What do red blood cells in urine mean during pregnancy?
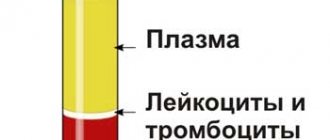
Red blood cells are found in plasma, the main function of which is to saturate tissues with oxygen, nutrients and remove carbon dioxide, which is necessary for the development of the fetus inside the womb.
During intrauterine development, this blood function is important for the normal formation and development of the baby. There are two types of red blood cells found in the body:
- unchanged cells - are caused by a bright red hue due to the high hemoglobin content;
- altered - characterized by the absence of hemoglobin; due to being in urine for a long time and subsequent filtration, the cells lose color, and also increase in diameter and are leached. Quite often during pregnancy, in the presence of protein and casts, renal failure is determined in the analysis.
The formation and formation of urine occurs in the kidneys through plasma filtration and any components of hematopoiesis should not enter the biological fluid during normal operation of the urinary system. If a lot of red blood cells are found in the urine during pregnancy, then this is a clear sign of insufficient kidney function.
The cause is malignant tumors
If the laboratory test does not reveal the norm, then tumors may be the cause. Hematuria is a sign of kidney and bladder cancer. These malignant diseases are quite rare. The development of cancer, in most cases, begins long before pregnancy and childbirth. The following factors contribute to this:
- burdened heredity;
- smoking;
- exposure to carcinogens;
- chronic diseases;
- chronic renal failure.
Blood in the urine with bladder cancer appears when the organ grows. It is bright scarlet in color. Its volume is small (a few drops). In advanced cases, massive bleeding is observed. Other symptoms of the disease include pain when urinating, discomfort in the pubic area, and a false urge to urinate. Kidney cancer in the early stages is asymptomatic.
Hematuria is the main (pathognomonic) sign of the disease and appears against the background of complete well-being. There is no pain. Exceeding the norm of red blood cells in pregnant women with kidney cancer is an early sign. Gross hematuria is a consequence of vascular damage and tumor invasion of surrounding tissues. In advanced cases, blood clots are found in the urine.
Reasons why red blood cells are increased in urine during pregnancy
An increase in red blood cells in the urine during pregnancy is called erythrocyturia or hematuria in medical practice. Basically, based on the number of cells in the analysis, the results are divided into microhematuria and macrohematuria. In the latter case, blood in biological fluid is visible without a microscope.
If red blood cells are elevated, the reasons are mainly related to diseases of the genitourinary system:
- pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis - infection of the renal parenchyma or glomeruli, which leads to insufficient filtration of biological fluid;
- Chronic cystitis can be determined by analyzing urine in combination with accompanying symptoms and complaints (frequent urination, accompanied by a burning sensation);
- urolithiasis and the resulting stones injure the tissues during movement, and salts (urates or oxalates) will be present in the urea;
- cervical erosion, colpitis or vaginitis are accompanied by microbleeding.
Sexually transmitted diseases can also become a source of blood. Therefore, when collecting material, it is better to cover the vagina with cotton wool to eliminate this factor.
In the later stages, erythrocyturia is explained by significant compression of the internal organs, stagnation occurs, and the outflow is disrupted. Doctors do not rule out the onset of placental abruption, which leads to gross hematuria and the risk of death of the child.
Pathologies in which red blood cells are increased
Doctors consider a condition in which there are elevated red blood cells in urine to be a dangerous symptom, especially if a woman is pregnant. That is why a urine test during pregnancy is prescribed very often. Regular monitoring of the composition and properties of urine makes it possible to timely detect a pathological process and take measures to treat it. Diseases accompanied by an increase in red blood cells in the urine during pregnancy include:
- urolithiasis (UCD) – the formation of calculi (stones) in the organs of the urinary system, which damage the membranes and provoke the onset of microscopic bleeding;
- an increase in the size of the uterus in pregnant women, as a result of which the outflow of fluid is disrupted and deviations in the functioning of the organs of the urinary system occur;
- infection of the genitourinary system;
- bladder polyposis;
- inflammation occurring in the urinary system;
- erosive lesions of the cervix;
- bleeding of the genitourinary system;
- hormonal imbalance;
- colpitis is an inflammatory process affecting the vaginal mucosa;
- internal organ injury;
- diabetes;
- violation of the integrity of the skin in the groin area;
- serious emotional disturbances.
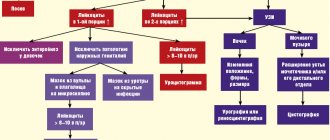
Red blood cells in the urine of pregnant women may be slightly elevated due to low mobility and hot weather conditions. In any case, additional examination is required to confirm the diagnosis. Depending on the existing symptoms and complaints, the doctor may prescribe the following diagnostic measures: colposcopy, bacterial culture for microflora, smear from the cervical canal and vagina, ultrasound of the pelvic organs and genitourinary system, MRI, and other types of urine tests.
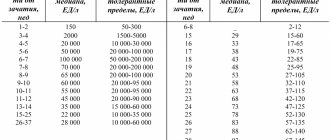
Table of norms of red blood cells in urine during pregnancy
Red blood cells in the urine of pregnant women are counted using a general analysis, which is taken at almost every doctor’s appointment, in order not to miss the onset of the infectious process. The research is done quite quickly and you can find out the results on the same day.
The norm of blood cells in the test material is no more than two per sample. When conducting diagnostics, all parameters are taken into account in order to determine the location of hematuria.
Table of norms for urine analysis during pregnancy
:
| Index | Normal during pregnancy |
| Color | yellow, straw yellow |
| Transparency | transparent |
| Smell | unsharp specific |
| Specific Gravity(Density) | 1003-1035 |
| Urine pH reaction | 5.0-7.0 (acidic, slightly acidic, neutral) |
| Protein | Not detected or up to 0.033 g/l |
| Sugar (glucose) | Not detected or up to 0.083 mmol/l |
| Bilirubin | Not found |
| Urobilin | Not found or traces |
| Ketone bodies | Not detected |
| Nitrite | |
| Hemoglobin | Not found |
| Red blood cells | 0-2 in sight |
| Leukocytes | 0-5 in sight |
| Epithelium is flat | 0-3 in sight |
| Transitional epithelium | single in the preparation |
| Renal epithelium | Not detected |
| Hyaline cylinders | 1-2 in the preparation |
| Other cylinders | Not detected |
| Bacteria | Not detected |
| Mushrooms | Not detected |
| Salts | Not found or in small quantities |
| Slime | Not detected |
How to reduce red blood cells in urine during pregnancy - treatment
An increase in the level of blood cells involves, first of all, diagnosing diseases of the urinary tract and identifying the primary source of the cause that affected hematuria.
Treatment for infection involves the use of antibacterial drugs, which are allowed during the fetal development stage. If stones are found, hospitalization and antispasmodics will be required.
Medicines based on herbal components will help reduce the slight appearance of blood in urine tests. For the same purpose, you can use decoctions of lingonberry leaves, cranberries or special mixtures, but only after medical consultation.
What pathologies can red blood cells in urine indicate during pregnancy?
It is important for expectant mothers to monitor their health. To do this, you need to undergo special examinations, including regular blood and urine tests. They will help detect diseases that a woman may not have known existed. For example, red blood cells in the urine during pregnancy are a sign of infection in the body or pathology of the genitourinary system.
The appearance of red blood cells in the urine of pregnant women is called hematuria. Depending on the number of red blood cells, macro- and microhematuria are distinguished.
Reasons for increased indicators
There are a fairly large number of different reasons due to which the level of red blood cells in the urine of pregnant women may increase. In this case, both pronounced or implicit pathologies in the form of diseases and syndromes, as well as physiological circumstances, have an influence. So, red blood cells in urine during pregnancy are increased in the following situations
- Poorly balanced diet. Too frequent consumption of hot and spicy foods in the presence of problems with the gastrointestinal tract can provoke hematuria;
- Emotional and physical stress. Quite often, the cause of a slight, sometimes even average, increase in the level of red blood cells in the urine of pregnant women is unbalanced circadian rhythms, severe fatigue after intense physical activity, regular stress and depression, which can accompany a representative of the fair sex in an interesting position at any stage of gestation;
- Alcohol intoxication. Naturally, drinking alcohol in any form during pregnancy is strictly prohibited. However, some women do not adhere to this rule and abuse alcohol, believing that light alcoholic drinks will not cause harm to health. In some cases, ethanol intoxication with the development of a number of other pathologies may also be accompanied by hematuria;
- Taking a number of medications. As modern clinical practice shows, with regular systemic use of methenamine, ascorbic acid in high dosages, sulfonamides and anticoagulants, the level of red blood cells in the urine increases;
- External climatic conditions. A long stay in a sauna, being in a stuffy, unventilated room and other environmental factors can affect changes in the basic parameters of laboratory tests, especially if they accompany a pregnant woman on an ongoing basis;
- Infectious lesions of the genitourinary area. They can be caused by a wide range of pathogenic microorganisms and are accompanied by cystitis, pyelonephritis, inflammation of the bladder, kidneys and other pathologies;
- Stone formation. Stones in the kidneys, bladder, liver and other organs significantly affect the structure of urine and can lead to the formation of hematuria, both in the classical version and in complicated forms;
- Direct injuries. Direct injury to the genitourinary organs carries potential risks not only for the child, but also for the mother;
- Gynecological pathologies. This includes a wide range of problems, from cervical erosion to the formation of benign neoplasms in the form of cysts, tumors, and so on;
- Systemic pathologies of the cardiovascular structure. Any type of cardiovascular insufficiency affects blood pressure and can lead to impaired blood circulation in important organs of the genitourinary system, which in turn sometimes causes hematuria;
- Uterine bleeding. It can be caused by both acute and pathological conditions in the uterus and placenta, and by foreign diseases;
- Hemophilia. Persistent bleeding disorders cause a wide range of pathologies throughout the body, often manifesting as a significant increase in the level of red blood cells in the urine;
- Dysmetabolic nephropathy. This includes all secondary kidney damage, the vast majority of causes are non-infectious in nature;
- Cancer. A malignant neoplasm in the genitourinary organs in the early stages practically does not manifest itself externally, but can be monitored within the framework of standard laboratory tests;
- Arteriovenous malformations of the kidneys. A rare hereditary pathology is almost always accompanied by a high level of hematuria;
- Urogenital schistosomiasis. In Russia, the disease is very rare, but in most countries of Africa and Central Asia it is the main cause of a pathological increase in the level of red blood cells in the urine;
- Specific lesions of the urinary system. These include such difficult-to-diagnose syndromes as Berger's disease, nocturnal paroxysmal hemoglobinuria, and so on;
- Complications after surgery. Doctors rarely resort to any surgical actions during pregnancy, carefully weighing all the pros and cons of the action. However, when performing a number of low-traumatic techniques, for example, intravenous insertion of a bladder catheter or other procedures, postoperative complications are possible, including hematuria.
It should be understood that quite often an increased content of red blood cells in the urine is formed as a result of exposure to several reasons at once, which together create conditions for the development of serious complications.
So most problems develop with a fairly weakened immune system, both local and general. In addition, certain changes are brought about by the presence of certain chronic diseases even in the stage of remission, frequent systemic allergies with autoimmune reactions, and other circumstances of both the pathological and physiological spectrum.
Red blood cells in urine during pregnancy: normal
The body of every pregnant woman undergoes serious changes with the onset of conception. Many physiological mechanisms proceed according to a changed scenario due to the growth and development of the unborn baby. That is why during pregnancy it is important for every woman to monitor her own health.
Elevated red blood cells in the urine during pregnancy are an indicator of trouble. Normally, pregnant women should not have red blood cells in their urine; one is allowed to appear in the field of view. If the red blood cells in the urine are elevated during pregnancy, there are more than 3-5 of them, then the woman is asked to take a urine test again.
Even a small amount of red blood cells in the urine during pregnancy is unacceptable; this phenomenon is called microhematuria. If the urine acquires a reddish tint due to the presence of a large number of red blood cells, we are talking about gross hematuria. Both of these conditions require diagnosis and elimination of the cause that caused them.
Normalization of red blood cell levels
According to modern domestic statistics, an increase in the level of red blood cells in the urine of pregnant women is primarily associated with the development of infectious diseases and various pathologies of the urinary system such as pyelonephritis, cystitis, and thunderonephritis. Also, the very presence of pregnancy plays a significant role, during which the immune system drops significantly, hormonal changes in the body occur, and chronic pathologies that previously reached the stage of remission are exacerbated.
Both a general urine test and the Nechiporenko test are not an unambiguous reliable method that allows one to clearly and unambiguously identify the presence of the disease.
Only on the basis of complex instrumental and laboratory research techniques and correct differential comparison can one adequately assess the condition of a pregnant patient. Before starting therapy, in any case, the woman is prescribed an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, cystoscopy, radiography of the kidneys, and also a biopsy in special situations.
The above procedures are supplemented by bacterial culture of urine for microflora , general ultrasound examination of the bladder, kidneys and ureters, which makes it possible to detect and localize possible foci of the inflammatory process. Complex therapy will depend on the identified disease. Possible techniques include:
- Complex drug therapy. Specific drugs, the scheme of their use and other data are selected individually for the patient by a gynecologist, nephrologist and other specialists;
- Diet. All heavy and fatty foods, spicy dishes, sweets, pickles, marinades, mushrooms, legumes, processed foods, alcohol in any case, carbonated drinks are excluded from the diet. The calorie content of the daily diet is limited to physiological norms, the list of healthy products is expanded, there is a transition to fractional meals and cooking dishes using boiling or baking;
- Local therapy. Most often this is the installation of medicinal solutions, as well as catheterization;
- Physiotherapy. In the absence of chronic diseases at the acute stage and with other restrictions, a wide range of techniques is used, including ultrasound and laser therapy.
- Supportive and modulation treatment. Includes the use of immunomodulators such as interferon, hepatoprotectors, probiotics and prebiotics, vitamin-mineral complexes and other medications as needed;
- Surgical intervention. Prescribed in exceptional cases, in severe forms of pathology, when the potential benefit of the intervention significantly outweighs the possible harm to the expectant mother and child.
Causes of high red blood cell count
If red blood cells are found in the expectant mother's urine, the doctor will find out the cause of the hematuria. First of all, he must exclude pathological conditions of the kidneys and cancer. In this case, a woman should not panic, since the appearance of red blood cells in the urine is not always an indicator of a serious illness. Perhaps we are talking about errors in urine collection or more harmless conditions.
Experts distinguish between true and false hematuria. In the case of true pathology, red blood cells are processed by the kidney tubules. This phenomenon means that pathological changes have occurred in the upper organs of the urinary system. If the analysis shows intact blood cells, it means that we are not talking about a true process, that is, the disease has affected the bladder and urethra.
Let us highlight the main causes of hematuria:
- urolithiasis (stones injure the walls of the bladder and ureters, causing minor bleeding);
- pressure of the uterus on the genitourinary system, which often causes stagnation of urine and provokes disorders of the urinary organs;
- bleeding from the genital tract;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- cystitis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis;
- cervical erosion;
- colpitis;
- hormonal disorders;
- injuries of the renal tubules and ureters;
- diabetes;
- quality composition of consumed water;
- scratches, cuts and scratches in the groin area;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- stress factors;
- hot weather.
To find out what caused the appearance of red blood cells in the urine during pregnancy, after examining the woman, a specialist prescribes the following additional tests:
- colposcopy - examination of the condition of the cervix using a special colposcope (microscope);
- gynecological vaginal smear;
- bacteriological culture from the mucous membrane of the cervix and urethra to study the microflora to exclude possible infections, in particular Trichomonas;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and pelvic organs;
- blood tests: repeated general and Nechiporenko tests.
List of dangerous diseases
If we are not talking about functional changes in the body, and the reasons are hidden elsewhere, then most likely it is worth checking for inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. Most often, such problems of an infectious nature cause pain, stinging, burning and problems with urination. To all this is added pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen, often a person may feel weak and have a headache.
The most common reasons for the appearance of red blood cells in the urine of a pregnant woman are:
- cystitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- infections of a sexually transmitted nature.
It is worth noting that in such cases, treatment with folk remedies or self-medication is strictly prohibited, since it can cause serious harm to the health of the mother and child.
The causes of hematuria may not only be infection. Often this condition manifests itself in hypertension, diathesis of hemorrhagic nature, fever, anemia, thrombosis, diabetes mellitus and a number of other problems.
Modern doctors have identified one and a half hundred conditions that may cause the appearance of red blood cells in the urine. Some situations require an examination of all systems in order to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Rules for collecting urine for pregnant women
To exclude the erroneous appearance of leukocytes and red blood cells in the urine during pregnancy, it is necessary to learn how to correctly collect urine for general analysis.
Urine should be collected strictly in the morning, after the usual hygiene - washing (in no case should it be confused with douching). It is advisable to collect urine in special containers designed for this purpose - they are sterile and are sold in every pharmacy.
Immediately before collecting urine, the vaginal opening is covered with a clean gauze swab. You need to collect a medium portion, so urination should begin not into the urine collection container, but past it into the toilet or bidet. Having collected the middle portion, the container must be closed with a lid and delivered to the laboratory as quickly as possible: the container cannot be stored for longer than 2 hours, otherwise this may affect the analysis results. When collecting urine, it is important to ensure that the surface and edges of the container do not come into contact with the woman’s skin and mucous membranes.
If red blood cells are still found in the urine, the doctor usually recommends a Nechiporenko urine test. The technology for collecting it will be the same. It is necessary to again collect an average portion of urine, in which the exact number of blood cells in quantitative ratio will be diagnosed. If the Nechiporenko test shows a positive result, most likely we are talking about kidney damage. This condition requires hospitalization of the expectant mother in a hospital to receive appropriate treatment under the supervision of doctors.
Hematuria and pregnancy
It is worth noting that any analysis can be erroneous, especially if the preparation for its delivery was incorrect. Changed urine color does not always indicate the presence of red blood cells. Sometimes the color may change due to the foods included in the diet. Most often, a general analysis is recommended first.
If red blood cells have been detected within it, the doctor may recommend a sample of three glasses. It is carried out to identify the nature of the origin of red blood cells. In particular, the test is carried out in three containers.
If red blood cells are present in the first portion of urine, then we are talking about lesions of the urethra. Finding them in the second container indicates damage to the kidneys or ureters. If red blood cells were found in the third portion, then we are talking about problems with the bladder.
In addition to the direct number of red blood cells, their structure is also assessed. Normally, blood levels during pregnancy can be from 3.8 to 5.5 10 to 12 degrees / l. Values both higher and lower may indicate the presence of pathology.
It is worth noting that the blood hematocrit indicator is also worth calculating. It indicates the ratio of red blood cells to the total blood volume, using percentages to express it. If this figure exceeds 45 percent, then the pregnant woman will need to be hospitalized immediately.
In this case, infusion therapy is prescribed, which thins the blood. This helps improve the nutrition of the woman and fetus. In general, a pregnancy that proceeds in accordance with the norms should not be characterized by any abnormal tests.
Why is it so important to regularly test your red blood cell levels?
Every person tries to monitor their health, especially for women during pregnancy. Hormonal changes in the body associated with bearing a child change the normal functioning of internal organs and often cause various problems and ailments. This is why pregnancy requires careful monitoring by various specialists.
Timely detection of red blood cells in urine makes it possible to prevent and avoid many diseases if they are treated at an early stage. The immune defense of the expectant mother is weakened, and any infection can harm her body, which will certainly affect the health of the baby, so it is necessary to take urine tests during pregnancy.
A normal pregnancy cannot proceed against the background of poor tests that diagnose hematuria. Red blood cells in the urine are not normal, so if they are detected, it is important to conduct additional research and make sure that there are no serious diseases in the body of the expectant mother. Otherwise, untreated conditions can negatively affect the woman and her unborn child. The decision to prescribe treatment is made by the doctor, taking into account other tests, diagnosis and the patient’s well-being.
Additional Research
If red blood cells were found in a pregnant woman’s urine, most likely she will have to undergo a whole range of additional tests. In particular, it is necessary to fully examine the reproductive system.
A cervical examination and colposcopy are performed. It is necessary to perform a culture, vaginal smear, and check for sexually transmitted infections. An ultrasound of the kidneys will be required, as well as a detailed urine test according to Nechiporenko. In this case, it is very important to follow all the rules for submitting it.
In particular, collection is carried out in the morning. Washing is done first; douching should be avoided. Before collecting urine, it is recommended to cover the vagina with a gauze tampon.
The first portion of the material is released into the toilet, the rest is collected in a container. The last portion is also not required. If it is not possible to accurately collect it at home, you have to use a urinary catheter.
The same delivery scheme should be used for a regular, general urine test. Analysis according to Nechiporenko will allow you to find out the quantitative ratio of red blood cells. It is worth emphasizing that many diseases identified with such an increase are treated inpatiently.
Main reasons for increased red blood cell levels
Red blood cells in urine during pregnancy characterize the condition of the genitourinary organs and kidneys
Increased levels of red blood cells in urine are observed against the background of renal, postrenal and somatic pathologies. Two main groups of diseases can be distinguished depending on whether the shape of the red blood cell is changed or not. This classification allows you to determine the localization of the pathological process:
- altered red blood cells indicate kidney pathologies; in the urine they are partially destroyed and colorless due to the loss of hemoglobin;
- unchanged in 95% of cases indicate pathologies of the bladder, lower organs of the genitourinary system, urogenital tract, while the structure of the cells and their shade do not change.
Other predisposing factors are glomerulonephritis, cervical erosion, diabetes mellitus, autoimmune diseases, nephritis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, urolithiasis, increased pressure of the uterus on the genitourinary organs, impaired outflow of urine of any nature. Excess body weight, pustular lesions, scratches, secondary infection of the skin, and physical inactivity can indirectly influence the occurrence of hematuria syndrome.
Dangerous causes are considered to be uterine bleeding, internal hemorrhages, oncological neoplasms, and tumors of various locations.
What is the reason
Most often the indicator is false. In the later stages, the fetus grows rapidly and puts pressure on surrounding organs, which, in turn, leads to bleeding in the urinary tract.
If we talk about pathologies, then a high rate is provoked by the following diseases:
- cystitis;
- all types of nephritis - pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, etc.;
- infections - genital tract and urinary system.
On forums, women often talk about how altered red blood cells helped prevent the development of pathology, since the mother’s general condition remained stable, that is, without changes. If we are talking about an inflammatory process, then leukocytes will be increased. Often, a woman is prescribed a urine test according to Nechiporenko for research.
It allows you to determine the condition of the genitourinary system and is a fairly effective study. But various ailments of the genitourinary system are not the only reason for the increase in red blood cells. This can also be caused by systemic diseases.
These include:
- high blood pressure, especially if it was observed in the mother and before the “interesting situation”;
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- diabetes.
In fact, this is not a complete list of problems against which there is an increase in red blood cells in the blood. It is clear that no measures to combat the violation will produce results until the cause is eliminated.
Symptoms and types of hematuria
There are two forms of hematuria: micro- and macrohematuria. In the first case, the increase in red blood cells is determined only in the laboratory under a microscope. In the second, the fact of bleeding is visible to the naked eye due to the pinkish color of the urine. Gross hematuria creates a life-threatening condition for the mother and fetus that requires emergency hospitalization. Based on the type of hematuria, the following types are distinguished:
- constant – the erythrocyte balance is disturbed for 7–14 days, while the analysis is carried out at different times of the day;
- recurrent - red blood cells appear along with the characteristic symptoms of inflammation, sepsis, and infectious diseases;
- isolated - the pathological process occurs when the filtration capacity of the kidneys is impaired, and is often combined with other deviations in the biochemical parameters of urine;
- combined, or mixed - an increase in red blood cells is combined with persistent leukocyturia, proteinuria. The appearance of protein in the urine sharply worsens the nephrological picture, allowing one to suspect chronic renal failure and a sharp decrease in creatinine clearance.
Potentially dangerous conditions for a pregnant woman and a growing fetus include constant and mixed hematuria, when an increase in the concentration of red blood cells sharply reduces the level of hemoglobin, impairs oxygen saturation of brain cells, and provokes the development of placental insufficiency.
The main symptoms for almost all diseases associated with the loss of red blood cells in the urine are weakness, malaise, severe drowsiness, depression, and fatigue. At the same time, the risk of edema, gestosis or eclampsia in late pregnancy increases.
Urolithiasis disease
Many women develop urolithiasis during pregnancy. Its prevalence among pregnant women is 0.2-0.8%. In most cases, the disease develops even before the child is conceived, but women are unaware of it. During pregnancy, every third woman experiences a deterioration in her condition.
At the beginning and very end of the period, stones most often move through the urinary tract. The situation is aggravated by the presence of pyelonephritis. Most often, this pathology is diagnosed in women aged 25 to 50 years. Stones can be located in the kidneys, ureters and bladder. The following risk factors for the development of urolithiasis in pregnant women and the appearance of hematuria are identified:
- disturbance of mineral metabolism;
- monotonous food;
- physical inactivity;
- improper drinking regime;
- developmental anomalies of the urinary tract;
- infectious diseases.
Urolithiasis in pregnant women is manifested by the following symptoms:
- renal colic;
- nausea;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- stone passage.
When the ureter is blocked or the bladder is injured, pain occurs during urination. Such women often empty their bladder. Microhematuria is most often observed. It is caused by damage to the veins. In severe cases, the urine takes on a reddish tint. The appearance of blood is observed after renal colic.
In 30% of cases, the disease in pregnant women occurs in an atypical form. In this situation, there are signs of an “acute abdomen.” Sometimes urolithiasis is complicated by pyelonephritis. In this case, there is a risk of developing toxicosis. In the absence of complications, the risk to mother and fetus is minimal. Spontaneous abortion is sometimes observed.
Reference values
The normal concentration of red blood cells in pregnant women does not exceed one cell in the field of view under a microscope
If red blood cells in the urine are elevated, doctors first make sure the data is accurate. A woman should have no more than one red blood cell excreted in her urine, and a man should have up to three. In the second trimester of pregnancy, the content of red blood cells should not change, even against the background of an increase in blood flow to provide the growing fetus with the necessary nutrition and oxygen. In the third trimester, the risk of developing preeclampsia, a severe complication of pregnancy characterized by the presence of edema, protein in the urine and hypertension, increases due to iron deficiency anemia.
Normally, the urine of pregnant women should not contain red blood cells. Even a slight increase should alert clinicians. They will definitely prescribe a repeat or clarifying study. The norm is characterized by a complete absence of red blood cells, therefore, if one cell is detected in the field of view, an additional analysis is performed.
Red blood cells often increase against the background of complicated leukocytosis, proteinuria (with protein in the urine). In many cases, doctors diagnose nephrourological diseases of an infectious and non-inflammatory nature, gestosis, and secondary arterial hypertension.
How can a woman feel?
Hematuria, which is what an increase in the level of red blood cells is called, may not manifest itself at all until a certain time.
But then the woman experiences the following signs of pathology:
- pain in the lower back and lower abdomen;
- burning, itching and speech when urinating;
- there may be an increase in temperature.
To all this is added malaise and weakness. All these are signs of disorders of the genitourinary organs. But with systemic diseases, not everything is so simple. Everything here is individual. For example, if disturbances are observed in the vessels, then bruises may appear on the body, a headache will occur, and the pressure will increase.
And every woman wonders why such phenomena are dangerous for the baby and for herself. If disorders are detected early, it is important to start treatment promptly and regularly see a doctor. In general, this is the case here – different causes and consequences are also different.
For example, in the third trimester, rupture of small vessels is often observed and at this stage of pregnancy this is quite dangerous. The doctor must determine how many red blood cells have penetrated into the body fluid. If it's a little, then there's no reason to worry. And if it is more than expected, then additional tests and treatment will be required.
With systemic diseases, the following complications are possible:
- infection of the baby with sexually transmitted infections;
- damage to the mucous membrane;
- postpartum complications.
But the most unpleasant thing is fetal hypoxia. I think you know what this means. This is oxygen starvation of the baby, the consequences of which can be the most tragic.
Treatment tactics
Red blood cells in urine during pregnancy require not only clarifying studies, but also high-quality, careful therapy. Treatment of hematuria is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause, preventing dangerous consequences for the fetus, and preventing relapse. Therapy is prescribed according to the nature of the underlying disease and includes the following drugs:
- antibiotics for a persistent inflammatory process, especially if the risks to the health of the woman and fetus exceed potential complications;
- plant-based uroantiseptics for long-term use;
- folic acid, iron and calcium supplements;
- infusion of glucose-based solutions;
- preparations for local antiseptic treatment of the genitals.
The norm of red blood cells and the reasons for its excess
The norm for elements such as red blood cells in urine during pregnancy is 0-4. If more of these particles are detected, the doctor may suspect that the pregnant woman is developing a serious illness. But this does not mean that red cells during pregnancy are detected in the urine only if pathology develops.
It is worth knowing that increased red cells in the urine can be not only due to the development of pathologies or indirect diseases, but for physiological reasons.
Red blood cells that have been processed by the kidney tubules are related to true hematuria. This means that the reasons for the increase in red blood cells lie in the urinary system. If blood cells are detected in an intact state, this means that hematuria is false and the reasons for its development lie in the bladder or urethra.
In a situation with true hematuria, the reasons that provoke the growth of red blood cells in the urine may be as follows:
- Venereal infection;
- Kidney diseases;
- Cystitis;
- Diabetes.
All these reasons are serious diseases that cannot be delayed in treatment. In rare cases, red blood cells of the true type appear in the urine due to anemia, hypertension, developing thrombosis and aneurysm. But these are not all the reasons due to which the norm of red blood cells becomes exceeded. So, they can become elevated due to the development of:
- Urolithiasis. The presence of kidney stones can provoke the appearance of blood cells by being located in one place. Here, the reasons for the increase in red blood cells lie in bedsores, which, when stones are constantly burned in one position, begin to provoke the release of blood elements. Sand can also provoke untrue hematuria. Moving along the urinary canal, it injures the internal surfaces of the urethra and ureter;
- Uterine bleeding. In this case, it does not mean that the urine turns red. Only 15 red blood cells are enough to detect bleeding. Most often, it is based on the results of a urine test that a doctor promptly identifies a risk of miscarriage in a pregnant woman;
- Cervical erosions. If a pregnant woman previously had untreated erosion on the cervix, then later during pregnancy, due to the dilation of the blood vessels in them, red blood cells begin to come out;
- Colpitis.
Clarifying the diagnosis
Uterine bleeding does not cause changes in the color of urine, so you can guess about it mainly from tests.
In case of uterine bleeding, the slide should contain from 1 to 15 red blood cells in the field of view (the area limited by the contours of the tube when viewed through a microscope).
Colpitis is an inflammation of the vaginal mucosa. It can also occur in pregnant women, due to the fact that their vaginal cells are filled with glycogen; colpitis can cause the appearance of blood cells in a urine test.
Glycogen in cells is a very nutritious and fertile environment for various kinds of microorganisms. They penetrate directly into the intercellular space and damage cell membranes. This is how red blood cells end up in the urine.
Urolithiasis is caused by large deposits of salts in the kidneys. Stones can be in one position, causing pelvic bedsores - trophic ulcers. Of these, red blood cells can enter the urine. Also, kidney stones can move with the flow of urine, causing severe pain.
If the stones have not yet formed, sand can also cause pain and damage. Moving along the urinary canals, it causes damage throughout the urinary canal, right down to the ureters and urethra. In this case, red blood cells appear in the urine, but not due to disease of the kidneys themselves, but due to injuries to the urinary system.
Of all the signs, cervical erosion is the least dangerous. Erosion is caused by softening of the cervix. Vaginal vessels dilate and may allow some blood elements to pass through.
Gross hematuria often occurs as a result of injuries or emotional and physical stress, or hormonal imbalances. It is not dangerous, but it is necessary to take a simple urine test over several days to determine the cause.
The appearance of blood cells in a urine test can also be influenced by the quality of water consumed. If a pregnant woman drinks a lot of water containing chlorine, there may be red blood cells in the urine. In this case, doctors prescribe more purified drinking water and special medications to neutralize the effect of chlorine.
Increased red blood cells in the urine during pregnancy also occurs in the tests of mothers who spend quite a lot of time at the computer.
Also, an increase in the level of red blood cells in the urine in the early stages of pregnancy can be caused by an enlarged uterus, which begins to put pressure on the bladder.
The outflow of urine is blocked and stagnation occurs. It can cause kidney problems and impair blood circulation.
Of all the reasons for the appearance of blood cells in a urine test, only uterine bleeding is a hidden threat of miscarriage.
When detecting red blood cells in urine, a three-glass test is used. When collecting urine, the first portion is released into the first jar, the second into the second and the third into the third.
If red blood cells are found in the first portion, the problem may be inflammation of the urethra. The presence of red blood cells in the second part of the urine indicates diseases of the kidneys and ureter. Red blood cells in the third indicate bladder problems.
In a general urine test, urine is examined for protein, leukocytes, red blood cells and other indicators. Increased red blood cells in urine - what does this mean? Diseases that may cause blood in the urine.
Sexual infections, urolithiasis, mechanical damage to the bladder - all this can cause a burning sensation when urinating. Read more about this pathology here.
Do you know what a high level of leukocytes in the urine of pregnant women indicates? In this topic https://mkb2.ru/tsistit-i-mochevoy-puzyir/u-zhenshhin/pri-beremennosti/norma-lejkocitov-v-moche.html you will learn what leukocytes are responsible for and what their normal indicators are.
Physiological reasons
Despite the fact that many of the reasons that provoke an increase in red cells during pregnancy are serious. There are also a number of reasons that, in fact, are not dangerous and can be eliminated by a pregnant woman on her own:
- Poor quality water. Frequent consumption of water with a high chlorine content. In order for the norm of red blood cells to be restored, you just need to start drinking high-quality water;
- Scratches and other types of injuries in the groin area. High-quality treatment of wounds and keeping them clean will help avoid the likelihood of infection and increased inflammation;
- Sedentary lifestyle. Frequent walking is recommended for pregnant women. The less a pregnant woman moves, the higher the risk of red blood cells appearing in the urine, as well as complications during childbirth;
- Stress factors. Of course, it is impossible to avoid them all, and in case of difficult changes in life, to reduce the risk of developing hematuria, it is recommended to visit a doctor and consult about taking sedatives;
- Heat. It can provoke not only the development of hematuria, but also provoke a number of other health problems. You can avoid its effects during pregnancy simply by not going outside during the day and taking a refreshing shower more often.
It is worth knowing, despite the fact that the reason for the increase in red blood cells in the urine may simply be such physiological factors. To exclude the possibility of developing serious pathologies, if a repeat analysis reveals an increased level of red blood cells, it is recommended to undergo an additional examination of the body.
As an additional examination, a pregnant woman may be prescribed a colposcopy, an ultrasound of the kidneys, a vaginal smear and a blood test.
Symptoms and possible complications
If the color of urine and its transparency do not change during pregnancy, a woman needs to pay attention to alarming symptoms:
- frequent urination, accompanied by a burning sensation, pain in the lower abdomen may indicate a urinary tract infection;
- heaviness or discomfort in the lumbar region, an increase in body temperature in the evening to 38°C and above are characteristic of kidney diseases.
Specific symptoms indicating that there are increased red blood cells in the urine are not clearly expressed, so a pregnant woman needs to pay attention to her general condition, poor appetite, weakness, and blood pressure levels. You cannot avoid scheduled tests and contacting a gynecologist, since hematuria is fraught with negative consequences:
- chronic renal pathologies, urinary retention in the body, edema;
- malignant tumors increase in size during pregnancy and can metastasize;
- even minor bleeding of the placenta affects the fetus - hypoxia occurs, and pregnancy can be terminated.
During this period, a woman is required to pay close attention to her health.
You cannot self-medicate or limit yourself to traditional medicine. Only timely diagnosis and qualified treatment will allow you to bear a healthy child.