Among other gastric pathologies, it ranks first in prevalence. In ICD-10, chronic gastritis is coded in section K29, with an additional value after the period for specified forms - from K29.1 to K29.9. Often the disease occurs without pronounced clinical manifestations and accompanies other digestive pathologies - cholecystitis, pancreatitis, peptic ulcer and others.
Inflammation and degeneration of the mucosa can be focal or diffuse; their chronic nature leads to the replacement of viable cells with connective tissue. As a result, the motor and secretory functions of the stomach suffer, which is accompanied by pathological symptoms.
Causes of the disease
The causes of chronic gastritis are varied: they can be divided into internal and external factors.
Domestic
- Disorders of nervous activity in which defects in the nervous regulation of the stomach occur.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Chronic infections.
- Chronic tissue hypoxia.
- Circulatory disorders.
External
Poor nutrition. This includes dry meals, snacks on the go, regular consumption of irritating foods and drinks, too hot or very cold foods.
- Non-compliance with the diet - irregular eating, overeating, eating at night.
- Food allergies.
- The influence of harmful production factors - inhalation of dust or toxic fumes.
- Vitamin deficiencies.
- Systematic use of certain medications.
- Protein deficiency.
- Poor chewing of food due to dental defects.
- Alcohol, smoking.
Also, the cause of chronicity of the disease is acute gastritis that has not been fully cured in combination with significant violations of nutritional recommendations.
Options for complications
Failure to provide specialized medical care in a timely manner can lead to serious consequences, including death. Aggravated gastritis, which is characterized by regular manifestations, negatively affects the functioning of the liver, intestines, and pancreas (pancreatitis).
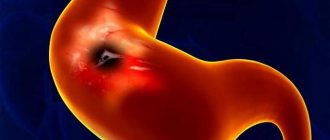
As complications of the disease, bleeding may begin, stomach ulcers, malignant tumors, and gastroduodenitis, which is characterized by inflammation of the duodenum, may develop.
Exacerbation of gastritis is a seasonal phenomenon. An attack of the inflammatory process of the digestive organ can be provoked by internal factors associated with the individual characteristics of the body, and external signs based on the influence of the external environment and level of vital activity.
Cure the chronic form of gastritis is a difficult task. For a complete recovery, it is necessary to follow preventive measures aimed at preventing repeated exacerbations of the gastric mucosa. The use of medications, diet, and timely medical examination will help avoid serious complications of the disease.
We recommend: How to prepare and use honey and aloe juice for gastritis?
About the classification of the disease
There are several officially recognized classifications of gastritis - the Houston classification of 1996, the Sydney system, and the OLGA classification system. According to the Houston classification, chronic gastritis is considered as follows:
- Non-atrophic CG (chronic gastritis). Non-atrophic gastritis is always associated with Helicobacter. Synonyms: antral hCG, superficial hCG, type B hCG, hypersecretory hCG.
- Atrophic immune hCG. Not associated with Helicobacter, the main cause is immune disorders. Synonyms: CG type A, diffuse CG of the body of the stomach, CG of the body of the stomach, associated with B 12 - anemia and decreased secretory function.
- Atrophic multifocal CG associated with the presence of Helicobacter, external factors and nutritional disorders. Synonyms: CG mixed type A and B.
- Special forms of hCG. These include:
- chemical (reactive);
- granulomatous (CG with isolated granulomatosis);
- radiation (CG for radiation injury);
- lymphocytic (CG for celiac disease);
- eosinophilic (allergic);
- giant hypertrophic (with Ménétrier's disease);
- other infectious forms of hCG.
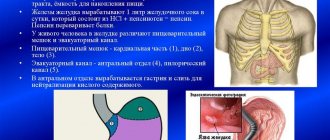
According to localization, CG of the antrum, CG of the body of the stomach and pangastritis are distinguished, in which changes in the mucosa are observed both in the antrum and in the body of the organ.
Gastritis is diagnosed using endoscopy and biopsy. Sometimes an X-ray of the stomach with barium and an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity are additionally prescribed. The test for Helicobacter in exhaled air is a relatively new diagnostic method, which is described in an interesting thematic video:
Since it is difficult to describe in detail each of the given forms of chronic gastritis within the scope of this article, we will take gastric secretion as a basis and consider the disease in this vein.
How long does an exacerbation of gastritis last?
It is impossible to name the exact time when and for how long gastritis worsens. Attacks often occur in the spring and autumn seasons. During this period, immunity decreases and the body is exposed to aggressive environmental factors.
Exacerbation of the chronic variety is characterized by a rapid change of sharp attacks of pain and the onset of remission. The course of the disease is associated with the individual characteristics of the body.
Chronic hypoacid gastritis
With a decrease in acidity, the disease is divided into 3 stages: compensated, partially compensated and decompensated.
Main clinical symptoms
When acidity decreases, along with dysfunction of the mucous membrane, the functioning of other organs is disrupted - the gallbladder, liver, pancreas, and intestines.
These processes are associated with a variety of symptoms of hyposecretory gastritis. In a third of patients, appetite decreases, sometimes to the point of complete aversion to food. Moreover, while maintaining appetite, patients with reduced secretion prefer hot, salty and spicy dishes.
Patients also note the appearance of an unpleasant metallic taste in the mouth, heaviness in the epigastrium after eating, belching like a rotten egg, and increased salivation.
During exacerbations of the disease, the clinical manifestations are identical to those of acute gastritis.
Treatment of hypoacid gastritis
With reduced secretory function, the main goal of complex treatment is to prevent exacerbations. If the disease worsens frequently, degenerative changes in the mucosa intensify and are replaced by atrophy.
The patient is recommended to eliminate all foci of chronic infections - cure carious teeth, sanitize the nasopharynx. If there are concomitant chronic diseases, you should methodically follow the recommendations of doctors to prevent their exacerbations.
To improve secretion, medications are also prescribed - enzymes, hydrochloric acid preparations, natural gastric juice.
To relieve spasmodic pain and inflammation, Plantaglucide is used, and Niacin is prescribed for prophylactic purposes.
The basis of therapy for any type of gastritis, including hypoacid gastritis, is nutritional therapy. In the classic version of the Pevzner diet, table No. 2 or No. 15 is recommended during the period of remission; carbonated mineral water is additionally recommended. It is taken 30 - 40 minutes before meals, 150 - 200 ml. Therapeutic exercise, physiotherapy, and herbal medicine are also used as part of complex therapy outside of exacerbation.
Rejection of bad habits
This will have to be done, since it is bad habits that often lead to the development of this pathology. Regarding alcoholic drinks: once in the stomach, the alcohol-containing drink begins to corrode the walls of the stomach, irritation occurs, and subsequently destruction of the epithelial layer of stomach cells occurs. In addition, along with alcohol, as a rule, a person eats various foods that aggravate the harmful effects of alcohol - fatty, fried and smoked.
For people who smoke, the situation worsens even more. Nicotine entering the body spreads to all organs, including gastric tissues, blood circulation is disrupted, vascular spasm occurs, and as a result, the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract and the regulation of gastric juice formation are disrupted. Thus, in order for remission to occur, doctors advise complete cessation of smoking and alcohol.
Hyperacid and normoacid gastritis
With preserved or increased secretory function, the disease can be divided into dyspeptic, mixed and painful forms. Disorders of other digestive organs are rarely detected during hyperacid and normoacid inflammation. If reduced secretion is observed more often in older people, then the contingent of increased and normal secretion is different - these are people of working age, from 30 to 40 years.
Clinical manifestations
Patients do not develop an aversion to food. Rather, there is a good or even increased appetite. The main complaints are related to dyspepsia - patients complain of sour belching, frequent heartburn, and a burning sensation in the stomach. The pain syndrome is not as intense as with an ulcer, but is still present. Pain of varying intensity occurs 30–40 minutes after eating, less often on an empty stomach.
Pain and dyspeptic symptoms can occur simultaneously or in isolation. The disease is characterized by alternating remission and exacerbations. In remission, pain and dyspeptic symptoms occur only with dietary violations and are mild. During an exacerbation, the clinical picture is very expressive: severe pain, persistent heartburn, nausea and heaviness are present daily. Manifestations of the disease must be differentiated from peptic ulcer disease.
Often, patients with high acidity develop neurasthenic syndrome. Exhausted by illness, the patient becomes moody, irritable, gets tired quickly, and suffers from headaches.
Hyperacid gastritis with regular diet violations can transform into peptic ulcer disease. To prevent this from happening, you must carefully follow all medical recommendations.
Treatment
Comprehensive treatment of hyperacid and normoacid gastritis begins with nutritional recommendations. The diet includes serious restrictions that must be observed to prevent exacerbations. During an exacerbation, the patient is prescribed fasting, and the diet is gradually expanded. Restrictions are removed gradually so as not to injure the inflamed mucosa. The diet during an exacerbation should be as gentle as possible.
Drug treatment is selected by a gastroenterologist. Prescribed drugs to reduce acidity, enzymes, antacids, antispasmodics. When Helicobacter is detected, eradication therapy is used.
Low-carbon mineral water is recommended an hour and a half before meals, warm. The course of treatment with mineral water lasts from 21 to 24 days.
Balneotherapy, therapeutic exercises, physiotherapy, herbal medicine are prescribed outside of exacerbation.
Characteristic features of the disease
Chronic gastritis in remission is similar in condition to a patient with a superficial form of the disease, which is the early period of the disease. To diagnose this type of disease, the gastroenterologist refers the patient to a gastroscopy procedure. At this time, the following is observed in the patient’s body:
- the gastric mucosa has a thickening, and with complete remission, the lining acquires a natural state;
- dystrophic changes have affected the integumentary pitted epithelial tissue, but this is practically not visible;
- the nuclei acquire a larger size and become hyperchromic;
- positive material is located above the cell nuclei in the cytoplasm;
- there is a layer of mucus on the surface of the epithelial tissue;
- the amount of RNA is significantly increased.
In the inactive stage of the disease, the patient has completely or partially no signs of the disease. The patient can stop strict measures aimed at treating the disease. But it is very important to understand that you will still have to carry out preventive measures and be constantly monitored by your doctor. This is necessary to prevent exacerbation.
Patients are often interested in what it is – remission of chronic gastritis. Doctors call this long-term illness the last stage of gastritis. It is important to realize that only effective recommendations from specialists will help minimize the manifestation of the disease.
General information
Patients often ask whether it is possible to get rid of chronic gastritis forever. There is no clear answer to this question - it all depends on the stage and course of the disease. If atrophic changes have already occurred in the mucous membrane, it will not be possible to get rid of them, but you can “keep” the disease in a stage of stable remission, avoiding exacerbations.
When Helicobacter is detected, careful adherence to the doctor’s recommendations promotes recovery - modern eradication therapy effectively fights the bacterium. If Helicobacter can be destroyed, the symptoms of gastritis disappear. It is important to prevent re-infection. Superficial forms of the disease, not associated with Helicobacter, can be easily cured with diet.
Chronic gastritis in young patients is not a reason for exemption from the army. The only exceptions are cases with significant changes in secretion and frequent exacerbations. However, in the “Schedule of Diseases” this item is described very vaguely, and the issue is resolved individually with each specific conscript. Young people with chronic gastritis are still called up, but with “slight restrictions,” as stated in Article 59 of the Schedule.
Prevention of chronic gastritis is a healthy diet and habits, active rest and lack of stress. Live a varied life, do not neglect medical examinations, monitor your health, and illness will bypass you.
Chronic gastritis: 1st, 2nd and 3rd degrees, and stages of remission
Published: June 15, 2020 at 05:43 pm
More than 80% of people in Russia suffer from stomach-related diseases, and the stage of chronic gastritis determines what kind of life a person suffering from this disease can lead. The number of those who experience difficulties with the gastrointestinal tract is growing steadily every year. This is understandable, poor nutrition, bad habits, the crazy pace of modern life sometimes forces us to eat on the go, people eat fast food, pies and hamburgers bought at a street kiosk, because they have no time to cook. Think about the last time you ate regular soup, a few months ago, six months ago, maybe even more. Meanwhile, a bowl of soup eaten at least once a week reduces the risk of this disease several times. Of course, it is also necessary to reduce the consumption of unhealthy food to a minimum, eat as little spicy, salty, sour, fried foods as possible; these are the foods that provoke the occurrence of this disease; you need to eat steamed or boiled food more often.
The following stages of chronic gastritis are distinguished:
- Superficial gastritis is the first stage of the disease, the healing process of which will not take much time, since the gastric mucosa is not yet damaged.
- If the initial stage of the disease is left unattended, the patient will develop chronic gastritis. This stage leads to serious health problems and there should be no delay in treatment. In cases of untimely treatment to the clinic, the inflammatory process can penetrate into the submucosal layer.
- The next stage is atrophic gastritis. During the course of the disease at this stage, it is typical to replace normal tissue with inactive tissue, which cannot perform the digestive function correctly.
In this case, the degrees of the disease: exacerbation, remission and incomplete remission replace one another. As the disease progresses, stages of remission (relief) occur. If gastritis at this stage is started or treated incorrectly, the cells of the stomach walls will change their shape, and this can trigger the development of cancer.
Degrees of chronic gastritis
There are many classifications of this disease, as well as its types according to the complexity of the disease and the cause of its occurrence. There is gastritis, which occurs due to the effects of Helicobacter pylori bacteria on the gastrointestinal tract. There are several degrees of it, depending on the level of damage and the number of bacteria contained in the body:
- Weak (+) – up to 20 microbial bodies in the field of view.
- Average. Chronic gastritis 2nd degree (++) – up to 50 microbial bodies in the field of view.
- High (+++) – more than 50 microbial bodies in the field of view.
The bacteria Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped microorganism that is able to survive and reproduce in an acidic environment, and it is the causative agent of many chronic infections. For a long time, there was a misconception that not a single bacteria could develop in the destructive acidic environment of the stomach; it was later found that this was not the case. More than half of the world's population has it, and ranks second after the well-known herpes, however, it can have a more serious impact. You can become infected with it orally, by drinking dirty water or by being in contact with an already infected person. If at least one family member becomes infected, the rest will become infected in 95% of cases.
To determine its presence, it is necessary to conduct a series of tests and cultures. Often a person lives with chronic gastritis for a long time without experiencing any symptoms; the disease makes itself felt only in the acute stage. You have to go to the hospital and only then it turns out that the person suffers from chronic gastritis. Remission occurs only after medical intervention. It is important not to start the disease; it is necessary to start treatment as soon as you feel the first signs:
- pain in the stomach after eating;
- pain on an empty stomach;
- constipation;
- heartburn;
- belching sour;
- coating on the tongue;
- seizures in the corners of the mouth;
- coating on the tongue.
Appetite, as a rule, is not impaired; very often at the first time of the disease, on the contrary, it is increased, but over time it worsens, and the patient begins to lose weight. Abdominal problems appear and more and more symptoms appear. It is important to put chronic gastritis into remission. It is worth understanding that if such a disease occurs, it is for life; in addition, scientists have proven that people who are carriers of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori are several times more likely to suffer from stomach cancer.
zhkt.guru
Forecast and prevention of the disease
People with a chronic form of the disease can remain productive for a long time. The possibility should be taken into account that without treatment a peptic ulcer will develop (localized in the duodenum). In cases of the erosive form of the disease, the occurrence of gastric bleeding cannot be ruled out. With the atrophic type, which occurs with inhibition of acid formation, the risk of developing stomach cancer increases. In order not to treat the disease, preventive measures should be followed, such as:
- maintaining a balanced diet;
- regular sanitation of the oral cavity;
- giving up alcohol and smoking;
- timely treatment of diseases against which gastritis may develop.
Symptoms
Gastroenterologists identify general symptoms that are characteristic of any type of chronic illness, after the appearance of which you should not delay visiting a specialist. You should consult a doctor if you experience:
- Cutting pain that appears during meals or after a short period of time. Sometimes it is cramp-like in nature.
- Due to impaired absorption of nutrients, the patient's nails and hair become brittle, and pale and dry skin may also appear.
- Sour belching, accompanied by heartburn and vomiting. All this appears after eating food and indicates increased acid secretion.
- Nausea with indigestion, as well as lack of appetite, indicate a low level of acidity.
It should be noted that when diagnosed with chronic gastritis, symptoms and treatment in adults and children may differ slightly. First of all, the doctor pays attention to the patient’s condition, and then explains what drug treatment he needs, and also prescribes a gentle diet, without which it is simply impossible to get rid of gastritis forever. Since some drugs have age restrictions, the doctor must select competent, safe treatment for children.
It is important to understand that only a doctor can give recommendations on how to treat chronic gastritis. You should not listen to the advice of others, since the disease progresses differently for everyone, so individual treatment is required for each patient.