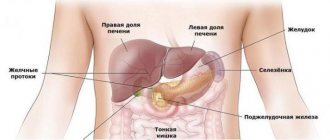
One of the most important trace elements in the human body is iodine. The body contains about 25 mg of this trace element, 15 mg of which is in the thyroid gland, the rest are distributed in the kidneys, liver, prostate gland, ovaries, skin, nails and hair.
The daily iodine requirement is 50-200 mcg. It participates in the formation of thyroid hormones, which are responsible for the development and growth of the body, the efficiency of metabolic processes, and heat production. Athletes value iodine for supporting the function of the thyroid gland, which contains hormones such as thyroxine and triiodothyronine - they are responsible for increasing the intensity of training, metabolism and reducing the percentage of body fat.
How much iodine does a person need per day?
Hormones produced by the thyroid gland are directly involved in the development of cells of the central nervous system, as well as skin and hair, so pregnant and lactating women should receive the maximum dose of iodine. For them, the daily dose is about 210 mcg per day. For an adult, 150 mcg of iodine is enough .
Children under two years of age need to be provided with at least 50 mcg of iodine. From two to six years, this dose should double. Well, schoolchildren need approximately 120 mcg of iodine per day.
Properties of iodine
When we all use the word “iodine,” we mentally remember a small bottle of brown liquid. But in fact, iodine is a solid substance. It looks like dark purple (sometimes black-gray) crystals that shine like metal in the light. Its smell is quite specific. When heated, violet vapor is released, which when cooled again turns into crystals.
To obtain the familiar liquid in bottles sold in pharmacies, iodine must be heated under pressure.
What foods contain iodine?
The most iodine is found in seafood . It is known that the inhabitants of the sea elements are able to accumulate iodine from salt water. In particular, just 150 grams of seaweed, or kelp, can provide the daily dose of iodine that an adult needs. Fucus contains a fairly large amount of iodine, but in our country it is quite difficult to find this algae in stores.
Cod liver is quite rich in iodine. Just 100 grams of this product contains about 350 mcg of iodine. Raw sea fish, such as flounder, halibut or herring, contain 100 to 200 mcg of this valuable micronutrient. Approximately the same amount of iodine is contained in 100 grams of squid, mussels, oysters and shrimp.
It should be remembered that iodine is a rather unstable compound that can volatilize during heat treatment. Therefore, it is advisable to consume seafood not fried: it is recommended to stew or boil them.
You cannot exclude cheeses and shelf products from your diet, which contain about 11 mcg of iodine per 100 grams of weight. Approximately 7 mcg of iodine is found in potatoes, carrots, tomatoes and sorrel.
Persimmons, strawberries, lemons and grapes contain no more than 5 mcg of iodine per 100 grams of weight. Therefore, nutritionists recommend purchasing fruits and vegetables that are grown in soils enriched with iodine.
We must not forget about such a valuable food product as chicken eggs. One egg contains not only proteins and fats that are valuable for the body, but also approximately 12 mcg of iodine.
Many people try to compensate for iodine deficiency in their diet by consuming special iodized salt. Just two grams of this salt can completely replenish the daily volume of this valuable microelement. Iodized salt was invented in America, where at the beginning of the last century there was a significant increase in the number of children born with cretinism (a severe form of mental retardation). Children with mental retardation were born in places where the soil, and therefore food, was not rich enough in iodine.
It is important to remember that iodized salt will only be effective if you add salt to your food after cooking. Otherwise, the iodine will evaporate during heat treatment.
Lack of iodine in the body and the causes of its occurrence
Almost two billion people on our planet suffer from iodine deficiency. A deficiency occurs when a micronutrient is consumed less than the daily requirement, that is, less than 0.05 mg.
According to research, the need for iodine increases with physical activity.
Subscribe to our INSTAGRAM account!
The human body is not able to produce iodine itself, so its balance constantly needs to be replenished with the help of external sources. They can be not only food, but also the atmosphere, air and water.
For example, people living far from the sea have lower blood levels of the microelement than those who daily inhale iodine-rich sea air.
Lack of iodine and excess weight
Hormones produced by the thyroid gland take part in a number of metabolic processes, in particular, in the breakdown and accumulation of fats and carbohydrates. If there is a lack of iodine in the diet, the thyroid gland changes its operating mode. In the process of evolution, a special mechanism has been developed: if the body is in danger in the form of a lack of food, the endocrine system begins to “work” to create reserves. As a result, fat deposits are formed, which often becomes the cause of obesity. At the same time, the production of growth hormones decreases: all metabolic processes in the body slow down in order to “wait out” the difficult period. This also affects the functioning of the nervous system: a person becomes inhibited, his memory deteriorates and his ability to concentrate decreases.
Iodine
Name:
Iodine
Name: Iodine (lodum) Indications for use: Iodine preparations are used externally and internally;
externally used as antiseptic (disinfectant), irritating and distracting agents for inflammatory and other diseases of the skin and mucous membranes, internally - for atherosclerosis, chronic inflammatory processes in the respiratory tract, for tertiary syphilis, hyperthyroidism (thyroid disease), for the prevention and treatment of endemic goiter (thyroid disease due to low iodine content in water), with chronic mercury and lead poisoning. Pharmacological action: Has an antimicrobial effect; participating in the synthesis of thyroxine, it affects the function of the thyroid gland, enhances the processes of dissimilation (the breakdown of complex organic substances into simpler ones), and has a beneficial effect on lipid and protein metabolism.
Iodine method of application and dose: Externally in the form of a 5% and 10% alcohol solution as an antiseptic (disinfectant), irritant and distracting agent. Orally, 0.02 g per dose for atherosclerosis, chronic inflammatory processes in the respiratory tract, tertiary syphilis, hyperthyroidism (thyroid disease), endemic goiter, chronic mercury and lead poisoning.
Iodine contraindications: When taken orally: pulmonary tuberculosis, nephritis (inflammation of the kidney), furunculosis (multiple purulent inflammation of the skin), acne, chronic pyoderma (purulent inflammation of the skin), hemorrhagic diathesis (high bleeding), urticaria, pregnancy, high sensitivity to iodine .
Iodine side effects: Possible phenomena of iodism (non-infectious inflammation of the mucous membranes in places where iodine is released during an overdose) or individual intolerance to iodine products - runny nose, urticaria, etc.
Release form: Crystalline iodine; 5% alcohol solution in bottles and ampoules of 1 ml in a pack of 10 pcs.
Iodine composition: Obtained from seaweed ash and oil drilling waters. Grayish-black plates or clusters of crystals with a metallic sheen with a characteristic odor. Volatile at ordinary temperatures; when heated, it sublimes, forming violet vapors. Very slightly soluble in water (1:5000), soluble in 10 parts of 95% alcohol, soluble in aqueous solutions of iodides (potassium and sodium). Incompatible with essential oils, ammonia solutions, white sedimentary mercury (an explosive mixture is formed).
Storage conditions: In a place protected from light.
Attention! Before using the drug "Iodine", you should consult your doctor. The instructions are provided solely for familiarization with “ Yod ”.
Group affiliation:
- Medicines that primarily affect tissue metabolic processes
- Medicines containing iodine
Why is iodine deficiency dangerous?
If the body does not receive the required amount of iodine for a long time, the following symptoms are observed:
- the thyroid gland increases in size (goiter develops);
- the functioning of the endocrine system suffers;
- children experience delays in both physical and intellectual development;
- drowsiness, constant feeling of fatigue, lack of energy;
- deaf-mute;
- disorders of the reproductive system: impotence, infertility, fetal development abnormalities, etc.
A lack of iodine in the diet may also cause problems with the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
Symptoms of iodine deficiency
If there is insufficient intake of iodine in the body, the thyroid gland is not able to produce the required amount of hormones. This condition is called hypothyroidism. This is a serious disease that is quite difficult to recognize.
Let's look at its main features:
- A slowdown in metabolism and energy processes leads to a person becoming overweight.
- Due to lack of energy, a person experiences weakness. Work that was previously easy to cope with is given with great difficulty.
- Even after resting all day, a person experiences unusual fatigue.
- If you notice a lot of hair falling out on the comb while combing, then think about the reason for this loss. In hypothyroidism, hair follicles cannot regenerate due to a lack of hormones.
- This factor also leads to dry skin, since skin cells do not have the opportunity to regenerate, and a lot of dead cells accumulate.
- You already know that the benefits of iodine for the body are expressed in proper energy and heat exchange. When there is a lack of hormones, the system fails, causing a person to begin to feel chilly, often freezing even in a warm room.
- A lack of iodine slows down the heartbeat, which is accompanied by headaches and frequent dizziness, and low blood pressure.
- A lack of iodine also affects the tendency to learn and remember.
- In women, hypothyroidism is accompanied by menstrual irregularities. The discharge can be either abundant or, conversely, scanty.
- In pregnant women, such a deficiency can lead to the birth of a defective child or even a miscarriage.
- The only obvious sign that patients usually immediately notice is an increase in the volume of the neck. Endemic goiter appears, affecting mostly women (about 20% of the country's population). This is explained simply, the thyroid gland tries to produce the required number of hormones, for this its tissue grows to compensate for the low amount of production.
Do I need to take iodine-containing medications?
Only a doctor can decide whether a person needs to take iodine. Typically, taking medications containing iodine is recommended:
- during pregnancy planning;
- during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- newborns whose mothers suffer from iodine deficiency;
- during heavy mental stress (during exams or when working on important projects).
Iodine is one of the most important elements necessary for the normal functioning of the body. However, we must not forget that excess iodine is no less dangerous than its deficiency. It is important for every person to eat right: only a balanced diet will provide the body with everything necessary for its normal functioning. Only a doctor can decide whether a person needs additional medications containing iodine.
Help for iodine poisoning
Poisoning by iodine vapor and overdose of drugs containing it occur frequently. Poisoning especially occurs among children. They learn to walk, they are interested in the world around them, which is why they come across pharmaceuticals on their way.
Treatment has many directions. To remove iodine from the body, diuretic tablets will help; in case of vomiting, droppers with saline solution will be effective, normalizing the water balance in the body. Iodine poisoning, the symptoms of which include pain, is treated with painkillers.
The main thing is not only to remove the trace element from the body, but also to eliminate the source of poisoning. After this, the victim’s condition stabilizes.
If you notice symptoms of iodine deficiency, you should contact a specialist in this field. Only he will be able to determine, based on the test results, whether a person needs to take a substance or, on the contrary, he should stop consuming products containing it.
In cases where a doctor prescribes iodine-containing medications, the instructions should be strictly followed. Increasing the dose on your own may lead to undesirable results.
It should be remembered that the drug is prescribed for a certain period, after which it is necessary to visit the doctor again for a further decision. Iodine-based drugs are available in pharmacies without a prescription, but consultation with a specialist is necessary in any situation.
Sources of iodine
A person receives iodine from almost any environment that surrounds him. The mineral content of plants depends on the level of this element in the soil in which they grew.
| Plants include: | Among animal sources we can note: |
|
|
About iodine
Its name comes from Greek, and represents the violet color typical of iodine. This substance is mainly found in the thyroid gland as part of its hormones, thyroxine and triiodothyroxine, which control metabolic processes. In this form, it affects the entire body: accelerates metabolic processes, prevents the deposition of cholesterol in the blood, burns excess fat, and controls the rate of energy production from food.
The best known is the effect of iodine on the nervous system, the quality of skin, hair, and nails. It affects the rate of oxygen absorption by the body's cells, thereby facilitating the process of energy release. Iodine is absorbed almost 100% in the intestines, from there it enters the thyroid gland and is excreted mainly by the kidneys.
Benefits of iodine
Iodine has many functions in the human body. The most important thing is to support the production of important hormones by the thyroid gland . Consequently, it is important for the development of the body (including intrauterine), the functioning of metabolism, and the mental state of a person. The most important functions of the microelement:
- Supports optimal thyroid function. Influence on the formation of 2 hormones: tyrosine, which significantly affects metabolic activity, and triiodothyronine, which affects the functions of almost the entire body.
- Supports the secretion of other hormones.
- Prevention of vascular and heart diseases.
- Burning internal fat deposits.
- Reducing high cholesterol levels.
- Boosting immunity.
- Correct functioning of the central nervous system.
- Supports the quality of skin, hair, teeth, nails.
Consequences of iodine deficiency
Since the human body cannot produce iodine on its own, it must be taken with food. A deficiency of an important micronutrient can have significant negative consequences for the body, but fortifying salt with it (iodized salt) allows most people to solve the problem of iodine deficiency. Thus, the problem of iodine deficiency is a problem of individuals, not the majority of the population.
The risk group includes people who significantly limit their salt intake (who have problems with excess weight or cardiovascular disease). Symptoms and consequences of iodine deficiency include, but are not limited to:
- Hypothyroidism.
- Goiter.
- Infertility.
- Intrauterine developmental defects.
- Fatigue.
- Anxiety.
- Decreased immunity.
- Constipation.
- Cardiac dysfunction.
- Deterioration of vascular condition.
- Increased risk of cancer.
- Deterioration of the condition of nails, skin, hair.
These signs do not necessarily indicate a deficiency of an important micronutrient. If you experience fatigue from time to time, you do not need to take an iodine tablet right away.
Trace element important for women
Iodine is extremely important, especially for women . If they do not get enough of it, their hormonal balance is disturbed, which is manifested by irregular menstrual cycles and various hormonal problems.
Organic iodine deficiency is a possible cause of more frequent cysts, breast tumors, problems with conception, or even infertility in both sexes. In addition, iodine is a powerful antioxidant that can eliminate harmful substances caused by oxidative stress due to the action of free radicals. The negative effects of free radicals can lead to the development of cancer.
How to support the thyroid gland: the role of iodine in sports
The trace element iodine plays an important role in the human body: it participates in the regulation of metabolic processes and has immunomodulatory properties. What is the role of iodine in sports and sports pharmacology? Athletes value this mineral because it helps support the thyroid gland. Its hormones, such as thyroxine and triiodothyronine, help reduce body fat and allow you to increase the intensity of your workouts. I would like to note that an excess of iodine suppresses the production of thyroid hormones.
It is important that iodine enters the body in the right amount, especially during intense strength training, since stress in the body reduces immunity. Another property is possessed by thyroid hormones of the thyroid gland, the synthesis of which involves iodine. They regulate the growth of tissues in the body, and therefore without these hormones it will not be possible to quickly build muscle mass. By the way, in bodybuilding, iodine is also necessary for athletes because it supports the heart. In addition, the concentration of thyroid hormones is important: when their levels are normal, they help accelerate protein synthesis and its breakdown slows down. Thus, these hormones have a fairly strong anabolic effect . But if there is an excess of iodine in the body, then there are too many of these enzymes and they begin to have a catabolic effect, accelerating the process of protein breakdown.
"Leveton Forte"
So, we can conclude that to maintain iodine balance, you must first ensure that it enters the body with food. To do this, it is useful to adjust your daily diet by adding foods rich in iodine and iodized salt.
In addition, some vitamin complexes can be recommended. For example, the drug Leveton Forte, which includes natural ingredients: bee pollen, Leuzea roots and drone brood, will help replenish the supply of necessary substances. This dietary supplement is especially useful for professional athletes and anyone watching their figure. But it is recommended to use iodine preparations only as prescribed by a doctor, due to the fact that their uncontrolled use can lead to an excess of this microelement. As a result, this can adversely affect your overall health.