Increased excitability of the nervous system
Everyone knows that our thoughts and fears have a strong impact on the body. Emotionality is especially increased in pregnant women. The closer the baby is due, the more nervous the expectant mother becomes. This could be fear of a meeting, of pain, of consequences, and many other fears. Many mothers are simply not psychologically prepared for this process, and it is precisely this state of the woman in labor that can become the reason for the rapid development of labor. Is it possible to prepare for this? Yes, you can. For this purpose, there are now many courses and trainings that will train not only the mother, but also her partner.
It all depends on the nervous system
There is an opinion that the higher a woman’s excitability, the faster her labor will go. There is some truth in this. If there are disorders of the nervous system, if the woman in labor is too worried and is not psychologically ready for the process of giving birth to a child, this can speed up the birth process. So you should mentally tune in to a favorable outcome of childbirth and not worry about trifles.
Doctors can also induce rapid labor, the consequences of which are not always predictable. It happens that contractions are sluggish and weak, and then a decision is made to stimulate them with the help of medications. But if you do not accurately calculate the dosage, then the birth of the fetus ahead of time is guaranteed.
Precursors of childbirth during the third pregnancy
A mother who is giving birth for the third time has enough experience not to miss the warning signs of an imminent birth. May be observed:
- lowering of the abdomen;
- false contractions;
- increased urination;
- an increase in the amount of clear discharge;
- pulling sensations in the back, groin area.
Unlike the first and second births, when the described symptoms are observed 2 weeks before delivery, the harbingers of the third birth come later, sometimes 2-5 days before the important moment. If such signs are detected, you should immediately go to the hospital so that rapid labor does not take the mother by surprise.
READ ALSO: rapid labor in multiparous women: consequences for the child
How to prevent
Actually, the answer to this question has already been stated above. If you are at risk for rapid delivery, then go to the hospital in advance. Perhaps the doctor will prescribe you medication to prevent rapid labor: antispasmodics that relax the uterine muscles (for example, No-shpu), drugs that improve uteroplacental blood circulation (Trental, Curantil).
Ask your mom how long labor took for her and her mom. Monitor your rest schedule, diet, and most importantly, your psycho-emotional state.
Ask your doctor to teach you what to do if labor suddenly progresses very quickly. Learn breathing and muscle relaxation techniques and look at everything positively. In the end, childbirth is the only way to the long-awaited meeting with the baby. May they pass safely and be happy!
Especially for beremennost.net - Elena Kichak
Don't be nervous and take care of yourself
None of the women of childbearing age who are expecting a child are immune from rapid labor. In many cases they can be predicted, but sometimes it happens that no external manifestations were observed before the contractions. There are general recommendations that will help minimize this risk. Here are the basic rules for all pregnant women:
- Get tested before conceiving a child. If it turns out that some diseases of the reproductive system were not cured before pregnancy, it is worth getting rid of them during the gestation period.
- Don't worry or be nervous. The nervous system should be normal, try not to conflict and avoid hysterics. Experience only positive emotions. Severe stress can seriously damage both your health and the health of your unborn baby.
- Avoid excessive physical activity and reduce your activity. For a pregnant woman, light exercise and short walks are enough. No weights, no dancing or active sports!
- Timely visits to the gynecologist. The doctor will be able to immediately recognize if the pregnancy has begun to proceed with disturbances. This will allow you to correct the process of bearing a child and help the mother’s body in the early stages.
How to prevent a speed scenario
In order to prevent or hinder something, you need to understand what you are dealing with. Timely detection of provoking factors will help predict rapid labor. If you experience anything from the list above, it is better to end up in the hospital before the obstetric due date. Don't forget that this is in your and your baby's interests.
Women at risk should take preventive psychological preparation for the process by trusting an experienced trainer or learning on their own methods of muscle relaxation and monitoring the tone of the uterine muscles
It is important to be in a balanced psycho-emotional state, to be categorically confident in a favorable result
During pregnancy, I advise you to attend courses for expectant mothers, where you will be informed about how physiological childbirth takes place and will be taught adequate behavior during this process so that you can rationally distribute forces and effectively connect energy capabilities for its successful completion. If future parents have any fears or worries about an upcoming event (for example, negative past experiences), during the courses they will be able to consult a psychologist. All together, this will contribute to the creation of a positive psycho-emotional background, and the pregnant woman will feel a surge of confidence.
Of the pharmacological agents for the prevention of excessively strong labor during pregnancy, antispasmodics that relax the muscles of the uterus are used, but only as prescribed by the attending physician!
Preventive measures to avoid rapid labor
Of course, having realized the danger of super-fast childbirth, a woman will want to know how to minimize their likelihood. Indeed, some measures will help avoid such a development:
- You need to ask your mother, grandmother, and sister in advance about how their birth proceeded. If there have been cases of super-rapid childbirth in the family (especially repeated ones), you should definitely inform your doctor about this. The gynecologist will probably advise you to go to the maternity hospital some time before the PDR.
- It is better to go to the maternity hospital in advance even if the previous birth was quite quick.
- The expectant mother must responsibly prepare for childbirth: read relevant literature, watch educational videos, it is advisable to attend special courses that provide practical skills (proper breathing, physical exercise, etc.).
- During the period of bearing a child, it is important to strictly follow medical recommendations and, if necessary, be treated in a hospital (for ICI, threat of miscarriage, gestosis, etc.).
- In the last trimester of pregnancy, significant physical activity and heavy lifting should be avoided.
- You must always monitor your diet, sleep and rest patterns, and most importantly, your psycho-emotional state (if necessary, visit a psychologist).
- If the expectant mother is at risk of increased contractility of the uterus, she is prescribed relaxing medications (for example, No-shpa).
It is advisable to attend courses for pregnant women, where a woman will be taught proper breathing, relaxation exercises, and psychologically prepared for childbirth
Possible complications during rapid labor
Rapid labor may occur without consequences, but complications for both the fetus and the mother cannot be ruled out. Excessively strong labor threatens the mother with the risk of placental abruption before the baby is born. This is due to the fact that the muscles of the uterus are almost constantly in a state of contraction, the uteroplacental vessels are compressed, and the blood circulation between the uterus and placenta is impaired. If the woman is not given medical assistance in time (and in this case, seconds count), then bleeding can lead to serious consequences. If, however, blood accumulates between the detached area of the placenta and the uterus, the uterus becomes filled with blood constantly flowing from the detachment area, the muscles of the uterus are “soaked” with this blood and lose the ability to contract, as a result of which the bleeding cannot be stopped. Such situations are fraught with removal of the uterus. For a baby, premature placental abruption can threaten acute hypoxia (lack of oxygen).
With rapid advancement through the birth canal, the fetal head does not have time to adjust and shrink due to the fact that the bones of the skull in the area of sutures and fontanelles (soft joints) are placed on top of each other, like tiles. Normally, the baby's sutures and fontanels are covered with connective tissue, which allows the baby's head to adapt to pass through the mother's pelvic bones. During rapid or rapid labor, the fetal head is subjected to rapid and strong compression, which can lead to injury and intracranial hemorrhage, and this, in turn, can cause various negative consequences: from reversible paresis and paralysis to fetal death.
The rapid movement of the child through the birth canal often causes quite serious injuries to the birth canal: deep ruptures of the cervix, vagina, and perineum.
Rapid emptying of the uterus can cause the muscles in the uterus to contract poorly after childbirth, which can cause postpartum bleeding.
Tactics for rapid labor
The danger of rapid labor lies in the fact that it can begin suddenly and take place outside the walls of the maternity hospital, that is, the woman may be left without qualified medical care, which poses a real danger to the mother and child.
If a woman in labor manages to be delivered to the maternity hospital with a cervical dilatation of 2 cm, but after a short period of time it suddenly dilates completely, doctors attempt to slow down labor by administering drugs aimed at relaxing the uterus.
If rapid labor is caused by excessive administration of medications into the body that stimulate contractions, they must be discontinued.
To prevent complications that often accompany rapid labor, mandatory monitoring of the condition of the woman in labor and the unborn child is carried out - heartbeat, frequency of contractions.
During contractions, the woman should be in a position on her side; active behavior during such childbirth is excluded. Her birth canal is constantly examined to provide timely assistance in case of threat of injury or rupture.
But despite the risk of complications, doctors give every woman in labor with rapid labor the opportunity to give birth naturally. Contraindications in this case are premature placental abruption with subsequent bleeding, weakness of the fetal cardiac activity, and therefore an emergency cesarean section is performed.
Why is rapid labor dangerous for a mother?
A faster birth is dangerous, first of all, for the mother. In rare cases, the rapid appearance of a baby leaves no consequences. So, let's look at the main risks associated with rapid childbirth:
- Severe bleeding associated with rupture of the uterus and cervix. In this case, childbirth ends with surgery. Sometimes it is not possible to save organs, which leads to infertility of the woman.
- Rupture of the perineum, if the genitals have not had time to prepare for the birth of the child, then the cervix and external organs suffer. This is probably the most “pleasant” consequence, since it only requires stitches and further care.
- Divergence of the pelvic bones.
- Placental abruption, accompanied by severe bleeding.
- Retained placenta, which requires cleaning after birth.
Severe bleeding poses a particular danger to a woman’s life. If timely assistance is not provided, the consequences can be very tragic.
Consequences of fast and rapid labor for the child and mother
A successful completion of an “accelerated” birth is possible, but consequences for the mother and child cannot be ruled out.
Threat to the patient:
- deep ruptures of soft tissues (damage to the cervix up to its separation, ruptures of the vaginal walls and perineum);
- symphysitis, rupture of the pubic symphysis;
- placental abruption, leading to massive bleeding, threatens the death of the woman in labor;
- disorder of fetoplacental blood flow leading to acute hypoxia;
- problems with separation of the placenta, causing retention of parts of the placenta in the uterus;
- hypotonic bleeding.
Dangers to the fetus:
hematomas of the subcutaneous fat layer and skin;- fractures of the collarbone, shoulder;
- cephalohematomas, intracranial hemorrhages;
- internal hemorrhages;
- hypoxic encephalopathy;
- spinal injuries;
- fetal asphyxia.
Carrying out labor under an accelerated program requires attention, professionalism and the ability to make immediate decisions from the obstetrician. If the doctor has the above qualities, it is quite possible that a healthy child will be born and the mother will not be injured.
Sozinova Anna Vladimirovna, obstetrician-gynecologist
6, total, today
( 42 votes, average: 4.67 out of 5)
Placental infarction: what the pathology threatens
Childbirth outside a hospital: what to do, first aid
Related Posts
How do they proceed?
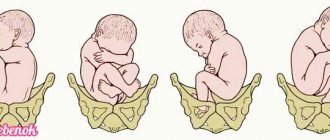
Any birth consists of three periods, which successively replace each other. In the first period, the cervix opens. When it expands to a maximum of 10-12 centimeters, the second period begins - pushing. During the pushing, the baby is born. In the third period, the placenta comes out.
With normal urgent (that is, occurring within normal terms) childbirth, the first period is the longest - contractions take approximately two-thirds of the total labor time. The intensity, strength and duration of contractions increases smoothly and gradually. The second period in normal childbirth also proceeds smoothly and ends with the birth of a child. Childbirth ends with the release of the remnants of the membranes and the “baby place”. The total duration of the three periods can be 10, 12, or more hours.
With a quick birth, the course options may be different. If the birth was spontaneous and was caused, presumably, by uterine factors (stretched cervix, weak muscles due to multiple births or for other reasons), then already in the first period the contractions intensify very quickly and are repeated after an hour and a half more than 3 times every five minutes of time.
Another unfavorable scenario is spastic labor. This is a rapid birth that occurs against the backdrop of increased contractions - within half an hour after the onset of labor, a woman can experience one contraction every 2 minutes. The contractions themselves are very painful, protracted, long, rest periods are minimal, the woman quickly gets tired, worries, and is nervous. Very often, blood pressure rises, heart rate increases, vomiting and nausea appear. The waters are usually poured out almost in full and ahead of schedule. The prognosis for the woman and child is less favorable.
During spastic labor, the placenta often detaches, bleeding develops, the child receives injuries to the head and cervical spine, and he has brain hemorrhages, which can have irreversible consequences in the future. The baby is usually born in just a couple of attempts.
There is another option for the development of events in the maternity hospital. It's called rapid birth. This is essentially a quick birth, which begins and in its first period proceeds as normal, uncomplicated, but the time balance between the first and second periods changes. That is, the attempts last less than normal and instead of one and a half to two hours they last only a few minutes. Most often, this occurs when the fetus has low body weight, its severe malnutrition, for example, against the background of a severe Rhesus conflict or chronic hypoxia, as well as in women with a wide pelvis.
Causes of fast and rapid labor
The following etiological factors of hyperdynamic uterine dysfunction are distinguished:
- Genetic predisposition. It consists of a congenital pathology of myocytes, which is accompanied by their increased excitability. As a result, only a small potential is needed to contract muscle cells. This feature is inherited through the maternal line and is taken into account when determining the risk group of pregnant women. Women whose sisters, mothers or aunts have had rapid labor in the past are at risk of developing this anomaly during their current pregnancy.
- High excitability. Emotionally unstable women, prone to depression, neuroses or anxiety, or not psychologically prepared for childbirth constitute a high-risk group for the development of hyperdynamic uterine dysfunction. Also, excessive nervous excitability is caused by hypertension, anemia, pathology of the heart and blood vessels, and infectious diseases.
- Endocrine and metabolic pathology. High production of thyroid hormones during thyrotoxicosis or increased production of norepinephrine and acetylcholine by the adrenal glands affect the state of the nervous system, ensuring its increased excitability, which is fraught with the development of hypertensive uterine dysfunction.
- Complicated anamnesis. What matters are endometritis, adnexitis, cycle disorders, various neoplasms of the internal genitalia, endometriosis, genital infantilism and abnormalities of the uterus. From the obstetric side, the presence of “accelerated” or prolonged labor in the past plays a role.
- The course of pregnancy. This group includes various complications of the gestation period: severe early toxicosis, gestosis, excess or lack of water, large fetus, abnormalities in the location of the placenta, post-term pregnancy, Rh-conflict pregnancy, kidney disease.
- Iatrogenesis. Inadequate labor stimulation (overdose or unreasonable prescription of contractile drugs).
- Discharge of water. “Acceleration” of labor can lead to rapid rupture of water during polyhydramnios (a sharp drop in intrauterine pressure, a decrease in its volume leads to irritation of the myometrium and its excessive contractions). Therefore, in case of polyhydramnios, an early amniotomy is performed, during which a careful opening of the amniotic sac is performed, and the speed of discharge of the waters is controlled by hand.
- Prolonged period of contractions. The prolonged course of contractions without moving the head along the pelvic planes irritates and compresses the cervix, which ends with the rapid movement of the baby and the rapid opening of the cervix.
Risk factors
Obstetricians place pregnant women at high risk for hypertensive uterine dysfunction if they have the following triggers:
parity (3 and more births);- ICN;
- wide pelvis;
- constant threat of interruption;
- low estimated weight of the child;
- age (under 18 and over 30);
- predisposition to nervous disorders;
- suffered premature birth.
Consequences
A rapid birth may occur without consequences for both the child and the mother, but the risk of its development remains high.
Maternal complications
- Damage to the soft tissue of the birth canal. Grade 3 - 4 ruptures of the cervix, vaginal walls and fornix, perineum, rupture of the cervix, as well as uterine rupture are accompanied by severe bleeding and threaten the woman’s life.
- Divergence of the symphysis pubis. It is characterized by severe pain and requires either surgery (osteosynthesis) or long-term (up to a month or more) stay in a fixed position (lying on your back with legs apart and bent at the knees).
- Premature placental abruption. An extremely dangerous complication for both the woman and the fetus. The birth ends with an emergency caesarean section.
- Violation of uteroplacental blood flow. Leads to the development of acute intrauterine hypoxia and also requires immediate delivery (caesarean section).
- Violation of placenta separation. It is accompanied by retention of placenta lobes and membranes in the uterus, provokes bleeding and requires manual control of the uterus.
- Hypotonic bleeding. Develops in the early postpartum period (the first 2 hours after the completion of labor). Uterotonics (oxytocin) are administered intravenously; if ineffective, manual control of the uterine cavity and massage of the uterus on the fist are performed.
Consequences for the child
- Injuries to the soft tissues of a child. Hemorrhages of varying intensity in the subcutaneous fat layer.
- Damage to the clavicle and humerus. Due to a violation of the biomechanism of childbirth, the fetus does not have time to complete turning after the birth of the head and the birth of the shoulders occurs in an oblique size, which is accompanied by fractures of the clavicle and humerus.
- Cephalohematomas. The rapid advancement of the fetal head disrupts the biomechanism of labor; the head does not have time to configure itself, which leads to hemorrhage under the periosteum of the cranial bones).
- Hemorrhages into internal organs. Massive hemorrhages in parenchymal organs (liver, kidneys and adrenal glands) are possible.
- Cerebrovascular accident. Due to spasm of cerebral vessels, blood circulation in the brain is disrupted, which leads to strokes and death of brain cells. Increased intracranial pressure also impairs blood flow in the brain. The listed factors can lead to the death of the child or his disability in the future.
- Spinal injuries.
- Acute hypoxia and birth of a fetus in asphyxia. Requires resuscitation measures. In the distant future of the child, it is possible that he will lag behind in neuropsychic and physical development.
How to give birth quickly
At an appointment at the clinic, a high-risk group of pregnant women for the development of hypertensive uterine dysfunction is identified and sent to the hospital 10–14 days before the expected due date. When rapid labor begins outside the maternity hospital, the pregnant woman is urgently hospitalized, and must be transported on a gurney until the patient is placed in the ward.
The tactics of conducting “accelerated” labor involve the following measures:
- Purgation. Performing a cleansing enema on a woman in labor with suspected rapid labor is contraindicated, although its administration is advisable in other situations in order to intensify contractions.
- Lying position. The patient is in a horizontal position throughout the entire period of contractions; she is forbidden to stand up or walk. The woman in labor is placed on her side opposite the baby’s position (relaxes contractions). The pushing period is carried out in the same position.
- Tocolysis. Tocolytic agents are infused intravenously, which reduce uterine contractile activity (partusiten, ritodrine, ginipral). The administration of tocolytics is contraindicated in the presence of asthma, liver, kidney, heart diseases, glaucoma, endocrine pathology, allergies to drugs, placental abruption. After reducing the frequency and strength of contractions, they switch to intravenous infusion of antispasmodics (no-spa, magnesium sulfate) and narcotic analgesics.
Important
If it is impossible to administer tocolytics, calcium antagonists (verapamil) are prescribed intravenously.
Epidural anesthesia. According to indications (excessively violent contractile uterine activity), EDA is performed (management of periods 1 and 2).- Normalization of fetoplacental blood flow. The following medications are prescribed: pentoxifylline, ATP, glucose with vitamin C.
- Introduction of cutting measures. It is carried out immediately after the birth of the baby (methylergometrine), which prevents the development of bleeding caused by impaired contractility of the uterus.
- Manual examination of the uterine cavity. It is carried out after the birth of the placenta, examination of the cervix and vagina to exclude retained placental lobules in the fetal sac.
note
Emergency caesarean section is indicated when placental abruption and intrauterine hypoxia occur.
Causes
Pathology is always associated with impaired uterine contraction. This happens for the following reasons:
- hereditary predisposition;
- excessive nervous excitability, tendency to neuroses, emotional instability of the psyche, unpreparedness for childbirth;
- metabolic disorders;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland or adrenal glands;
- toxicosis in early or late pregnancy;
- history of rapid labor;
- inflammation of the reproductive system;
- kidney disease;
- hypertension;
- short cervix or insufficiency;
- physiological features, for example, low fetal weight with a wide pelvis of the woman in labor.
Sometimes the rapid birth of a baby can be caused by the action of medications, for example, an overdose of stimulant drugs.
At risk are teenage girls, first-time pregnant women over the age of 30, as well as women with a history of more than 2 births.
Factors that provoke rapid labor
The immediate cause of ultra-fast labor is increased excitability of the muscles of the uterus, when at a certain moment it begins to contract rapidly with little effort. Many factors play a role in this:
- Heredity. If rapid labor was not uncommon in a pregnant woman’s family, then there is a high probability that her child will be born in the same way.
- Age of the expectant mother. The risk category includes pregnant women under 18 years of age and women who give birth for the first time after 30. In the first case, the reproductive system is not yet fully developed, in the second, abortions, chronic or cured diseases often already occur.
- Frequent childbirth (short intervals do not give the reproductive organs the opportunity to fully recover).
- Features of the nervous system. This is increased nervous excitability (tendency to hysteria, neurasthenia, adverse reaction of thyrotoxicosis). The cerebral cortex may not adequately regulate impulses coming from the uterus. Due to a violation of the feedback mechanism, oxytocin, adrenaline, and other substances that affect the contractility of the myometrium are intensively produced. Another important point is the pregnant woman’s psychological unpreparedness for childbirth.
- Gynecological pathologies. Ultra-fast childbirth can provoke even slight inflammation of the genital area (endometritis, adnexitis, etc.), as well as the absence of one fallopian tube, ovary, genital infantilism, shortened cervix, increased level of estrogen in the body.
The cause of accelerated labor may be gynecological pathology, for example, a short cervix - Pathologies of pregnancy. Frequent threats of interruption, gestosis (hence swelling, high blood pressure), polyhydramnios. This also includes breech presentation and large fetal weight.
A pathological pregnancy (for example, with gestosis) can result in rapid labor - Erroneous actions of medical staff. Sometimes a woman is unreasonably given too large a dose of a drug to stimulate labor (and perhaps it is not needed at all in a particular situation).
Regarding the last factor, I can give a specific example from life. My former work colleague Svetlana told me that when she started having contractions, her husband took her to the maternity hospital (there was a preliminary agreement with the doctor). The doctor gave the woman a pill (explaining that it stimulates labor) and told her to take a walk with her husband for an hour or two. But Svetlana intuitively felt that there was no need to drink anything. They simply drove for the indicated time, and when they arrived at the hospital again, labor itself had already begun to actively develop. It can be assumed that if the woman did take the drug, labor would have accelerated significantly and, possibly, would have become pathological.
Meanwhile, if a woman belongs to one of the listed categories, it is not at all necessary that she will certainly have a rapid labor (it is not for nothing that their percentage is so low). With a high degree of probability, this pregnancy outcome can be assumed if in the past the child was born very quickly.
However, here you need to take into account the provoking factor. After all, if, for example, the reason is the actions of health workers who unreasonably administered a drug that accelerates contractions, then next time you just need to prevent such a situation. Well, if it’s a matter of heredity or gynecological pathology, then you already need to prepare for such a development of the scenario and take measures in advance.
Features of the first birth
Very often you can hear the opinion that the first birth is always harder and more painful than subsequent ones. To some extent, it is true, but not in terms of pain, but rather because of the fear that a woman in labor experiences during her first birth. The lack of labor experience makes it difficult for a woman to choose a comfortable position during contractions; from time to time she forgets what she was taught in preparatory courses at the antenatal clinic. At such moments, some begin to panic. From the point of view of psychological readiness, women who have given birth before behave more disciplined in subsequent births.
The birth canal of a primigravida woman is narrower and less elastic. They are more difficult to stretch, and therefore even pushing feels different and lasts longer. The cervix also takes longer to open, and nothing can be done about this physiological aspect.
The first birth is often accompanied by complications. It cannot be said that during the second birth unforeseen difficulties will not arise, there are always chances, but it is first-time mothers who most often encounter such a phenomenon as primary or secondary weakness of labor forces, when contractions do not lead to dilatation of the cervix, and attempts do not move the baby forward . In first-time mothers, ruptures or tears of the perineum and cervix are more common.
Features of the rehabilitation period
As for the rehabilitation period, it depends on the presence of complications that arose during rapid labor. Of course, there are many cases when everything goes quite well (this largely depends on the correct actions of the medical staff). In such a situation, the mother and child spend the usual time in the maternity hospital and are then discharged.
If there have been injuries, ruptures, inflammation of the reproductive organs and other undesirable consequences, then the time of stay in the medical institution increases until the patient’s condition stabilizes. When problems arise in the baby, he is observed for some additional time, and if everything is serious enough, he is transferred to a children's hospital.
If the rapid birth went well, mother and baby are in the maternity hospital for the standard number of days
More on the topic “Rapid labor”:
Training contractions?
Rapid birth. If this is childbirth, then you will feel them...the contractions will become stronger. I honestly wouldn’t go anywhere :)) I would wait at home for the full start of the process.
Halle Berry commented for the first time on the rapid divorce
Just two weeks ago, 49-year-old actress Halle Berry was enjoying a happy family life - with her husband Olivier Martinez and their 3-year-old son Maceo. And suddenly - completely unexpectedly - the news broke about the couple’s divorce. Today, a few days later, Halle Berry commented for the first time on this sad event: “I’m doing well, I continue to live. And I try to visit different places: to take a break from soul-searching and switch to other things - this is the best medicine in any situation.” On the…
Keira Knightley: photos after childbirth and impressions of motherhood
30-year-old British actress Keira Knightley, while pregnant, participated in all the main winter and spring film ceremonies this year. At the end of May, according to the English press, Keira Knightley gave birth to a girl. The actress and her husband, musician James Righton, never made any public statement, so the date of birth and the name of the child were still unknown. Which, however, did not at all prevent young parents from enjoying their new life. Finally, Keira Knightley gave her first interview...
But if the first birth was rapid
Doctors can predict rapid labor even if a sufficient amount of time has passed from the first contraction to birth, i.e. Initially, labor may even be protracted.
To take or not to take your husband to the birth?
The presence of a loved one during childbirth is very important for the expectant mother. The staff of maternity hospitals do their job, of which there is a lot, and no matter how hard midwives, nurses and aides try, they do not know your weaknesses and fears
If you and your husband have a close and trusting relationship, and you think that your husband’s presence at the birth will help you get through this difficult period, talk to him in advance. It is possible that the husband will need time to get used to this idea. What can a husband...
when to go to RD?
rapid birth is hereditary. And the statistics that two from this conference gave birth in 1 hour does not mean anything at all) I think...
Questionnaire about third births.
1) At what week did the third birth begin??? 2) Is the birth weight of boys and girls different? 3) How did labor begin? During the day? At night?
Home birth Death of a child!
The birth began quickly, the waters broke, and the contractions were very strong from the very beginning. I couldn’t tell the difference between the beginning and the end at all.
Can labor start suddenly?
rapid childbirth is not so rare >. rapid labor is not such a rare thing (more than 1%, but I don’t remember exactly how much) And it often starts with one very strong...
Childbirth in 15 minutes
As far as I know, rapid labor is more likely if it is not the first. And every woman’s body is different - some warn, some don’t, but...
Is it true that the “speed” of childbirth conveys
They wrote on my chart that I was in rapid labor (I think so). I was generally doing well during my pregnancy (health, mood, and somehow it coincided...
Consequences
Usually such births end successfully, however, there is still an increased risk of complications. Let's look at them:
For a child
- Hypoxia (lack of oxygen) or asphyxia.
- Injuries of the spine and bones of varying severity. When moving quickly through the birth canal, the baby does not have time to position itself comfortably. Therefore, fractures of the humerus and collarbones are common consequences of rapid labor. In the worst case scenario, spinal injury may occur.
- Damage to soft tissues of varying severity.
- Poor blood circulation in the brain, vasospasm.
For mother
- Premature placental abruption. The constantly contracting muscles of the uterus do not have time to relax, as a result of which premature placental abruption may begin, which causes uterine bleeding, which is very dangerous not only for the mother, but also for her baby.
- Injuries of the birth canal. Often during rapid labor, ruptures of the vagina, perineum, and cervix occur. Uterine rupture is very dangerous, threatening a woman’s life.
- Divergence of the pelvic bones at the symphysis pubis. A very unpleasant and painful complication that requires long-term treatment (1-2 months).
- Poor uterine contraction after childbirth, incomplete expulsion of the placenta. These consequences entail postpartum hemorrhage.
How is rapid labor going?
If it has already become clear that the birth will be quick, there is no need to panic, but you should listen to the doctor’s instructions so that complications are minimal. Let's take a closer look at how rapid labor occurs.
First stage
- The uterine os expands. In first-born women, the opening of the pharynx occurs in 3 hours, in multiparous women - in 1 hour.
- Periodic contractions appear. At first, the pain appears in the upper abdomen, but after 3 hours it moves to the lower abdomen. Painful attacks are repeated after 7-8 minutes, lasting up to 20-25 minutes.
- The impact of contractions in the uterine cavity increases pressure, shortens the cervix, after which it quickly opens.
- Rapid labor is characterized by enormous force. Just before birth, contractions repeat with an interval of 2 minutes. At this stage of labor, hypoxia, placental abruption, death of the gestating fetus may occur, and problems with fetal-placental blood flow may occur.
Second phase
Upon successful completion of the first stage, the pushing stage begins.
- For first-time mothers, it takes no more than one hour; for women who have given birth before, it lasts about 15 minutes.
- The contraction occurs with attempts. By pushing we mean involuntary contractions of the uterine muscle layer. However, the woman in labor is able to somewhat hold them back or, on the contrary, strengthen them.
- Against the backdrop of contractions and pushing, the diaphragm lowers and the abdominal area tenses. The pressure in the uterus increases sharply.
- The fetus begins to move rapidly towards the exit. At this stage, the child may experience injuries, and the mother may experience ruptures.
Third stage
This postpartum stage is characterized by all the moments that are present during normal childbirth:
- The period lasts about half an hour.
- The placenta and placenta are separated.
Often, during rapid labor, bleeding can occur, which can even lead to death. But with the help of doctors, the situation is usually resolved successfully. In cases of rapid labor, a competent approach is always required. Medical practice confirms that childbirth can take place without problems for the child and mother if the pregnancy period proceeded without any complications. And yet, in such a complex birth, much depends on the experience of the doctor delivering the child.
Let's define the terms
The total number of births accounts for 0.8% of “expedited” births.
- What kind of birth is called rapid? If labor is “shortened” to 4 – 2 hours for first-time mothers and lasts 2 hours or less for multiparous women.
- Which ones are fast? If labor lasts 6 to 4 hours for firstborns and from 4 to 2 hours for multiparous women, it is called rapid.
Separately, they talk about “street childbirth,” when the labor process and subsequent birth of a child takes a woman by surprise (on the street or in transport). Moreover, this happens in a vertical position (the woman is either standing/sitting or actively moving.
This type of birth, and specifically its rapid completion, is a complete surprise for the woman due to the absence of contractions and pushing and any painful sensations. Both the woman’s inexperience (if the birth is the first) and the lack of resistance of the cervix (during normal childbirth, it performs the function of “constipation” and opens gradually, preventing the rapid passage of the fetus through the birth canal) cannot be ruled out. The cervix does not offer resistance in the case of isthmic-cervical insufficiency or in women with a history of multiple births.
Labor activity during rapid or rapid labor
Obstetricians-gynecologists distinguish the following options for rapid labor:
• “street” - pass very quickly and almost painlessly;
• rapid labor that occurred due to isthmic-cervical insufficiency of organic or functional origin. In this case, at one moment the amniotic labor ceases, and the child is born immediately;
• rapid movement of the child along the birth canal.
With normal or slow opening of the uterine pharynx, the fetus begins rapid movement along the birth canal, while the child does not have time to adapt to the planes of the pelvis. Often in such situations, the birth biomechanism is disrupted, which leads to ruptures of the birth canal. For a child, this risks cerebral, subdural or subarachnoid hemorrhages, and he may also experience hematomas and injuries. Rapid fetal movement may occur due to the pharmacological influence of oxytocin or PGF2α. This may also be a consequence of dysfunction of uterine contractions during the third rapid labor.
The main symptom of rapid labor is intense contractions that last 2-3 minutes, and the period between them is less than two minutes. In this case, the period of relaxation is so shortened that contractions overlap each other and uterine cramps occur. The pressure inside the uterus can exceed 200 mm Hg.
The woman in labor rushes about and screams in pain. She has increased sweating, high body temperature, nausea and vomiting, tachycardia, VSD, hypertension. All this indicates significant overexcitation of the symptomatic-adrenal systems. In severe cases, when the fetal head appears, a circular segment of the cervix may tear off. It is important to distinguish this pathology from placental abruption or uterine rupture.
The process of normal labor consists of three stages:
• period of cervical dilatation – begins with regular contractions every 3-4 minutes and gradually their intensity increases, and the cervix opens wider (up to 10-12 cm). The first stage takes up two-thirds of the entire duration of labor. At the end of the period, the intensity of contractions subsides slightly;
• the period of expulsion of the fetus (the period of pushing) - begins after the cervix of the uterus has fully opened. During this period, with each contraction, the child moves towards the exit. The woman in labor has a desire to push, which is associated with the pressure of the fetal head on the rectum. As the fetus slowly moves along the birth canal, it slowly stretches and is not damaged, and the child has time to adapt to the planes of the pelvis, which prevents injuries or hemorrhages;
• the succession period is the shortest stage of labor. At this time, the placenta and the remains of the umbilical cord (afterbirth) depart. This period is characterized by one contraction.
With rapid and rapid labor, the following options for the course of labor are possible:
1. All periods accelerate uniformly. Childbirth begins with the opening of the uterine pharynx, while the distensibility of the perineum, vagina and cervix is increased. The soft tissues of the birth canal practically do not resist contractions, which is why labor speeds up. This option mainly occurs in pregnant women with isthmic-cervical insufficiency or hyperestrogenism;
2. This option is characterized by frequent and painful contractions (with an interval of no more than 2 minutes). This can lead to damage to the birth canal. What are the dangers of rapid labor with such a course? They can be complicated by uterine bleeding, placental abruption prematurely, circulatory disorders in the placenta, fetal hypoxia during rapid labor. The child rapidly moves along the birth canal, which disrupts the biomechanisms of labor;
3. Childbirth in the first stage proceeds normally, but the second stage is significantly accelerated and takes up to 5 minutes. This type of birth is observed in multiparous women and in women in labor with a wide pelvis. Rapid labor can be relieved only with special drugs that belong to the group of tocolytics.
Of the above options, the fastest delivery in terms of time is the third.
Rapid birth - what are they like?
Conventionally, medical workers divide childbirth into three stages:
- period of contractions;
- birth of a child;
- birth of the placenta.
The average duration of labor is about 10 hours, but for some women it can last only six (in which case a rapid labor is said) or less than four hours (in which case a rapid labor is called). The duration of labor also differs between primiparous and multiparous women. In the latter, it is reduced, so rapid labor can take only 2 hours. Doctors believe that this is dangerous for both the mother and the unborn child, so they try to prevent such a rapid progression, calling the process pathological.
If there is a very short period of time between the first contractions and the birth of the baby, then this is a rapid birth
How long should labor last?
The duration of labor pains for each woman depends on a number of factors - what type of birth it is, whether there are hereditary diseases, what physical shape the woman is in, and so on.
Typically, labor lasts from 7 to 14 hours for those who give birth for the first time, and from 5 to 12 for multiparous women. Rapid labor is a labor process that lasts 3-6 hours for first-time mothers, and 2-4 hours for those who give birth for the second and subsequent times. If the time is even shorter, then such births are called pathological. Overall, rapid and precipitate labor accounts for approximately 0.8% of all cases.
Consequences for the newborn
But rapid labor is not only dangerous for the mother. The consequences for the child can also be very serious. Indeed, with normal obstetric care, when contractions increase gradually, and the mother’s body prepares for the birth of the child for the required time, the fetus takes the desired position inside the womb. He is not pushed out of the uterus, but smoothly emerges into the world.
Here are the dangers that can await a newborn in the event of rapid labor:
- Hypoxia. The fetus does not receive enough oxygen, and this can lead to impaired brain activity and disorders in the nervous system.
- Damage to bones in the shoulder girdle, fractures of the collarbone, and in extremely severe cases, the spine.
- Cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral vasospasm.
- Hemorrhage into internal organs.
- Damage to soft tissues - bruises, abrasions.
During a normal birth, the fetus gradually moves along the birth canal and also gradually prepares for the first breath. With rapid labor, asphyxia is possible. In this case, the newborn will require forced oxygen supply.
What it is
First you need to understand why the body is trying to suddenly “push out” the child. Natural childbirth can be complicated by the fact that contractile function in the uterus is disrupted. Initially, you need to prepare for the fact that the birth will be somewhat delayed:
- The cervix will dilate much more slowly than usual.
- The presenting part of the fetus, or rather the head or gluteal part, will be pressed tightly against the entrance to the pelvis for a long time, which is not a normal phenomenon.
- After some time, this part will begin to move very rapidly along the birth canal.
If we consider how long rapid labor lasts, then this period will be equated to generally accepted norms, but the process of the birth of the child itself is significantly accelerated. But in some cases, the period of contractions is also shortened. In such cases, rapid labor in first-time mothers takes place in just six hours, and in multiparous women in four hours.
View gallery
Complications
A quick birth can begin and end safely for the mother and baby, but it is possible that a rapid birth will have consequences for the child and his mother. For example, for a woman this may result in placental abruption beginning even before the baby is born. Why is this happening? Because the uterine muscles practically do not come out of the state of contraction, and also the blood circulation between the placenta and the uterus is severely disrupted, the vessels are pinched.
In such a situation, a woman in labor needs immediate medical attention, and, as we already know, here the count is not even in minutes, but in seconds. Lack of timely medical care can result in severe bleeding, which will lead to even more serious consequences. Even more serious developments are possible. When bleeding begins, blood may pool between the uterus and the area of the placenta that has detached. Thus, the muscles of the uterus are saturated with blood, which accumulates in it, and cannot contract. In such cases, it is almost impossible to stop the bleeding. In most cases, such complications end with doctors being forced to simply remove the uterus. But this is about the mother. But a child with premature placental abruption is at risk of hypoxia, which translated into more understandable language means a lack of oxygen.
Why is rapid labor dangerous for a baby? For a child, rapid progress through the birth canal may also not end in the best way. After all, when it moves, the head must configure, or rather decrease. At this moment, the bones of the skull seem to fold to fit in the neck, and during rapid labor they do not have time to do this naturally and they are compressed. At best, there will be deformation of the skull, which in most cases ends in alignment. But it is also possible that hemorrhage will begin inside the skull, and this will already lead to paresis and paralysis and, in the worst case, even the death of the fetus.
During rapid progress, the mother may experience various ruptures not only in the cervix, but also in the vagina and even the perineum. All this can be sewn up, but the procedure is not the most pleasant, especially for a woman who has already experienced childbirth. There are also cases of postpartum hemorrhage. This occurs due to the fact that the uterine muscles contract very poorly after this type of birth. As we can see, fast and rapid labor has an impact on the fetus and the woman in labor.
Norms for the duration of labor
The normal duration of labor for primiparous women is approximately 7–14 hours. At the birth of subsequent children, this period is reduced to 5–12 hours (this is due to the fact that the reproductive organs are more prepared for the important process).
Labor, which lasts slightly less than the specified norms, is considered rapid (however, it still lasts more than 4 hours, with repeated births - more than 2 hours). In obstetrics, labor that takes up to 4 hours (for multiparous women less than 2 hours) is classified as rapid. According to statistics, they are observed in 0.8% of women.
It is interesting that some doctors do not strictly differentiate the concepts of “quick” and “rapid” labor, and sometimes simply use them as synonyms. Thus, there is a definition that the first lasts 4–5 hours, and the second lasts within 3 hours (meaning first-time women). Thus, it is not entirely clear what category to include a birth that takes, for example, 3.5 hours.
Rapid labor goes beyond the norm (it is pathological in nature), since it is a consequence of disorders that affect the contractility of the muscular uterine layer. The organ immediately begins to contract too often and actively, in some cases even developing a continuous spasm of the myometrium (or tetanus of the uterus). As a result, the cervix opens too quickly, and the fetus quickly overcomes the birth canal and is born.
Meanwhile, normal contractions are repeated after a certain period of time, at first it is quite long (20 minutes). Then the interval gradually shortens, and the force of tension in the muscles of the uterus increases. And these periods of time are very important: the woman in labor has the opportunity to rest, gain strength, and her uterus relaxes.
The interval between contractions is very important - it allows the woman in labor to rest and gain strength.
When in the next period (pushing) the baby gradually moves along the birth canal, he avoids injury, stress, and has enough time to prepare for his first breath.
In a normal birth, the baby moves through the birth canal gradually, avoiding injury and stress.
Ultra-fast childbirth can occur in two scenarios:
- All stages of labor are accelerated evenly.
- The first period passes normally, only the second stage is significantly accelerated (maybe only 1-2 attempts) - up to 5 minutes. This often occurs in multiparous women with a wide pelvis.
Although many pregnant women wish in their hearts that their birth would be very quick (they would have to suffer less), you need to realize that the pain that accompanies this process is compatible with life and is simply necessary for the natural physiological course of the process.