to prevent complications from the flu. Once and for all, it is necessary to understand that antibacterial medications are not a means of prevention. Moreover, treating a disease that does not yet exist with such powerful medications is not allowed.
This group of drugs for influenza can only be prescribed in special situations when infectious foci are present. That is, there must be a real possibility of a bacterial complication from the flu. In all other cases, it is strictly forbidden to self-medicate and prescribe antibacterial agents on your own.
What to do after illness
After the flu, the body of adults and children is weakened, energy exchange is disrupted, and metabolism is slowed down. The consequences of the virus can be
- low pressure
- weakness
- insomnia
- headache
- slight increase in temperature.
To recover, you need to finish treatment, walk and rest more, eat more animal protein. After antibiotics, treatment may be required - a course of lactomedicines for the intestinal flora. The intestines are the most important part of the immune system, and malfunctions in its functioning can lead to a relapse of the infection or re-infection with SARS.