Medical certificate
Bilirubin is a substance that is a product of the processing of old blood cells and hemoglobin. In a healthy body, they are excreted along with feces. If this process is disrupted, they remain in the blood. As a result, a person experiences yellowing of the whites of the eyes, some areas of the skin, and changes in the composition of bile. The enzyme glucuronyltransferases is considered an important component of the bilirubin metabolism process. In the case of Gilbert's disease, a deficiency of this element is diagnosed.
The pathology was first described by the French gastroenterologist Augustin Nicolas Gilbert. Later it was named after the name of its discoverer. In medical reference books you can find several more of its names: familial jaundice, constitutional liver dysfunction. Gilbert not only managed to identify the hereditary nature of the disease. He was also able to prove the relationship between deviations in bilirubin levels and impaired functionality of the liver or gall bladders. This discovery was recorded in 1901.
According to medical data, Gilbert's disease affects 10 percent of the world's population. Its timely diagnosis and accurate statistics are complicated by a blurred clinical picture. Patients usually consult a doctor with complaints of yellowness of the sclera and certain parts of the body. Before severe symptoms develop, the disease can only be detected using a blood test.
Normally, free bilirubin appears in the blood mainly (in 80-85% of cases) during the destruction of red blood cells, in particular the GEM complex, which is part of the structure of hemoglobin. This occurs in the cells of the macrophage system, especially actively in the spleen and Kupffer cells of the liver. The rest of the bilirubin is formed from the destruction of other heme-containing proteins (for example, cytochrome P-450).
An adult produces approximately 200 mg to 350 mg of free bilirubin per day. This bilirubin is slightly soluble in water, but is highly soluble in fats, so it can interact with phospholipids (“fats”) of cell membranes, especially the brain, which may explain its high toxicity, in particular its toxic effect on the nervous system.
Initially, after the destruction of the GEM complex in plasma, bilirubin appears in an unconjugated (free or unbound) form and is transported in the blood using albumin proteins. Free bilirubin cannot penetrate the renal barrier due to adhesion to the protein albumin, and therefore remains in the blood.
In the liver, unbound bilirubin passes to the surface of hepatocytes. In order to reduce the toxicity and excrete free bilirubin in liver cells using the enzyme UDPGT1*1, it binds to glucuronic acid and is converted into conjugated (direct or bound) bilirubin. Conjugated bilirubin is highly soluble in water, it is less toxic to the body and is subsequently easily excreted through the intestines with bile.
In Gilbert's syndrome, the binding of free bilirubin to glucuronic acid is reduced to 30% of normal, while the concentration of direct bilirubin in bile increases.
Gilbert's syndrome is based on a genetic defect - the presence of an additional TA dinucleotide in the promonitor region of A(TA)6TAA of the gene encoding the enzyme UDPGT1*1. This causes the formation of the defective region A(TA)7TAA. Elongation of the promonitor sequence disrupts the binding of transcription factor IID, and therefore the quantity and quality of the synthesized enzyme UDPGT1, which is involved in the process of binding free bilirubin with glucuronic acid, decreases, converting toxic free bilirubin into non-toxic bound one.
The second mechanism for the development of Gilbert's syndrome is a violation of the uptake of bilirubin by microsomes of the vascular pole of the liver cell and its transport by glutathione-S-transferase, which delivers free bilirubin to the microsomes of liver cells.
Ultimately, the above pathological processes lead to an increase in the content of free (unbound) bilirubin in the plasma, which causes the clinical manifestations of the disease.[6]
Main causes and risk factors
The main cause of the development of Gilbert's disease is considered to be a defect in the second chromosome in the location responsible for the binding and further transport of bilirubin in the liver. Since this function is impaired, the substance begins to accumulate in the organ, causing characteristic skin pigmentation.
For a long time, the pathology may not manifest itself with obvious clinical symptoms. The following factors serve as a kind of impetus to trigger the exacerbation mechanism:
- viral infections;
- frequent stress;
- poor nutrition;
- lack of sleep/insomnia;
- alcohol abuse;
- taking antibiotics;
- surgical interventions.
The disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. This means that the probability of a pathology occurring in a child is 50% if one of the parents has the mutation gene.
Mendel's law and principles of inheritance of Gilbert's syndrome
This disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Let's consider some options for transmitting Gilbert's syndrome to offspring:
- If both parents are carriers of this syndrome, then the probability of having sick children will be 25%, 50% will be carriers, and the remaining 25% will be healthy.
- If both parents have Gilbert's syndrome, all their children will be affected.
- If one parent is a carrier and the other is sick, then the probability of the disease will be 50%.
- If one parent is a carrier and the other is healthy, then 50% of the children will be carriers and 50% will be healthy.
From the above examples it is clear that even phenotypically (externally) healthy parents can give birth to a child with Gilbert's syndrome. Therefore, if there are cases of this disease in a person’s pedigree, it is recommended to undergo a molecular genetic examination for mutations in the genes responsible for the development of Gilbert’s syndrome. Based on the test results, a geneticist can determine whether a person is a carrier and how the syndrome will be inherited.
Clinical picture
The functioning of the liver is directly influenced by the male hormone androgen. Therefore, the first symptoms of Gilbert's disease usually appear in adolescence, when puberty and hormonal changes in the body occur. It is worth noting that it is precisely because of the influence of the androgen hormone that pathology is most often detected in males.
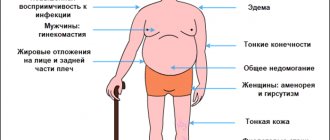
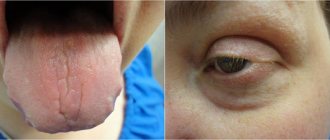
Its main symptom is yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. This phenomenon is spontaneous and at the same time chronic. Among other manifestations of the disease, doctors note:
- constant discomfort in the pancreas;
- heartburn;
- nausea after eating sweet foods;
- lack of appetite;
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- bloating, diarrhea.
Patients with Gilbert's disease often complain of health problems characteristic of the common flu (lethargy, drowsiness, tachycardia, aching limbs). Neurological symptoms are possible. We are talking about obsessive disorders and depression.
Symptoms of Gilbert's syndrome
The symptoms of the disease in question are divided into two groups – obligatory and conditional.
Mandatory manifestations of Gilbert's syndrome include:
- general weakness and fatigue for no apparent reason;
- yellow plaques form in the eyelid area;
- sleep is disturbed - it becomes shallow, intermittent;
- appetite decreases;
- patches of yellow skin that appear from time to time; if bilirubin decreases after an exacerbation, the sclera of the eyes begin to turn yellow.
Conditional symptoms that may not be present:
- pain in muscle tissue;
- severe itching of the skin;
- periodically occurring trembling of the upper limbs;
- increased sweating;
- heaviness is felt in the right hypochondrium, regardless of food intake;
- headache and dizziness;
- apathy, irritability – disturbances of the psycho-emotional background;
- bloating, nausea;
- stool disorders - patients are bothered by diarrhea.
During periods of remission of Gilbert's syndrome, some of the conditional symptoms may be completely absent, and in a third of patients with the disease in question they are absent even during periods of exacerbation. [adsense2]
Diagnostic methods
When the first signs appear, you should consult a therapist. Diagnosis of pathology begins with a study of the patient’s medical history, his family, and physical examination. Then they move on to laboratory methods. The patient must be given a blood test. With Gilbert's disease, a reduced hemoglobin content and the presence of immature red blood cells are detected.
Diagnostics also includes tests with fasting, nicotinic acid and Phenobarbital. In the first case, the analysis is carried out on the first day on an empty stomach. It is re-prescribed after 48 hours. All this time, the patient must follow a special diet, in which the calorie content of the daily diet should not exceed 400 kcal. If the bilirubin concentration exceeds 50-100%, the preliminary diagnosis is confirmed. A nicotine test involves administering the drug intravenously. If after 2-3 hours an increase in bilirubin is observed, the disease is confirmed. As for Phenobarbital, this drug must be taken within 5 days. The test is considered positive if after this time there is a decrease in bilirubin.
Additionally, it is recommended to do an ultrasound of the abdominal organs. The most informative is the DNA analysis for Gilbert's disease. With its help, a specialist can accurately determine the likelihood of the disease occurring or its presence.
Indications
Gilbert's test is prescribed when the following symptoms appear:
- Abdominal pain localized on the right side, mainly under the ribs;
- Changing the shade of the epidermis and whites of the eyes to yellow;
- Bursting sensations and a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- Increased gas formation;
- Problems with stool;
- Nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- Frequent dizziness;
- Depressed state;
- Problems with going to bed at night, short and poor quality sleep.
With this pathology, there is an increase in the size of internal organs such as the liver and spleen, which is also a purpose for conducting blood tests for Gilbert's syndrome.
Drug therapy
The disease is not life-threatening. Its symptoms go unnoticed for a long time. However, psychological discomfort to patients is caused by yellowness of the skin.
Medical treatment of Gilbert's disease involves taking several medications. For example, during exacerbation of the pathological process, Phenobarbital is prescribed. The dosage and duration of its use are selected individually. Prolonged or uncontrolled use can negatively affect the liver and central nervous system.
Several times a year, patients are advised to take Ursosan. The drug prevents the formation of stones in the liver and artificially creates protection for it from negative factors. The prophylactic course usually lasts several weeks.
Additionally, patients are prescribed drugs from the following groups:
- choleretic to reduce jaundice of the skin (“Karsil”, “Cholenzim”);
- barbiturates to reduce bilirubin in the blood (Surital, Fiorinal);
- diuretics (“Furosemide”, “Veroshpiron”);
- enterosorbents (“Polyphepan”, “Enterosgel”);
- hepatoprotectors to protect liver cells (“Heptral”).
During the entire course of treatment, the patient must undergo tests periodically. This is required to control the progress of therapy and its effectiveness. If necessary, drugs are replaced with analogue drugs to avoid the development of complications.
Changing your diet
Diet is an important component of the course of therapy. It helps relieve the symptoms of Gilbert's disease. Both treatment and nutrition plan should be selected by a doctor. As a rule, diet No. 5 is recommended. It is very tough and strict, and involves giving up many foods. On the other hand, with its help you can get rid of unpleasant symptoms and keep the level of bilirubin in the blood under control.
Compliance with the diet comes down to the following recommendations:
- all food should be at room temperature;
- Do not drink strong tea, coffee, carbonated and overly sweet drinks;
- everything fried and fatty should be excluded;
- you need to eat often, but in small portions;
- spicy foods and spices should be excluded;
- Eggs, cholesterol-containing products, and flour are prohibited;
- You must not drink alcohol or smoke.
The daily diet should consist of low-fat and lean foods. Vegetables and non-acidic fruits are allowed. All foods should be steamed or baked in the oven.
Specific studies
To diagnose the pathology, if a genetic blood test for Gilbert's syndrome has not been performed, additional tests are also prescribed. The essence of such tests is the use of certain drugs that affect the level of bilirubin in the blood.
Drug tests
There are several types of tests that help diagnose Gilbert's syndrome:
- The use of drugs containing nicotinic acid. The drug in an amount of 50 mg is injected into the bloodstream through a vein. Three hours later, the blood is taken for analysis. If the study showed an increase in bilirubin concentration several times, Gilbert's syndrome, hepatitis or hemolysis are suspected;
- The use of products containing phenobarbinal. The drug is used in tablets. The product is consumed for 5 consecutive days before the study. The recommended dosage is 3 mg per 1 kg of body weight. If after the analysis a decrease in the concentration of bilirubin in the blood is detected, a positive test result is determined;
- Use of products that contain refampicin. The essence of testing is to inject 900 mg of the drug into the bloodstream. If the concentration of bilirubin in the blood increases, this means that the test for Gilbert's syndrome showed a positive result.
Other samples
There is another study for diagnosing Gilbert's syndrome - a non-drug test. In this case, no drugs are used. For testing, fasting blood is taken and the bilirubin level is determined. After this, the patient should not consume anything other than pure still water for 2 days.
If it is not possible to maintain such a strict diet, you are allowed to eat, but the calorie content of the daily diet should not exceed 400 kcal. After this, a repeat study is carried out. The test will be positive if the analysis shows an increase in pigment levels by more than 2 times.
A blood test for Gilbert's syndrome helps to identify pathology in the early stages of its occurrence and begin therapy. In this case, doctors give a favorable prognosis, but only if certain nutritional rules are observed.
© 2020 – 2020, . All rights reserved.
Help from traditional medicine
What is Gilbert's disease and how to treat it correctly, the doctor will tell you after diagnosis. Some doctors recommend various traditional medicine recipes to their patients as a supplement to the medication course. Their main goal is to reduce the yellowness of the skin. For example, teas made from medicinal herbs are often used for this purpose. Making this drink is quite simple. It is necessary to pour boiling water over a handful of dry raw materials and let it brew. Calendula, milk thistle, rose hips, corn silk or barberry can be used as medicinal plants.
Herbal baths and lotions prepared on their basis also have a positive effect. In this case, calendula is usually used.
Prognosis for recovery
The prognosis is favorable, but it is determined by the course of the disease. Hyperbilirubinemia persists for life. Progressive changes in the liver are diagnosed extremely rarely. If you follow the doctor’s recommendations and competent drug treatment, the bilirubin level can be reduced to standard levels. However, jaundice may reappear after missing meals or vomiting.
Doctors note the high sensitivity of patients to various hepatotoxic effects. We are talking about taking alcohol and some medications. Inflammation of the biliary tract and psychosomatic disorders may develop. Before planning a pregnancy, both parents, if one of them has been diagnosed with Gilbert's pathology, should consult a geneticist.
Prevention methods
Gilbert's disease is a genetic pathology. Therefore, modern medicine has not developed methods for its prevention. Many people for a long time do not even suspect the presence of such a pathology in the body. This continues until one of the provoking factors triggers the disease. Therefore, doctors recommend avoiding this kind of mechanism: eating a healthy and balanced diet, avoiding stress, and giving up bad habits. In addition, once a year you need to visit your primary doctors as part of a medical examination. Timely detection of the disease allows you to avoid its complicated course in the future and immediately begin therapy.