After hearing the diagnosis, many wonder if the cervix is soft, what does it mean? A healthy woman has a firm neck with a smooth surface and a pale pink color. At the end of pregnancy, the cervix prepares for delivery and gradually softens. But such a course of events can start much earlier than the physiological period; in such situations, the soft cervix is treated.
A soft cervix is its natural state during the period of ovulation and some time after fertilization. After one to two weeks it becomes hard again. This creates suitable conditions for the fetus to develop normally. If the pregnancy is proceeding correctly, then the next time a soft cervix is noted is already in the last weeks before childbirth.
Causes
As for the reasons, softening may be the result of pathological changes or be a normal phenomenon.
Pathological changes
Factors leading to changes in the consistency of the cervical region may be the following:
- The use of medications without a doctor's prescription during pregnancy (papaverine, no-spa), which are often used to relieve nagging pain, but have a relaxing effect on the cervix.
- Pathological birth, which was accompanied by deep tears and injuries, resulting in stitches.
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency is a pathological condition in which the cervical section of the uterus shortens and softens prematurely. This syndrome can be caused by both mechanical and hormonal causes. Mechanical causes imply defects in the structure of the organ: the content of muscle and connective tissue is not proportional in favor of the latter. As a result, the cervix cannot withstand the pressure of the growing fetus. The causes of this condition are congenital defects in the structure of the organ. Hormonal factors that lead to ICI are an increase in the production of male sex hormones in the body of a pregnant woman. 17-OH-progesterone and DHEA sulfate increase. With this cause of ICI, labor may begin prematurely and urgently at 17 or more weeks of gestation. Mechanical causes often trigger labor at 30 weeks or more.
- Inflammatory processes in the female genital area – endocervicitis. As a result, the likelihood of infertility also increases.
- Neoplasms.
- Congenital anomalies of the structure of the internal genital organs.
- Multiple artificial abortions.
Ovulation period
Under the influence of a number of hormones that regulate a woman’s menstrual cycle, the cervix changes its consistency, the width of the cervical canal and the nature of the discharge. The main hormone that has a significant effect on the hardness or softness of cervical tissue is estradiol. Normally, by the middle of the cycle, its level in the blood increases to its maximum, reaching a peak at the moment of rupture of the follicle - the period of ovulation. The egg passes through the fallopian tube, where it can hypothetically meet a sperm. In order for sperm to freely penetrate into the uterine cavity, the cervix must become soft and the cervical canal wide.
The time for the release of the egg from the follicle and the softening of the cervix during the average menstrual cycle occurs on days 12–15. If the length of the cycle is not 28–32 days, but 33–45, then the cervix becomes soft on days 17–30.
Course of pregnancy
Often, a soft cervix is observed during pregnancy earlier than expected. This reaction of the body is considered natural only from the 36th week of gestation.
But often ignoring this fact leads to irreparable consequences. If such a reaction is observed during the formation and growth of the embryo, when pressure is placed on the lower part of the uterus, a course of treatment should be undertaken and this often happens in a hospital setting. If the muscle tone of the uterus is too strong, then the cervix may open, and this is always accompanied by its softening and shortening.
Such a reaction can be recorded from 20 to 30 weeks, occasionally in the first trimester. In a normal state, softening is noted already before childbirth.
First week after conception
The change in cervical density in the early stages is due to the formation of a more complex network of blood vessels that are responsible for feeding the uterus and baby in the womb. In addition, the corpus luteum of the ovaries does not yet produce progesterone strongly enough, a hormone that ensures the density of the cervical region. Over time, during a healthy pregnancy, the cervix becomes dense in consistency and also long. The cervical canal closes, and the mucous contents protect the amniotic membranes from the penetration of microorganisms. Sometimes an obstetrician-gynecologist during an examination determines a soft cervix during early pregnancy. This is a reason to prescribe progesterone drugs.
The period before delivery
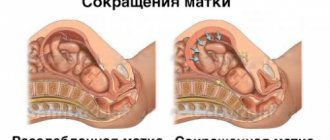
A soft cervix before childbirth is considered to confirm the readiness of the female body for childbearing. It is at this point that the organ is no longer able to hold the mucus plug and becomes more susceptible to expulsion of the fetus. At this stage, the cervix is soft, short and opens gradually. Often, women notice stretching in the lumbar region and the gradual removal of the mucus plug. Such processes, as a rule, are observed from the end of the 37th week, but can also begin at the 39th week. If the cervical region does not dilate sufficiently, and labor has already begun, then additional stimulation is required.
Softening occurs due to a cascade of reactions that occur at the time of delivery. This process is very complex and begins in advance, covering changes both at the level of the fetoplacental system and at the level of the brain. Not everyone's neck becomes soft in due time. Often its softening and shortening occurs either too early or does not occur at all. Ultrasound and palpation are used to monitor the cervix. The gynecologist regularly examines the woman before childbirth, determining her readiness, and takes appropriate measures if any deviations are detected.
Why does it appear?
Doctors identify several causative factors that lead to the development of this condition during pregnancy. The most common option is the development of hormonal disorders, which are associated with the different effects of numerous hormones formed during this specific period in the female body.
experience cervical softening The risk of developing this pathology increases significantly if the expectant mother had any problems with the cervical canal or cervix during the previous pregnancy of her first child.
Frequent scraping of the uterine mucosa after abortions is another risk factor leading to softening during pregnancy. Also, any combined diseases of the internal genital organs that developed in a woman before conceiving a baby can lead to the development of this pathology.
Taking certain types of hormonal medications can also cause softening of the cervix. Usually, the formation of this condition is caused by excessively long-term use of incorrectly selected oral contraceptives . Some of the remedies can also cause a whole range of unfavorable symptoms that worsen a woman’s well-being.
It is important to remember that even in the second half of pregnancy, monitoring the condition of the cervix is very important.
The growing amniotic sac puts strong pressure on the cervical canal. This can cause the amniotic fluid to be released prematurely, and the woman may go into premature labor.
Symptoms
Softening of the cervical region may be accompanied by a number of clinically significant signs. In the 1st and 2nd trimester, the patient most often learns about a short and soft cervix at the next ultrasound screening. Since early pregnancy is often accompanied by nagging pain in the area of the uterus and ovaries, a woman may not think about the warning signs of isthmic-cervical insufficiency. Stretching of the uterine ligaments, intense work of the corpus luteum of the ovary, and concomitant inflammatory pathology of the pelvic organs can cause pain. But changes in the aspect of softening of the cervical region are also accompanied by nagging pain. A pregnant woman cannot differentiate these sensations on her own. Therefore, regular visits to your obstetrician should be mandatory.
The main symptoms of pathological premature softening are mild nagging pain in the lumbar region, hypertonicity of the uterus (a feeling of petrification in the lower abdomen) and increased discharge from the genital tract.
Consequences and possible complications
Based on the pathology that accompanies the softening of the cervix, certain consequences will be noted. Basically, this process is natural and physiological. But if it becomes pathological during gestation, then the consequence in this case may be a miscarriage. In non-pregnant women, a constantly soft cervix is a sign of diseases of various origins that can lead to a violation of its consistency. Chronic inflammatory processes and neoplasms localized in the cervical region change its structure.
Definition
What does the uterus look like in its normal state? During most of the menstrual cycle it is quite hard and dense. Has a light pink tint. Its surface is smooth on the outside. However, normally this condition may change in the third stage of the menstrual cycle. After ovulation, the organ becomes more loose, its throat opens slightly - this happens in order to create optimal conditions for conception and attachment of the embryo. If conception does not occur, then menstruation begins and the organ gradually returns to its normal state.
What does a loose cervix mean? This is a condition in which the density and elasticity of the tissues of this organ is slightly (or significantly) reduced. The tone of the cervix decreases, the pharynx may even open slightly. This is normal in early pregnancy and also just before giving birth. However, if this condition occurs during mid-gestation, it can lead to premature birth and miscarriage. Therefore, upon hearing such a diagnosis, many expectant mothers begin to worry. But is this justified, are such changes always associated with pathology?
Treatment options
If a soft cervix is diagnosed between 13 and 25 weeks, doctors carry out a number of therapeutic measures to prevent the threat of miscarriage.
Treatment mostly depends on the causes that caused the pathology. In case of hormonal imbalance, in a hospital setting, the pregnant woman is prescribed medications to stabilize hormone levels. At the same time, medications are used that reduce tone, thereby strengthening the density of the pharynx. Complete rest is also recommended to avoid premature birth.
A soft and short neck becomes an indication for the installation of a pessary. The device, in the form of a ring, is attached to the os of the uterus, prevents premature dilatation and evenly transfers the weight of the growing fetus around the entire perimeter.
If the risk of labor starting prematurely is too high, then surgical intervention is used by suturing the cervix. The operation is performed under general anesthesia for 15-20 minutes, while the internal os is tightened with special threads, which helps maintain pregnancy until the normal period of 37-38 weeks.
Once the baby is fully formed, the sutures are removed, and the decision about the choice of delivery method depends on additional factors. It is not uncommon for a woman to give birth on her own without a cesarean section.
If a pathology is detected, it is necessary to understand that the risk of miscarriage is very high, therefore maximum rest is required, avoid lifting heavy objects, and also refuse sexual activity so as not to provoke labor.
Why is this happening?
What are the main reasons for this phenomenon? It can be caused by many features and factors. Among them are:
- Frequent mechanical damage, for example, during abortions, operations, diagnostic studies, accompanied by the introduction of instruments into the uterus through the cervical canal;
- Weakening of general organic and/or local tissue (which often happens after operations or injuries) immunity;
- A significant drop in the tone of the uterus and small pelvis as a whole;
- Hormonal imbalances, both from the reproductive system and as a result of certain endocrine diseases;
- Recent or fairly long past difficult childbirth;
- Some types of congenital changes (hypoplasia, infantilism of the uterus, other deviations and pathologies of this type, a small number of elastic compounds in tissues, hereditary predisposition to low tone of organs in general, and the pelvis in particular).
It is important to understand that the phenomenon is not only quite serious in itself (especially during pregnancy), but is also caused by serious pathological processes. Therefore, even if no negative symptoms appear, it should still be treated in a timely manner.
During pregnancy
During this period, changes occur under the influence of hormones. The uterus softens in the first days of pregnancy so that the embryo can better attach and be provided with adequate nutrition. But gradually, even during the first month, the organ returns to its more or less normal state. Now it will undergo some changes during gestation, but the next time a loose uterus will appear only a few days before birth.
At the same time, the cervical canal will slightly expand, the tone of the cervix will drop, and it will shorten. All this happens as part of the body’s preparation for childbirth and is designed to make the birth process easier for the expectant mother. That is, such changes are considered normal and do not require treatment.
However, if this phenomenon occurs at 20-30 weeks of gestation, then it is necessary to begin treatment, since this condition can lead to premature birth. At the same time, the most critical period in this regard is considered to be 24 weeks. If loosening occurs this week, it is often impossible to avoid premature birth.
Without pregnancy
If during pregnancy, loosening is considered normal at some stages, and pathological at others, then in the case of absence of pregnancy, this phenomenon is always a sign of pathology. Most often in such cases, the diagnosis of ICI - isthmic-cervical insufficiency - occurs. It can be functional (developing as a result of an excess of the male sex hormone, or a lack of progesterone), or organic (forming as a result of injuries from surgical interventions and procedures or as a result of difficult childbirth).
In fact, the first type causes a decrease in muscle tone, organ elasticity and a slight change in tissue composition (not always). The second type is dangerous because scars and tears form on the neck. In this case, the elastic fibers of the tissue are replaced by connective, fibrous ones, which ultimately also negatively affects the tone of the organ.
The first weeks after fertilization
After the fertilized egg attaches to the uterine cavity, the complex process of restructuring the circulatory system necessary to nourish the fetus begins. The ovaries, under the influence of the corpus luteum, begin to produce more and more progesterone, which is responsible for the texture of the cervix. The cervical canal closes and is filled with mucous contents. This provides protection to the membranes from various bacteria. The cervical spine itself becomes dense after a few weeks. This keeps the growing fetus in the uterus.
But it happens that a soft cervix during pregnancy in the first trimester is a reason to take medications. Your doctor may prescribe hormone therapy. Preparations containing progesterone are usually prescribed.
Symptoms
Does this phenomenon have any negative symptoms and can you suspect it in yourself? It can be completely asymptomatic or give some nonspecific manifestations. Among them:
- Aching pain, heaviness or feeling of fullness in the lower abdomen;
- In rare cases, discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- Sharp pain or tingling sensations in the vagina that are short-term;
- Normal but excessive cervical mucus discharge;
- Blood in vaginal discharge;
- Bleeding outside of menstruation.
This condition is most difficult to diagnose in women who have not given birth. This is due to the fact that in the vast majority of cases, in this category of patients the pathology does not manifest itself at all and is discovered by chance.
Treatments
Treatment depends on the type of pathology and its causes:
- If the condition develops as a result of hormonal imbalance, it is treated with progesterone drugs (Duphaston) for two weeks or more. Also in this case, a Mayer ring can be installed - a pessary, which will now bear the entire load;
- If the condition is caused by injuries, then non-steroidal painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac), broad-spectrum antibiotics (Amoxiclav) and drugs that restore uterine tone are prescribed. Antibacterial drugs are used for up to two weeks, drugs for uterine tone - up to two months.
If the lesion is traumatic, surgical intervention is performed only in the presence of significant defects and scars. During pregnancy and when this condition has hormonal causes, the cervix can be sutured to prevent miscarriage. This manipulation is carried out at early or later stages.
How is the treatment carried out?
If during a gynecological examination the doctor determines the presence of signs of a softened cervix, then he will definitely recommend that the expectant mother monitor her daily routine. In this case, all physical activity and heavy lifting are necessarily excluded.
A woman should spend more time in bed and rest . For mild violations, doctors will allow the expectant mother to take short walks in the fresh air. They will be useful not only for her, but also for her baby.
Any psycho-emotional stress is excluded. It is strictly forbidden for the expectant mother to worry and be nervous, especially over trifles. This can worsen her well-being and also significantly harm the baby.
If, against the background of severe softening of the cervix, a woman exhibits clinical signs of hypertonicity, then the obstetrician-gynecologist may suggest that she be hospitalized in the hospital. This forced measure will help preserve the life and health of the baby, and will also reduce the likelihood of premature birth.
To eliminate moderate uterine hypertonicity, medications that have an antispasmodic effect are also suitable. “No-spa” is a good remedy for relieving spasms from the smooth muscle muscles of the female genital organs.
In a hospital setting, the woman will receive a range of necessary treatment. Medicines can be prescribed in different ways. Most often they are used parenterally through injections and intravenous drips. Such therapy helps to achieve a good therapeutic result in a shorter time.
To compensate for hormonal imbalances that have arisen, doctors may recommend that the expectant mother use various hormonal medications. One such remedy is Utrozhestan . It is usually prescribed in suppositories. This remedy is prescribed for a complex treatment. When prescribing such hormonal therapy, the doctor must monitor it by conducting regular examinations.
For many women, the soft neck may also shorten. Typically, this condition is registered in pregnant women at 20-28 weeks of pregnancy. In some cases, this pathology may occur later - by 30 weeks.
To eliminate such symptoms, the doctor may recommend that his patient install a special device called an obstetric pessary . In appearance it resembles a regular ring. It is inserted into the cervix and fixed there. This fixation helps secure the fetus and reduces the likelihood of premature birth.
The expectant mother should not be afraid of this procedure if her doctor recommended it. The installation of a pessary does not cause any pain or significant discomfort. The duration of the procedure is usually 25-35 minutes. Doctors will remove the pessary 1-2 weeks before giving birth. This procedure is usually performed in a maternity hospital.
If a soft cervix is one of the manifestations of isthmic-cervical insufficiency, then suturing may be required . This procedure also often causes real panic among expectant mothers.
No need to worry! In this case, stitches are not applied for life, but only until childbirth. This manipulation is forced. Otherwise, there is a high risk of losing the baby or getting a premature birth.
Doctors most often apply sutures for isthmic-cervical insufficiency at 24-26 weeks of pregnancy. These periods are not constant and may vary depending on the initial condition of the expectant mother.
Before carrying out this procedure, the doctor must conduct a thorough extended examination of the genital tract. It is very important that the stitches be applied by an experienced and qualified doctor who has sufficient clinical experience in such work.
Obstetrician-gynecologist V. G. Khorun will talk about isthmic-cervical insufficiency during pregnancy in the next video.
Conclusion
From everything written above, we can conclude that a loose uterus is considered normal only in three cases - on the eve of menstruation, in the earliest stages of pregnancy and immediately before childbirth. In all other cases, excessive loosening of the organ, and especially its neck, is a pathology that should be treated in a timely manner. If the patient has been given such a diagnosis, then she must strictly follow the doctor’s instructions in order to preserve reproductive function, and most importantly, the general health of the body.
What does this mean?
For normal intrauterine development, it is very important that the cervix is sufficiently firm and dense. It must also be in a closed state. This is very important, especially in the early stages of pregnancy. A softened cervix can lead to the threat of spontaneous abortion.
For many women, the tone of this organ changes significantly closer to childbirth. This reaction is completely physiological. Typically, this condition develops closer to 37-39 weeks of pregnancy. A soft cervix at this time is necessary for the baby to move well through the birth canal during birth.
This pathology can have extremely negative consequences . Experienced obstetricians and gynecologists know how to distinguish a hard cervix from a soft one.
They regularly conduct such research during the entire period of pregnancy. It is necessary especially if a woman has any diseases of the cervical canal or there are concomitant diseases of the reproductive system.
What does the uterus look like during pregnancy?
The uterus changes dramatically during pregnancy. This is understandable, because this is where the fetus develops for 9 months. And a lot depends on the health of this organ. How does the uterus change in the early and late stages of pregnancy? What is considered normal, and what is a reason to consult a doctor?
Physiological changes
In its normal state, the uterus has a height of 4.5-5.5 cm, while the size of the uterus during pregnancy reaches 38 cm in length (at the end of the third trimester, before childbirth). No other organ has the ability to stretch like this. That is why an ectopic pregnancy, when the fertilized egg begins to develop in the ovary, fallopian tube or abdominal cavity, cannot be carried to term and, if diagnosed untimely, has dire consequences.
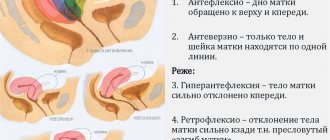
The position of the uterus changes during pregnancy as it grows. But the most favorable situation is when the uterus is located approximately on the same plane as the cervix and vagina, without bending or deviation to the side. This makes it easier to conceive and give birth.
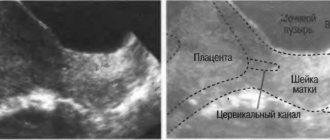
During pregnancy, the cervix is dense, long, closed, located deep in the vagina and has a bluish tint - this is one of the early signs that a woman is pregnant. The gynecologist examines the cervix with his fingers and using a special mirror.
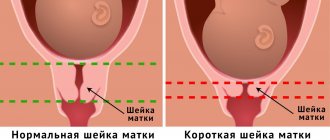
If the cervix is short (less than 30 mm), or slightly open, the woman may be advised to have sutures to avoid further dilatation and miscarriage, or a removable ring pessary.
Uterine tone
There is probably no woman whose pregnancy proceeds ideally. Hypertonicity, expressed in nagging pain and uterine tension, is one of the most common complaints, especially in the first trimester. And this is also the reason for most hospitalizations. In fact, periodic tone of the uterus during pregnancy is the norm, since this organ has a muscular layer. Any muscle in our body contracts. Hypertonicity is dangerous if it is accompanied by dilatation of the cervix and bleeding.
When examined by a gynecologist, it is not often that the uterus is soft during pregnancy, since even touching can tone the muscle. The same thing happens when an ultrasound probe is passed over the abdomen. However, most doctors continue to write in their reports “local hypertonicity along the anterior wall of the uterus” in such cases. Perhaps it exists, but it is completely harmless and usually lasts only a few seconds.
If the uterus during pregnancy is almost always hard to the touch, and in addition, the tone is painful, the doctor may prescribe antispasmodics.
Observation by a doctor
All those weeks and months while a pregnant woman is under the supervision of a gynecologist, he monitors the condition of the child and the uterus. Gynecological examinations are carried out no more than 2-3 times during the entire pregnancy (if there are no deviations). And measurements of the uterus (its length and abdominal volume) at each woman’s visit. The received data is recorded in its exchange card. And if the records show that the uterus has not enlarged at all in 1-2 weeks, and a woman at more than 20 weeks does not feel or rarely feels the baby moving, she is urgently sent for an ultrasound. This can occur when the fetus dies or there is a lack of oxygen and nutrients. In the second case, the doctor will be able to help.
This is why observation by a gynecologist is so important. Don't miss your appointments.
Diagnostic role of cervical changes during pregnancy
Changes in the cervix during gestation are so pronounced that it becomes possible to determine pregnancy by the cervix. The most significant signs include:
- Color change. The cyanosis of the cervix is completely physiological and is explained by increased blood supply. In healthy, non-pregnant women, the cervix is pink.
- Change in position relative to the uterus. The cervix descends during pregnancy.
- Change in consistency. The cervix becomes less dense to the touch as pregnancy progresses.
Interesting fact! The way the cervix looks depends on whether the woman has had childbirth before or not. In nulliparous women, the cervix is cylindrical in shape, while in those who have already given birth, the shape is cone-shaped.
Changing the position of the cervix
The cervix in the early stages of pregnancy is located lower than usual. The cervix descends after conception to retain the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. This process is ensured by the action of progesterone. If the cervix is located high, then this may confirm the high tone of the uterus and be a threat to pregnancy.
However, the high location of the neck can also be an anatomical feature of the body. The risk to pregnancy must be assessed by a doctor: perhaps a change in the position of the cervix will cause the woman to be hospitalized in order to maintain the pregnancy.
Changes in the consistency of the cervix
A looser cervix during pregnancy is due to the growth of the vascular network, swelling and an increase in the number of glands that produce mucous secretion. Also, the cervix becomes looser due to the effects of progesterone.
Note! In the early stages, the cervical structure retains its density. The Horwitz-Geghar sign of pregnancy indicates the preservation of the elasticity of the cervix, which makes it possible to approach the fingers during a two-handed gynecological examination.
During early pregnancy, the cervix narrows, the elasticity of the tissues remains, and they are difficult to stretch. The density changes with increasing age, but there is no need to fear that if the cervix is loose to the touch, it will not be able to hold the fetus.
During pregnancy, a more active production of mucous secretion by glandular cells occurs. The mucus itself becomes thicker, its viscosity is higher than in the absence of pregnancy. The cervical canal is closed during pregnancy by a mucous plug, which performs the following functions:
- preventing pathogens from entering the uterine cavity;
- maintaining optimal vaginal microflora;
- ensuring the normal functioning of the organs of the reproductive system.
Insufficient mucus production can cause the progression of infectious diseases.
Pathologies of cervix consistency
If the cervix is hard during pregnancy, this may indicate excessive tension in the organ (hypertonicity). This condition is quite dangerous, so when it is detected, the doctor must prescribe therapeutic correction measures, in some situations deciding whether the pregnant woman needs to be hospitalized in a hospital.
It is impossible to determine on your own, at home, that something is wrong with the cervix. You should regularly visit a specialist who is managing your pregnancy. Only a doctor can determine the pathological or normal condition of the cervix in the early stages of pregnancy.
Excessive looseness of the cervix at the beginning of pregnancy is also an alarming sign. This, combined with a short cervical length and loose closure of the cervical canal, may indicate a risk of spontaneous miscarriage.
The discovery of large loose areas in the cervical canal most often indicates the presence of an infectious-inflammatory process, the causative agents of which can be the following microorganisms:
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasma;
- gonococci;
- adenoviruses;
- cytomegalovirus.
If your stomach hurts early, you should immediately consult a doctor!
Usually the pathological process is accompanied by nagging pain, vaginal discharge, and upon examination, ulcerations are revealed on the mucous lining. Such symptoms indicate the need for additional diagnostic methods to identify the pathogen and determine the optimal measures to eliminate it.
What contributes to the enlargement of the female organ?
This condition is common among women before menopause. Age affects the size of the uterus, and this is normal. But if a woman experiences painful symptoms, then pathology may develop. A thorough diagnosis will help identify it.
The uterus is enlarged in the following diseases:
- Myoma is a benign tumor. This is the most common disease in which the size of the uterus changes. The disease occurs in women of reproductive age. It is dangerous due to its complications: possible transformation into a malignant tumor, miscarriage, infertility. Myoma is caused by hormonal imbalance, irregular sexual intercourse, sexual disharmony, past abortions, hereditary predisposition, obesity, diabetes and many chronic diseases. Insufficient physical activity is also considered a provoking factor.
- An ovarian cyst is a cavity filled with fluid. The development of a cyst often leads to an increase in the size of the uterus. Abdominal trauma and hormonal imbalance in the female body can cause a cyst.
- Adenomyosis of the uterus is the growth of the endometrium into the uterine layers. With this disease, there is an overgrowth of the muscle membrane, which leads to an enlargement of the organ. If the hormonal balance is disturbed, some kind of surgery was performed on the organ, or abortions were performed, then the development of adenomyosis is possible.
- Oncology. Malignant neoplasms are observed in women of all ages. But those who have started menopause are especially susceptible to them. An enlarged uterus is one of the symptoms of the disease. The development of a tumor is more likely in women who are prone to obesity, in nulliparous women and in those who approach menopause at a late age.
- State of molar pregnancy. This pathology is associated with abnormalities of the placenta. With it, the fetal tissue begins to grow. Molar pregnancy is associated with genetics - a genetic error occurs during fertilization.
Any of these pathologies requires examination and treatment.
By what symptoms can a woman understand that the uterus is enlarged?
If a woman has an enlarged uterus, she will first begin to experience pain in the lower abdomen. The pain occurs due to the pressure of the enlarging uterus on the bladder. This can also lead to urinary incontinence.
Another symptom of an enlarged uterus is heavy menstruation. They are called menorrhagia. They come irregularly. Not only blood is released, but also clots. Between menstruation, bleeding from the vagina is observed. Large blood loss leads to the development of anemia.
Enlargement of the female organ leads to problems in a woman’s reproductive activity. This means that infertility may develop, and the resulting pregnancy often ends in spontaneous abortion or premature birth.
Along with these symptoms, migraines and common headaches, flatulence and bloating are also observed.
Abdominal pain and urinary incontinence are symptoms of other ailments, and not only serve as an indicator of an enlarged uterus. The definition of the disease remains with the doctor, and the woman just needs to contact him in a timely manner.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
To diagnose the disease that contributed to the enlargement of the uterus, different methods are used.
The very first is a routine examination by a gynecologist. The doctor will ask the patient about the symptoms and conduct an examination in a gynecological chair.
The next study is ultrasound. This may be a transabdominal or transvaginal examination. In the first, the sensor is moved around the woman's abdominal cavity, and in the second, the sensor is inserted into the vagina.
If ultrasound is not enough, then hysterosonography is done. This test is performed using a saline solution that is infused into the uterus. An ultrasound is then performed, which gives the doctor more information than a regular ultrasound.
Cervix in different phases of the cycle and during pregnancy
Most women undergo an examination by a gynecologist once a year, unless there are any abnormalities in their health. If you suspect pregnancy, you should consult a doctor. This must be done after the delay occurs. Until this moment, many ladies worry and wonder whether conception has occurred.
The cervix looks different before menstruation and during pregnancy. A woman will not be able to see the changes on her own, but it is quite possible to feel them. How this diagnostic method is used, its advantages and disadvantages should be considered in more detail.
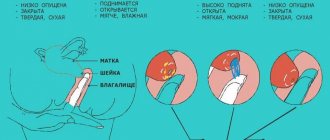
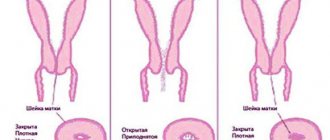
Cervix - classic changes
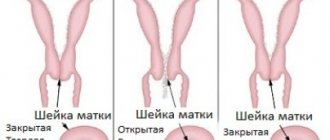
On the eve of possible menstruation, the uterus and its cervix undergo the following physiological changes. Changes can be diagnosed the day before the start of menstruation - the uterus descends (the difference can be felt when comparing the uterus in the “high” position before ovulation), the diameter of the cervix increases slightly (for adequate discharge of menstrual blood) and softens.
Some people ask the question: “What does the uterus look like before menstruation or what does it feel like?” The visual image is quite problematic, and when palpated, the uterus before menstruation (that is, during the infertile period) is hard, resembling the tip of the nose.
Thus, the woman’s body creates all the conditions for monitoring the regularity of her cycle, as well as protecting herself from unwanted pregnancy or, conversely, helping to identify the day with the maximum opportunity for conception.
Cervix and its condition
The lower part of the uterus is called the cervix. It looks like a tube connecting the vagina and the cavity of the reproductive organ. The average length of this section is 4 cm, and the length is 2.5 cm.
Changes occurring in this organ make it possible to diagnose early pregnancy, as well as the period of ovulation or regular menstruation. A gynecologist can observe its changes and determine its consistency: there is a hard and soft cervix.
This organ also makes it possible to determine whether there are any pathologies in the functioning of the female reproductive system.
An experienced gynecologist will be able to evaluate various conditions of the cervix.
If it is not possible to visit a doctor frequently, a girl has the opportunity to determine some conditions on her own. This must be done correctly.
A woman can only assess what the cervix looks like at different periods by comparison, as well as by theoretically knowing its parameters.
Cervix during menstruation
From the first day of the cycle, the uterus begins to reject the overgrown endometrium. To do this, the cervix opens slightly. This happens a few days before the start of the critical days. The position of the uterus becomes lower.
When the organ opens slightly, infections should be avoided in the vagina. To do this you should:
- Observe personal hygiene rules.
- Do not visit the pool.
- Do not swim in bodies of water.
- Wipe the anus away from the vagina.
- Do not insert foreign objects or fingers into the vagina.
- Don't douche.
Small discharge from the cervical canal that appears at this time is designed to protect the internal environment from infection. But it's not worth the risk.
Cervix after menstruation
A healthy cervix in the first phase of the cycle prepares for future conception. Her channel is narrowing. The bleeding stops. The uterus is pulled high, and the endometrium begins to grow in it.
After your period ends, your cervix becomes dry and hard. The cervical canal is closed. This position of the organ allows you to avoid infection getting inside.
The cervix feels firm to the touch. To conduct an examination at home, a woman should compare tactile sensations over two, or preferably three, cycles.
Ovulation period
A soft cervix is determined upon examination when it is time for ovulation. During this period of the cycle, the gynecologist can determine that the pharynx of the organ is open. This is called the pupil sign.
You can feel your cervix at home during ovulation and note its increased humidity. During this period, it rises a little.
If during the examination the cervical canal is open, abundant mucus is released from it with a soft surface, it means that the egg is preparing to leave the ovary. The uterus is ready to receive sperm.
After this, either conception occurs, or the body begins to prepare for the next menstruation. If fertilization does not occur, on the 16th–17th day of the cycle the canal closes and the organ takes a different position.
The period preceding menstruation
The cervix is low before menstruation. It is dry and hard to the touch. During examination, the gynecologist will note tight compression of the cervical canal. This means that the uterus is not ready to receive sperm.
By the last days of the cycle, after the absence of fertilization of the egg, the organ also undergoes a number of changes. The cervical canal enlarges.
The cervix before menstruation, the day before it begins, looks a little like what it looks like during ovulation. Only this time it opened not to accept sperm, but to tear away a layer of endometrium.
Cervix during pregnancy
The uterus undergoes a number of changes during pregnancy. In the early stages, even an experienced gynecologist will not be able to accurately diagnose the conception that has occurred. After examination, the doctor can determine what changes have occurred in the organ.
First, hidden changes within are observed. They cannot be seen so easily. In the early stages, before the delay, it looks almost like the uterus before menstruation. However, visible changes will appear very soon.
You can feel a tight cervix with a soft uterus. The pregnancy begins to appear. It is difficult to determine how many days the body will need for this. In the early stages of pregnancy, the uterus changes in the following parameters:
When fertilization has occurred, the color of the cervix begins to change. It can be described as cyanotic. There are objective reasons for this condition of the mucous membrane. They consist of increasing blood flow.
A loose uterus is a sign of early pregnancy. If during ovulation the cervix is located high, then after fertilization progesterone changes its position. During the cycle following ovulation, it drops in the absence of pregnancy.
With successful cell implantation, the size of the reproductive organ increases, and by the end of 4 weeks it is already comparable to a chicken egg. After fertilization and fetal development, you can feel it in the pelvic area.
If the gynecologist examines during this period, he may reveal mobility of the cervix due to softening of the isthmus. How long it takes for the body to carry out all these changes depends on its characteristics.
A soft cervix during pregnancy is one of its first signs.
What happens to the cervix during pregnancy?
On the eve of menstruation
During menstruation, the cervix drops and becomes soft. The uterus itself increases in size during menstruation. The throat of the cervix opens slightly, the edges are smoothed. In this case, such a condition is necessary not for rapid fertilization, but for the release of menstrual flow. In the uterus, the outer layer of the mucous surface is rejected. The endometrium comes out gradually, separating in layers.
During this period, special attention must be paid to hygiene. A slightly open pharynx allows microorganisms to easily penetrate the internal genital organs. To avoid infection you should:
- wash yourself after each urination, moving from the vagina to the anus;
- change sanitary pads or tampons promptly;
- wear comfortable underwear made from natural fabrics;
- Avoid swimming in open water and visiting public baths and saunas.
After conception in the early stages, characteristic changes begin in a woman’s body. First of all, the uterus changes: it becomes softer, and the pharynx becomes harder. Visible signs appear a few weeks after fertilization. This time is necessary for the egg to enter the uterine cavity from the fallopian tubes and attach to its surface. After this, changes occur under the influence of the hCG hormone.
The neck of the reproductive organ is located high, while the pharynx does not allow a finger to pass through during examination. Upon examination, it can only be felt with the tip of a finger; the pharynx is compressed. The color of the neck changes, it acquires a bluish tint. This is due to an increase in the intensity of blood supply to the organ.
Before you start, you first need to take care of hygiene. Since the entire procedure will be done with your hands, they must be washed thoroughly. It is advisable not to have a manicure on your hands with excessively long nails, in order to avoid damage to the mucous membranes, as well as a manicure without decorative elements (rhinestones, beads, etc.).
), since at any moment they can come off the nail plate and remain in any part of the internal organs, which can lead to not the most favorable consequences. So, having decided on the hygienic condition, you should move on to choosing a position that is convenient for the examination. This is completely individual for each woman.
The most successful positions:
- sitting on the toilet;
- squatting;
- raising one leg to an elevated position, such as a chair.
Using one or two fingers, the cervix is examined by touch.
Due to the fact that many women know what the uterus should feel like before menstruation, they try to feel the organ themselves. But still this should not be done.
Firstly, if hygiene is not observed, there is a risk of infection, because through the hole, microbes can enter the uterus itself and cause inflammation.
Secondly, on different days of the menstrual cycle the position of the uterus and its cervix may change. The neck can either fall or rise slightly. Therefore, without additional information, a woman can injure her cervix. And of course, no matter how much experience the girl has, for accurate results, especially if pregnancy is suspected, you need to contact a gynecologist, an experienced specialist who has all the necessary knowledge and modern equipment for examination.
Palpation at home
Many women, before going to the doctor, would like to confirm or refute their assumptions about a possible pregnancy. Knowing the basic characteristics, there is a chance to determine the development of a new life at home before the delay. The uterus is soft during pregnancy. But in women who have not given birth, the cervix is tightly closed and located high. Before menstruation, its position is lower.
Even an experienced specialist would not risk diagnosing pregnancy solely on the basis of an examination.
Palpation technique
This method is used only if it is impossible to visit a doctor often. It should not be used before menstruation to avoid infection. When deciding to use this technique, you need to remember its disadvantages.
If you want to carry out an inspection on your own, you must follow a number of recommendations:
- Before palpation, it is necessary to cut the nails on the middle and index fingers.
- Wash your hands thoroughly and wear sterile gloves.
- Two fingers are inserted deep inside.
- The tubercle inside should be palpated and conclusions drawn about the condition of the cervix.
Disadvantages of self-palpation
There are a number of negative qualities of the presented diagnostics. These include the following facts:
- There is a possibility of infection and causing various diseases.
- If you accidentally move it inaccurately, there is a risk of injuring the neck, which will cause erosion.
- It is impossible to determine with a high degree of probability whether pregnancy has occurred.
- You will still need to see a medical specialist.
Self-diagnosis is considered a rather risky approach. Even having sufficient theoretical and practical experience on this issue, it is almost impossible to draw accurate conclusions about the state of the reproductive system based on palpation at home.
Only a proper examination by a qualified specialist will be an adequate means of determining pregnancy.