Acute glomerulonephritis is an immune-inflammatory disease that damages the glomeruli of the kidneys. The process sometimes involves tissue and tubules of the organ. Pathology occurs as a separate disease or is a concomitant disease. Mostly develops between the ages of 2 and 12 years. Men are more susceptible to the disease. The foundation for the formation of pathology is humidity and low air temperature.
What is glomerulonephritis?
Glomerulonephritis (laminated nephritis, glomerular nephritis) is an immunoinflammatory disease associated with the functioning of the kidneys.
The inflammatory process affects the tissues and small vessels of the organ. This pathology affects the glomeruli and interstitial tissue. When such a pathology occurs, the organ ceases to perform its assigned function, that is, to produce urine and cleanse the body of toxic elements.
If we compare with pyelonephritis, then with glomerulonephritis, not one kidney is predominantly affected, but two at once. It should be noted that the development of glomerulonephritis is caused by an incorrect immune response of the body to the emerging inflammatory process.
According to statistics, this disease is in second place among all ailments in adults associated with kidney function after infectious damage to the organ.
The disease occurs in most cases in the male half of the population. The disease usually affects people under the age of forty . The pathology often occurs in young children under the age of fourteen.
According to the nature of its course, this disease comes in two forms: acute and chronic.
The danger of this disease lies in the fact that the acute stage can be cured in almost one hundred percent of cases, but in the chronic form it is difficult to treat.
If left untreated, glomerulonephritis will lead to the development of kidney failure.
The World Health Organization has developed a special classification for diseases. Health professionals around the world use the tenth edition with its revised classifications. In it you can learn about any of the existing diseases, as well as learn about how it is diagnosed and what methods can be treated.
Glomerulonephritis in ICD-10 is assigned codes N03 (chronic nephritic syndrome). The code denotes chronic nephritic syndrome, with characteristic damage to the glomeruli in the organ, as well as their gradual destruction.
What is nephritic syndrome, read our article.
Diagnosis, treatment and prevention
When diagnosing glomerulonephritis, the results of laboratory tests are very important. Protein, red blood cells, and casts are found in the urine, the number of which significantly exceeds the norm. The Zimnitsky method allows you to establish the concentration function of the kidneys and daily diuresis.
Blood parameters are characterized by leukocytosis and accelerated ESR. There is a lot of residual nitrogen, urea, creatinine, alpha and beta globulins in the blood. Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis is detected by a serological blood test.
The clinical picture of the disease is supplemented by ultrasound of the kidneys and examination of the condition of the retinal vessels. In complex cases, structural renal lesions can be identified by biopsy.
Main purposes in the treatment of nephritis, glomerulonephritis:
- hospitalization and bed rest;
- the use of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, as well as immunosuppressants and cytostatics (rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis);
- symptomatic treatment of hypertension, swelling;
- treatment of various complications of glomerular nephritis;
- therapeutic diet – table No. 7.
Prevention of glomerulonephritis should be aimed primarily at eliminating infectious foci: caries, sinusitis, tonsillitis, pneumonia, adnexitis, etc.
In production conditions, it is necessary to exclude chemical or bacteriological intoxication of the kidneys. And in everyday life, to eliminate the risk of developing glomerulonephritis, prevention should include measures to combat hypothermia. The most effective are hardening procedures.
Glamorous (glomerular) nephritis is a kidney disease that occurs as a result of infectious diseases. Mostly found in children. The main danger of the disease is the rapid development of renal failure, which can lead to disability in childhood. However, glazed jade can appear at any age.
There are several types of disease. According to the nature of the flow, jade is divided into:
- Spicy. It occurs suddenly and resolves quickly with proper treatment. If timely treatment is not provided, the disease may become chronic.
- Chronic.
- Subacute. It is malignant and difficult to treat. If left untreated, it is life-threatening for the patient.
- Hematuric . There are blood clots in the urine, the protein content increases, and slight swelling. After a while, an increase in blood pressure appears.
- Nephrotic . Characterized by edema, but blood pressure is within normal limits.
- Hypertensive . Blood pressure rises sharply, the protein content in the urine and the presence of blood cells increase.
- Mixed . Any clinical manifestations of this disease are possible.
- Latent (hidden) . It practically doesn't show up at all. There may be a slight increase in blood pressure, but the patient does not feel it. The appearance of oliguria is characteristic.
Based on clinical manifestations, the following forms are distinguished:
Depending on the stage of development, there are forms:
- Primary . It is distinguished as a separate kidney disease.
- Secondary . Develops after infectious diseases.
- Mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis . A separate disease, the cause is streptococcal infection.
Classification of the disease
The disease is classified according to several criteria such as:
- form of the disease;
- types of disease;
- by etiology.
According to the course, the disease is divided into the following types:
- acute diffuse glomerulonephritis;
- subacute;
- chronic form of glomerulonephritis.
Acute diffuse glomerulonephritis
The manifestation of the acute form begins with rapid damage to the tubules in the organ. Symptomatically, this form is accompanied by fever and increased blood pressure. The patient has hematuria and nagging pain in the lumbar region.
If the pathological process is not associated with the penetration of a virus or bacteria into the body, this course of the disease is often caused by uncontrolled use of medications.
Subacute form
This form of disease development resembles the acute form. The disease rapidly affects the tubules and tissue of the organ. Symptoms include increased blood pressure, pallor, rapid heartbeat and swelling.
The prognosis for this form is often unfavorable.
Chronic form
The chronic form of the disease is the most common. In order for glomerulonephritis to be considered chronic, it must last in the body for more than one year .
Chronic glomerulonephritis develops in two forms: the first consists of nephrotic syndrome, that is, an inflammatory process occurring in the kidneys, and the second is characterized by hypertensive manifestations, that is, frequent increases in pressure.
Symptoms, with this course of the disease, weaken slightly, except for the manifestation of polyuria .
Causes and course of varieties of the disease
Acute glomerular nephritis is characterized by a latent and cyclic form. In the first case, the clinical picture is weakly expressed, and in the second it has a rapid onset, but recovery often occurs faster. There may also be non-infectious causes of glomerulonephritis: individual intolerance to certain substances and vaccines, poisoning with alcohol, insect poison or pollen.
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is malignant. The pathology is characterized by a rapid course. Acute renal failure can develop over a period of months, weeks, or even days.
Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis is the most common and most thoroughly studied form of the disease. Most often it occurs after infections caused by streptococci: tonsillitis, pneumonia, measles, scarlet fever, chickenpox, ARVI. It is characterized by an asymptomatic course in 85% of cases.
Mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis occurs when glomerular cells become overgrown. At the same time, they penetrate into the capillaries, the walls of which thicken. This form causes nephrotic syndrome in 10% of cases, more often in men than in women, and in 15% of cases in children and adolescents. Glomerulonephritis in the mesangiocapillary form is less common, but this form is one of the most unfavorable prognosis of the disease.
If acute glomerulonephritis does not completely go away within 1 year, then it becomes chronic. Its manifestations can be different:
- nephrotic form (with edema, sudden exacerbation of symptoms, renal vein thrombosis);
- latent (with mild renal dysfunction);
- hypertensive (with increased blood pressure);
- mixed;
- hematuric (in the presence of kidney bleeding).
Differences in pathogenesis and origin
Based on its origin, glomerulonephritis is divided into primary and secondary .
In the case of primary origin, glomerulonephritis occurs as a result of existing pathological processes in the kidneys , which resulted in the occurrence of the disease.
The secondary form of the origin of the disease appears as a complication after previous illnesses. Such diseases include lupus, Wegener's disease, vasculitis and others. In addition, the disease can occur after taking toxic drugs or due to the formation of malignant diseases in the body.
Causes
The main causes of the development of glomerulonephritis are considered to be other diseases and infections. Streptococcus plays a special role in the formation of this disease. It is after streptococcal tonsillitis, pneumonia, scarlet fever, streptoderma that this form of nephritis is most often diagnosed.
The disease can also be caused by past diseases such as influenza, herpetic viral infection, typhoid fever, tuberculosis, rubella, and autoimmune diseases. Risk factors for the development of this disease are:
- hereditary predisposition to this disease;
- hypothermia;
- foci of chronic infection in the body;
- avitaminosis;
- decreased immunity;
- carriage of streptococcus.
Types of disease course
Depending on the course of the disease, it is divided into four types, while there is another one called mixed. It received this name because it contains characteristics from different types. So, according to the type of clinic, the disease is divided into:
- Latent.
- Hematuric.
- Nephrotic.
- Hypertensive.
- Mixed.
Latent
The latent type of the disease manifests itself in the chronic form of the disease, with symptoms appearing slowly. They consist of changes in blood pressure and changes in the composition of urine according to chemical indicators.
The prognosis for this course is about ten years of life in ninety percent of cases of this disease.
Nephrotic
The disease proceeds in a moderate mode, the symptoms sometimes make themselves felt. First of all, this manifests itself in decreased diuresis, increased swelling and pronounced proteinuria.
In some cases, exacerbations occur, expressed in increased body temperature and
thrombosis of the renal veins .
However, the survival prognosis is not critical.
Hematuric
This type of disease is quite rare and affects mainly the male population at a young age. Most often, it occurs against the background of a previous acute respiratory viral infection. the following symptoms appear :
- proteinuria;
- no swelling;
- stable blood pressure;
- there may be bloody discharge in the urine;
- the kidneys are working at full capacity.
If you seek medical help in time, the prognosis for recovery is very good.
Hypertensive
Symptoms in the hypertensive type of the disease proceed slowly, sometimes manifesting themselves in changes in the composition of urine and in electrocyturia.
This type is characterized by left ventricular hypertrophy and pronounced changes in the fundus . The general clinical picture by all indications resembles the latent form, so the patient often does not seek help because he does not feel the effects of pronounced symptoms.
If you do not notice the manifestations of the disease, then the consequences of this disease in a person may occur: a heart attack, stroke or failure in the left ventricle.
Mixed
With a mixed type, the manifestation of symptoms is similar to nephrotic and hypertensive types of the disease. The patient experiences surges in blood pressure and urine mixed with blood . Often, in addition to these symptoms, anemia and protein in the urine appear. The kidneys are not working properly.
How to recognize pathology
The disease in its acute form rarely requires special therapy. But when the symptoms of acute glomerulonephritis do not cease to appear a year after the first attack, it is necessary to visit the clinic and consult with a specialist. After all, such a course of the disease indicates its transition to a chronic form. Treatment is prescribed only after an accurate diagnosis. To begin with, the doctor examines and interviews the patient, after which he is sent for a series of examinations:
- General examination of urine to determine the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, proteins and casts in the urine. To ensure accurate results, the fluid is donated twice over several days.
- Ultrasound of the urinary organs. The kidney in acute glomerulonephritis is usually enlarged.
- A serological blood test will show an increase in the titer of antibodies to streptococcus.
- Biopsy. Prescribed if the preliminary diagnosis is confirmed. The procedure shows what form the disease takes and whether there is a concomitant disease with similar symptoms.
Doctors must diagnose the acute form of the pathology in order to distinguish it from an exacerbation of the chronic course of the disease. Symptoms of AGN appear one to three weeks after the body is infected. When symptoms appear after a few days, then we are talking about chronic glomerulonephritis. It is difficult to recognize it in the case of a latent course. The diagnosis is confirmed if more red blood cells are detected in the urine than leukocytes, and there are no pale and active white blood cells.
Morphological forms of the disease
The classification of glomerulonephritis by morphological forms was compiled back in 1930. At that time it included only two forms, but gradually medical specialists began to study this disease more and added several more forms.
Mesangioproliferative
The mesangioproliferative type is characterized by damage to the renal system caused by an autoimmune nature. This is a kind of response from the immune system to certain diseases in the body.
Scientists are increasingly inclined to believe that the cause of such a response on the part of the body may be a genetic predisposition . Children and adolescents are most susceptible to this type of occurrence.
The body, with such a disease, tries to secrete antibodies in order to protect the kidneys from harmful factors, but in the end the antibodies contribute to the progression of the disease .
The mesangioproliferative type of the disease affects the capillaries in the kidney, as well as tissue in the glomeruli (see photo). Thus, there is a failure in the filtration and excretion of urine, which leads to an imbalance of chemical components in the body. It is this type that is accompanied by nephrotic syndrome.
This type is dangerous due to its possible complications.
Fibroplastic
The fibroplastic type is rarely characterized by glomerulonephritis alone. Often another disease is added to it. This type is classified as mixed, and it is rarely possible to identify the main cause of the disease. This species is further divided into two subspecies, which differ in the degree of damage to the organ.
The first type is called focal ; not all segments in the glomeruli are affected. Experts called the second diffuse , in which pathological processes occur in the entire area of the glomeruli.
The consequences of such a lesion are the proliferation of connective tissue. This subsequently leads to atrophy of the tubules and renal tissue.
Chronic with isolated urinary syndrome
This syndrome passes without any complaints. After a general urine test, a patient may discover that the urine contains traces of protein and blood. Such glomerulonephritis is often curable, but only in cases of timely treatment .
Autoimmune
The autoimmune type of glomerulonephritis is a type of disease that was caused by an autoimmune process. When the body reacts incorrectly to the production of antibodies, malfunctions occur, leading to kidney disease.
Poststreptococcal
Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis develops against the background of the appearance of streptococci in the body. After streptococcus bacteria appear in the body, it tries to produce antibodies, which, if malfunctioning, begin to kill its own tissues in the kidney .
Then an additional antibody production system is activated, but only with the participation of the kidneys. The result is a so-called “vicious circle”.
Symptoms are expressed in nephrotic syndrome , as well as a decrease in the amount of urine and the presence of protein in it. Many patients at this moment are tormented by a feeling of thirst.
Hemorrhagic
The hemorrhagic form manifests itself as a result of past diseases associated with infectious damage to the body by bacteria. This may be a consequence of diseases such as lupus, toxoplasmosis or mononucleosis.
In addition to viral infections, the hemorrhagic form can appear as a result of taking medications or intoxication after drinking alcoholic beverages.
Mesangiocapillary
This is one of the rarest forms that is found in patients today.
However, the mesangiocapillary type also has the most unfavorable treatment outcome.
With it, partial deposition of globulins occurs in the tubules, capillaries and glomerulus. This pathology develops quickly and becomes noticeable after the first week of the inflammatory process. Most often it is caused by the appearance of streptococcal infections , as well as irradiation of the body.
This form has no clear signs, except for the manifestation of hematuria and increased blood pressure.
Membranous
Membranous nephropathy is a disorder in the general metabolism of water-salt, lipid, and protein metabolism in the body. Capillaries and glomeruli with this type of disease thicken significantly. This occurs due to the deposition of immune complexes .
This form manifests itself in proteinuria and nephrotic syndrome. The size of the kidneys during this course of the disease can change, significantly increasing in size. Their color can change to a yellow tint.
If significant deposition of antibodies occurs in the glomerular membrane, then this form can develop into a malignant form.
Classification of glomerulonephritis
Chronic glomerulonephritis is usually understood as a group of nephropathies that differ in etiology and pathomorphological features. Against the background of long-term, low-grade inflammation, damage to the glomerular apparatus and renal tissue occurs, which leads to the formation of microthrombi in the capillaries and gradual vascular sclerosis. As a result, the filtration capacity of the paired organ is impaired and renal failure develops.
In the CIS countries, the classification of E. M. Tareev is considered relevant, according to which the following forms of chronic glomerulonephritis are distinguished:
- Latent. The most common form, characterized by mild urinary syndrome and the absence of edema and arterial hypertension.
- Nephrotic. Accompanied by pronounced symptoms of renal failure: increased blood pressure, swelling, oliguria, lack of appetite, nausea, weakness, and the smell of ammonia.
- Hypertensive. It manifests itself as signs of arterial hypertension - increased blood pressure, polyuria, and increased urination.
- Hematuric. It is characterized by the presence of blood in the urine, causing it to turn pink or red. A general urine analysis reveals an increased concentration of red blood cells.
- Mixed. It has a clinical picture of several forms at the same time.
It is important to know! According to ICD-10, chronic glomerulonephritis has code N03. It is characterized by diffuse damage to the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys with subsequent development of sclerosis and functional failure.
Signs and symptoms of the disease
The main signs of the disease include the following factors:
- Infectious lesion of the body. It could be viruses or bacteria. According to statistics, a large number of patients were exposed to streptococcal infections.
- Oncological diseases often lead to inflammation in the kidneys.
- Hereditary syndromes due to malfunctions of the kidneys.
- Hypothermia can also lead to illness.
- Drugs and toxic substances can have a direct effect on the appearance of glomerulonephritis.
The mechanism of occurrence of the disease is not the entry of an infectious factor into the body, but an allergic reaction to it.
Therefore, the first symptoms may be noticeable only after the first two weeks after the illness or after certain factors provoke the onset of the inflammatory process.
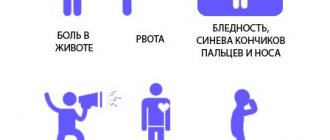
Symptoms of glomerulonephritis include:
- nausea and headache;
- temperature increase;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- presence of shortness of breath;
- presence of blood in urine;
- the density of urine decreases during the course of the disease;
- in the first days of the disease the amount of urine decreases, after a couple of days its amount is restored;
- blood pressure rises;
- gain in body weight.
If a person has a latent form of the disease, the symptoms may be hidden or appear in a mild form. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor to exclude the presence of other pathological processes in the body.
The disease has become chronic and makes itself felt during short-term exacerbations.
If treatment measures are not taken, each time the manifestations will intensify and occur in a more severe form than before.
According to the signs, women, like men, experience the same symptoms, but in addition they may experience aversion to food and drowsiness.
What is the cause of the disease?
A disease of an infectious or allergic nature can cause the development of a specific reaction of the immune system in the human body, which in turn causes kidney damage.
Main causes of the disease:
- complication after diseases of streptococcal origin (tonsillitis, erysipelas, scarlet fever, relapse of chronic tonsillitis);
- chronic and acute infections (mononucleosis, herpetic lesions, adenovirus, rubella);
- rheumatic diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, polyarthritis nodosa, vasculitis);
- introduction of microbiological preparations into the body;
- allergic reactions to foods, pollen, household allergens;
- taking medications that have a toxic effect on the kidneys;
- snake or insect bites;
- alcohol abuse;
- helminthic infestations;
- chronic stress;
- malignant neoplasms of any organs;
- heredity;
- complicated course of pregnancy.
Acute glomerulonephritis can develop due to hypothermia in adults, and in young children due to the anatomical and physiological immaturity of the nephrons.
What is nephrotic syndrome?
Unfortunately, in most cases, glomerulonephritis is accompanied by nephrotic syndrome , the characteristic features of which are swelling and a sharp increase in blood pressure. This syndrome can be provoked by the influence of streptococcus bacteria or the presence of a viral infection such as herpes.
Often the occurrence of nephrotic syndrome is caused by
improper use of medications .
If a course of this form is not eliminated within a year, then there is a risk of kidney failure. It is possible to identify the onset of such a pathology using a urine test, where protein up to 3 grams . In addition to protein, experts find albumin, which indicates nephrotic syndrome.
Prevention
The basis of prevention is the timely identification of a drug that is toxic to the kidneys and informing the patient about the inadmissibility of further taking such drugs. If secondary nephritis develops (against the background of another disease), treat the underlying disease. Treatment should be carried out until complete recovery with subsequent observation by a specialist.
The use of medications, especially antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, should be limited. Avoid exposure to toxic substances and the use of illegal "medicinal" products, including herbal preparations without a certificate issued by official government agencies.
Chronic abuse of painkillers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, especially at high doses, as well as lithium drugs should be avoided.
It is also necessary to avoid exposure to toxic substances such as lead and cadmium, and to promptly and effectively treat metabolic disorders and diseases that cause persistent tubulointerstitial nephritis.
Diagnostics
When talking with the patient, the doctor tries to identify the main signs indicating the presence of glomerulonephritis and differentiate this disease from others, such as:
- Diabetes.
- Allergy.
- Disorders in the autoimmune system.
In order to ensure that the diagnosis is correct, the medical specialist must order a series of tests and ultrasound examinations for the patient.
The patient will need to submit:
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko;
- general urine analysis;
- analysis according to Zimnitsky;
- immunogram;
- blood chemistry;
- test for allergic reactions.
Kidney pathology will be revealed by ultrasound examination. Sometimes the doctor prescribes a kidney tissue biopsy and urography.
After receiving the results of the study, the urologist will make a diagnosis and prescribe a treatment regimen .
Diagnosis of acute glomerulonephritis
Instrumental methods for studying glomerulonephritis:
- An ultrasound of the kidneys shows the following signs of the disease: the size of the organ is normal, the glomerular filtration rate is reduced, and the echogenicity of the organ tissue is reduced.
- A kidney biopsy allows one to establish such symptoms of glomerulonephritis as cell proliferation, filling the glomeruli with antibodies, and migration of immune cells into the glomeruli.
Laboratory tests for glomerulonephritis:
- General urine analysis. In patients with glomerulonephritis, a pink color of urine is observed, an excess of the norm of red blood cells, cylinders, and protein is detected, as well as an increase in urine density.
- Biochemical blood test. This analysis allows you to detect in the patient’s blood a decrease in protein levels, an increase in cholesterol, the presence of C reactive protein and sialic acids.
- Zimnitsky's test. Patients have increased urine density and a significantly increased daily volume.
- An immunological blood test is performed to detect an increase in antistreptokinase, antideoxyribonuclease B, and antihyaluronidase in the blood.
Glomerulonephritis during pregnancy
Glomerulonephritis occurs in pregnant women, as in other patients.
First of all, the appearance of the disease is explained by the vulnerability of the female body during this period of life. If the disease occurs, the woman experiences severe swelling and headaches, which are difficult to eliminate with any of the drugs. In this case, a woman experiences changes in the chemical composition of her urine, after which it may turn red .
Women during this period may suffer from anemia . If treatment is not carried out or is ineffective, this condition can lead to hemodialysis.
We must not forget that glomerulonephritis in pregnant women also affects the condition of the fetus, causing hypoxia .
Doctors allow pregnancy only in the first degree of glomerulonephritis.
Symptoms of acute glomerulonephritis
The first symptoms of acute glomerulonephritis usually appear a couple of weeks after exposure to a predisposing factor (allergic reaction or infection) on the body. In this case, three main syndromes prevail in the clinical picture: hypertensive, edematous and renal.
- Hypertensive syndrome. Typically, in acute glomerulonephritis, arterial hypertension is quite moderate, since 60-70% of patients have blood pressure no higher than 160/100 mm Hg. But it is worth noting that prolonged hypertension has a negative effect on the patient’s body. For example, hypertension is often accompanied by bradycardia, which can last for a couple of weeks.
- Edema syndrome. Swelling is considered the main symptom of the disease, since it manifests itself at its early stage. Swelling appears mainly in the morning in the face area. Edema syndrome is accompanied by complications such as ascites, hydropericardium, hydrothorax. Edema provokes various cerebral disorders such as headaches, vomiting, nausea, decreased hearing and vision. Moreover, eclampsia may occur: cyanosis of the neck and face, loss of consciousness, tonic-clonic convulsions, decreased pulse, swelling of the neck veins.
- Kidney syndrome. Patients with glomerulonephritis experience oliguria and anuria, accompanied by extremely strong thirst. Depending on the stage of the pathology, decreased or, on the contrary, increased urine output, as well as a change in its color, may be observed.
- Pain syndrome. Often the pain is localized in the lower back. It occurs due to disturbances in urodynamics and stretching of the renal capsules.
Differences between glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis
Unlike pyelonephritis, the disease glomerulonephritis changes the composition of the blood , which negatively affects the general well-being of the patient. In addition to this, there are a number of differences (for more details, see the table):
- Urination is released in small doses.
- There are disturbances in the functioning of the brain.
- With pyelonephritis, the pathology affects one organ, and with this disease two.
- Urine enters the blood, creating increased pressure, which does not happen with pyelonephritis.
- Pyelonephritis excludes edema, and with glomerulonephritis they are present in large quantities.
Treatment
Help with this disease involves taking medications, ensuring rest, and limiting the consumption of certain foods. In the initial period, bed rest should be observed, since physical activity can lead to an increase in the production of toxic nitrogen compounds. It is best for the patient to stay in bed constantly for the first time and not get up unless absolutely necessary.
In acute glomerulonephritis, treatment requires diet. As the disease progresses, water and electrolyte balance is disrupted, protein and other useful substances are lost. Proper nutrition will help compensate for these disorders. In case of severe edema, it is recommended to avoid salty foods and consume large amounts of liquid.
It is important to include as many foods high in potassium in your diet as possible. You can use vegetable proteins, fats, complex carbohydrates. Fatty meat and fish should not be eaten. Smoked meats, canned food, stale and low-quality products, and fast food should be excluded. To replenish protein, you can eat low-fat cottage cheese and chicken eggs.
Treatment of acute glomerulonephritis with drugs is aimed at relieving symptoms and syndromes of the disease. Blood thickening due to fluid loss can lead to thrombus formation. For liquefaction, disaggregants and anticoagulants (Dipyridamole, Heparin, Ticlopidine) are used.
To reduce the destructive effect of immune complexes, substances are used that reduce the activity of the perverted defense mechanism. For this purpose, glucocorticoids (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone) or cytostatics (Chlorambucil, Cyclosporine) are used.
To relieve high blood pressure, peripheral vasodilators (Verapamil, Sodium Nitroprusside) or symptomatic agents (Reserpine) are used. At the same time, the patient is given diuretics (Furosemide), which reduce blood pressure and eliminate swelling.
If the connection of the disease with a source of chronic infection is proven, then it is sanitized using broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs. The doctor selects them after checking for the sensitivity of the pathogenic flora and taking into account the patient’s tolerance of the drugs.
Treatment of acute glomerulonephritis
How long do they live - forecast
The life prognosis depends on the period of time when a person noticed manifestations of glomerulonephritis and sought medical help.
Of course, the degree of damage to the tissues and filtration mechanisms of the kidney plays an important role.
Effective treatment can also prolong the patient’s life, and sometimes save him from this disease.
The most favorable prognosis is observed in acute forms of the disease. Chronic is more difficult to treat, and often the disease progresses to renal failure, which can be fatal .
Complications
The acute form of glomerulonephritis, if treated incorrectly and untimely, can lead to the following complications:
- Acute heart and kidney failure.
- Hypertensive renal encephalopathy (eclampsia and preeclampsia).
- Stroke.
- Decreased vision (sometimes blindness).
- The disease can become chronic.
Glomerulonephritis is especially dangerous due to its complications, so it is important to use preventive measures. In this regard, it is very important to promptly and correctly treat any viral and bacterial diseases and avoid hypothermia. A proper diet, moderate exercise and walks in the fresh air are also useful.
Diet recommendations
For kidney glomerulonephritis, special dietary nutrition should be provided. This diet is called table number 7 , which limits food that can irritate the kidney tissue. First of all, it is necessary to limit protein foods and foods containing sodium in your diet.
Products that can have a detrimental effect on the nervous system should also be excluded. These products include foods containing fat and essential oils. You must stick to no more than three thousand calories . You should not go beyond these limits.
In order for food to be a joy and not cause additional pain and inconvenience to the patient, it must be prepared correctly. To do this, the meat should be baked or boiled . Food is taken in small portions four times a day.
The program “Live Healthy!” about the disease, its pathogenesis, symptoms and diagnosis:
Regime and diet
When treating glomerulonephritis, bed rest is prescribed in order to provide warmth to the affected organ. This improves blood circulation and the functioning of the renal system, and also speeds up the healing process.
On average, hospital treatment lasts about three weeks. However, if acute symptoms have not resolved, then therapy can be continued. After recovery, the patient should not perform heavy physical activity or become hypothermic. In the chronic form of the disease, even during the recovery period, preventive therapy should be used.
A diet must be prescribed that requires limiting salt or refusing to consume it. In addition, it is necessary to exclude fried, smoked, spicy, salty foods and spices from the diet. This will help reduce swelling and lower blood pressure, as well as normalize test results.
Treatment methods
Treatment of glomerulonephritis is usually complex. Therapy is carried out under the supervision of a nephrologist. If the symptoms of the disease are severe, hospitalization in a specialized department of the hospital may be required.
Drug therapy
Medications are an important part of the treatment of glomerulonephritis. With their help, it is possible to achieve the disappearance of most signs of the disease. To treat the disease, medications with different mechanisms of action are used:
- antibiotics successfully fight the infectious component of the disease: Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone;
- diuretics are necessary to maintain normal fluid balance in the body: Lasix, Furosemide;
- steroid hormonal drugs weaken the destructive inflammatory process: Metypred, Prednisolone;
- cytostatic drugs are used to suppress immune aggression against one’s own tissues: Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate, Endoxan;
- membrane stabilizers improve the structure of the vascular wall of inflamed glomeruli: Trental, Curantil;
- uroantiseptics prevent the development of infectious complications: Nitroxoline, 5-NOK, Canephron.
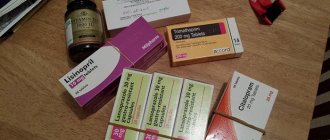
Drugs for the treatment of glomerulonephritis - table
| Drug name | Active substance | Pharmacological group | What is the drug prescribed for? | Release forms | Contraindications | Side effects |
| Brusniver |
|
|
| plant materials for preparing infusions and decoctions | individual intolerance | allergic reactions |
| Methylprednisolone | methylprednisolone | steroid hormones | elimination of immune inflammation in the kidneys | pills | acute infectious diseases |
|
| Phytolysin | plant extracts | herbal uroantiseptics |
| paste for preparing a solution for oral administration | phosphate urolithiasis | allergic reactions |
| Furosemide | furosemide | diuretics | diuretic |
|
|
|
| Penicillin | penicillin | antibiotics | elimination of bacteria | injection |
| allergic reactions |
| Endoxan | cyclophosphamide | cytostatics | elimination of immune inflammation of the glomeruli | injection |
|
|
| Nitroxoline | nitroxoline | uroantiseptics | prevention and treatment of kidney infections | pills | hypersensitivity | allergic reactions |
| Metipred | methylprednisolone | steroid hormones | elimination of immune inflammation in the kidneys | pills | acute infectious diseases |
|
| Ceftriaxone | ceftriaxone | antibiotics | elimination of bacteria | powder for solution for injection | individual intolerance | allergic reactions |
| Trental | pentoxifylline | membrane stabilizers | improves blood flow in the glomeruli | pills |
|
|
| Atorvastatin | atorvastatin | anticholesterol drugs | normalizes blood cholesterol | pills | severe liver failure |
|
| Canephron |
| herbal uroantiseptics | prevention and treatment of kidney infections |
|
| allergic reactions |
| Chime | pentoxifylline | membrane stabilizers | improves blood flow in the glomeruli | pills |
|
|
| Prednisolone | prednisolone | steroid hormones | elimination of immune inflammation in the kidneys |
| acute infectious diseases |
|
| Polyoxidonium | azoximer bromide | immunomodulators | immune activation | pills |
| allergic reactions |
Drugs for the treatment of glomerulonephritis - photo gallery
Trental improves blood flow in the glomeruli
Furosemide has a diuretic effect
Canephron is a herbal uroantiseptic.
Endoxan is a cytostatic drug that suppresses the aggression of the immune system.
Prednisolone effectively prevents glomerular inflammation
Surgery
There is no surgical treatment for glomerulonephritis as such. Intervention is necessary in case of complications and associated conditions:
- paranephritis - inflammation of the fatty tissue surrounding the kidney;
- renal carbuncle - a limited abscess in the kidney tissue;
- urolithiasis.
An abscess is a reason to ensure the outflow of inflammatory contents (drain). For urolithiasis, depending on the size of the stones, crushing or removal through an incision in the lumbar region is used.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is an effective method of eliminating inflammation in the kidneys. The following techniques are used:
- Magnetic therapy significantly reduces the severity of inflammatory changes in the kidneys;
- electrophoresis has a beneficial effect using direct current;
- ultrasound therapy improves blood circulation in the kidneys;
- therapy with sound waves in the decimeter range reduces the activity of the inflammatory process;
- mud therapy improves blood movement through blood vessels;
- massage improves blood supply to the kidneys;
- treatment with leeches (hirudotherapy) improves blood flow in the renal glomeruli.
Leeches release substances into the blood that improve its fluid properties.
Diet
Diet is an important component of the complex treatment of glomerulonephritis. On the recommendation of a doctor, it is necessary to reduce the intake of liquid and salt to a minimum. Meals should be fractional; the heat treatment methods should be boiling and baking. Products prohibited for consumption:
- salt;
- salty canned foods;
- meat products;
- confectionery;
- margarine;
- fast food;
- duck and goose meat;
- fatty sea fish;
- concentrated meat broths;
- cereals;
- spicy seasonings;
- strong tea;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- alcohol.
Products recommended for use for glomerulonephritis:
- bread made from salt-free dough;
- lean meats in limited quantities;
- dairy products;
- fresh vegetables.
Traditional treatment
With the permission of a doctor, some remedies from the arsenal of traditional medicine can be used in the treatment of glomerulonephritis.
Traditional medicine in the treatment of glomerular inflammation - table
| Raw materials | Cooking method | Mode of application |
| 2 tbsp. l. collection, pour half a liter of boiling water, leave | drink as tea, half a glass three times a day |
| Fresh cranberries | squeeze juice from fresh berries | take half a glass three times a day |
| 2 tbsp. l. pour 1.5 cups of boiling water over the mixture, simmer over low heat for 15 minutes, then leave for an hour | take half a glass three times a day |
| Erva woolly (floor fell) | 1 tsp. pour a glass of boiling water over the raw materials, simmer over low heat for 10 minutes | take half a glass three times a day |
Plants in the treatment of glomerulonephritis - photo gallery
Rose hips contain a lot of vitamin C
Erva woolly is used for glomerulonephritis
Lingonberry has an anti-inflammatory effect
Cranberries contain many vitamins
Signs
Symptoms of autoimmune glomerulonephritis most often manifest themselves acutely
. In order to begin treatment of glomerulonephritis on time, you need to know the signs and symptoms of this disease, which will allow you to diagnose it at an early stage, when you can completely get rid of the disease.
Symptoms of autoimmune glomerulonephritis most often manifest themselves acutely:
Symptoms of drug-induced kidney damage and treatment
- headache;
- general weakness and malaise;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased body temperature;
- pain in the lumbar region.
Among the specific symptoms of glomerular nephritis are the following:
- swelling (limbs and face may swell);
- due to difficulty in the outflow of urine, pressure increases;
- urinary syndrome (the composition, smell and color of urine differ from the norm).