What is hepatitis D
Hepatitis D is a disease caused by hepatitis delta viruses (HDV). It can be considered a kind of parasitic virus, since it cannot exist separately and only infects people with an existing hepatitis B virus (HBV). By its nature, the pathogen is very aggressive and affects the liver, which often leads to tissue necrosis, cirrhosis and even cancer.
Hepatitis delta is unique; it mutates quickly and creates different genotypes. However, despite its high pathogenicity, it has a small RNA that contains genetic material.
The peculiarity of HDV is that it cannot reproduce itself; for this it needs to borrow a protective outer capsule from the hepatitis B virus. Having multiplied in liver cells, the pathogen makes it difficult for hepatocytes to work, fat begins to accumulate in them, and this leads to necrosis. The incubation period ranges from two days to several weeks.
The genetic apparatus of the virus is based on a single-stranded RNA molecule
Features of the disease in children
The course of the disease in children is not much different from the symptoms in adults. The methods of infection are the same, but in children the chronic form and cirrhosis of the liver develop faster. The virus can be transmitted from the mother during childbirth or breastfeeding. In infants, the course can often pass without jaundice, which can interfere with early detection of the disease.
Video: hepatitis D virus - epidemiology, clinical picture and treatment
Diagnostics
It is impossible to diagnose the disease solely by external signs. Therefore, if infection with hepatitis D is suspected, the patient is prescribed:
- biochemical blood tests that detect specific antibodies;
- Ultrasound and rheohepatography of the liver, which can be used to assess the condition of liver cells;
- puncture biopsy is a study of liver cells, which allows us to determine the presence of hepatitis with almost 100% probability.
Modern medical methods make it possible to quickly and accurately diagnose the disease in patients
Classification: acute and chronic form
The acute form is the most noticeable - its symptoms are difficult to overlook. The disease begins to develop rapidly, the patient’s well-being worsens every day, there is a phase of acute intoxication of the body and disruption of the liver cells. If treatment is started on time, the chances of recovery are high. If you leave everything to chance, the disease will become chronic. The danger lies in the frequent asymptomatic course of the disease. The patient may believe that the disease is cured and recovery has occurred, but at this moment irreversible necrotic processes occur in his liver.
Instead of following a diet and effective treatment, the patient may continue to take toxic substances and eat junk food, which only worsens his situation. The liver is greatly enlarged, you can feel it yourself, dull pain appears in the right side, constant nausea exhausts the patient. Hepatocytes are gradually replaced by connective tissue, the functions of the organ are disrupted and this leads to cirrhosis.
In liver cirrhosis, hepatocytes are replaced by fibrous connective tissue
Cirrhosis is a fast-acting, progressive disease. The affected cells are quickly replaced by connective tissue, liver function fades, which leads to acute liver failure. Toxic products are no longer processed, and acute poisoning of the entire body occurs. In the future, cirrhosis leads to primary cancer.
Prevention
Of primary importance in prevention are testing blood products for markers of forms B and D and the use of disposable syringes and needles. The widespread introduction of vaccination into everyday practice is considered promising, which will also reduce the possibility of developing delta infection.
Primary prevention of hepatitis D has not been developed. Secondary prevention consists of early recognition and adequate treatment. Children who have suffered acute viral hepatitis B, C, D must be registered at the dispensary for at least one year. During the period of clinical observation, it is recommended, in addition to an examination to determine the size of the liver, to conduct a biochemical study of blood serum (total bilirubin, transaminase activity, sediment samples, specific markers, etc.). Refusal from medical vaccinations, limitation of physical activity, strict adherence to a diet, sanatorium treatment (outside exacerbation). Widespread introduction of vaccination will solve the problem of not only acute but also chronic hepatitis.
Now you know the main symptoms and methods of treating hepatitis D in a small child. Health to your children!
Pathways of pathogen transmission
Hepatitis D develops exclusively if the patient has the hepatitis B virus. You can become infected with them both at the same time (co-infection) or get HDV after the primary HBV disease (superinfection).
Sources of infection can be people with a chronic or acute form of the disease, or even simply carriers of the virus who do not have symptoms. The pathogen is transmitted through blood and body fluids. The most common transmission methods are:
- sexual contact is the main route of infection. During unprotected sexual intercourse, when sperm and biological fluids come into contact with the partner’s mucous membrane, the virus is transmitted;
- use of donor blood. Despite careful testing and study of blood, there are known cases of blood transfusion from infected donors;
- tattooing, piercing, manicure, dental treatment - it is possible to become infected with the hepatitis D virus if the instruments were improperly sterilized;
- drug use. Drug addicts often use one syringe for several people, thereby infecting others;
- the vertical route is the transmission of the virus to the child from the mother during childbirth. When breastfeeding, there is also a risk of infection if there are wounds and cracks on the mother’s nipples;
- using other people's personal hygiene products. Do not use a toothbrush, razors, or nail scissors from an infected person;
- non-compliance with safety precautions by medical and beauty salon workers. It is imperative to use disposable gloves to avoid the patient’s blood getting into areas of the skin where there are injuries.
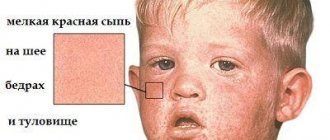
Symptoms of the disease
The course of the disease depends on the type of infection. If there was a case of co-infection, then first there is an increase in the number of hepatitis B viruses, a feverish state and jaundice appear. Afterwards, the hepatitis delta virus begins to multiply intensively, intensifying the symptoms of the disease. Often the pathology becomes chronic.
If a superinfection occurs, the disease rapidly progresses, hepatocytes are quickly affected, cirrhosis develops, and even death is possible. Typical symptoms of hepatitis D infection include:
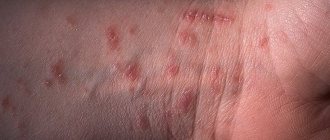
- yellowing of the sclera of the eyes, skin, mucous membranes;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- dark color of urine;
- light, sometimes even white, stool;
- temperature increase;
- chronic fatigue;
- nausea, vomiting, decreased appetite;
- pain in joints and muscles;
- liver enlargement;
- weight loss.
Diagnostics: necessary tests and their interpretation
The first diagnostic method is a superficial examination of the patient. The doctor conducts a questionnaire, identifies possible methods of infection, and palpates the liver.
After the examination, the doctor prescribes a blood test. Laboratory diagnostic methods include:
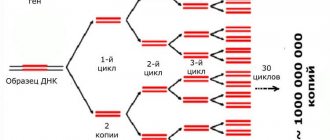
- ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay);
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction);
- blood chemistry.
ELISA and PCR can detect the presence of various antigens, antibodies and RNA of the virus:
- IgM anti-HDV is a class M antibody produced by the immune system. Their presence in the blood indicates the very height of the disease; they appear in the first weeks after infection and disappear after a couple of months if the patient begins to recover;
- IgG anti-HDV - class G antibodies, indicating the body's fight against the virus. The patient is either infected or has already overcome the infection. If there are a lot of them, we should talk about superinfection, the hepatitis D virus superimposed on previously acquired hepatitis B. If only these antibodies are detected, they speak of a chronic form of the disease and the presence of immunity to further infection after recovery;
- HDAg are antigens derived from part of HDV. Indicates the presence of hepatitis D virus;
- HBsAg - parts of the virus shell B and D, appear long before the first symptoms of infection, speak of co-infection;
- HDV-RNA - detected by PCR and indicates the presence of hepatitis D virus RNA;
- Anti-HD total - a comprehensive analysis of the amount of G and M antibodies.
Biochemical blood tests are performed repeatedly during the course of the disease. The following deviations from the norm will indicate liver pathology:
- increased levels of liver enzymes (ALT, AST), which appears with necrosis of liver cells. The norm for women is 31 IU/l, for men - 37 IU/l;
- increase in alkaline phosphatase (normally up to 150 IU/l);
- increase in total and conjugated bilirubin (normally up to 27–34 µmol/l), causing jaundice;
- decreased albumin levels and increased gammaglobulins (normal gammaglobulins are from 12 to 22%);
- increase in triglyceride levels (normally up to 2.26 mmol/l).
Ultrasound examination is suitable for a superficial examination of the liver, determining its size, and identifying tumors.
A biopsy is used to assess the condition of liver cells. Using a puncture, the doctor removes a small area of the organ. The resulting material is studied under a microscope and the degree of cell degradation, the level of connective tissue proliferation are determined, and lesions are identified. Currently, there are additional tests to avoid a biopsy:
- fibrotest;
- actitest;
- fibroactitest;
- fibromax.
They assess the level of replacement of hepatocytes with connective tissue, the degree of inflammation, liver destruction and the severity of fatty degeneration.
Types and causes of hepatitis D
The causative agent of the disease is the HDV virus, which has many features and is considered much more contagious than other known infections. It is distinguished from many other viruses by its extreme stability in the external environment and survives at low temperatures, heat, and under the influence of acids and other toxic substances. That is why, even with short-term contact of damaged areas of skin and mucous membranes with poorly disinfected objects, there is a huge likelihood of infection with the HDV virus.
The HDV virus has the smallest genetic material among all known pathogens, but it does not know how to independently create an envelope.
Therefore, the main condition for infection with hepatitis D is the presence of the hepatitis B virus.
In modern medicine, there are two main types of this disease:
- co-infection, which occurs when hepatitis B and D viruses enter the human body at the same time and is characterized by a passive course of the disease;
- superinfection, which is observed when infection with hepatitis D occurs after the hepatitis B virus has entered the human body. Superinfection is characterized by the rapid development of the disease, possible complications and requires immediate treatment.
Structure of the HDV virus
Depending on the geographical distribution, there are several types of hepatitis D:
- genotype 1 – occurs in people from all countries of the world, but is most widespread in Europe and America;
- genotype 2 – common in Asian countries, mainly in Japan and Taiwan;
- genotype 3 - found in the Tropics, Africa and Latin America.
Treatment of viral hepatitis D
Treatment of hepatitis D is a long and complex process and includes several stages:
- antiviral therapy simultaneously for two types of hepatitis;
- maintenance therapy to restore liver cells;
- cleansing the body of toxins and a strict diet.
It is possible to cure hepatitis D after destroying the hepatitis B virus, which will prevent the first one from reproducing. There is a chance to completely get rid of the disease, but only with timely diagnosis and proper treatment.
Antiviral drugs
There are no narrowly targeted drugs specifically against hepatitis D; broad-spectrum drugs are used. Many drugs that help with hepatitis B have proven completely useless in treating HDV. The most effective remedy is interferon, including the drug Altevir, developed on its basis.
There are different forms of release of the antiviral drug Altevir: in ampoules, vials and syringes
The main active ingredient in the drug is recombinant human interferon alpha 2b. Produced by genetic engineering. Escherichia coli is used as a producing organism, into which a human gene is inserted. With its help, the synthesis of the necessary substance occurs. Since the life cycle of the bacillus is short, and these bacteria multiply very quickly, a large amount of interferon is released in a short time. Despite the use of microorganisms, the resulting substance is completely identical to that produced by humans and has very high activity.
The drug has antitumor, antiviral, and immunomodulatory effects. There are many analogues of the drug Altevir with different dosages:
- Alfaron;
- Reaferon-es;
- Eberon alpha R;
- Laifferon;
- Interferal and others.
Symptomatic treatments
In addition to destroying the virus, it is necessary to provide support and restoration of the liver, as well as rid the body of the toxic load.
Drugs from the group of hepatoprotectors are prescribed without fail. One of the most common medications is Essentiale Forte. It consists of natural phospholipids from soybeans that restore liver cells. Heptral and Hepa-merz will help improve metabolism, reduce fatty deposits in the liver and protect against toxins.
Essliver forte is also an effective remedy and allows you to restore lost hepatocytes.
Video: liver function and the effect of Essliver Forte
While paying attention to the restoration of liver cells, we should not forget about the removal of harmful substances accumulated in the body. Various types of adsorbents perform this function well. These include Enterosgel, Polysorb.
Video: beneficial effect of Enterosgel on the body
Diet and lifestyle
Treatment of hepatitis D is closely related to adherence to a strict diet, Table No. 5 is recommended. The following rules must be observed:
- avoid overeating;
- eat 5 times a day in small portions;
- do not eat cold or hot food, all cooked food should be warm;
- Grind food thoroughly in advance;
- drink up to 2.5 liters of water per day as directed by your doctor;
- Limit salt intake to 4 g per day.
The basic rule of nutrition: elimination of fatty, spicy, salty foods, rich broths and fruits rich in essential oils.
In addition, eliminate smoking, alcohol, and limit physical activity.
When treating viral hepatitis D, it is recommended to include in the diet such foods as:
- lean meat and fish, boiled, baked or steamed;
- wheat, rye bread;
- vegetable broths;
- low-fat dairy products;
- tomatoes, cucumbers, carrots, cabbage;
- baked and boiled zucchini, potatoes, pumpkin, eggplant;
- sweet ripened fruits;
- pasta;
- diet sausages, ham;
- vegetable oils;
- lightly brewed black tea.
Prohibited foods for hepatitis D:
- chocolate;
- fatty meat and fish;
- meat broths;
- pickled, smoked, spicy and salty dishes;
- sour foods;
- eggs;
- fresh white bread, confectionery flour products;
- legumes;
- fresh garlic, onion, sorrel;
- coffee;
- lemonades;
- alcohol.
Compliance with the diet is necessary throughout the entire period of treatment and even for a long time after recovery - to maintain liver function.
Photo gallery: recommended products for hepatitis D
Lean meat, such as beef, is a dietary product
Wheat and rye bread are allowed for consumption
Preference should be given to low-fat vegetable broths
Vegetables can be eaten raw, boiled or baked.
Ripe sweet fruits make an excellent dessert
Vegetable oils must be included in the diet
Table No. 5, diet rules - video
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
The prognosis for treatment varies greatly for different types of infection. If co-infection occurs, the chances of recovery increase significantly. Only 3% of cases become chronic. If there was a case of superinfection, then the percentage of those recovered greatly decreases. About 70–80% of cases of hepatitis D infection end in chronicity of the process.
Hepatitis itself is not an indication for disability. But if the disease develops into cirrhosis of the liver and the functions of the organ are impaired, the medical commission will confirm the person’s loss of ability to work and determine the degree of disability.
Treatment of other diseases starting with the letter - g
| Treatment of sinusitis |
| Treatment of galactorrhea |
| Treatment of pulmonary hamartoma |
| Treatment of lung gangrene |
| Treatment of gastritis |
| Treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease |
| Treatment of hemolytic leukopenia |
| Treatment of hemorrhagic stroke |
| Treatment of hemorrhoids |
| Treatment of pulmonary hemothorax |
| Treatment of hemophilia |
| Treatment of hemochromatosis |
| Treatment of genital herpes |
| Treatment of hepatitis G |
| Treatment of hepatitis A |
| Treatment of hepatitis B |
| Treatment of hepatitis E |
| Treatment of hepatitis C |
| Treatment of hepatosis |
| Treatment of hepatorenal syndrome |
| Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma |
| Treatment of herpes |
| Treatment of hydronephrosis |
| Treatment of pulmonary hydrothorax |
| Treatment of gynecomastia |
| Treatment of overactive bladder |
| Treatment of hyperbilirubinemia |
| Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia |
| Treatment of hyperprolactinemia |
| Treatment of hypertensive crisis |
| Treatment of hypertension |
| Treatment of tonsil hypertrophy |
| Treatment of hypospadias |
| Treatment of hypothyroidism |
| Treatment of hypothyroid coma |
| Treatment of glycogenosis |
| Treatment of worms |
| Treatment of glomerulonephritis |
| Treatment of ulcers on tonsils |
| Treatment for tension headaches |
| Treatment of gonorrhea |
| Treatment of liver granuloma |
| Treatment of nail fungus |
| Flu treatment |
The information is for educational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; For all questions regarding the definition of the disease and methods of its treatment, consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal.