Increased uterine tone at different stages of pregnancy
Pregnant women experience major adaptive changes in anatomy, physiology and the functioning of internal organs, which determine the normal course of pregnancy and successful childbirth.
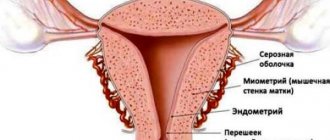
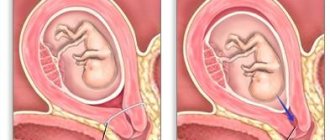
The uterus, which has three layers: outer serous, inner epithelial, intermediate muscular - myometrium, undergoes radical changes. The middle layer is quite elastic, which allows it to stretch and contract during childbirth and return to its previous state after childbirth. However, against the background of the development of certain factors, contractile activity of the uterus may appear earlier than expected.
Various symptoms appear in the form of heaviness or nagging pain in the lower abdomen; in such cases, uterine hypertonicity is often diagnosed. Such a diagnosis is not a reason to panic, but this condition should not be considered the norm, so you need to make an appointment with a gynecologist as soon as possible.
Signs of hypertension
Symptoms indicating uterine hypertonicity are similar in their manifestations to the pain that occurs during the menstrual cycle: painful sensations in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back, sacrum and perineum. In the third trimester, palpation of the abdomen clearly identifies the contours of the uterus. Sometimes bloody smears from the genitourinary tract appear. This type of discharge is very dangerous and requires an immediate visit to the gynecologist.
If an increase in the activity of the child's place occurred in the first two trimesters, then such symptoms indicate the development of pathology and require immediate treatment. Therapeutic measures for excessive uterine tension at 38 weeks of pregnancy are necessary to slow down premature birth.
For the last three months, the mother’s body has been busy preparing for the upcoming birth. At this time, episodic uterine contractions occur. The main thing is that the preparatory contractions that occur at the 38th week of pregnancy are not confused with the onset of labor. These contractions are called false contractions, and they have the following symptoms:
- short duration and irregularity;
- painless course;
- no bleeding.
Another important fact is that contractions that occur at 38 weeks of pregnancy are not the beginning of labor and pass without dilation of the cervix.
Uterine tone during pregnancy - symptoms
The uterus is located in the pelvis between the rectum and bladder. The fallopian tubes are located symmetrically on both sides of the uterus, thanks to which the fertilized egg is transported. The uterus consists of three parts: the fundus, the body, and the cervix. The organ wall is formed by three types of tissue: perimeter, myometrium, endometrium.
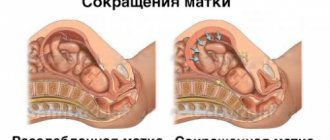
At the moment of bearing a child, the uterus has the ability to increase 10 times, its muscles stretch, and its walls thicken. The main role in increasing the tone of the uterus is played by the myometrium, represented by a layer of smooth muscle. Throughout pregnancy, the myometrium remains relatively motionless, providing a suitable environment for the developing baby. In the short term, rhythmic and prolonged contractions of the muscle layer and expansion of the cervical region combine and physiological labor occurs.
If contractile activity of the uterus appears long before childbirth, in the first or second trimester, then the doctor often diagnoses uterine hypertonicity. Of course, such a phenomenon is not in all cases considered as a pathological process. But, if hypertonicity is observed all the time, this phenomenon can lead to critical consequences. The present symptoms of increased uterine tone during pregnancy can cause spontaneous abortion in the 1st trimester, and in the 2nd-3rd trimester lead to oxygen starvation of the fetus (hypoxia).
It is worth noting that the clinical manifestation of tone does not differ in characteristic signs; usually the expectant mother complains of discomfort and soreness in the lower abdomen, similar to menstrual pain.
The pain syndrome in most cases is not of a pronounced type, but can radiate to the lower back.
In the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, the symptoms of increased uterine tone do not differ much from the first, but upon palpation you can notice that the abdomen has become denser. In rare cases, a woman observes a spotting reddish-brown discharge from the vagina. If such a symptom develops, you should consult a doctor as an emergency.
It is also worth describing the symptoms of uterine hypertonicity during late pregnancy, in the 3rd trimester. At the end of the 38th week, tone has a completely different meaning and is considered as a manifestation of training contractions. This tone has the scientific name of a Braxton-Higgs contraction. Braxton Hicks contractions are designed to strengthen the muscles of the uterus in preparation for subsequent labor. Contractions usually last about 30-45 seconds. However, in the eighth and ninth months of pregnancy they can even occur every 20-30 minutes. Braxton Hicks contractions are called “predictive contractions” and have an average duration of no more than two minutes.
In some women, hypertonicity is asymptomatic and is diagnosed during ultrasound examination.
Factors influencing the occurrence
Increased activity of the uterus during pregnancy is influenced by two groups of factors:
- somatic – caused by physiological and biological changes in the body of a woman carrying a fetus;
- psychosomatic – caused by emotional overload affecting the central nervous system of a pregnant woman.
These factors contribute to the occurrence of increased tone throughout pregnancy, including in the 3rd trimester.
Somatic group
The first group includes infectious diseases transmitted through sexual contact and hormonal imbalances.
Infections provoke the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the pelvis and uterus, which negatively affect the intrauterine development of the baby
Hormonal imbalance, which provokes increased tension in the child’s place, is caused by:
- insufficient progesterone levels;
- excess male sex hormones (hyperandrogenism);
- excess blood prolactin;
- hyperthyroidism;
- hypothyroidism
Psychosomatic group
Like the entire human body, the uterus is permeated with myriads of receptors and nerve endings that send impulses to all parts of the nervous system. From the first days of pregnancy, a woman’s instinct of motherhood, which prevails over everything, turns on. When stressful situations occur or during excessive physical activity, the uterus becomes overexcited and increases its tone. During the entire period of gestation, the nerve endings of the uterus and spinal cord are in a state of low excitability. By the time of childbirth, their excitability increases many times over.
In addition to the factors described above, there are other reasons that cause increased excitability of the child’s place:
- endometriosis (abnormal growth of the endometrium);
- uterine fibroids, inflammation of the appendages;
- pathologies in the structure of the uterus (bicornuate, saddle-shaped);
- multiple pregnancy and very large fetus;
- Rhesus conflict;
- previous abortions and curettages;
- severe toxicosis in the 3rd trimester;
- altered intestinal motility;
- drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking.
Reasons for increased uterine tone during pregnancy
The causes of uterine tone during pregnancy are varied, for example, changes in hormonal levels, in which there is a deficiency of progesterone or an increase in the concentration of testosterone. A disease or pathological process, somatic disorders and even stress can also be a provoking factor.
An increase in the contractile activity of the reproductive organ may be observed for the following reasons:
- Lack of progesterone
- Intense physical activity
- Stress
- Oncological diseases
- Hormonal disorders
- Acute infections
- Activation of chronic processes
- Alcohol abuse, smoking
- Genetic disorders in the fetus
- Micronutrient deficiency
- Large fetus, several fetuses in the uterus
- Large volume of amniotic fluid
- Increased blood clotting
The most important role of progesterone is to prepare the uterus for embryo implantation. Thanks to this, the mucous membrane thickens and expands, its blood supply becomes more intense, and nutrients accumulate. Progesterone also allows the uterus to gradually grow and limits its contractility, which allows pregnancy to proceed physiologically. But a reduced level of progesterone disrupts the natural course of pregnancy and can cause uterine hypertonicity.
Other factors:
- Psychological problems
- Long trips
- Flying an airplane
- Overweight
- Age over 35 years
- Violation of fetal position
- Intestinal motility disorder
- History of miscarriages
Separately, doctors note a diet that negatively affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which often becomes the cause of hypertension. Doctors recommend excluding the following foods:
- Legumes, cabbage: provoke gas formation.
- Blue cheese: contains mushrooms that are dangerous for expectant mothers.
- Coffee: intensively removes fluid from the body, which can cause hypertension.
- Raw eggs: are a potential source of salmonellosis and cause disruption of the digestive tract.
Many experts argue that tone is very dangerous, and not as harmless as it seems. In fact, such a condition is not always dangerous; contractile activity may be present normally.
But with such clinical manifestations, you should consult a gynecologist to determine possible deviations, as well as decide on tactics to combat them. If you do not pay attention to hypertonicity and do not take timely measures, the long-awaited pregnancy may end in miscarriage or severe fetal hypoxia.
The tone of the uterus during pregnancy in the earliest stages almost always requires appropriate intervention. Because in the first trimester there is the greatest risk of sudden miscarriage. If moderate hypertonicity is present, the woman is recommended to take antispasmodics. In cases where increased tone is caused by hormonal disorders, products containing progestin are prescribed.
Increased uterine tone in the second trimester of pregnancy in most cases is part of the natural process of preparing the body for labor, but it can also be a sign of pathology.
If clinical signs of hypertonicity develop, you should inform your doctor. As a treatment, it is possible to prescribe B vitamins and special sets of exercises.
Treatment and prevention
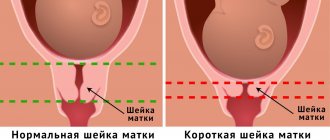
If the uterus is in good shape at 40 weeks of pregnancy, then labor will begin soon. This condition is natural and does not require treatment. Conservation therapy is prescribed to expectant mothers if, due to hypertonicity, premature shortening of the cervix and opening of the internal pharynx begins.
- Bed rest – sexual, emotional and physical rest.
- Taking sedatives that improve sleep and prevent stress - Motherwort, Valerian, herbal teas for pregnant women.
- Medicines that reduce the contractile activity of the reproductive organ - antispasmodics and tocolytics.
- Vitamin complexes – groups B, E, magnesium, potassium.
It should be noted that all medicines, including those of herbal origin, should be used only as prescribed by a doctor. Some medications, for example, Ginipral, can be taken no earlier than the third trimester of pregnancy.
To prevent premature myometrial contractions, it is recommended:
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- do not neglect physical activity, but also do not engage in heavy sports;
- avoid stress;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- take vitamins and medications prescribed by your doctor;
- if in previous trimesters there were voluntary contractions of the genital organ, in case of recurrence, immediately use Papaverine suppositories or Drotaverine tablets;
- choose comfortable clothes according to the size of your tummy;
- in the 3rd trimester, use a support bandage if there are no contraindications for this.
Usually, by the third trimester of pregnancy, women know what training contractions are. If pain occurs for the first time or is more intense than before, you should consult a gynecologist and find out how to prevent similar situations from occurring in the future.
Diagnosis of hypertension and related diseases
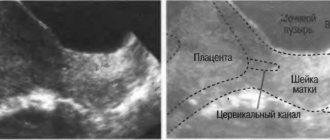
There are several methods for diagnostic confirmation of the presence of hypertonicity. Ultrasound examination is considered the simplest and most accessible. Ultrasound allows you to assess the condition of the uterine muscles, determines possible pathological processes and directly indicates ongoing hypertonicity.
Another, more modern method of determining tone is tonusometry. The essence of the diagnostic method is that sensors are placed on the woman’s stomach, which send a signal to a special device that visualizes the presence of tone.
If hypertension is confirmed, the doctor prescribes a number of additional studies:
- General clinical analysis of blood and urine
- Determination of hormone levels in the blood
- Diagnostics of blood clotting
- Research for STDs
Diagnosis using a warm shower
Contractions can be easily relieved with a warm shower - this method can be used to diagnose the condition of a pregnant woman in order to understand whether contractions are false or not. You need to shower for 10 minutes, after which you need to lie down. If the tone goes away and the woman falls asleep peacefully and sleeps all night, this is definitely not contractions before childbirth. This is a workout. The tone that occurs in this case does not need to be reduced by taking medications. It's better to trust your body and let it do what it's programmed to do. However, there are cases when the tone needs to be removed at the end of pregnancy.
Uterine tone in the 3rd trimester
Uterine tone in the third trimester is difficult to distinguish from preparatory contractions. Therefore, when a typical clinical picture of tone develops, cardiotocography is prescribed. This is monitoring the fetal heart rate along with simultaneous recording of contractions of the reproductive organ. The examination is carried out as part of intensive prenatal care and allows us to identify early changes that threaten the life of the fetus.
The study is initially conducted as a stress test. It involves recording fetal heart function and uterine contractions for 30 minutes. The test can be extended up to 60 minutes.
Training contractions
Not all women experience false contractions in the third trimester. They are felt as short-term tension of the uterine muscles. The uterus tenses for no apparent reason, remains in this position for several seconds or minutes, and then relaxes. The next episode of tension can repeat completely spontaneously - either after a few hours or after a few days. There is no systematicity in such contractions, which distinguishes them from birth contractions.
For some women, the first such contractions appear as early as 20 weeks of pregnancy, but for most, only in the third trimester of pregnancy . As the gestational age increases, the intensity of training contractions may increase. Moreover, their complete absence is also an absolute norm.
Braxton-Hicks contractions do not affect the fetus, do not harm its development, do not advance the onset of labor, do not have any effect on the condition of the cervix, do not lead to its dilatation, do not increase the likelihood of premature birth and therefore should not frighten a woman. They are considered a manifestation of the preparatory activity of the uterus before the complex process of childbirth.
There is also a theory that false contractions are a consequence of disturbances in the functioning of a woman’s nervous system . During pregnancy, uterine tissue grows, and in the third trimester, the number of nerve fibers in the uterus naturally begins to decrease - this is part of the prenatal preparation of the female body. The occurrence of nerve impulses that strain the uterus may be partially associated with this process.
How to make it easier?
Symptoms of training contractions in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy can be relieved by taking a warm shower, changing body position, adequate physical activity, taking an antispasmodic tablet if agreed with your doctor, a cup of warm herbal tea and a positive attitude. Sometimes it’s enough just to lie down for a while and breathe correctly , as taught in courses for expectant mothers, and the tension in the uterus goes away. Yoga and walks in the fresh air are useful.
False contractions do not require treatment, but if they appear frequently and cause significant inconvenience and anxiety, the woman must report them to her obstetrician-gynecologist at a scheduled appointment at the antenatal clinic.
medical reviewer, psychosomatics specialist, mother of 4 children
Among deviations from the norm, uterine tone in the third trimester is the most common. The normal course of pregnancy should take place during the entire nine months with a calm state of the uterine muscles.
How to relieve uterine tone, what to do if it increases
What to do and how to properly remove excess uterine tone during pregnancy? If the problem is of an unexpressed nature, you can try to relieve it without resorting to taking medications. If symptoms develop, light physical activity such as walking or swimming is recommended. You can also do the following exercise: tilt your head as low as possible, relax, take a few deep breaths and exhales. All this can be done only after consulting a gynecologist.
Doctors also recommend attending classes for pregnant women. Experts will show you what exercises can be used to reduce tone and how to help the body prepare for further childbirth. Even a slight tone does not cancel a visit to the gynecologist.
How to help yourself without medications?
You can relieve the tone of the uterus without using drug therapy. One of the simplest ways is the “Cat” exercise:
- starting position – standing on all fours with emphasis on the elbows;
- raising the head and arching the back;
- freeze in this position for 5 seconds;
- leisurely return to the starting position.
The exercise is done 3-4 times, after which you need to lie quietly for at least an hour. A positive result is obtained by relaxing the muscles of the face and neck; breathing should be done through the mouth evenly and calmly.
It would be a good idea to drink a cup of soothing herbal tea of lemon balm, motherwort, mint and valerian. You shouldn’t suddenly get out of bed after the stress has passed; you need to let your body recover.
Carrying out preventive measures does not require much effort. It is necessary to minimize physical stress and emotional distress. It is advisable to strictly adhere to the daily routine (pay special attention to adequate sleep) and follow the recommended diet. A prerequisite is regular visits to the gynecologist leading the pregnancy. A woman carrying a baby must completely give up bad habits: smoking, alcohol, drugs.
In the final third trimester of pregnancy, women often encounter such a phenomenon as increased tone of the uterine muscles. In the last three months of gestation, the uterus is large, it occupies almost all the space in the abdominal cavity, and therefore its tension, which was sometimes indistinguishable in the early stages, is now clearly felt by the woman, and is also easily diagnosed by an obstetrician-gynecologist by palpation.
Is hypertonicity dangerous in the later stages? This article will tell you.
Uterine hypertonicity as a threat of premature birth
If the uterus is in good shape for a long time, and even long rest does not help, the expectant mother should immediately consult a doctor. A doctor who suspects a threat of miscarriage will suggest that the woman undergo a thorough examination - on an outpatient or inpatient basis. First of all, the condition of the fetus and the activity of the uteroplacental blood flow should be assessed using ultrasound. After 34 weeks, CTG (fetal cardiotocography) is required. This method allows you to quickly and painlessly calculate the fetal heartbeat and thereby indirectly learn about its condition.
There are many reasons for toning the uterus when there is a threat of miscarriage. Here are just the most important of them:
- hormonal disorders;
- disturbances of uteroplacental blood flow;
- pathologies of the blood coagulation system;
- connective tissue diseases;
- exacerbation of chronic maternal diseases;
- pathologies of the fetus (including congenital malformations);
- infections;
- gynecological diseases (uterine fibroids, endometriosis and others);
- congenital malformations of the uterus.
Doctors are not always able to find out the exact cause of this condition. There is only one result - by increasing the tone of the uterus, the body tries to trigger the birth of a child ahead of schedule. This manifests itself as severe nagging pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back and tailbone. Bloody discharge from the genital tract in the third trimester indicates the beginning of placental abruption. This condition can be very dangerous for the expectant mother and her baby, because the placenta is the organ that supplies oxygen and nutrients to the baby. If bleeding occurs at any stage of pregnancy, a woman should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance.