The respiratory organs play an important role in the life of the body. Normally, a healthy person can hear clear breathing without wheezing or mucus discharge. Some diseases of the respiratory system are accompanied by the release of blood from deep parts. What caused this disorder, and what is the danger of the pathology?
Some diseases of the respiratory system are accompanied by the release of blood from deep parts
Causes of manifestations
Hemoptysis and bleeding differ in the amount of mass released from the lungs during coughing. When sputum with clots is produced, the symptom is not pronounced. If the patient loses more than 100 ml of body fluid, this refers to pulmonary hemorrhage. At higher rates there is a risk of death from severe blood loss or suffocation.
What can trigger:
The causes of the development of pathology can be chronic bronchitis, asthma, tuberculosis.
- chronic bronchitis, asthma;
- pneumonia (pneumonia);
- tuberculosis, abscess;
- various tumors, including cancer;
- chest injuries with damage to lung tissue;
- heavy physical activity;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- various infections.
Even a small amount of bleeding can result in a sudden breakthrough that must be stopped.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis use:
- Taking anamnesis, examining, tapping and listening.
- Blood test (general + coagulogram).
- Lung examination (x-ray, ultrasound).
- CT or MRI.
- Bronchial arteriography.
- Pulmonary angiography.
- Echocardiography.
- Bronchoscopy.
- Sputum examination.
- Serological tests.
- PCR.
The doctor prescribes research methods taking into account the patient’s complaints, symptoms and factors that may be present.
Sometimes differential diagnosis from gastrointestinal bleeding is required.
Types of blood loss
The source of hemorrhage can be located in different parts of the respiratory system. These include the lungs, bronchi, tracheal lumen and vocal cord area. The intensity of hemoptysis is related to the type of pathology and its location.
Blood is released when coughing, and streaks are noticeable in the sputum.
According to statistics, one of the common complications is the release of clots from the bronchial arteries. They are highly developed and instantly respond to the appearance of any inflammatory process. Blood is released when coughing, and streaks are noticeable in the sputum.
With the destruction of lung tissue associated with chest trauma, the arteries and veins in the lungs are affected. Blood pressure rises and coagulation is impaired. Profuse bleeding has the form of a stream and is released in liquid form when coughing. There are no clots.
Forms
The different forms are:
- hemoptysis. This is the process of coughing up or releasing blood from the bronchi and lungs, released like streaks in spit. In such a situation, blood loss is minimal and amounts to a maximum of fifty milliliters in 24 hours;
Coughing up mucus containing blood clots is a form of bleeding in the lungs. May be caused by various diseases
- Bleeding in the lungs is a process in which blood or clots are released from the organs of the respiratory system. Types of blood loss are presented: minor bleeding. Losses range from 50 to 100 milliliters in 24 hours;
- average Here the figures vary from 100 to 500 ml per day;
- massive or profuse. Blood loss reaches more than 500 milliliters in 24 hours.
Symptoms
Patients with bleeding in the respiratory system develop a severe dry cough. Gradually, breathing softens and sputum is released. It shows scarlet foamy blood or clots, depending on the type of bleeding.
If symptoms are detected, the patient should receive emergency treatment for pulmonary hemorrhage as quickly as possible:
Tachycardia and wheezing when inhaling or exhaling appear.
- shortness of breath, shallow rapid breathing;
- the body feels weak;
- discomfort and increasing pain in the chest;
- chills, fever;
- the skin becomes pale and acquires a marbled tint;
- blue skin appears in the lung area;
- tachycardia, wheezing when inhaling or exhaling;
- lowering blood pressure;
- dizziness.
Pulmonary hemorrhage is a sudden pathology. Initially manifests itself in the form of an infrequent cough, then a change in the color of sputum is detected. In some cases, the cough cannot be stopped, which is accompanied by massive hemorrhage. The patient may experience seizures. With some types of bleeding in the lungs, asphyxia occurs.
If emergency treatment for pulmonary hemorrhage is not provided, loss of consciousness may occur. With hemoptysis, the symptoms are less pronounced and the prognosis is more favorable for the patient.
Hemorrhage is always present when a pulmonary infarction develops against the background of pneumonia.
With a lung abscess, not only blood, but also purulent impurities are found in the sputum. After spitting out the mucus, relief occurs for a short time, but the signs of intoxication do not disappear. When bleeding from the lung is associated with cancer, the patient’s health sharply worsens. Over a short period of time he loses weight. The cough is painful and dry and becomes productive. Hemorrhage is always present when a pulmonary infarction develops against the background of pneumonia.
Diagnosis and treatment
Depending on the clinical case, to identify the cause and source of pulmonary hemorrhage in a hospital setting, the following diagnostic measures are performed:
- X-ray of the lungs;
- bronchoscopy;
- bronchial angiography;
- blood tests;
- CT scan of the chest (if the cause of bleeding is unclear);
- Echo-CG (if pulmonary hypertension is suspected).
After identifying the cause of bleeding from the lungs, the patient is prescribed symptomatic therapy, antibiotics to prevent aspiration pneumonia, and bronchoscopy is performed to sanitize the respiratory tract and stop bleeding (obstruction of the affected bronchus, coagulation, hemostatic agents, adrenaline, etc.).
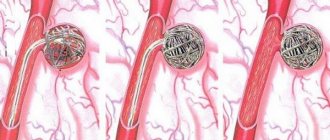
If conservative treatment is ineffective, surgical operations are performed:
- thoracoplasty;
- selective embolization of the bronchial artery;
- ligation of bronchi and pulmonary vessels;
- different methods of lung resection;
- cavernotomy, etc.
First aid for pulmonary hemorrhage
The algorithm of actions includes pre-medical and medical care. To relieve anxiety or fear in the patient, he is provided with physical and psychological peace. Be sure to transfer the victim to a sitting or reclining position to prevent suffocation from bleeding from the lungs. Ice wrapped in cloth is placed on the chest. The patient is given cold water in small sips or given pieces of ice to chew.
The patient is placed in a semi-recumbent position and a cold compress is placed on the chest.
Only specialists should treat lung pathology, so immediately when providing first aid for pulmonary hemorrhage, medical personnel are called.
The patient is hospitalized in the department of pulmonology or thoracic surgery. They prevent narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi by blood clots and restore patency of the passages. The blood is removed using a catheter or bronchoscopic device, then the spasm is stopped.
In case of suffocation, emergency intubation is performed to remove blood, and the patient is connected to equipment for artificial ventilation of the lungs. To reduce blood clotting disorders, aminocaproic acid is administered. With massive pulmonary hemorrhage, anemia can develop, which is an indication for red blood cell transfusion - direct transfusion from a healthy person to a patient.
Urgent Care
In case of pulmonary hemorrhage, it is very important to provide first aid in a timely and correct manner. Due to this, you can hold out the time necessary until the doctor arrives. You should be guided by the following algorithm of actions:
- The patient must be seated correctly. The correct position of the injured person during pulmonary hemorrhage should be sitting, with the torso slightly tilted forward, as well as the head . This will prevent the patient from choking on blood. It is strictly forbidden to tilt the patient's head back, as this can lead to choking.
- If it is not possible to sit a person down, then he is placed in bed on the side on which the lung is damaged. This position somewhat compresses the lung and reduces blood loss; in addition, blood from the damaged organ does not flow to the healthy side.
- An ice pack or cloth soaked in cold water is placed on the chest area. If there is no ice in the house, then you can use frozen fruits or vegetables from the freezer. Due to the cold, small blood vessels spasm and blood loss decreases. The cold is applied for 15 minutes, after which a break of a couple of minutes is taken and the procedure is repeated.
- The victim must be provided with complete rest. He should not talk or be nervous.
It is strictly forbidden to give water to a person with pulmonary hemorrhage. If he is thirsty, you can moisten your lips with a piece of bandage dipped in cold water with the addition of a few drops of lemon juice.
First aid can be provided not only by a health worker, but also by one of your relatives.
It is advisable to use medications only after examining the patient by a doctor. Only in exceptional cases, when the doctor cannot arrive quickly, is it allowed to administer Vikasol to the patient intramuscularly. This medicine helps to quickly stop pulmonary bleeding. The drug Dition can also be used as an emergency aid, but this medicine must be administered intravenously, after preliminary dilution with saline solution. If convulsions are observed, the patient is prescribed Seduxen or Diazepam. To eliminate pain, Promedol is recommended.
Previously, Morphine was used to relieve pain during pulmonary hemorrhages, but now this drug is used extremely rarely.
Disease in infants
This pathology is extremely rare in newborns. The mechanism of development of the complication has not been fully established, but there may be several factors predisposing it.
- Intrauterine infection or infection after childbirth.
- Immaturity of lung tissue and its edema during prematurity.
- Various hematological causes (blood clotting disorders, hemophilia, hemostasis disorder).
- Severe congenital pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Typically, when there are disorders, pulmonary hemorrhage in a newborn occurs in the first few hours after birth. This is accompanied by pronounced external symptoms. The course of the pathological process is lightning fast, which leads to infant mortality in 90% of cases.
It is important to remember that the life of a child or adult suffering from pulmonary hemorrhage depends on how quickly he is hospitalized. In such a situation, you should first of all provide him with qualified emergency medical care.
Treatment of pulmonary hemorrhage
- Providing the patient with a semi-sitting position with legs down.
- Removing blood from the respiratory tract (suction using special devices).
- Administration of hemostatic drugs.
- Therapeutic bronchoscopy is a method that allows you to examine the respiratory tract from the inside, determine the source of bleeding and perform manipulations to stop the bleeding: blocking the bleeding vessel using special means.
- Surgical treatment is open surgery on the lungs with suturing of the bleeding vessel or removal of part of the lung.
- If there is a large volume of lost blood, transfusion of blood and its components, administration of drugs that restore the volume of circulating blood.
- Antibiotics – to prevent infection.
- Treatment of the underlying disease that led to pulmonary hemorrhage.