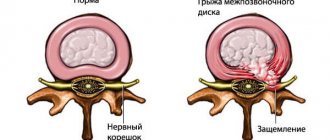
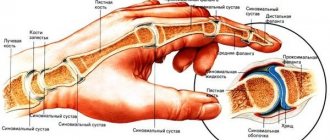
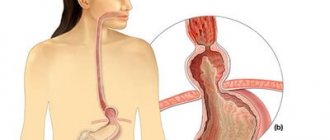
Osteophytes of the spine are growths of bone tissue, shaped like spikes or hooks. Changes in the structure of the intervertebral space cannot be completely cured, so preventive measures should be taken at a young age.
- Conservative methods
We suggest you spend 7-10 minutes of your free time reading the article to find out how to prevent the formation of osteophytes.
How are osteophytes formed?
Healthy vertebrae are located at a certain distance from each other, but with the development of degenerative processes, these gaps decrease and the space is filled with pathological neoplasms. As a result, the edges of the spine are modified, acquiring a hook-shaped and spiky shape.
Osteophytes are divided into the following types:
- Posterior - develop on the posterior parts of the spine, causing noticeable pain.
- Anterolateral - grow on the vertebrae that are most subject to pressure.
- Anterior - formed on the anterior parts of the spine, causing virtually no noticeable discomfort.
- Posterolateral - osteophytes, which are most often found in the cervical spine. They are dangerous because they can damage the spinal cord.
Depending on the shape, structure, and cause of occurrence, the following osteophytes are distinguished:
- Post-traumatic – occur as a result of bruises or fractures.
- Degenerative-dystrophic - develop as a result of a pathological process and pose a serious health hazard because they limit the mobility of the spine.
- Periosteal - processes that appear after inflammation of the periosteum.
- Massive - growths that form as a result of bone tumors.
Causes and provoking factors of osteophyte
Before starting treatment for osteophytosis, you should understand what it is and what the causes of this disease are. The reasons for the formation of osteophytes can be:
Excessive physical stress on the body.
Overload of cartilage and bone tissue leads to its destruction and the formation of bone growths - osteophytes - at the sites of damage.
Various injuries (mainly fractures).
A bone callus forms at the fracture site, which is eventually replaced by osteoid tissue. During the healing process, osteophytes may form around the osteoid. In the presence of additional factors that complicate the process of bone tissue regeneration during a fracture, osteophytosis is difficult to treat. These factors include inflammation of bone tissue.
Sedentary lifestyle.
A sedentary lifestyle and prolonged stay in one position lead to overload and subsequent destruction of the cartilage tissue of the joints. Being under constant load, bone tissue begins to grow and form osteophytes.
Also, staying in an uncomfortable and forced position for a long time leads to the occurrence of disorders such as spondylosis and osteoarthritis.
Metabolic disorders in the body.
With metabolic disorders in the body, as well as with insufficient nutrition, a lack of a group of vitamins and minerals develops, among which calcium occupies an important place for the formation, regeneration and normal development. It is its lack that can lead to bone damage and further development of osteophytosis.
Pathological processes in bone tissue.
Pathological processes of bone tissue that provoke the occurrence of osteophytes include spondylosis and osteoarthritis.
Spondylosis is a disease accompanied by deformation of the vertebrae of the spine. Spondylosis is characterized by thinning and degeneration of vertebral tissue, resulting in osteophytes.
Osteoarthritis is accompanied by the structural breakdown of elements of cartilage tissue and the further formation of bone growths.
Inflammation of bone tissue.
Inflammation of bone tissue occurs when a bacterial infection enters the bone body. There are two ways of infection of bone tissue:
- specific - the infection originates in the body itself. The source of infection can be gonorrhea , syphilis , tuberculosis , brucellosis, etc.;
- nonspecific - bacteria enter the body from the outside, that is, during open fractures, severe bruises and surgery.
Due to the development of a bacterial infection in the bone body, various inflammations arise, the general name of which is osteitis.
Treatment of osteitis depends on the advanced stage of the disease and the presence of complications. The healing process is often accompanied by the formation of osteophytes, due to the separation of the periosteum from the bone body.
Benign and malignant tumors.
Tumor diseases of bones lead to the formation of massive osteophytes. This occurs during the destruction and subsequent regeneration of bone. These diseases include the following:
- osteogenic sarcoma (malignant tumor disease that affects bone tissue);
- Ewing's sarcoma (tumor of the bone skeleton);
- osteochondroma (benign bone tumor of cartilaginous nature).
Metastases from prostate and breast cancer also lead to the formation of growths on bone tissue.
Diseases of the endocrine system.
During some diseases of the endocrine glands, serious changes occur in the skeletal system, which lead to the formation of osteophytes. Such diseases include acromegaly, a pathology caused by excessive production of growth hormone.
Also, hormonal imbalances leading to the development of osteophytosis include diabetes mellitus.
Causes
Like all diseases, pathologies of the spine are rapidly becoming younger. Previously, osteophytes were diagnosed mainly in people over 55 years of age. Today, bone spurs are also found in younger people.
Causes of osteophytes:
- A history of infectious diseases of the joints or spine - arthrosis, arthritis, osteoarthritis.
- Regular loads on the spine.
- Wrong lifestyle, wearing uncomfortable shoes.
- Various spinal deformities - kyphosis, scoliosis, lordosis.
- Excess body weight, which increases stress on the back.
- Genetic factor - if many members of your family began to be bothered by spinal diseases at a young age, you need to be very attentive to your health.
- Injuries of various parts of the spine.
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system.
What causes osteophytes?
Bone growths form due to metabolic disorders. Provoking factors are:
- inflammatory processes in the joints;
- fractures and bruises of the feet;
- degenerative changes;
- oncological diseases;
- prolonged high loads on the lower limbs;
- obesity;
- longitudinal flatfoot.
Osteophytes of the calcaneus can be either single or multiple. Their shape is also different: the growth can be a thorn, a tooth, or a massive growth. The following types of heel spurs are distinguished:
- compact;
- osteocartilaginous;
- spongy;
- metaplastic.
Osteophytes are also classified based on their formation:
- Degenerative - dystrophic ones appear when the blood supply and nutrition of the joint are disrupted.
- Post-traumatic are the consequences of a bruise, fracture or dislocation. Malignant neoplasms contribute to the formation of tumor cells.
- Endocrine occurs against the background of hormonal disorders.
- Neurogenic are considered the result of damage to the central or peripheral nervous system.
Most often, osteophytes are formed in diseases such as arthritis and arthrosis. Permanent damage to the tendon contributes to the development of a persistent inflammatory process.
Symptoms
Symptoms of osteophyte development differ depending on which part of the spine is affected.
Thoracic region
The vertebrae in the thoracic region are characterized by low mobility, so the appearance of osteophytes in most cases is asymptomatic. Most often, the disease manifests itself in severe form, when marginal osteophytes of the vertebral bodies have already formed. Thoracic spondylosis has similar symptoms to intervertebral herniation, which sometimes makes it difficult to make a correct diagnosis.
Cervical region
The cervical spine, due to its special structure, is very susceptible to any disturbances occurring in the structure of the spine. When osteophytes appear, damage to the nerve roots and displacement of the discs are observed, which entails further compression of the vessels. As a result, the following symptoms appear:
- Dizziness, severe headaches, which are most often localized in the back of the head.
- Loss of coordination of movements, tinnitus.
- Painful sensations when turning the head, especially sharp ones.
- Visual impairment.
In some cases, pain due to osteophytes in the cervical spine becomes so unbearable that a person experiences vomiting and severe weakness. This is a very dangerous symptom, indicating that you should immediately consult a doctor.
Lumbar
The lumbar region is a part of the skeleton that experiences regular stress, so the symptoms of osteophyotes are pronounced here.
The patient begins to worry:
- Aching pain in the lower spine, aggravated by prolonged walking or staying in one position;
- Feeling of tingling and numbness in the upper and lower extremities;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract or bladder are symptoms that appear much less frequently than those listed above.
You can find out more detailed information about the disease from this video:
Symptoms of the disease
At first, it is difficult to recognize osteophytes of the hip joint or patella, since the disease can be asymptomatic. First, general signs of the disease appear, and then local ones. The patient may confuse them with other diseases, so if at least one of these factors occurs, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination. Symptoms of the presence of osteophyte in a joint include:
A developing pathology can be suspected by the appearance of swelling in the joint.
- pain in the area where the growth occurs;
- impaired joint mobility;
- the appearance of a “crunch” when turning the joint;
- the appearance of swelling.
Marginal osteophytes themselves are not dangerous if they do not cause pain and do not lead to a deterioration in the quality of life. They are treated with topical remedies and tablets. But as they grow, they can injure surrounding tissues and pinch nerves. In case of injuries, fractures and diseases of the musculoskeletal system, osteophytes occur in only one joint, usually on the right. During infection and inflammation, they appear on many bones and joints. This phenomenon is called osteophytosis.
Diagnostics
When you first contact a specialist, the examination is carried out using palpation. The presence of osteophytes can be determined without additional research only in advanced stages. In other cases, additional examinations will be required:
- Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to obtain the most detailed picture of the condition of bone tissue, spinal cord, and nerve roots in various parts of the spine.
- X-ray examination is one of the most accessible methods for diagnosing pathologies of internal organs using X-rays.
- Electroneurography is necessary to study damage and conduction of nerve fibers. This procedure is contraindicated for patients with epilepsy, high blood pressure, and diseases of the cardiovascular system.
What it is?
An osteophyte is the growth of bone tissue at a joint. The growths can be isolated on one joint or spread throughout the entire limb or body. Osteophytes take different shapes, most often they are bone formations in the form of a hook or spike of varying thickness. Localized mainly on the following parts of the body:
- ribs;
- spine;
- elbow;
- hips;
- fingers;
- feet;
- knees;
- neck;
- small of the back.
In the absence of synovial lubrication, the joints begin to rub against each other, and ossification occurs in the places of their contact, and a growth of bone tissue appears. The appearance of osteophytes at the corners of the bone and joints stops their destruction, but at the same time, pinching of the nerve roots can occur in the process on the tibia, and then every movement of the joint will bring pain to the person.
Treatment
Osteophytes are bone growths that cannot be gotten rid of even with the best treatment. But by following all the doctor’s prescriptions and recommendations, you can maintain a decent lifestyle for many years.
Conservative methods
To relieve pain and improve motor activity with osteophytes, the patient is prescribed drug treatment using tablets. In cases of severe inflammation, epidural steroid injections are prescribed.
Do not take medications based on the advice of friends or recommendations on the Internet. Each case is individual and often the appearance of osteophytes develops along with other pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. Self-medication will only worsen the situation and reduce the chances of a favorable outcome. You should also be careful when using traditional medicine, the effectiveness of which is highly questionable.
In case of acute pain, the patient is prescribed bed rest, and any physical activity is prohibited. You can begin auxiliary treatment methods only after complete relief of the pain syndrome. To maintain the patient’s immunity, complexes with a high content of vitamin B, phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium are recommended.
Pathogenesis of Haglund's deformity
During constant friction of the Achilles tendon, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bursa begins. This chronic multi-month impact is transmitted to the posterior calcaneal tubercle and pathological cartilage slowly begins to form, changed, often with sharp spines. This can even be seen on an x-ray. The formation of this cartilage occurs due to the body’s protective reaction.
The pressure on the bursa and Achilles tendon increases even more, which increases inflammation, pain and swelling. Inflammation of the mucous bursa and Achilles tendon without bone deformation is called achillobursitis (posterior calcaneal bursitis). Typically, bursitis precedes Haglund's deformity.
Patients do not pay much attention to the “bump,” thinking that it is a callus until it hurts. And as a rule, this condition is quite difficult to treat conservatively. This is why it is so important to see an orthopedist in the early stages of Haglund's disease.
Physiotherapy
A set of special exercises for osteophytes will help normalize motor activity and strengthen the muscular system. You can attend special group training sessions or conduct classes at home. But initially, a specialist must show and set the correct technique for performing the exercises, otherwise exercise therapy can cause even greater harm to health.
Physical therapy, like other physical activities, is contraindicated in the acute stage of the disease. All exercises should be performed slowly, increasing the number of repetitions gradually as the muscular system strengthens.
Manual therapy
A competent specialist in just one course of treatment will help get rid of pain in damaged vertebrae, normalize blood circulation and relieve muscle tension caused by the appearance of osteophytes. But such a result is only possible if the correct technique is performed, so you should be especially careful when choosing a specialist. Often people who have completed short-term courses and, therefore, have absolutely no understanding of the structure of the spine, call themselves chiropractors. Don't forget that your health is at stake, so don't hesitate to ask about having a medical school diploma.
Massage
Specialists will often include a massage course in a comprehensive treatment program for osteophytes in order to relieve excess tension, eliminate pain and inflammation. To achieve a good result, you will need to undergo at least 10-12 procedures.
Physiotherapy
In modern physiotherapy offices, patients who have osteophytes are offered two effective procedures:
- HILT therapy is a technique based on the use of a pulsating impulse that blocks pain. High-intensity laser therapy can speed up the tissue healing process, reduce swelling and inflammation in the area of osteophyte development. The procedure is contraindicated for pregnant women and people suffering from epilepsy.
- UVT therapy is treatment using acoustic waves. About 90% of patients with osteophytes, after completing a full course of physiotherapeutic procedures, report a noticeable improvement in their well-being. SWT therapy is not performed in the presence of a pacemaker and diseases associated with blood clotting disorders, pregnant women, and persons under 23 years of age.
Hirudotherapy
Treatment with leeches is the most unconventional method of getting rid of discomfort and swelling when osteophytes appear. Used in combination with drug therapy, exercise therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Surgery
If all of the above methods are ineffective and the patient’s well-being does not improve, the only way to return to normal life is surgical intervention. But surgery to remove osteophytes is effective only if the nerve roots have been compressed for a short time. When the pathology has already progressed, the pain syndrome will remain even after removal of bone growths.
Prevention
Spinal osteophytes cannot be completely and irreversibly removed, but their development can be prevented. To do this you need to follow a few simple rules:
- Be active - this is especially true for those who spend a lot of time at the computer, in one position, or simply lead a sedentary lifestyle. If you have a sedentary job, then once an hour you need to get up and do exercises aimed at strengthening the cervical and lumbar spine. Twice a year it is recommended to undergo preventive massage sessions, which will prevent not only the appearance of osteophytes, but other pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
- Eat right - make sure that your diet has enough calcium and proteins, which not only have a beneficial effect on the condition of the muscular and skeletal system, but also strengthen the body’s protective properties.
- Giving up bad habits is a point that can be safely recommended for the prevention of absolutely all diseases. Addictions weaken the immune system and the body, like a magnet, attracts various pathologies.
- Wear the right shoes - this point especially applies to women who spend a lot of time in uncomfortable heels that squeeze their feet.
- Watch your posture - if you notice that it is difficult for you to keep your back straight, you get tired quickly and begin to slouch, wear orthopedic corsets. Special purpose products are not intended for regular use. Initially, you need to wear the corset for 15-20 minutes a day, gradually increasing the wearing time to several hours a day. To experience minimal discomfort, choose a model in your size.
- Exercising regularly - just a few hours a week allocated to physical activity will help you strengthen the muscle corset in all parts of the spine. You don't have to spend a lot of time in the gym. Simple exercises for the prevention of back diseases can be performed at home. Even regular walking is useful for the prevention of osteophytes, so don’t be lazy to walk a couple of bus stops every day. Swimming is also beneficial for the health of the spine - a sport that has a minimum of contraindications at any age.
- Properly arrange your sleeping area - avoid a pillow that is too high, and if possible, purchase an orthopedic mattress. The sleeping area should not be too soft.