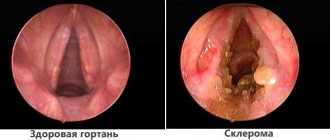
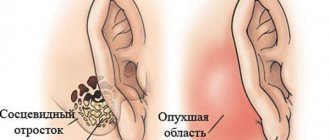
A throat abscess can occur both at the acute stage of the disease and after the patient’s condition has stabilized. Untreated acute inflammation of the throat can have many complications with fraught consequences. The most common are infiltrative and purulent processes of the peri-almond tissue. In most cases, this happens due to unfair therapy.
Symptoms of a throat abscess
| Localization | Pathogen and mechanism of development | Clinical manifestations |
| Peritonsillar, or paratonsillar: acute inflammation of the fatty tissue located near the palatine tonsils on one or both sides. There are types: posterior (between the tonsil and the velopharyngeal arch), lower (at the lower pole of the tonsil), anterior (between the palatine lingual arch and the upper pole of the tonsil), external (outside the tonsil). | Most often it is a complication of acute inflammation of the tonsils, called acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis, as well as pharyngitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane and lymphoid tissue of the pharynx). Pathogens: group A β-hemolytic streptococcus, staphylococcus, or a combination thereof. Children, adolescents, and people with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to the disease. | Sore throat of increasing intensity, dysphagia, high fever, chills, intoxication (weakness, headache, etc.), regional lymphadenitis, bad breath, restriction of movements in the temporomandibular joint, as a result of which it is difficult for the patient to open his mouth. |
| Retropharyngeal, or retropharyngeal: suppuration of the lymph nodes and tissue of the retropharyngeal space. | It is a consequence of the penetration of infectious agents through the lymphatic vessels from the nasal cavity, nasopharynx, auditory tube and middle ear; complicated course of influenza, scarlet fever, measles infection; damage to the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall by a foreign body or too hard food. It is usually observed in weakened children. | Sharp pain when swallowing, choking, sometimes accompanied by food getting into the nose; if the focus of pus is located in the nasopharynx - impaired breathing through the nose, nasal voice; when the process spreads to the lower parts of the pharynx, difficulty in inhaling, accompanied by wheezing, which intensifies in an upright position of the body; swelling behind the angle of the lower jaw; forced position of the head (throwing back with an inclination to the painful side); high fever. |
| Peripharyngeal: a purulent inflammatory process of the tissue of the peripharyngeal space limited by a capsule. | It is a complication of the inflammatory process in the pharynx, oral cavity, middle ear, acute paratonsillar abscess, mastoiditis. Develops as a result of trauma to the pharynx or after surgery to remove the tonsils - tonsillectomy. Infectious agents: streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus, spindle coli and Escherichia coli. Occurs more often in adults. | Sharp pain in the throat, aggravated by attempts to open the mouth and movements of the head, difficulty swallowing, tonic spasm of the masticatory muscles, the appearance of a bulge or node in the area of the lateral wall of the pharynx, tonsil and palatine arches on the affected side, a significant increase in body temperature (40 ° C and higher). |
Symptoms and signs
There are quite a few symptoms indicating the development of an abscess. Signs of the pathological process appear literally from the first hours from the beginning of its development. It can be:
- pain radiating to the ear;
- spasm of the masticatory muscles;
- sensation of a foreign object in the throat;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- high temperature, fever;
- unpleasant odor (pus) from the mouth;
- hoarseness of voice.
The child exhibits general weakness, lethargy, and may experience insomnia. In adults, it can also occur with less severe symptoms. The patient's condition improves slightly when spontaneous autopsy occurs. The pain decreases and the feeling of fullness disappears.
Upon examination, the doctor notes an enlargement of the tonsils, severe tissue hyperemia and swelling of the paratonsillar region. If the abscess is extensive, the mobility of the palatine arches and uvula may be impaired.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis includes:
- collection of complaints;
- studying the history of the disease;
- general examination;
- pharyngoscopy;
- laboratory examination (detailed blood test, bacterial culture to identify the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs);
- ultrasound examination of the neck area;
- computed tomography of the neck;
- radiography of soft tissues of the head and neck.
The last three studies listed are not performed as often. They are prescribed in difficult cases for the purpose of differential diagnosis, to exclude the spread of the pathological process beyond the pharynx.
Identification of diseases that cause the appearance of a purulent process in the throat may require:
- otoscopy;
- rhinoscopy;
- radiography of the paranasal sinuses (photo of the paranasal sinuses).
What is it, classification and code according to ICD 10
The abscess affects the pharynx, forming a purulent collection. Most often, an abscess in the retropharyngeal space appears in children under five years of age due to the structure of the fiber and the presence of lymph nodes in the area. Children aged two months to one year are at risk.
Depending on the location, an abscess can be of different types:
- retropharyngeal epipharyngeal – focus above the velum palatine;
- hypopharyngeal - inflammation under the root of the tongue;
- paratonsillar – damage to the tonsils;
- retropharyngeal mesopharyngeal - suppuration at the border of the lingual root with the outskirts of the palatal arch;
- mixed - several zones are affected, the most dangerous type.
The international classification (ICD-10) identifies retropharyngeal suppurations as other diseases of the upper respiratory tract under code J39.0, including parapharyngeal and retropharyngeal abscesses.
Possible complications
A throat abscess can be complicated by life-threatening conditions.
| Localization | Possible complications |
| Peritonsillar | Cellulitis of the neck, mediastinitis, necrosis, or necrosis, of tissue, sepsis, thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus. |
| Retropharyngeal | Acute swelling of the entrance to the larynx, suffocation during spontaneous opening of an abscess, the larynx is blocked by purulent masses, compression of the trachea, purulent mediastinitis, sepsis, purulent meningitis. |
| Peripharyngeal | Edema of the larynx, suffocation, purulent anterior mediastinitis, phlegmon of the neck, osteomyelitis of the lower jaw, cervical vertebrae, purulent meningitis, sepsis. |
The development of complications requires immediate medical attention. To prevent them, it is necessary to correctly and timely treat purulent processes in the throat, especially sore throat, which is complicated not only by the formation of a pharyngeal abscess, but also in the later stages (2-4 weeks) by damage to the heart (fibrous changes in the valves, carditis) and kidneys (glomerulonephritis).
Retropharyngeal abscess: what is it?
This term refers to inflammation of the tissues located in the retropharyngeal space: fiber and lymph nodes, accompanied by the release of pus. It develops due to trauma to the tissues of the pharynx or the spread of harmful microorganisms from the source of infection located in the nose or throat.
More often, this disease affects young children under four years of age, since their tissue is quite loose and contains lymph nodes, which atrophy at a later age. Thus, tissue damage in young children is much easier, and there are more ways for the inflammatory process to occur. Most often, an abscess occurs in children under one year of age.
In adults, this disease is often a complication of another nasopharyngeal disease or injury; in general, it is diagnosed extremely rarely in adults. Although recently there have been quite a lot of people falling ill for various reasons.
Depending on the location of the abscess, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- epipharyngeal, when located above the velum;
- mesopharyngeal, when located between the base of the tongue and the velum palatine;
- hypopharyngeal, when located below the base of the tongue;
- mixed, if the inflammatory process occupies several zones.
Regardless of the location of the inflammation, treatment must be started as quickly as possible to prevent severe complications from developing.
Causes
Retropharyngeal abscess in children is much more common for a number of reasons.
In them, the infection more easily enters the lymph nodes and penetrates deep into the tissues; an abscess can develop against the background of many diseases of the nasopharynx: sore throat, nasopharyngitis and others; the likelihood is present, including with inflammatory diseases of the ears. This condition can also be triggered by a systemic viral infection: measles, scarlet fever, diphtheria and others.
In infants, an abscess can develop due to infection if the nursing mother has a cracked nipple or mastitis at an early stage. Also, factors influencing the development of the disease include weakened immunity, lack of nutrition, and other diseases that weaken the body.
Retropharyngeal abscess in adults is usually provoked by various mechanical injuries of the retropharyngeal space; the disease due to infections is quite rare.
Injury can occur in everyday situations: a sharp fish bone, a foreign body entering the throat, damage due to the rough structure of food.
Fiber can also be injured during improper medical procedures: gastroscopy, bronchoscopy and others.
The likelihood of an abscess increases in the presence of endocrine diseases. The disease is more often diagnosed in people with diabetes, malignant tumors, and HIV infection.
Important! In rare cases, the disease occurs due to specific microflora present in tuberculosis or syphilis.
Symptoms
If an abscess forms against the background of an already developed infection in the body, a sharp deterioration in well-being occurs. The temperature rises to 37 - 39 degrees, weakness increases, and chills occur. Small children become whiny and refuse to eat.
One of the main signs of an abscess is the appearance of severe sore throat. Its localization depends on the location of the inflammation. Painful sensations are accompanied by breathing problems, the voice becomes hoarse and nasal. The pain may be so severe that the patient cannot eat. The pain may also resemble the sensation of a foreign body in the throat.
It is also worth paying attention to the lymph nodes. With an abscess, the cervical and occipital lymph nodes become inflamed; upon palpation, you can notice that they are swollen, touching them and moving the head become painful. In special cases, swelling and a local increase in temperature may be observed due to the formation of an abscess.
Important! With this disease, gurgling in the throat may occur during sleep due to the accumulation of purulent discharge in the throat.
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, symptoms alone are not enough. A pharyngoscopy, bacteriological analysis of a throat smear, and a full examination by an otolaryngologist are required. In addition, a blood test is taken to detect the presence of infection and inflammation in the body. It is also important to find out the causative agent of inflammation in order to select the most appropriate treatment.
Depending on concomitant diseases and symptoms in the body, additional tests, such as x-rays, may be prescribed. A characteristic radiological sign for a retropharyngeal abscess is the expansion of the shadow, its appearance in the lumen of the pharynx.
Depending on the cause of the abscess, help from other specialists may be needed. A traumatologist is required if there is suspected mechanical damage to the tissues of the pharynx or osteomyelitis of the cervical vertebrae, a phthisiatrician is required if tuberculosis is suspected, and an oncologist is required if there are signs of malignancy.
Complications
Complications may arise due to the spread of infection through the respiratory tract. In this case, the disease can provoke the development of pneumonia and other inflammatory lung diseases.
There is also a danger of infection entering the brain through the bloodstream, in which case purulent meningitis is likely to occur.
In general, the appearance of a retropharyngeal abscess can worsen the course of the disease that caused the development of this condition.
A more dangerous, but rather rare consequence is asphyxia, suffocation that occurs if an abscess blocks the airways. This can be caused by swelling of the larynx or spontaneous opening of the inflammatory focus, as a result of which pus spills out and closes the lumen.
In this case, vascular damage may occur when pus penetrates through the tissue; this can lead to thrombosis of the jugular vein, phlebitis, and sepsis.
Important! Complications can also arise due to improper treatment of the inflammatory disease.
Treatment
Self-medication for a retropharyngeal abscess is often extremely dangerous, and in most cases it is impossible. Typically, patients, especially children, are subject to hospitalization in acute conditions to relieve inflammation and drain the source of suppuration.
Treatment at home is acceptable after the main inflammatory process has resolved, when emergency intervention is no longer required, but complications must be prevented. In general, the prognosis for this disease is favorable; usually therapy after opening the abscess takes a week or two, depending on the severity of the condition.
After opening the abscess, older people may be prescribed rinses with antiseptic solutions and physiotherapy, usually using UHF therapy.
Surgical intervention
Since spontaneous opening of an abscess is dangerous due to the occurrence of asphyxia and the spread of infection through the bloodstream and respiratory tract, when a focus of inflammation is detected, they try to open it surgically as quickly as possible. The operation can only be performed by a trained doctor - an otolaryngologist.
During the operation, a needle is inserted through the mouth, the abscess is punctured, after which the pus is sucked out using a syringe. Depending on the age and condition of the patient, local anesthesia or general anesthesia may be used. After opening the abscess, drug therapy is required; further treatment can be carried out at home if there are no indications for a hospital stay.
This is interesting! Biliary sludge in the gallbladder: causes of appearance, characteristic manifestations, treatment complex
Important! Specific “cold” abscesses that occur with syphilis or tuberculosis are usually not opened.
Drugs
With a retropharyngeal abscess, in most cases there is a bacterial infection; to get rid of it, antibiotic treatment is prescribed. A suitable drug is selected by a doctor, the course of treatment lasts 5–10 days, depending on the indications. The most common drugs in this case include Flemoxin Solutab and its analogues.
In some cases, antihistamines and various anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed. Any drug should be discussed with your doctor before taking it.
Treatment with folk remedies
Treatment with traditional medicines is only permissible at the stage of inflammation subsiding; they should not be used before opening and immediately after. Usually, based on folk recipes, rinsing solutions are prepared that have disinfecting and healing properties.
- Sea salt based rinse solution. For one glass of warm, but not hot water, take a teaspoon of salt, less if possible. It is advisable to rinse at least once a day.
- Camomile tea. One teaspoon of dried herb should be poured into a glass of hot water, left for 20-30 minutes, then cooled. You should rinse at least once a day.
After the main course of treatment with antibiotics and other drugs, you need to be tested again to make sure that the infection is completely gone. In general, if the focus of inflammation in a retropharyngeal abscess was eliminated in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable and complications should not arise.
Source: https://lechim-prosto.ru/zaglotochnyj-abstsess-simptomy-prichiny-lechenie.html
Treatment of throat abscess
Elimination of abscess inflammation in the throat involves a set of measures. The basis of treatment is surgical intervention against the background of antibacterial and symptomatic therapy.
Opening a throat abscess in combination with antibiotic therapy is the main treatment regimen
| Localization | Complex of therapeutic measures |
| Peritonsillar | In a hospital setting, opening the purulent cavity and ensuring its adequate drainage. Ineffectiveness of therapy, spread of the process, recurrence of the disease may require abscessonsillectomy (surgical removal of the abscess along with the affected palatine tonsil). Prescription of antibacterial drugs of the lincosamide group, semisynthetic penicillins in combination with clavulanic acid, cephalosporins, and after obtaining the results of bacteriological culture - antibiotics to which the pathogen is sensitive. Symptomatic therapy involves the use of analgesics, antipyretics, intravenous infusions of solutions for the purpose of detoxification, and antiseptics for mouth rinsing. |
| Retropharyngeal | Surgical opening of the purulent cavity with simultaneous suction of pus, preventing it from entering the respiratory tract, drainage. In parallel, systemic therapy with antibacterial drugs is carried out according to the principles listed earlier, the existing foci of infection in the nasopharynx or ear are sanitized, antipyretic and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antihistamines and vitamin preparations, and antiseptics in the form of rinses are prescribed. |
| Peripharyngeal | Surgical treatment involves opening the abscess. In the postoperative period, broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs and analgesics are prescribed, infusion therapy is carried out to eliminate intoxication, and, if necessary, anti-gangrenous serum is administered. |
Causes of abscess
Statistics show that young people aged 16–20 years are most susceptible to purulent inflammation in the throat. The main cause of this pathological condition is pathogenic agents that have penetrated the soft tissue. Most often these are streptococci, but there may also be staphylococci, Klebsiella, Proteus or E. coli. Under what circumstances do they enter the body?
1. Most often, such an inflammatory process is a consequence of untreated pharyngitis or tonsillitis. In this case, purulent foci form directly on the tonsils. Perhaps the disease was simply not fully treated or the patient refused to take antibiotics, as a result of which, after a short improvement in the condition, the disease developed with renewed vigor and resulted in the development of an abscess in the tissues of the throat.
2. However, about 25% of abscess cases are not associated with untreated sore throat or pharyngitis. People with low immunity, vitamin deficiency, hypothermia or severe stress, as well as people who have recently had the flu, ARVI or scarlet fever, can also develop this serious condition. Sometimes an abscess develops as a result of removal of the tonsils, especially if a small area of the tonsils was left during the operation.
3. An abscess can be caused by mechanical damage to the soft tissues of the throat, for example, in the case of trauma to the tonsils with hard food or a fish bone. In rare cases, such a complication becomes a consequence of gastroscopy, bronchoscopy or tonsillectomy.
4. A dental cause of the abscess cannot be ruled out, when suppuration in the throat provokes an unsatisfactory condition of the oral cavity. This can occur against the background of periodontal disease, periodontitis, as well as the presence of teeth destroyed by caries.
5. In addition, the likelihood of encountering a throat abscess increases in people who smoke, diabetics, and people with chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis and adenoiditis.
6. Unfavorable climatic or social conditions can also cause an abscess in the throat.
Prevention
Measures aimed at preventing the formation of purulent pathology and its dangerous complications include:
- early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, nasopharynx, and middle ear;
- following the rules for performing diagnostic and therapeutic procedures that involve inserting a breathing tube or endoscopic device into the pharynx;
- exercise caution when removing foreign bodies from the throat;
- avoiding violation of surgical techniques during tonsillectomy, removal of tumors, adenoids.
It is of great importance that patients seek medical help in a timely manner.
Pathology treatment methods
In case of a retropharyngeal abscess, the patient should be hospitalized for treatment as soon as possible.
Home treatment with pharmaceutical drugs or traditional medicine is strictly prohibited. Such actions are ineffective and endanger the patient’s life.
If symptoms of an abscess of the retropharyngeal space are detected, you should contact the clinic to see an otolaryngologist (ENT), therapist or surgeon for examination, diagnostic testing and prescribing a method of therapy.
Conservative
Conservative treatment is used as an adjuvant therapy after diagnosis.
To improve the condition of a patient with a retropharyngeal type of abscess, antibiotics are prescribed to fight the infectious agent. To restore immune defense - vitamin complexes.
To prevent relapses, they sanitize all foci of inflammation, nasal and ear canals. Problem areas are treated with antiseptics and antibacterial agents. The patient is prescribed the procedure of gargling with antiseptic drugs before and after opening the abscess. Anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs and antihistamines are prescribed.
Invasive, but non-surgical procedures include abscess puncture, which involves drawing out pus from the cavity of the retropharyngeal abscess. The method is relevant for the syphilitic and tuberculous nature of the abscess, when conventional autopsy is contraindicated due to the risk of secondary infection. In addition to puncture, specialized medications are administered for treatment.
Treatment of an abscess with folk remedies consists of care - rinsing the throat and mouth with decoctions or infusions of medicinal plants only on the recommendation of a doctor.
Surgical
Surgery is the only effective method of eliminating an abscess, excluding retropharyngeal abscesses of syphilis or tuberculosis origin.
An incision is made in the area where the abscess bulges, and its cavity is opened with a scalpel. At the same time, a tube is inserted to drain pus from the capsule. This allows you to avoid the spread of purulent mass to the respiratory tract and the occurrence of phlegmon.
To prevent pus from leaking out during opening of the abscess, a preliminary puncture technique with suction of the contents is recommended.
If the abscess is deep enough in the retropharyngeal region, it is opened through an external incision on the anterior side of the neck.
If the patient has difficulty breathing during surgery, intubation is contraindicated. To restore normal breathing, as an emergency measure, the cricoid cartilage is cut and a tube called a cricostomy is inserted into the hole. The procedure is called cricotomy. When hypoxia is eliminated, oxygen therapy is performed.
After eliminating the purulent focus, the abscess is sanitized, special medications are administered, and drained. The last action is necessary for the drainage of residual pus and the possibility of repeated disinfection of the wound cavity.
Preventive measures
To prevent an abscess from occurring, you must follow some simple rules:
- For any tonsillitis, it is important to start proper treatment in a timely manner, listen to the advice of doctors and strictly follow their instructions.
- It is necessary to maintain immunity at a decent level: lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right throughout the year.
- Visit the dentist regularly and monitor your oral health;
- In the event of an infectious disease, it is worth using antibacterial agents (antibiotics).