Chronic dehydration can be mild or severe. In some cases, this problem requires hospitalization. Certain groups of the population, such as older adults or athletes, are more susceptible to fluid imbalance.
Dehydration can develop when the human body loses significant amounts of water and does not replenish its reserves. Potential causes of dehydration include acute vomiting or diarrhea, exposure to high temperatures, intense athletic training, and certain medications.
Chronic dehydration occurs over a long period of time. It usually does not cause serious problems, but it can lead to significant complications.
In the current article we will talk about chronic dehydration. In particular, we will look at the signs and symptoms of this condition, talk about its effects on the body, and discuss treatment options and preventive measures.
How much water does a person need?
When dehydrated, people may develop headaches and problems concentrating
It is difficult to estimate the volume of water that a particular human body needs daily, since norms may differ from person to person. A person's fluid intake requirements depend on metabolic rate, environmental factors, and level of physical activity.
American experts suggest estimating the required volumes of fluid intake based on the amount of water, drinks and specific foods taken. Thus, they advise men aged 19 to 30 to consume 3.7 liters of water per day. Women in the same age range are recommended to drink 2.7 liters of water.
However, the authors of a scientific review published in 2012 by the respected medical journal Nutrition Reviews noted that scientists do not have general recommendations for daily water intake.
Dehydration can develop if a person loses 3% of their weight or more due to lack of fluids.
Treating More Severe Dehydration at Home
In conditions of more pronounced dehydration of the body, drinking plenty of fluids should be supplemented by following the following recommendations:
- ventilate the room in which the patient is located, ensure air movement using a fan or air conditioner;
- lay the person down and wipe his body with a sponge moistened with water at room temperature (but in no case with cold or ice water);
- Place a cool compress on the patient's forehead.
If you are moderately dehydrated, drink water in small sips through a straw. The baby is sealed using a syringe without a needle.
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms of dehydration depend on the degree of lack of fluids in the body. Thirst is one of the first symptoms indicating that a person needs to replenish the body's water reserves.
Other signs and symptoms of chronic dehydration include:
- headache;
- difficulty concentrating;
- secretion of dark urine;
- fatigue;
- muscle weakness or spasms;
- constipation;
- dry and flaky skin;
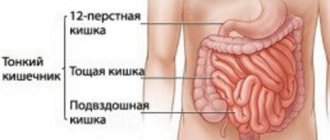
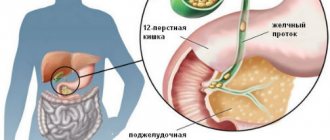
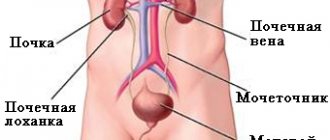
- deterioration of kidney, heart and digestive system function.
Video
- Headache
- Thirst
- Retraction of the fontanelle
- Difficulty defecating
- Lack of tears when crying
- Mood swings
- Darkening of urine
- Loss of consciousness
- Irritability
- Urinary disorders
- Strong odor of urine
- Decreased skin elasticity
- Drowsiness
- Confusion
- Dry mouth
- Dry skin
- Dry mucous membranes
- Fatigue
- Rapid breathing
- Cardiopalmus
Dehydration is a process that occurs due to a large loss of fluid by the body, the volume of which is several times greater than the volume that a person consumes. As a result, the normal functioning of the body is disrupted. It often presents with fever, vomiting, diarrhea and increased sweating. It occurs most often in the hot season or when performing heavy physical activity without taking too much fluid. Every person is susceptible to this disorder, regardless of gender and age, but according to statistics, children, people in the elderly age group, and people suffering from the chronic course of a particular disease are most often predisposed.
Since dehydration causes blood to thicken, rapid replacement of lost fluid can lead to swelling or death. The human body consists largely of water; it is consumed throughout life and cooked with it. The liquid is a good assistant in the elimination of waste waste products and is involved in respiratory function. A person cannot live more than ten days without drinking water.
As a rule, initial and moderate dehydration is easy to correct; you just need to take more fluids. Severe dehydration is more dangerous, so it is necessary to seek professional help as soon as possible or take the victim to a medical facility for immediate treatment. Dehydration is especially dangerous for newborns and children under three years of age, which is why parents often wonder how to determine dehydration. To do this, you just need to monitor the color of the urine and the general condition of the child - in such cases it will be quite difficult to wake him up, there will be no tears while crying, the baby will be constantly restless. At the first signs of dehydration in children, you should immediately call a doctor and begin proper treatment.
How does chronic dehydration affect the body?
The effect of chronic dehydration on the body depends on the severity of the problem. Drinking insufficient amounts of water daily can lead to constipation, poor concentration and stress. All these symptoms can significantly worsen the quality of life.
A scientific review published by American scientists in 2012 found that the only medical condition associated with chronic lack of water intake is urolithiasis, characterized by the formation of stones in the kidney, bladder or urethra.
Drinking significant amounts of water can help you lose weight
Some studies have shown that increasing your water intake can help manage your weight. However, scientists cannot explain in detail the mechanism of this effect.
There is also some evidence that drinking significant amounts of water reduces the risk of developing certain types of cancer. Although it should be recognized that the results of scientific work carried out in this regard are not fully convincing.
The water balance in the human body changes daily. Scientists note that it is difficult to monitor this indicator, and at the same time emphasize the connection between the imbalance and the development of various medical conditions. This is why it is difficult to explain how dehydration affects health, especially when it comes to diseases that develop gradually over several years, such as cancer.
How to take Regidron for diarrhea?
Take care of your health - save the VKontakte link
Due to the fact that this remedy is medicinal, it is necessary to follow certain rules for its preparation and use. Before you start taking the suspension, it is advisable to weigh yourself, since the required daily dose of the drug should be equal to double the loss of body weight. That is, if the patient, during diarrhea and possibly vomiting, lost 400 g, then during the first 10 hours of the development of the pathology he should drink 800 ml of the solution. This rule of rehydration for diarrhea is advisable to follow for both children and adults.
To properly prepare a solution that effectively restores the water-salt balance of the body, disturbed by diarrhea, you should dissolve the entire contents of the bag in a liter of slightly warm boiled water. It is contraindicated to add any flavoring additives to the resulting suspension, as this reduces the effectiveness of the drug. Regidron is taken for diarrhea as prescribed by a doctor or in accordance with the instructions indicated on the bag. It is allowed to store the finished drug for no more than a day and only in a cool place.
Often young parents are interested in how to properly take Regidron for diarrhea in children and whether the procedure for preparing the suspension differs from that in adults? The general rules for preparing and using the medicinal product for children are the same, the only difference is that they need to reduce the dosage. And before giving this solution to a child with diarrhea to drink, it should be warmed to body temperature. This way it will be better absorbed.
Causes
Chronic dehydration occurs when people lose more water than they consume over an extended period of time. The most common causes of this problem include the following:
- consumption of insufficient volumes of liquids;
- a diet that includes small amounts of foods high in water content, such as fruits and vegetables;
- intense physical activity with profuse sweating;
- high ambient temperature;
- prolonged vomiting or diarrhea;
- taking diuretics;
- some medical conditions.
Factors contributing to moisture loss
Among the possible factors that provoke dehydration, external and internal ones need to be considered.
External
Among the external ones, the following are significant:
- high ambient temperature;
- high wind force;
- incorrect (not appropriate for climatic conditions) clothing per person.
All of the above leads to profuse sweating. With sweat, a person loses both water and electrolytes. Violation of water and electrolyte balance leads to severe (sometimes irreversible) changes in the functioning of the kidneys and cardiovascular system.
Domestic
Internal factors can somewhat conditionally include diseases that are accompanied by loss of fluid and electrolytes:
- oncological processes of the digestive canal;
- endocrine pathology (diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus);
- intestinal infections (salmonellosis, cholera, foodborne illnesses).
A prerequisite for successful rehydration is the elimination of the provoking factor, otherwise the loss of water and electrolytes will continue.
Treatment and prevention
If dehydration is suspected, doctors perform a physical examination and also offer patients blood or urine tests.
They may prescribe medications to replenish electrolytes for people who are dehydrated due to diarrhea or vomiting. If a person develops severe dehydration, they may need to be hospitalized to receive intravenous fluids.
If the patient is in generally good health, the doctor will simply recommend restoring fluid balance by consuming significant amounts of fluids throughout the day.
The body's need for water can be significantly influenced by the level of physical activity and ambient temperature. During grueling workouts, some athletes lose 6 to 10% of their body weight through sweat. This can lead to dehydration if fluids are not replenished.
However, significant sweat loss is often difficult to replace within a short period of time. Therefore, people who become dehydrated due to physical activity or high ambient temperatures usually rehydrate by drinking fluids and eating foods high in water over an extended period of time. In addition, products that replenish electrolyte reserves often come to the rescue in such situations.
Electrolytes, including sodium, potassium, magnesium and calcium, are minerals that maintain fluid balance and support a number of important functions in the human body. After intense physical activity, it is necessary to replenish electrolytes with special drinks or solutions prepared at home.
People can ensure they are drinking enough fluids using smartphone apps. Such programs remind you that it is time to drink water if a person is busy, infrequently thirsty, or plays sports.
Consuming significant amounts of caffeine and alcohol can also lead to dehydration, especially when combined with other risk factors such as high levels of physical activity or hot weather.
Risk group and causes of dehydration
Of course, everyone can become dehydrated (every day we lose moisture through sweat and urine). However, there are factors that are especially dangerous due to the fact that they lead to very rapid dehydration.
At risk:
- People with disorders and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract), because they often experience symptoms such as vomiting and diarrhea, in which a person loses moisture from the body very quickly.
- People with urinary tract infections are also more likely to become dehydrated quickly.
- Small children (especially newborns and infants). In them, fluid loss occurs faster (due to the characteristics of the body that has not yet formed and the ratio of body proportions).
- Older people with poor kidney function.
Dehydration in the elderly
Elderly people should drink water even if they are not thirsty.
Older people are more likely to experience dehydration because as we age, we tend to feel less thirsty, and the body retains water reserves less well during this period of life.
In 2011, American scientists published a scientific review showing that older people should drink water even when they are not thirsty, and also consume moderate amounts of salt during active sweating.
Diagnostics
A doctor can diagnose dehydration based on physical symptoms, such as:
- deficiency or absence of urine;
- sunken eyes;
- lack of elasticity and skin tone.
If a person is dehydrated, it is possible:
- there will also be low blood pressure, especially when the person stands up;
- your heart will beat faster than usual;
- problems with blood circulation in the extremities will begin.
To confirm the diagnosis and determine the degree of dehydration, additional tests may be prescribed, for example:
- Blood test: This test can be used to monitor various factors, such as electrolyte levels (especially sodium and potassium) and kidney function.
- Urinalysis : Used to determine the degree of dehydration.
If the dehydration condition cannot be diagnosed with certainty, your doctor may order further tests to rule out diabetes or liver or kidney problems.
Review of effective treatments
To get rid of a pathological condition, you need to make every effort. An integrated approach to treatment methods will save the situation.
Medicines and droppers
Moderate and severe forms must be treated with droppers. Infusion therapy promotes rapid restoration of fluid volume in the blood. Regular saline solution, Ringer's solution, glucose, trisol, disol are perfect for combating the pathological condition. Hemodez, Poliglyukin are plasma-replacement drugs that fight intoxication, bleeding, and prevent further fluid loss.
High body temperature requires cooling the body and administering antipyretic medications. Vomiting is treated with antiemetic drugs (sturgeon).
Additionally, medications with sodium and potassium salts are prescribed (Pedialit, Oralit, Regidron).
Folk remedies
You can use folk recipes only when the first symptoms of the disease appear, in the initial period. Other cases require qualified assistance. Traditional healers recommend:
- Add a small amount of salt to a glass of water. You need to drink four glasses a day + don’t forget to eat light cereals (cereals, buckwheat).
- A similar recipe - you need to add a little sugar to a glass of water.
- Healing herbal drinks will replenish the liquid environment and reduce the manifestations of intoxication. Tinctures with chamomile and rose hips put the body in order. Take a few spoons every 20 minutes.