Pregnancy is the most extraordinary and beautiful event that can happen to a woman’s body in her entire life. This condition gives life to a developing child and instills confidence in a bright and happy future in a home filled with children's laughter. However, pathological conditions also occur during pregnancy. One of these conditions includes a condition in which there is no embryo in the fertilized egg. This pathological process in gynecological circles is called anembryony, when no embryo is visible in the fertilized egg.
When a fertilized egg appears without an embryo, the reasons can be completely different.
There is a fertilized egg, but no embryo: why?
This pathology is not very rare and accounts for about 20% of cases of pregnancy loss in women. A fifth of all reproductive losses is quite an impressive figure. Anembryonia belongs to one group of frozen pregnancies. The second option for this pathology is the death of the embryo. In the case of anembryony, there is simply no embryo, and the fertilized egg develops independently. Of course, the fertilized egg cannot reach too large a size in the absence of timely diagnosis.
Anembryony
Anembryony is a special case of frozen pregnancy, when the death of the embryo occurs so early that the fertilized egg is empty.
Anembryonia occurs in 15% of all cases of early pregnancy termination. What it is? With anembryony, either the embryo does not lay at all, or it dies at such an early stage that nothing is found in the cavity of the fetal egg. This diagnosis requires a repeat ultrasound because there are quite often cases in which anembryonia is not confirmed by ultrasound after a week or two. The reason that the embryo was not seen may be that the examination was too early, and then, of course, there is hope that you will still become a mother.
Causes of anembryonia
If a woman is diagnosed with anembryonia, the reasons are most often that either a vicious conception occurred, there was an incomplete zygote, or the embryo was affected by harmful factors that killed it. Sometimes this happens in a completely healthy woman and the reasons cannot be determined.
The most common factors are:
1. ARVI and other infectious diseases in the mother in the first weeks of pregnancy.
2. Intoxication and poisoning, taking embryotoxic drugs prohibited during pregnancy, alcohol, smoking.
3. Radiation exposure
4. Stress and significant physical activity
5. Overheating or high temperature in the early stages
6. Hormonal disorders in mother
Ultrasound diagnosis of anembryonia
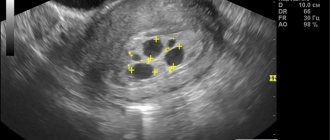
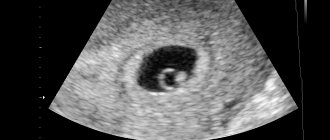
As already mentioned, this diagnosis is always made during an ultrasound examination. There is no other way to install it. The ultrasound doctor sees the fertilized egg with a cavity, but does not see the embryo and the heartbeat.
As you know, with an ultrasound in the early stages, there should be two formations in the cavity of the fetal egg, a yolk sac and an embryo next to it. In anembryony, the yolk sac can be detected, but the embryo itself is not visible. If the ultrasound was done very early, there may be an error, so it should be repeated after a week or two.
HCG for anembryonia
The way hCG rises during anembryonia may not be at all indicative. The fact is that this pregnancy hormone is produced by the chorion, that is, the fetal membranes, and in anembryonics there is a fertilized egg, and these are living cells; of course, the level of hCG in anembryonics can remain high and even increase. However, the development of this pregnancy is in any case pathological, and therefore the growth of hCG during anembryonia is slowed down.
If you suspect this diagnosis, your doctor will prescribe control tests for hCG with an interval of 2 days to make sure whether the hCG is increasing. With anembryonia, there will not be a doubling of the hormone level every 2 days, which is characteristic of a normally developing pregnancy.
Symptoms and signs of anembryonia
Like normal pregnancy, anembryonia is accompanied by characteristic changes in the mother’s body. Since the membranes are present and hormones are being produced, you may experience all the symptoms of a normal pregnancy.
There are no signs of anembryonia that could indicate that the child is no longer developing; all the usual symptoms may be present, such as delayed menstruation, breast engorgement, drowsiness, weakness, irritability. Even toxicosis with anembryonia can be the most common, quite strong and pronounced.
The basal temperature during anembryonia remains elevated, and the expectant mother cannot possibly guess that there is no longer any hope for motherhood. Only ultrasound allows one to suspect this pathology; anembryonia cannot be diagnosed in any other way.
Only sometimes the body reacts to a non-developing pregnancy of the anembryonic type with a miscarriage; the body itself gets rid of the dead embryo. Then signs of a threat of interruption appear, such as pain in the lower abdomen, spotting, and the woman consults a doctor.
Treatment of anembryonia
If a woman has heard such a sentence as anembryonia, there is only one treatment, the pregnancy must be terminated as soon as possible. Of course, in some cases of anembryonia there may be an erroneous diagnosis, so doctors are in no hurry, ordering a repeat ultrasound and waiting for some time.
Miscarriage with anembryonia sometimes occurs spontaneously, but most often the pregnancy can continue indefinitely and must be terminated. For a very short period of time, interruption with pills is possible, but more often doctors resort to curettage, popularly called cleansing. The procedure is similar to a regular abortion. Curettage for anembryonia is done in a gynecological department under short-term anesthesia. The woman is then prescribed antibiotics and discharged home after a few days.
Planning pregnancy after anembryonia
If such a misfortune has happened in your life, planning a pregnancy after anembryonia should be postponed for at least 6 months.
Prevention of unwanted pregnancy is carried out using hormonal contraceptives. You and your husband definitely need to be examined before your next pregnancy. Examination after anembryonia allows us to identify all possible diseases and health conditions that could lead to the death of the embryo. If there is an objective reason, and the expectant mother does not receive adequate treatment after anembryonia, everything can happen again.
Anembryonia does recur, and no matter what happens, pregnancy must be planned.
Absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg: reasons
Anembryonia is a polyetiological disease. This pathology in embryo development has many factors.
Empty fertilized egg or absence of embryo: reasons.
- The most common etiological factor among identified anembryonia is genetic abnormalities. Rough changes that are incompatible with life are interrupted by the female body itself as unviable. 80% of threats of abortion that are recorded in gynecological departments are caused by genetic transformations. Women must write a receipt stating that if they insist on carrying the pregnancy to 8 weeks, they are aware of the high risks of genetic abnormalities in the embryo, and subsequently in the fetus.
- The second leading cause among the occurrence of an empty ovum is the impact of viral agents on pregnancy. TORCH infections can have fatal consequences for pregnancy. The influence of toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, rubella and other pathogens of infectious diseases can both cause frozen pregnancy and anembryonia. If these viruses do not have a detrimental effect on the body of the developing baby, then they can cause severe developmental defects, which, unfortunately, are sometimes incompatible with life.
- Some medications and chemicals that cause the development of blastomeres to stop may also have a detrimental effect on the embryo. That is why all doctors recommend limiting the consumption of any drugs as much as possible until the end of the first trimester.
- The influence of ionizing radiation, such as X-ray, can also affect the arrest of embryonic development.
Clinic
The clinical picture of this pregnancy pathology is not specific. It is simply impossible to diagnose anembryonia based on any signs. The only facts that can indirectly suggest an unfavorable development of pregnancy is the presence of a threat of miscarriage, which manifests itself in the form of pain in the lower abdomen of various types, spotting, bloody or copious discharge from the genital tract. Also, an unfavorable picture of pregnancy may be indicated by a history of acute respiratory viral infections, when they manifest or worsen, for example, a herpetic infection.
Symptoms
A fertilized egg without an embryo does not have clear symptoms. But despite this, certain features can be identified in the clinical picture that make it possible to suspect obstetric pathology. As a rule, we are talking about the following manifestations:
- The size of the uterus does not correspond to the gestational age.
- Signs of pregnancy gradually disappear.
- Uterine tone is reduced.
- Scanty bleeding from the vagina appears.
Diagnostics
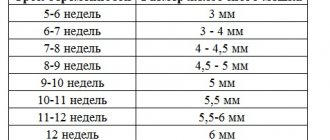
There are quite a few diagnostic criteria for identifying anembryonia. A reliable sign of the absence of a developing embryo in the fertilized egg is visualization using ultrasound. Of course, there are cases when there is a pregnancy in the fertilized egg, but the embryo is not visible. This situation applies to short periods. However, if there is no embryo in the fertilized egg for 6 weeks or there is no embryo in the fertilized egg for 7 weeks, then we should talk about pathology.
A clear sign of unfavorable development of pregnancy, which indicates a pathology such as anembryonia, is the absence of the yolk sac when the size of the fertilized egg is 18.25 mm, and when its size exceeds these indicators, the absence of the embryo itself. If the fertilized egg is 5 weeks old, then the embryo is not visible, but if there is no embryo in the fertilized egg for 8 weeks, then in this case we can safely talk about the presence of such a pathology.
It is possible to assume that a pregnancy is not developing indirectly based on the level of human chorionic gonadotropin. Of course, hCG will tend to increase. This is the difference between anembryonia and frozen pregnancy, in which the hCG level will rapidly fall down. In the absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg, hCG will increase, but without the necessary dynamics. These indicators can be recorded at the lower limit of normal. This should alert the attending physician and be a reason to prescribe ultrasound diagnostics. A reliable diagnosis can be made at 7-8 weeks of pregnancy.
The condition during pregnancy in the form of the absence of an embryo is also classified into 3 types.
The first type is the absence of an embryo. This is a condition in which its remains are not recorded at all by an ultrasound diagnostic device; the size of the fertilized egg does not correspond to the gestational age.
Anembryonia of the second type is also characterized by the absence of any elements of the embryo, however, the uterus is fully consistent with the terms of pregnancy.
Anembryony of the second fertilized egg. Situations are also recorded when resorption of one embryo occurs. In one fertilized egg you can visualize a normally developing embryo, in another there is a complete absence of its elements. Of course, the main diagnostic criterion for anembryonia is ultrasound diagnostics.
Features of the growth and structure of the fertilized egg
The amniotic egg is formed at the moment of fusion of the sperm and the egg; it initially consists of an embryo and a membrane; as the fetus grows, the structure of formation becomes more complex and the volume increases.
Important!
The main tasks are to provide the embryo with nutrients, support blood circulation at the initial stage of development, create the basis for the formation of the placenta, secure the fetus in the uterine cavity, and synthesize the hormone hCG.
Stages of formation:
- 7 days after conception, the chorion is formed - the outer dense shell of the embryo, through which oxygen and all useful substances are supplied to the embryo, protecting against infection. As pregnancy progresses, the chorion transforms into the placenta.
- There are many villi located on the surface of the chorion; they help the fertilized egg to gain a foothold in the uterus.
- Gradually, the hairs fall off, remaining only at the site of attachment of the egg to the uterus, the rest of the surface of the chorion becomes smooth.
- On the 20th day after menstruation, the yolk sac is formed - it performs the functions of the liver, kidneys, spleen, the first germ cells, blood cells, and blood vessels are formed in it. The absence of such a sac is a sign of pregnancy pathology.
- Inside the membrane that surrounds the embryo is the amnion, which produces amniotic fluid.
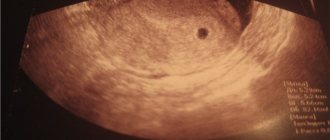
A small round or oval area is the fertilized egg.
An amniotic egg can be seen on ultrasound as early as 4–5 embryonic weeks, approximately 15–20 days after a missed period. Usually on the screen and in photos it looks like a small area of dark gray color with a regular round or oval shape.