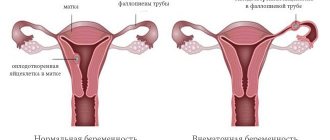
Not every conception leads to childbirth. Sometimes the fetus stops developing and dies. What are the signs of a frozen pregnancy and why is it not always possible to identify the problem? Statistics report that every 4-5 pregnancies end in miscarriage. Is it possible to prevent the process if we understand its causes?
Photo: pexels.com
Why does pathology develop?
Why pregnancy stops, many ladies are interested. Doctors attribute the following factors to most of the reasons that provoke fetal death:
- Infectious and viral diseases suffered during pregnancy.
- Blood diseases and diagnosis of Rhesus conflict.
- Congenital or acquired pathology of the uterus, frequent abortions.
- Violation of hormonal levels and poor nutrition, consumption of harmful foods in the diet.
- Constant stress and a woman’s genetic predisposition.
- Harmful and unfavorable working and living conditions, as well as previously performed IVF or artificial insemination.
In addition, bad habits and previous infectious diseases, pathogenic microorganisms, and STDs pose a certain danger.
Why embryo development stops, possible causes of pathology
Doctors cannot always determine exactly why a pregnancy stalls. However, the main causes of pathology may be as follows:
- genetic failure - in the majority of women (70%), if fetal fading occurs during pregnancy up to 2 months, it is due to chromosome abnormalities in the fetus. Such anomalies appear quite early and are almost always incompatible with life. Bad genetics can be passed on from both the mother and the father, and an unsuccessful combination of parental genes is also possible. And if a woman’s fetus freezes more than 3 times, then this is precisely because of a genetic failure;
- hormonal disorders - in this case, the fetus freezes for 2 reasons: 1 - due to a deficiency in the female body of the hormone progesterone, without which it can neither survive nor develop in the uterus; 2 – on the contrary, excess androgen hormones;
- infections. A pregnant woman's immunity often weakens, and she becomes vulnerable to various bacteria and viruses. In this case, infectious diseases worsen, the vaginal flora becomes more active, and then a dangerous moment comes for the unborn child, threatening infection;
- ARVI is usually quite severe, since the immune system works at half capacity. Moreover, the danger is not the causative agent of the disease, but precisely its symptoms: intoxication of the body and an increase in temperature (it leads to a malfunction in the circulatory system: the fetus does not receive the required amount of oxygen and nutrients);
- rubella and cytomegalovirus. They are dangerous in case of infection during pregnancy; with early infection, on the contrary, antibodies have already been developed that prevent the exacerbation of the disease;
- bleeding disorders;
- incorrect and inadequate diet, lack of exercise, insufficient exposure to fresh air, etc. harmful factors - in this case, the first signs of a frozen pregnancy may appear without delay.
Fetal freezing can also occur at a later stage
Who is at risk
It is worth noting that not a single woman is insured against a frozen pregnancy. And even in absolutely healthy representatives of the fair sex this pathology can be detected. So women may be at risk:
- over 40 years of age with an untreated sexually transmitted infection;
- exposed to increased emotional and physical stress. loads;
- having in their honey. biographies of abortion or recurrent miscarriage;
- with somatic diseases such as diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis or thyroid dysfunction.
Pregnant women are also at risk if the embryo has abnormalities incompatible with life.
Frozen early pregnancy
In the first trimester, freezing may not show itself; later, it can be attacks of pain in the form of contractions, profuse vaginal discharge, when the placenta separates and the fertilized egg is expelled. And a sharp cessation of toxicosis is also a sign that indirectly indicates fetal death.
The most dangerous period in this matter is considered to be exactly 8-9 weeks of gestation - at this stage of development, the embryo is especially susceptible to adverse factors that can provoke fading. In the 1st trimester, special attention should be paid to the period from 3 to 4 weeks, and as noted earlier - 8-9 weeks.
Only every second woman notices signs of a frozen pregnancy in the early stages. Others consult a doctor if they experience unbearable pain and strange vaginal discharge.
Why can there be two missed pregnancies in a row?
After a woman has already experienced miscarriage once, the biggest fear in her life is the subsequent conception, during which intrauterine fetal death occurs. Those who have experienced such a shock often do not know how to move on and whether they will be able to get pregnant again and give birth to a healthy child.
Doctors say that if a woman promptly sought medical help in case of fetal death, and was prescribed appropriate treatment, then she has a high probability of becoming a mother.
A repetition of the sad experience is possible in situations where a woman does not have a completely adequate attitude towards sex life and motherhood, if a subsequent pregnancy occurred spontaneously, and appropriate treatment was not carried out after the first case of intrauterine fetal death. Doctors advise refraining from conceiving for 6-12 months so that the body recovers from the loss of a child and prepares to accept a new life.
2 missed pregnancies in a row sometimes happen, however, this is not a pattern, because the reasons for repeating the sad experience may be as follows:
- uncontrolled sexual life within a year after pregnancy fading;
- identified genetic disorders that require consultation with a geneticist at the stage of family planning;
- an infectious disease that has not been completely cured (this is especially true for sexually transmitted infections, when treatment is required for both partners);
- hormonal disorders that have not been treated.
If a woman is serious about her health and is determined to become a mother, then she will listen to all the advice of the attending physician and follow his recommendations, which will reduce the likelihood of the pregnancy fading again.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics involves the following basic methods:
- Conducting a laboratory blood test to determine the level of hCG - hormone levels will be lower than normal.
- Carrying out ultrasound diagnostics, where there will be no fetal heartbeat indicators on the screen.
- Conducting a gynecological examination, during which the doctor measures the basal temperature and examines the uterine cavity.
If necessary, the doctor can refer the woman for additional diagnostics, but this is quite enough to make a diagnosis. Only an experienced doctor can visually recognize the signs of a frozen pregnancy in the first trimester.
What tests need to be done before planning your next pregnancy?
Doctors recommend planning your next pregnancy 5-6 months after a failed one. To do this, you need to undergo an ultrasound, be tested for thyroid hormones, and be examined for all possible infections, both individual and sexually transmitted. A blood test is needed to check for autoantibodies and homocysteine levels in the blood.
The main thing is that after termination of pregnancy such a mistake is not allowed. There is no need to panic or become depressed. If the cause of a failed pregnancy is known, then treatment and constant monitoring using ultrasound provide a 95% guarantee that all subsequent pregnancies will be successful.
And let the next ultrasound show such a long-awaited photo of a smiling baby.
Based on materials from delaiuzi.ru
What do specialists do during a frozen pregnancy?
The tactics of behavior of doctors with this diagnosis depends on the individual characteristics of the female body and the course of pregnancy. In some cases, in the early stages of fading, doctors recommend waiting until spontaneous miscarriage, but more often they carry out curettage of the uterus, which is reminiscent of an abortion in its technique.
The practice of vacuum aspiration is also applicable in the practice of doctors. After 1-2 weeks, doctors send the patient for an ultrasound to diagnose the uterine cavity, determining how well the curettage or aspiration procedure was performed, whether the uterine cavity is healthy and clean .
The cleaning method is determined individually by the doctor, but during the rehabilitation period after the procedure, his supervision of the patient’s health is required. The attending doctor will tell you how long it will take to become pregnant after a frozen pregnancy.
Treatment and recovery
So, a diagnosis of “frozen pregnancy” was made. What does it mean? That the woman will most likely be prescribed treatment.
Modern medicine recognizes the following methods:
- medical abortion – it is indicated for up to 8 weeks;
- surgical intervention - mini-abortion or curettage, which is done under general anesthesia. In this case, the resulting material will be sent for analysis to determine the causes of pregnancy failure. After the procedure, the woman may be prescribed a course of antibiotics to prevent inflammation.
Prevention
Before further planning a patient's pregnancy, partners should receive all necessary vaccinations. It is also worth undergoing an examination and, if detected, curing all STDs and strengthening the immune system.
Symptoms of a frozen pregnancy in the second or first trimester cannot be ignored. Timely response to changes in the body allows you to save yourself from severe inflammation.
If the diagnostic results of the woman’s health condition are normal, no treatment is required as such. Doctors say the best protection against fetal death is maintaining a healthy lifestyle and avoiding bad habits.
What can a woman feel?
A change in general condition, for example, a feeling of weakness and weakness, apathy and an increase in temperature should be a reason to contact an antenatal clinic.
Those women who have previously had a frozen pregnancy or other pathologies associated with subsequent fetal rejection have knowledge and alertness that will not allow the symptoms to worsen.
In addition, in some cases, pregnant women may experience false symptoms, which are formed under the influence of hormones or emotions.
Consequences
When diagnosing a pathological process, the development of events may include:
- Miscarriage - most often this happens in the early stages of pregnancy, when the uterus itself “pushes out” the dead embryo.
- And surgery. If this is not done in a timely manner, the dead embryo will decompose, causing peritonitis, inflammation and intoxication of the body.
In addition to physical factors, the consequences can also be psychological – stress and understanding of one’s own inferiority. That is why it is so important to lead a healthy lifestyle during this period of time, not abuse alcohol and strengthen the immune system.
Read about the consequences of diabetes during pregnancy
3 reasons for too thick sperm are described here
How to do IVF for free under a quota from the Ministry of Health: https://hochu-detey.ru/reproduct/eko/besplatnaya-kvota-na-ehko.html
Causes
The causes of frozen pregnancy in the early stages are varied and it is not always possible for a doctor to determine the exact etiology of the complication in a particular woman. The most common factors in the development of pathology include:
Genetic abnormalities
This reason occupies a leading place in the list of factors for termination of pregnancy.
The division of germ cells as a result of meiosis (eggs and sperm) is a very complex process. Due to violations of this phenomenon, the embryo has a broken genome containing various anomalies. The most common chromosomal pathologies are an increase or decrease in their number. Also, genomic abnormalities lead to pregnancy failure - the absence or duplication of maternal or paternal DNA material. Much less often, intrauterine embryo death is caused by a gene pathology - a point mutation of one trait. Most often, termination of pregnancy due to congenital anomalies is observed in the earliest stages of pregnancy - up to 6-8 weeks. Usually very severe pathologies incompatible with life lead to the death of the unborn child.
Pathologies of sex hormones
Progesterone is the main hormone during pregnancy, responsible for maintaining pregnancy.
In the first weeks, its production occurs in the corpus luteum. With pathology of this organ or abnormal activity of the endocrine glands, a deficiency of progesterone in the blood is observed. Lack of the hormone causes changes leading to intrauterine death of the fetus. Much less often, miscarriage occurs due to a lack of female sex hormones estrogen. Most of them are produced by the ovaries. Lack of estrogen causes pathologies of the uterine epithelium, which is why the embryo cannot receive adequate nutrition. Also, intrauterine death of the unborn child can occur due to excess testosterone. Normally, male hormones are produced in small quantities in the ovaries and adrenal glands. Excess androgens inhibit the synthesis of progesterone and negatively affect the uterine mucosa.
Hypothyroidism
This disease is characterized by decreased thyroid function. The endocrine organ synthesizes the hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine. Most often, hypothyroidism is a consequence of iodine deficiency due to poor diet. Thyroid hormones are involved in all processes and reactions of internal metabolism. If they are deficient, premature termination of pregnancy is possible.
Infections
The most common cause of intrauterine death of an embryo is the penetration of bacteria from the vagina into its body.
Existing sexually transmitted diseases may not have clinical symptoms for a long time, but after pregnancy, active reproduction of microorganisms is observed. This feature is associated with a decrease in immunity in the body of the expectant mother. Infection after conception is also possible. Much less often, a frozen pregnancy is a consequence of common somatic diseases - colds, poisoning, flu, etc. Pathogenic microorganisms are able to penetrate with maternal blood through the membranes of the chorion.
Immune pathologies
Autoimmune diseases are characterized by the presence of antibodies to the body's own cells. Sometimes this group of pathologies may appear for the first time during pregnancy. The pathogenesis of intrauterine embryonic death in autoimmune diseases is based on the massive production of antibodies against the body of the unborn child. Pathologies such as antiphospholipid syndrome, diffuse toxic goiter, lupus erythematosus, etc. lead to the fading of pregnancy. Much less often, intrauterine death of an embryo occurs due to incompatibility of the genetic makeup of the mother and father.
Environmental factors
Prolonged hypothermia, injury, physical and emotional stress can cause the death of an unborn child.
Also, the death of the embryo is possible due to alcohol, nicotine or opioid intoxication. How to avoid frozen pregnancy in the early stages?
Signs
You can recognize a frozen pregnancy in the first days by the following signs:
Bloody vaginal discharge
As a result of intrauterine death of the fetus, uterine bleeding is possible. The discharge is light and its color can vary from pinkish to dark brown. When the uterus is inert, they are not accompanied by cramping pain in the lower abdomen - the first and main clinical sign of premature termination of pregnancy such as miscarriage.
Fall in basal temperature
In order to determine the basal temperature, the expectant mother should insert a thermometer into the anus for 3-5 minutes immediately after waking up, avoiding physical activity before measurement. Normally, during pregnancy, the basal temperature should not be lower than 37.0-37.1 degrees Celsius. Its increase above these values is due to the action of progesterone. When the fetus dies, the amount of the hormone in the blood falls, this is accompanied by a decrease in basal temperature.
Abrupt absence of symptoms of pregnancy and toxicosis
These include engorgement of the mammary glands, morning nausea and vomiting, sensitivity to smells, perverted sense of taste, and frequent urination.
An abrupt cessation of these symptoms in the first trimester of pregnancy should alert the expectant mother. Their occurrence is associated with changes in hormonal levels and the response of the female body to the appearance of the fertilized egg. The absence of pregnancy symptoms, if present earlier, may indicate the miscarriage and death of the unborn child. Over time, the dead tissue of the embryo undergoes processes of inflammation and decay as the mother's body strives to get rid of it. After a week or longer, the woman experiences a deterioration in her general health associated with intoxication of the body with decay products.
In the absence of medical care, over time, the expectant mother may complain of nausea and vomiting, increased body temperature, abdominal pain, chills, and decreased performance. Also, when a dead embryo remains in the uterine cavity for a long time, a lag in abdominal girth from the gestational age is observed.
A prolonged course of frozen pregnancy is a risk factor for the development of sepsis. This pathology is accompanied by the migration of pathogenic microorganisms into the woman’s blood. Sepsis is a severe syndrome, it leads to a strong increase or decrease in body temperature, increased heart rate and respiratory rate, and weight loss.
Symptoms of frozen pregnancy in the second trimester and at the end of term
Externally and internally in later stages, the cessation of the baby’s vital activity is expressed in many ways similar to how the signs of a frozen pregnancy appeared in the early stages. But, since the baby himself has already grown up, the mother will have more problems after his death.
Especially if a woman is inattentive to herself, she will miss the first symptoms of trouble, and even the doctor will not track the dysfunction. If the decomposition of the fetus continues for more than five weeks, then irreversible changes may occur in the tissues of the mother’s body.
In isolated cases, the tragic ending is the death of the woman herself. Experts cite cancer and acute infections, as well as the consequences of severe intoxication, as specific causes of the mother’s death.
Such serious consequences are possible when the doctor and the woman herself missed the signs of a frozen pregnancy in the early stages, and the pathology managed to acquire a lot of complications. Let’s still look at what will help avoid such an outcome, what nuances of a woman’s condition make us think and be wary.
Stopping movements
One of the most touching moments of waiting for a baby is the first tremors. The baby makes itself known, actively moves inside the fetal membrane, and finally, the mother begins to feel them subjectively. If this is the first child, the joyful moment usually dates back to the 20th week of the term. You can hear and feel the second and third baby a couple of weeks earlier.
When it suddenly calms down and shows no signs of activity for more than 10 hours, this is a good reason to suspect some kind of abnormality. In particular, such a lull may be one of the alarming signs of a frozen pregnancy in the second trimester.
Responsible mothers do not forget to listen to themselves and monitor the frequency of movements. Normally, about ten series of tremors are observed per day. If they stop, the baby may experience hypoxia (lack of oxygen). By promptly consulting a doctor, you can prevent a tragic outcome.
Uncharacteristic changes in the mammary glands
And what will become a definite signal of trouble in an earlier period, when movements are not yet recorded? For example, are there obvious signs of a frozen pregnancy at 15 weeks? Experts pay attention to one such factor, which the mother herself is quite capable of tracking.
We are talking about how the mammary glands change. Hormonal changes at the beginning of pregnancy make them dense, “heavy,” and slightly painful. But if growth stops and then the baby dies, the breast cannot help but react.
Approximately 3-4 days, sometimes several days later, its noticeable softening occurs. At later stages, at 25 weeks or more, the glands not only become soft, but also begin to secrete colostrum, and a little later, milk.
General weakness
Carrying a child is not easy work and a significant burden on the body of the expectant mother. For different women, this period proceeds in its own way, but most still get tired both physically and emotionally.
We have already said above that a sign of a frozen pregnancy in the first trimester can be a state of chronic fatigue that lasts quite a long time. A similar condition is sometimes observed in later stages.
This is not just weakness, but rather a deep general asthenic disorder. A woman loses her ability to work, even simple household chores become a burden for her. Often apathy is accompanied by chills and dizziness; vision deteriorates, “spots” flash before the eyes.
You shouldn’t reassure yourself that this happens to women in this situation. It is better to consult a doctor and undergo additional examination.
Although the “pendulum can swing” in the opposite direction, suddenly a sharp improvement in the condition will occur, lightheadedness, vomiting, and other manifestations of late toxicosis will disappear.
Bloody discharge and pain
This is another sign that is universal for different periods of gestation. Painful sensations and brownish vaginal discharge can become symptoms of frozen pregnancy in the early stages and at any other time.
It is especially dangerous if the discharge is accompanied by pain that does not go away, no matter how the woman changes her body position. Doctors advise that if such manifestations occur, do not even go to an appointment, but call an ambulance. Otherwise, the condition will worsen, and irreversible consequences may occur: miscarriage or intrauterine fetal death.
Increased body temperature
If an increase in basal temperature in a “special situation” is really the norm, then the usual body temperature, measured externally, should not change. Of course, mommy can catch a cold, catch the flu or another viral disease accompanied by fever.
But even in this case, it is better to resort to hospitalization in order to quickly and effectively cope with the problem and prevent complications, including fetal pathologies.
But strong fever or even a slight rise in temperature in our case may also be the body’s reaction to pathology, a sign of a frozen pregnancy in the first trimester, as well as in the second and third. The tissues of the dead fetus, decomposing, infect the placenta, the epidermis of the uterus and neighboring organs.
The body gives an “alarm bell” with a rise in temperature, so it shows inflammation and at the same time tries to cope with this problem. By dismissing the hint, a woman risks missing the critical moment of no return.
The likely consequences of a delayed visit to the doctor: the inability to give birth in the future, the need to remove the uterus, or even the death of the mother herself.
No heartbeat
At the turn of the midterm, that is, 20 weeks, you can not only track the baby’s kicks, but also listen to his heartbeat without complex instruments. During the examination, the doctor also uses such a simple tool as an obstetric stethoscope.
This is a tube with two cones at opposite ends, which amplifies the beating signals of a small heart and makes them audible to the doctor. A pronounced symptom of a frozen pregnancy is the absence of these sounds at the next appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist.
True, doubts may arise here too. The placenta adjacent to the anterior wall, as well as a solid layer of fat on the abdomen, can muffle the heart sounds. Therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes other studies, primarily ultrasound diagnostics.
Laboratory techniques
Modern equipment and routine laboratory tests are already undeniable diagnostic methods. Above we talked about the rather subjective symptoms of frozen pregnancy in the early stages and in subsequent periods.
Objective, scientifically accurate data can be easily obtained by examining urine and blood, primarily for the presence and concentration of hormones characteristic of this condition.
Urine. 2000 per milliliter or a little less - this is how much leukocytes should be normal in the urine. The protein content should not exceed the norm of 0.14 grams per liter. If deviations from these indicators are observed, pathology should be suspected.
Progesterone. The average values at the beginning of the period are 20.57 nmol/l; in the later stages they increase to 301 nmol/l. Progesterone is not called the pregnancy hormone for nothing; it is intended by nature to protect the fetus.
If, for various reasons, a serious malfunction occurs, the death of the fetus in utero, then the body automatically reacts by reducing the level of this hormone.
HCG. A test for the concentration level of human chorionic gonadotropin is one of the main ones in monitoring the dynamics of pregnancy. It also serves as a criterion for the presence of various pathologies, in particular, its fluctuations can signal an ectopic pregnancy or Down syndrome in a baby.
If any primary signs of a frozen pregnancy appear in the early stages and in other, later periods of gestation, the doctor is obliged to prescribe such an analysis. These numbers mean little to the woman herself, but the specialist knows both the normal indicators and the list of conditions that lead to deviations.
Soon after fertilization, hCG begins to grow very rapidly, the level of the hormone increases exponentially: it doubles every two days. Against this background, the noticeable external manifestations of pregnancy are understandable, including women’s emotional outbursts.
By the end of the first trimester, the hormone level reaches the upper limit, then gradually decreases slightly, and remains steady until childbirth. This is normal. But if the analysis shows a significant drop in this indicator, then the chance of a serious pathology is extremely high.
How are frozen pregnancy and hydatidiform mole related?
Then why is histological examination of aborted material carried out all over the world? To exclude hydatidiform mole . This is a separate anomaly when the normal development of the embryo does not occur (it is either present, but defective, or there are separate parts of it, or is completely absent), and the chorionic villi grow in the form of blisters filled with liquid.
The danger of hydatidiform mole is that in some cases it can cause a malignant tumor to appear in a woman’s body - chorionepithelioma, which can give metastases.
Most often, women are successfully cured of it, but it is important to make a diagnosis in time, conduct careful monitoring and supervision of such a woman after termination of pregnancy and start treatment (chemotherapy) on time, if necessary, since hydatidiform mole does not always transform into a malignant tumor (depending on type), and, accordingly, not all women need it.
Medication method
In the first trimester of frozen pregnancy, it is possible to use tablets. The woman takes drugs that suppress the secretion of progesterone, which ensures the expulsion of the fetus.
Sometimes this technique is also used in the 2nd trimester. If the embryo dies at a later stage, then it is possible to use means that will start labor.
As a result, a frozen pregnancy is eliminated in the least traumatic way. If parts of the fertilized egg remain in the uterus, then surgical intervention is required.