Where do such pathologies come from?
Duodeno-gastric reflux accompanies such chronic diseases of the digestive system as gastritis and peptic ulcers. This pathology is not considered an independent disease, therefore gastritis and duodenitis are considered to be the causes of disturbances in the unilateral conduction of food along the gastrointestinal tract. In turn, gastritis is associated with serious abnormalities in the functioning of the duodenum. Often, when GDR is detected, a complex disease is detected - gastroduodenitis.
Several factors associated with a violation of a healthy lifestyle can provoke the occurrence of pathology:
- tobacco smoke and drugs;
- alcohol abuse;
- use of unapproved medications during pregnancy.
DGR can be formed under the influence of internal
sources: insufficient tone of the circular muscles of the orifices of the stomach or hernia of the diaphragm in the esophagus. The sources of pathology may be the consequences of too high pressure in the duodenum: cholecystitis, pancreatitis, Botkin's disease. It is possible that pathology may be detected after surgical interventions in the abdominal area: removal of the gallbladder, anastomosis with fastening of intestinal loops. The concentrations in the gastric juice that are contained in the bile acids, pancreatic enzymes and enzymes that break down lecithin contribute to deviations from the norm.
Typologies and degrees of development of reflux
Depending on the progress of reflux, there are 3 degrees of pathology,
Rejection of gastric juice into the esophagus
identified by diagnostic methods when a concomitant disease is detected.
Half of the patients with reflux of duodenal contents had grade 1 GHD, in which the mixing of gastric contents with duodenal contents was insignificant.
With reflux disorder, four out of ten patients had a greater disturbance in the stomach, which corresponds to grade 2 pathology.
Approximately one patient out of ten showed, as a result of diagnosis, serious disturbances in the movement of duodenal contents into the stomach, which characterizes stage 3 of the disease.
It should be understood that gastric reflux is identical in type to gastroduodenitis. The following manifestations indicate gastroduodenitis:
- halitosis;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- urge to vomit.
There are other signs of gastroduodenitis that make it similar to gastritis:
- violation of stool both in the liquid direction and in the direction of constipation;
- flatulence;
- decreased appetite;
- frequent belching.
According to the typology of destructive processes, there are 4 types of reflux:
- Superficial type, in which only the cells of the mucous membrane are affected. The integrity of the glandular exocrine epithelium is not impaired.
- When reflux is accompanied by inflammatory processes, swelling and redness of the mucous membrane, it is customary to talk about the catarrhal type of pathology.
- With the erosive type of reflux, the mucous membrane is characterized by focal atrophy.
- The biliary variety is associated with a violation of the outflow of bile from the gallbladder into the duodenum.
Reflux symptoms
Duodeno-gastric reflux in its individual form is not easy to detect, since the symptoms of the pathology repeat the symptoms of almost any disease of the digestive system. The most characteristic of DGR is:
- intense, sharp pain in the epigastric region accompanying the digestion of food;
- constant painful feeling of heartburn;
- flatulence;
- thick yellow coating on the surface of the tongue;
- entry of bile acids from the duodenum through the stomach into the esophagus, resulting in belching and bitterness in the oral cavity.
If the patient's diet contains a large amount of carbohydrates, then with DGR there is bad breath. The foul odor is caused by the penetration of bile into the stomach from the duodenum through the pylorus.
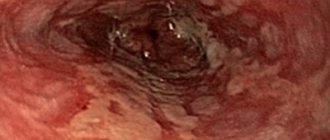
Gastric reflux is also detected during diagnostic examinations that exclude suspicion of reflux of duodenal contents, for example, fibrogastroduodenoscopy or other diagnostic methods that reveal the presence of other pathological conditions of the gastrointestinal tract.
The presence of reflux is also indicated by signs of dry hair and quickly breaking nails, unhealthy skin color, congestion and hyperemic corners of the mouth.
Symptoms
Bile reflux, as GDR is also called, can occur completely unnoticed at first, or masquerade as a completely different gastrointestinal pathology. But still, with careful attention to yourself and your health, it is quite possible to suspect that the digestive tract needs help.
Having recognized the first signs of pathology, describe them to your gastroenterologist in as much detail as possible. Knowing the symptoms and treatment, your doctor will easily select the right one
Signs of GHD can be extremely similar to symptoms of reflux gastritis and other gastrointestinal pathologies. The most pronounced of them are:
- heartburn (burning, sensation of heat throughout the entire esophagus and stomach). Most often occurs immediately after eating;
- belching, most often not with air, but with the contents of the stomach. After all, the viability of the sphincter, which limits the esophagus from the underlying sections of the gastrointestinal tract, also suffers;
- pain in the epigastric region. The activity exhibited by the bile ducts (through which the liver supplies its secretions) provokes a spasm of the muscles of the entire gastrointestinal tract, which causes a severe pain attack;
- coating on the tongue (most often yellow);
- unpleasant odor (stench – halitosis) from the mouth;
- bloating, vomiting;
- loss of appetite, etc.
As it becomes clear, the symptoms are extremely close to the manifestations of most pathologies of the digestive tract.
Diagnosis of reflux
GHD is detected during a visual examination of the patient and history taking. If the doctor has a suspicion, several referrals for examination are prescribed to refute or confirm the disease. Helps identify reflux:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. During the ultrasound examination, the nature and sources of disturbances in the stomach, gallbladder, pancreas or duodenum are revealed;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy is the most accurate picture for detecting reflux, when the data obtained allow cytological and histological assessment of the degree of damage to the mucosa and the nature of its damage (malignant or benign process);
- chemical analysis of gastric juice, which makes it possible to determine by titration even small concentrations of pancreatic enzymes and bile acids;
- measurement using gastric juice pH indicators throughout the day. If after eating the pH shifts to the alkaline side, it is judged that duodenal fluid has penetrated into the stomach and the two fluids have mixed.
Treatment
Diagnosis and therapy of this disease require an integrated approach. Pharmacological treatment will undoubtedly have a positive effect, but without a special diet it will be unstable, and after some time the pathology will again make itself felt. The goal of therapy is to normalize the motility of the stomach and duodenum and improve the ability to clot bile acids.
With the help of pharmacological treatment, pain relief, stimulation of motility, and also mitigation of the effect of bile on the stomach environment are produced. Drugs are prescribed to eliminate symptoms - heartburn, pain, flatulence, and so on. The duration of treatment is usually from one and a half to two months. In especially severe cases, therapy is longer - up to six months. The following pharmacological groups are used:
- antacids;
- H2-histamine blockers;
- proton pump inhibitors.
Medicines to relieve symptoms – heartburn, pain, flatulence
Cases when the body does not respond to conservative treatment methods are rare. However, if this happens, as well as when certain complications develop, they resort to surgery.
Successful therapy is impossible without diet. In addition to normalizing nutrition, treatment of duodenogastric reflux requires:
- normalization of body weight;
- quitting drinking alcohol and smoking;
- avoiding heavy physical activity;
- combating physical inactivity;
- regular feasible exercises;
- hiking in the fresh air.
How is reflux treated?
The treatment regimen for DRG is complex and only a qualified physician can do it.
A problem discovered during diagnostic examinations can be eliminated in a short time with the help of the correct selection of a treatment regimen, which will include drug treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures and normalization of the diet. The influence of traditional medicine cannot be ruled out. The goal of complex physiotherapeutic treatment is to restore the elastic state of the abdominal muscles. This direction includes not only physical exercises, but also procedures (electric myostimulator for the abdominal muscles).
Drug treatment has several objectives: to reduce the irritation of pancreatic juice on the gastric mucosa and restore intestinal motility to pass food unilaterally. To achieve these tasks, the doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- prokinetics (Motilium, Passazhiks) restore the movement of food in a progressive manner and provide tone to the circular muscle muscles of the digestive tract;
- Ovenson and Choludexan tablets and suspensions, as well as their analogues, help reduce the harmful effects of bile acids on the gastric mucosa;
- Omeprazole and its analogues reduce gastric acidity, which creates a barrier to the activity of bile acids in the stomach;
- When erosive reflux occurs, drugs such as Almagel or Pilorid are prescribed.
Drugs and physiotherapeutic procedures are effective only when the patient’s nutrition is normalized, so diet for reflux is the main direction in the treatment of pathology.
In case of detection of GHD, herbal medicine produces an effect, but the selection of herbs is carried out individually depending on the body’s individual tolerance of plant components, the degree of the disease and concomitant gastrointestinal disorders. Otherwise, you can aggravate the situation and cause irreparable harm to the body.
Celery root juice is one of the easiest remedies to treat reflux. It is enough to drink a spoonful of juice half an hour before eating. Another simple remedy - dandelion flower syrup is prepared from the flowers of the plant and 0.5 kg of sugar. If there are contraindications to sugar, it is replaced with fructose. The flowers of the plant are filled into a 3-liter balloon, until the juice is released and sprinkled with layers of sugar (fructose). Take a spoonful daily to prevent reflux. If DGR has already been detected, dosage is increased to 2-4 times a day. The same syrup is prepared from chamomile flowers with sugar to obtain syrup. Use in the same way as with dandelion.
Several herbal infusions are used as decoctions. Here is one of them, which is not difficult to purchase and prepare. Mix 1 part chamomile flowers, 2 parts each wormwood and mint well, add up to 1 liter of boiling water and leave for 2 hours. After the specified time, filter the solution and consume 0.1 liter before eating.
Menu for every day
The basic principle of nutrition for reflux esophagitis is the exclusion from the patient’s diet of foods that can excessively irritate the walls of the stomach and cause heartburn.
What should be completely excluded?
The reflux diet involves completely avoiding a number of foods and supplements. These include:
- tomatoes;
- citrus fruit;
- cocoa, chocolate, sweets and confectionery (especially with rich cream);
- alcoholic drinks;
- spicy dishes;
- fried foods;
- fruit juices;
- herbs and spices (cloves, allspice, cinnamon);
- garlic;
- vinegar, citric acid;
- cucumbers;
- radish, turnip, radish;
- strong meat broths;
- Rye bread;
- freshly baked white bread (yesterday’s is ok);
- fatty meat and poultry (pork, lamb, goose, duck);
- lard, butter, margarines;
- fatty fish in any form;
- preserved food (fish, stewed meat, pickled vegetables, canned fruit);
- some cereals: pearl barley, wheat, barley;
- sharp and fatty cheeses;
- some legumes: beans, chickpeas;
- mushrooms, mushroom broth;
- raw onions;
- eggplant;
- ice cream, halva;
- various sauces (mayonnaise, ketchup, mustard, curry);
- carbonated drinks;
- kvass.
What can patients eat and drink?
The patient's diet should include the following foods and drinks:
- milk;
- decoction of rose hips (completely without sugar or with a small amount of it);
- dried fruit compotes;
- low-fat fermented milk products: cheeses, cottage cheese, fermented baked milk, kefir, sour cream, ayran, tan, yoghurts;
- crumbly porridge with water or milk (millet, oatmeal, buckwheat, rolled oats, rice);
- non-acidic fruits: bananas, pears, peaches, watermelons, strawberries, grapes, strawberries;
- stale white bread, crackers from it;
- biscuits;
- eggs (2 per day), preferably without yolk;
- lean meat (rabbit, veal, beef);
- chicken;
- beef tongue;
- doctor's sausage (limited), low-fat ham;
- low-fat mild cheeses;
- butter (low fat, up to 50%) – a teaspoon per day;
- pasta;
- vegetable soups with pasta, chicken;
- carrots, beets, green peas, broccoli, zucchini, cauliflower, pumpkin, potatoes;
- some spices: parsley, dill, vanilla;
- green and black tea (weak brew).
Prevention of GHD
When treating and preventing GHD, it is not recommended to resort to the following dietary actions:
- smoking and abusing “hard” drinks. At the moment of exacerbation of the disease, completely give up alcohol;
- Avoid drinking drinks with high caffeine content, take medications only as prescribed by a doctor;
- do not exceed normal body weight;
- adhere to dietary nutrition.
Dietary nutrition involves excluding some foods from the daily diet and including others more. You should temporarily stop consuming:
- chocolate products;
- baked goods, especially soft warm bread;
- smoked, salted, spicy and fried foods;
- garlic and citrus fruits.
The daily diet should include fish products and lean meats, lactic acid products, vegetables, fruits and berries, pureed soups containing a large amount of vegetables.
The number of meals per day should be increased and the portion size reduced. Thus, the pressure in the cavity of the duodenum is reduced. After eating, you should not perform physical work, as well as take a lying position, in order to prevent the reflux of duodenal contents into the stomach cavity.
Products allowed
Treatment of gastroduodenal reflux with diet involves a varied diet with protein foods, digestible carbohydrates and healthy fats. The food consumed must contain essential amino acids, vitamins and microelements and minerals necessary for the body.
List of allowed foods and dishes for bile reflux:
- slimy soups based on cereals and vegetables; puree soups;
- boiled porridge (barley, buckwheat, rice, oatmeal);
- lean fish (hake, pollock), boiled or steamed;
- steamed omelette, dry eggs;
- “yesterday’s” or slightly dried bread;
- lean boiled meat; meat soufflé, cutlets, steamed meatballs;
- vegetable purees;
- fine-grained unleavened cottage cheese, whole fresh milk;
- it is allowed to add butter or vegetable oil to dishes in small quantities;
- cottage cheese casserole, marshmallows;
- dried fruit compote, weak black tea, herbal infusions.
The listed products and dishes in liquid, pureed, semi-liquid consistency, in the form of purees and soufflés contribute to easier and better digestion and do not irritate the mucous and muscular membranes of the digestive system.
Disease prognosis
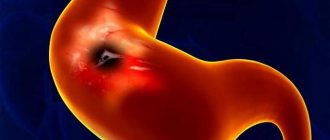
In case of a severe violation of the diet, as well as the patient’s untimely seeking of qualified medical help, the development of gastric ulcers cannot be ruled out. Improper lifestyle and nutrition are the cause of neoplasms, including malignant ones.
If duodeno-gastric reflux is detected in time and correctly diagnosed, then its treatment produces the desired effect, in which the symptoms and clinical picture of the pathology are reduced and eliminated completely, i.e. The prognosis of the disease with proper treatment is favorable.
RepostTweet
Duodeno-gastric reflux - treatment with folk remedies
This disease can be treated with alternative methods. But still, most experts recommend resorting to them only as part of complex therapy. When diagnosed with duodeno-gastric reflux, folk recipes should be selected by doctors and only after determining the causes of the disease. Otherwise, the patient's condition may only worsen.
How to cure duodeno-gastric reflux with herbs?
Preparation and use:
- Mix the ingredients in any quantity in one bowl. You can use it “by eye”; you don’t need to follow precise proportions in this recipe.
- The herbs are poured with boiling water and infused for 10-15 minutes.
- It is recommended to drink the resulting tea every day, morning and evening.
Treatment of duodeno-gastric reflux with flax seeds
- flax seeds - 1 tbsp. l.;
- water – 100 ml.
Preparation and use:
- The seeds are filled with cool water.
- The mixture should be infused until the seeds begin to swell. At this stage, beneficial mucus begins to secrete from them.
- The resulting liquid should be drunk on an empty stomach, ¼ - ½ cup.
Calamus and sage against duodeno-gastric reflux
- calamus root – 50 g;
- sage – 50 g;
- angelica root – 25 g;
- water – 1 glass.
Preparation and use:
- Take one teaspoon of each dry mixture.
- Boil water and add herbs.
- The medicine needs to sit for about 20 minutes. After that, you can strain it and drink it.
- To make the mixture more tasty, you can add honey to it.
- You need to take the medicine three times a day, an hour after meals.