A disease of the body, such as radiation sickness, can occur in people as a result of exposure to a large number of ionizing rays, which causes damage to cell structures in various forms. Today, such diseases are rare because they can develop after a single exposure to a high dose of radiation. Chronic disease can occur as a result of constant exposure to small amounts of radiation. With such irradiation, all body systems and internal organs are damaged. For this reason, the clinical picture of such a disease may always differ.
Radiation sickness
This disease develops after exposure to high radioactive radiation from 1 to 10 Gy and above. There are situations when radiation exposure is recorded at doses of 0.1 to 1 Gy. In such a situation, the body is in a preclinical stage. Radiation sickness can occur in two forms:
- As a result of the overall relatively uniform exposure to radioactive radiation.
- After receiving a localized dose of radiation to a specific part of the body or internal organ.
There is also the possibility of a combination and manifestation of a transitional form of the disease in question.
Typically, the acute or chronic form appears depending on the radiation load received. The peculiarities of the mechanism of transition of the disease into an acute or chronic form completely exclude a change in condition from one to another. It is known that the acute form always differs from the chronic form in the rate of receiving a radiation dose of 1 Gy.
A certain dosage of the received radiation causes a clinical syndrome of any form. The type of radiation may also have its own characteristics, since the nature of the damaging effect on the body may differ significantly. Radiation is characterized by an increased ionization density and low penetrating ability; therefore, the destructive effects of such radiation sources have certain volume limitations.
Beta radiation with a low penetrating effect causes tissue damage precisely at the points of contact with the radiation source. Y-radiation contributes to penetrating damage to the structure of body cells in the area of distribution. Neutron radiation may be heterogeneous in terms of its effect on cell structure, since its penetrating ability may also differ.
If you receive a radiation dose of 50-100 Gy, the nervous system will be damaged. This variant of the development of the disease will lead to death 4-8 days after irradiation.
If you gain 10-50 Gy of radiation, radiation sickness will manifest itself in the form of damage to the digestive system, resulting in rejection of the intestinal mucosa. Death in this situation occurs within 2 weeks.
Under the influence of a lower dose of 1 to 10 Gy, symptoms characteristic of the acute form normally appear, the main symptom of which is considered to be hematological syndrome. This condition is accompanied by bleeding and various infectious diseases.
Read in more detail about the causes and degrees of radiation sickness in this article.
Doses of dangerous radiation exposure
To prevent the occurrence of consequences that result from radiation, it is necessary to constantly monitor the background radiation and its level at work, in residential premises, in food and water. In order to assess the degree of possible damage to living organisms and the impact of radiation exposure on people, the following quantities are used:
- exposure dose. Exposure to ionizing gamma and x-ray radiation in the air. It has the designation kl/kg (pendant divided by kilogram);
- absorbed dose. The degree of influence of radiation on the physical and chemical properties of a substance. The value is expressed in a unit of measurement - gray (Gy). In this case, 1 C/kg = 3876 R;
- equivalent, biological dose. The penetrating effect on living organisms is measured in sieverts (Sv). 1 Sv = 100 rem = 100 R, 1 rem = 0.01 Sv;
- effective dose. The level of radiation damage, taking into account radiosensitivity, is determined using sievert (Sv) or rem (rem);
- group dose. Collective, total unit in Sv, rem.
Using these conditional indicators, you can easily determine the level and degree of danger to human health and life, select the appropriate treatment for radiation exposure and restore the functions of the body affected by radiation.
Acute form, its symptoms and signs
Most often, radiation sickness develops in the bone marrow form in several stages.
Let's consider the main symptoms characteristic of the first stage:
- General weakness;
- Vomit;
- Migraine;
- Drowsiness;
- Feeling of bitterness and dryness in the mouth.
When the radiation dosage is more than 10 Gy, the above symptoms may be accompanied by the following:
- Diarrhea;
- Arterial hypotension;
- Fever;
- Fainting state.
Against this background, the following may appear:
- Unnatural redness of the skin.
- Leukocytosis progressing to lymphopenia or leukopenia.
At the second stage, the overall clinical picture improves, but during diagnosis the following features can be observed:
- Unstability of heartbeat and blood pressure;
- Poor coordination of movements;
- Deterioration of reflexes;
- The EEG shows slow rhythms;
- Baldness occurs 2 weeks after receiving a dose of radiation;
- Leukopenia and other unnatural blood conditions may worsen.
In a situation where the dose of radiation received is 10 Gy, the first stage can immediately develop into the third.
The patient's condition at the third stage worsens significantly. In this case, the symptoms of the first stage can increase significantly. In addition to everything, you can observe the following processes:
- Bleeding in the central nervous system;
- Damage to the lining of organs in the gastrointestinal tract;
- Blood from the nose;
- Damage to the oral mucosa;
- Skin necrosis;
- Gastroenteritis;
- Stomatitis and pharyngitis may also develop.
The body lacks protection against infections, so the following may occur:
- Angina;
- Pneumonia;
- Abscess.
Dermatitis can develop in situations where the dose of radiation received is very high.
Iodine prophylaxis
It is necessary to take iodine before the body is exposed to radiation. And when a person falls into a risk zone, he needs to take medications where iodine is the active substance.
But, if it so happens that at the moment there are no drugs containing iodine, it is allowed to dilute iodine in milk and drink it as a medicine (1 drop of iodine is enough for 150 - 200 ml of milk). The effectiveness of this remedy is not so high, but many patients continue to take this drink, hoping for protection from radiation. It is best to give preference to the drug Eslial Forte. Its effectiveness has been proven by multiple positive patient reviews. Thanks to this remedy, it is possible to improve metabolism, increase the barrier function of the liver and detoxify the body.
Symptoms of the chronic form
If the form is chronic, all symptoms may appear a little slower. The main ones include:
- Neurological;
- Complications in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Problems with the digestive system;
- Hematological disorders.
With a mild degree, reversible changes appear in the body:
- General weakness;
- Deterioration in performance;
- Migraine;
- Sleep problems;
- Poor mental state;
- Appetite worsens all the time;
- Dyspeptic syndrome develops;
- Gastritis with impaired secretion.
Endocrine system disorders manifest themselves as follows:
- Libido worsens;
- Men experience impotence;
- In women it manifests itself as untimely menstruation.
Hematological abnormalities are unstable and do not have a specific severity.
The chronic form, to a mild degree, can proceed favorably and can be completely cured without any consequences in the future.
The average degree is characterized by vegetative-vascular anomalies and various asthenic formations.
Doctors also note:
- Dizziness;
- Emotional instability;
- Memory impairment;
- Periodic loss of consciousness.
In addition to this, the following trophic disorders are observed:
- Rotting nails;
- Dermatitis;
- Alopecia.
Sustained hypotension and tachycardia also develop.
Treatment of radiation sickness
After irradiation, it is necessary to provide the person with the following assistance:
- Remove his clothes completely;
- Wash in the shower as soon as possible;
- Conduct an examination of the mouth, nose and mucous membranes of the eyes;
- Next, it is necessary to perform a gastric lavage procedure and give the patient an antiemetic medication.
During treatment, it is necessary to carry out anti-shock therapy and give the patient the following medications:
- Eliminating problems in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- Promoting detoxification of the body;
- Sedatives.
The patient needs to take a medicine that blocks gastrointestinal damage.
To cope with the first phase of radiation sickness, you need to use antiemetics. Aminazine and atropine are recommended to be used when vomiting cannot be stopped. A saline drip should be given to the patient if he or she becomes dehydrated.
If the patient is severely ill, it is imperative to detoxify within the first three days after receiving the radiation dose.
All kinds of isolators are used to prevent the development of infections. The following is supplied to specially equipped premises:
- Fresh air;
- Necessary medications and devices;
- Products for patient care.
Visible mucous membranes must be treated with antiseptics. The work of the intestinal microflora is blocked by antibiotics with the addition of nystatin.
With the help of antibacterial agents it is possible to cope with the infection. Biological medications help fight bacteria. If the effect of antibiotics is not observed within two days, the medicine is replaced and the drug is prescribed taking into account the tests taken.
First aid algorithm
Poisoning by radioactive radiation is dangerous because it is impossible to isolate the damaging agent; it is only possible to neutralize the symptoms of the disease. The victim must be urgently placed in a sterile box to completely eliminate the additional effects of radiation on the body. The patient is transported only after his vital functions have stabilized.
It is allowed to remove a person from the lesion only if the heart rate and breathing are normal.
It is necessary to remove the victim’s clothing, it contains radiation particles, carry out sanitary treatment: wash the eyes, rinse the mouth, rinse the stomach and intestines, drink an absorbent (reduces the likelihood of repeated “infection” and poisoning). In case of internal exposure, it is necessary to immediately administer medications that neutralize the effects of radiation. At high doses of radiation, platelet and red blood cell transfusions are indicated to prevent the development of hemorrhagic shock and disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome. Emergency measures include antibiotic therapy with broad-spectrum drugs to prevent the addition of a bacterial infection.
Consequences of the disease
The prognosis for the development of radiation sickness in each specific case depends on the dose of radiation received. A favorable outcome can be expected if the patient manages to survive 12 weeks after receiving the radiation dose.
After irradiation without death, people are diagnosed with various complications, disorders, hematological malignancies, and oncological processes. Loss of reproductive function often occurs, and genetic abnormalities are often observed in the children born.
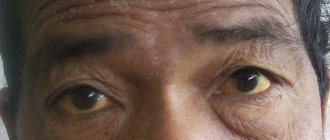
Often aggravated infectious diseases develop into a chronic form, and all sorts of infections of blood cells occur. After receiving a dose of radiation, people may experience problems with vision, the lens of the eye becomes cloudy, and the appearance of the vitreous body changes. So-called dystrophic processes can develop in the body.
To protect yourself as much as possible from possible diseases after radiation sickness, you need to contact specialized medical institutions in a timely manner. It must be remembered that radiation always hits the weakest points in the body.
Radioactive radiation
The concept of radiation refers to the propagation of radiation as waves and individual particles. There are three main types of radioactive radiation:
- Alpha rays, in which helium nuclei are observed;
- Beta rays are a stream of directed electrons;
- Gamma rays travel as high-energy photons.
The main properties of radioactive radiation are based on its energy, the type of particles emitted, as well as their carrying capacity.
Alpha radiation spreads in the form of many positively charged corpuscles and is stopped by air density or special clothing. Such radiation does not enter the body and is contained by the skin. However, through cuts, particles can still enter the circulatory system, which always negatively affects the condition of internal organs.
Beta rays have high power, the speed of electron flow is quite high, and their dimensions are negligible. For this reason, beta radiation enters the body unhindered and affects it at the cellular level. You can protect yourself from beta particles using an aluminum partition or wooden fence of a certain thickness.
Gamma radiation is a stream of high-power electromagnetic waves that can penetrate any material. To protect yourself from such radioactive radiation, you will have to use a thick concrete partition or sarcophagus-like structure, which is used in nuclear power plants. Lead or platinum is also used to protect against gamma rays.