Womanjournal » Motherhood » Pregnancy » How to feel the uterus during pregnancy? How to detect pregnancy in the early stages without a test?
How to feel the uterus during pregnancy? Usually, it is by feeling the uterus that it is possible to determine whether the girl is in position. In general, pregnancy can be determined at fairly early stages due to suggestive and reliable signs. Many external signs of an “interesting situation” were learned to be recognized in ancient times, but even today they remain quite relevant. It goes without saying that almost all of them relate to speculative, probable signs.
Thanks to the development of medicine, an excellent opportunity has arisen to compile a whole range of reliable, obvious signs. However, they become reliable and effective only in the fourth or fifth month of gestation. Therefore, to determine pregnancy in the initial stages, you can only be guided by probable signs. These include: cessation of the menstrual cycle, severe irritability of the girl, nausea accompanied by vomiting, changes in taste preferences, addiction to spicy and sour-salty foods, the appearance of fat (especially in the abdominal area), pigmentation on the face. In addition, probable signs of early pregnancy include a bluish tint to the vaginal mucosa, an increase in the size of the uterus, changes in its shape and consistency, as well as hardening of the mammary glands.
However, all of the above signs make sense only when they are present together. That is, individually, similar signs can occur in girls who are not pregnant, in which case they will arise for completely different reasons. For example, the cessation of menstruation can occur as a result of hormonal imbalances, infectious diseases, nervous strain, or be associated with vitamin deficiencies of the current season. The size of the uterus may increase due to a growing tumor, and skin pigmentation can be caused by a number of other reasons. Therefore, if you are wondering whether it is possible to feel pregnancy yourself, then remember that this can only be done in combination with other signs.
What is the complexity of the method?
The female body is designed in an amazing way - immediately after fertilization of the egg, the active growth of the fertilized egg begins and moves into the uterus.
Active hormonal and physiological changes immediately begin - the woman prepares for the successful bearing and birth of a child. But how can you independently determine pregnancy by looking at the cervix, even before going to the antenatal clinic? When examined by a gynecologist, you can even determine the gestational age by touch - the specialist uses palpation to determine the size of the organ with the embryo growing inside. You can give a more precise date if you keep a cycle chart where the days of ovulation are marked. At home, self-diagnosis will only be approximate. It is necessary to have at least a general idea of the size and shape of the cervix, its density and color before conception and after the fact, as in the figure.
Not all women, even those who have given birth, have a complete understanding of the internal genital organs and how they work. What is the role of each reproductive segment in PA, during fertilization and gestation? If you do not have this basic knowledge, it is difficult to understand how to determine pregnancy by the cervix.
Looking into yourself “there”, even with a mirror, is problematic, especially for overweight ladies. The only way to compare the cervix before and after pregnancy is to feel yourself in the vagina during hygiene procedures to compare the changes.
Attention: This type of diagnosis is very accurate, but it is also considered in terms of sensations and symptoms. Due to the difficulty of conducting a self-examination, it is rarely used even by those who know how to determine pregnancy themselves by looking at the uterus.
Pregnancy examinations
The uterus undergoes significant changes during pregnancy. After conception, a woman should be more attentive to her health and not ignore changes that signal possible pathologies. If, after the first examination, the fact of fertilization is established, then the cervix should be checked throughout the entire period of gestation. This will help avoid complications and promptly identify some pathologies and diseases. In 9 months, the woman will have to visit a doctor in order to get tested for flora. For this purpose, a smear is taken, and cytology tests are also performed. These basic procedures are performed at least 4 times. A special schedule for such examinations is provided.
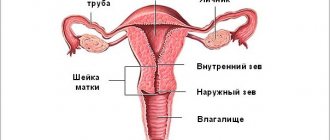
This canal is one of the most important organs not only for the woman, but also for the child during childbirth. This is the path for the baby through which he is born. Therefore, it is very important to monitor the condition of this part of the uterus.
Where is the cervix located?
The uterus is an internal organ and is therefore not visible. The lower part of the cervix extends into the vagina; this is the visible part, which is used to make a visual diagnosis of the organ. It is tightly rooted in the vagina, so all sensations are transmitted from the walls of one organ to another (during PA and touching).
You can detect pregnancy by palpation by the uterus, and visually by the cervix. The internal cavity of the uterus constantly produces mucus, including spotting during menstruation. A plug is formed in its neck, clogging the internal organ to protect against infections and moisture from the external environment.
Attention: Do not think that the cervix is a secondary organ; the level of protection of the fetus and its retention during pregnancy depends on its condition. If it has lost firmness and elasticity, the doctor, upon examination, can determine an upcoming miscarriage and take measures to preserve the pregnancy. The specialist also knows how to determine pregnancy with uterine fibroids (internal neoplasm from pathological tissue proliferation). During a visual examination, the doctor can evaluate only the cervical part, but this is enough to assess the health of the entire reproductive organ.
The cervix has the simplest structure - a rounded muscular body, slightly protruding in the upper part of the vagina. It differs in tissue structure and color from the vaginal walls. This pinkish lump is covered with mucus and has a small hole in the center - the cervical canal. It is closed in the normal state, but expands slightly during menstruation.
The passage to the uterus is filled with a mucus plug. The size of the cervix is small - approximately 2.5 cm in circumference to 4 cm in length. It's amazing how this miniature light pink "tunnel" opens and widens during childbirth to allow the baby's head to emerge into the passage!
During ovulation, the mucus plug liquefies so that the most active sperm can overcome this barrier. The cervix rises slightly and becomes softer, making the vagina more free for penetration of the male organ.
How to detect pregnancy by touch
Every gynecologist knows how to determine pregnancy by the uterus, even in the early stages - the lower part of this organ is informative. It shifts, the color, size and density of tissues change, they say that the cervix can be soft and “oaky”. These changes are considered the most significant signs of pregnancy, along with the absence of menstruation on time. In addition, traces remain on the cervix:
- transferred operations;
- abortions and miscarriages;
- safe birth;
- internal uterine pathologies.
You can understand a lot by the state of the vaginal part, for example, if the neck is flat - the woman has not given birth, if the neck is cone-shaped - there has been childbirth. But it is not only possible to determine pregnancy by touch by touching the cervix. Really understand the phase of the cycle (preovulation, ovulation, premenstrual).
A specialist can easily diagnose the accomplished fact of fertilization, even the approximate gestational age. In nulliparous women, this pharynx is small and rounded; after childbirth, it closes like a slit. After a caesarean section, the cervix is more similar to the cervix of a nulliparous woman, although the cervix becomes slightly larger in size.
You need to know about this before determining pregnancy by touch in the uterus:
- In women, before pregnancy, the cervix is hard, approximately like the wings of the nose; after conception, it is softer, approximately like lips.
- Before pregnancy, the cervix has a velvety pink color, after which it turns blue (from active blood circulation and the proliferation of the vascular network in order to actively supply the fetus with nutrients).
- Under the influence of progesterone (hormone), the cervix lowers - a consequence of completed fertilization.
Let's return to the question “how to determine pregnancy by touch?” Considering the above - only in terms of relative softness and lowering of the neck. Visual changes are difficult to notice without a special inspection tool.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
One of the main tasks of gynecology is to prevent miscarriages and premature births. A bad signal in this case is the deterioration of the composition of the cervix and the opening of the internal pharynx. Very often, the woman herself does not notice such a deterioration in her condition, so a certain procedure for medical examinations has been established for pregnant women.
Palpation
Only a doctor can correctly diagnose using a vaginal examination by touch; you yourself will not be able to determine anything, but will only cause hypertension or get injured, which threatens miscarriage and erosion. For this reason, you should not self-diagnose if you want to continue your pregnancy.
Upon palpation, the following characteristics are determined:
- What color is the cervix?
- Where is it?
- What is its length?
- What shape does it have?
- What density is it?
Ultrasound
After 12, 20 and 30 weeks of pregnancy, a woman should undergo a routine ultrasound, but a transvaginal sensor (internal) is used only if palpation suggests a short cervix. This pathology is the reason for more frequent ultrasound scans at intervals of approximately 2 weeks. Indications for such frequent examinations also include:
- Twins.
- Low progesterone.
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI) - early dilatation of the cervix.
- Previous miscarriage.
- Previous premature pregnancy.
- Presence of scars.
- The presence of deformations and anomalies of organ development.
- Polyhydramnios.
- Large child.
In such cases, cervicometry is useful - this is a type of ultrasound that allows you to measure the length of the lower part of the uterus during pregnancy.
Did you know? The largest baby on record, weighing 17.04 kg, was born in 2012 in China.
What changes occur in the cervix after conception?
Only a specialist can determine minor deviations in the condition of the reproductive organs. There are individual characteristics of the body and pathology, but usually you have to focus on average indicators before determining pregnancy by the cervix. It is very difficult to assess tissue density on your own without medical education and palpation experience.
Attention: If something “appeared” during self-examination, do not rush to inflate your fantasies and make a diagnosis for yourself! Up to 6 weeks, it is difficult to understand by self-feeling whether you are pregnant or not. Even if there is a pathology, this should be dealt with by a specialist who can really determine the condition of the reproductive organs. For example, a too hard cervix may indicate hypertonicity (muscle tension) and may “signal” an impending spontaneous miscarriage. This rarely happens in early pregnancy, so don't panic after feeling it. The best way to avoid pregnancy loss is to go to the nearest medical center.
During the examination, the specialist will pay attention to other signs of pregnancy:
- Blueness of the cervix and vaginal walls.
- Slight swelling of the external genitalia.
- Changes in the size, shape and consistency of the uterine walls (rounded and enlarged, becoming soft, called the “Horwitz-Hegar symptom”) over a period of 4–6 weeks.
- After conception, the uterus becomes easily excitable, prone to sudden contractions, becomes dense and sags when examined with both hands - from the vagina and from the abdominal side, this is “Snegirev’s symptom”, a little later it takes its primary position.
- Some mobility of the cervix or “Gubarev-Gaus symptom”, some women have a “Genter symptom”, this is a forward deviation of the uterus with a comb-like thickening in the center.
- Uterine asymmetry or “Piskáček’s sign” is observed in a bicornuate uterus, with one horn slightly larger than the other - a normal phenomenon as long as the embryo develops on one side of the organ. It will become rounder over time, around the 8th week of pregnancy.
These are the features - how can they be determined by touch during pregnancy, if not a specialist? Any pathology is examined using ultrasound. There may be an increase in watery and bloody discharge, rapid heartbeat (from an increasing load on the bloodstream), and frequent urination (due to displacement of the uterus). There are congenital pathologies and hormonal disorders. Only a doctor can assess the real condition of a pregnant woman. Especially if there is a suspicion of an ectopic pregnancy, when the embryo is stuck in the fallopian tubes. We hope you are doing well!
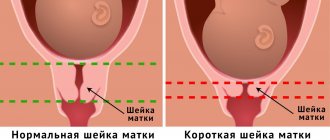
Cervical shortening
Pressure on internal organs increases as the fetus grows. The lungs rise up and the cervix flattens. She still performs her functions, but is gradually preparing for childbirth. In case of pathologies, the doctor notices that the neck has greatly decreased in size and has become too short. It can no longer perform its protective properties. In the early stages, this pathology develops due to hormonal imbalance. The woman’s condition in this situation requires constant medical supervision.
Symptoms that indicate shortening of the cervix:
- fabrics are soft to the touch when they should be dense;
- high organ mobility;
- the cervical lumen is increased.
Signs of the development of this deviation are mild, so you should not rely only on palpation. It is necessary to undergo ultrasound diagnostics to confirm the diagnosis. There are real chances of miscarriage due to a weakened cervix.
Along with tissue softening, bleeding is observed. This indicates that the tone is reduced and the organ is no longer able to perform its functions independently.
Table of normal cervical size:
Using ultrasound, the maturity of the uterus is determined:
Test results:
- 0-3 points - the neck is immature;
- 4-6 - not mature enough;
- 7-10 - mature.
Until 37 weeks, an immature cervix is considered normal. The situation changes when childbirth occurs. It should be ripe by the last weeks of pregnancy. The neck first drops low and then smoothes out. The passage to the child becomes open, and labor activity in the absence of pathologies is not in danger.
How the cervix changes after conception
When pregnancy occurs, physiological changes occur in a woman's body. The process can be monitored using a two-manual examination method during a gynecological examination. The changes are:
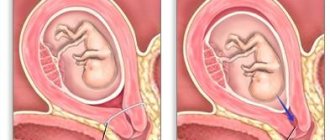
- Weeks 1–16. At the beginning of pregnancy, the cervix softens a little and becomes mobile. The color changes from pink to deep red. The muscular organ descends and moves towards the posterior uterine wall, and the cervical canal decreases in diameter.
- Weeks 16–28. There is slight swelling of the tissues. The organ descends lower, becomes softer in density, and its length decreases slightly. The cervical canal is tightly closed.
- Weeks 28–39. The internal pharynx expands. The cervix softens as much as possible, its internal segments are smoothed out. The opening of the organ begins before childbirth.
Cervical length in early pregnancy
The growth of the organ in the first weeks after conception is due to changing hormonal levels. Normally, the cervix in the early stages of pregnancy is 3.5–4 cm in length, as in the photo in gynecology textbooks. Changes in this indicator are monitored using ultrasound. Dilatation of the cervix during pregnancy according to the norms:
- 10–14 weeks – 3.5–3.6 cm;
- 15–10 – 3.8–3.9 cm;
- 20–24 – 4 cm;
- 25–29 – 4.1 cm;
- 30–34 – 3.7 cm;
- 35–40 – shortening to 2.9–2.7 cm.
Pregnancy position
The position of the uterus during early pregnancy does not change, but over time, when the fertilized egg turns into a fetus, it increases significantly in size. It is very important to monitor the cervix not only in the early stages of pregnancy; any changes that may threaten premature birth or miscarriage can be predicted by the appearance of the canal. The state of women's health depends on how the cervix looks in the early stages of pregnancy. During early fertilization, it becomes softer, this is due to the action of progesterone and increased blood circulation in this organ. If a woman has hypertonicity, which is dangerous for the baby’s health, then upon examination this part of the uterus will be hard. In such cases, it is necessary to take measures to eliminate the threat of miscarriage.
The specialist may recommend bed rest, calmness, and medication. It is possible to preserve the health of the woman and fetus in the pathology department. The earlier intrauterine pregnancy is diagnosed, the greater the chance that examination will reveal changes that are not typical for this condition. Then the necessary measures will be taken for the normal course of pregnancy.
Signs of pathologies
During pregnancy, especially multiple pregnancy, a woman’s risk of developing abnormalities increases. Pathologies include:
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency is a premature opening of the cervix at 8–12 weeks, often leading to spontaneous abortion.
- Ectopia (erosion) – purulent, mucous discharge, pain during coitus.
- Dysplasia – bloody discharge, especially after sexual intercourse.
- Human papillomavirus – an increase in the size of condylomas (warty formations) in the second trimester.
- Shortening of the cervix – pressure on the bladder, shooting pain.
- Endocervicitis - profuse bleeding, itching of the external genitalia at any stage of pregnancy.
Obstetrics - Palpation of the fetus in the uterus
Page 28 of 116
If there are reliable signs of pregnancy, it is necessary to determine the position and position of the fetus, the position in appearance, the number of fetuses, and also find out whether the fetus is alive or dead. All this should be carried out in strict sequence, according to the diagram below. Rice. 60. Gluteal (mixed) presentation. Second position. Posterior view During the examination, the pregnant woman should lie on the couch in a horizontal position on her back. The midwife stands or, better yet, sits on the right side of the pregnant woman, turning to face her. When externally examining the abdomen of a pregnant woman during long periods of pregnancy, four techniques are used. The first method of external examination (Fig. 61). Both hands placed on the fundus of the uterus are slowly brought closer together; having thus grasped the uterus, determine the height of its fundus in relation to the navel, and at a later date - in relation to the xiphoid process of the sternum; in this case, it is sometimes possible to identify a large part of the fetus located at the fundus of the uterus. This technique mainly determines the duration of pregnancy and the position of the fetus. The second method of external examination (Fig. 62). Both hands are moved from the bottom to the side walls of the uterus and, alternately with the right and left hands, they try to palpate parts of the fetus through the wall of the uterus; on the opposite side, where small parts cannot be palpated, it is possible to palpate the back of the fetus; This technique determines the position and position of the fetus. The third method of external examination (Fig. 63 and 64). With the right or left hand, with the palm of the hand and the thumb held wide apart, clasp the lower segment of the uterus; the fingers are carefully immersed into the depths, where they try to palpate the part of the fetus located at the entrance of the pelvis, i.e., determine which part of the fetus is present - the head or buttocks, or whether the presenting part is missing, which happens, for example, in the transverse position.
Rice. 61
External examination of a pregnant woman* First appointment.
Rice. 62. External examination of a pregnant woman. Second appointment.
Fig. 63. External examination of a pregnant woman Third appointment.
Rice. 64. Examination of a woman in labor at the third appointment
The head is usually palpable in the form of a dense ball and, if it is not yet established at the entrance of the pelvis, it easily moves, running between the thumb and other fingers. Rice. 65. External examination of a pregnant woman. Fourth reception. In everyday practice, this technique is used most often; however, it is not always done correctly and it is not always taken into account that its frequent use, especially if it is done roughly, is not indifferent to the pregnant woman. When roughly and quickly grasping the lower segment of the uterus, a response from the abdominal wall immediately occurs—the muscles of the abdominal wall tense, which makes further palpation extremely difficult and requires the use of great force, and this causes pain, which in turn leads to even greater tension in the abdominal wall. If the examination is continued in this way, it will most likely be of a violent nature, will cause pain and will not allow one to clearly palpate the presenting part of the fetus. It should be added that sometimes from the very beginning they grasp the lower segment incorrectly - not with all fingers, but, plunging into the depths, they press the ends of the fingers into the walls of the lower segment, which greatly injures the latter and can lead to the formation of significant hemorrhages under the peritoneal cover of the uterus. The third technique should be done first of all very carefully, gently, the fingers should be immersed into the depth slowly, without causing tension in the abdominal muscles, and only after reaching the depth, the presenting part of the fetus should be carefully squeezed between the thumb, index and middle or middle and ring fingers. In this case, it is better if the other hand lies on the fundus of the uterus and correctly positions and fixes the uterus.
The fourth method of external examination (Fig. 65) is usually used in cases where the third method fails to obtain a clear impression of the presenting part, when the presenting part has descended into the pelvis. To carry out the fourth reception, stand with your back to the pregnant woman’s head and, grasping the lower segment of the uterus with the ends of the fingers of both hands, try to very carefully penetrate as deep as possible into the entrance of the pelvis. With a cephalic presentation, the ends of the fingers rest against the round body, and sometimes you can feel the back of the head on one side and the chin on the other; when presenting with the pelvic end, the fingers feel the large, but softish consistency part of the fetus. Rice. 66. Listening to the fetal heartbeat with an obstetric stethoscope. The same technique makes it possible to determine which part of the head, as they say, which segment of it (larger or smaller) is located above the pelvic inlet and which head entered the pelvic inlet (located below the plane of the pelvic inlet).
Auscultation
After determining the position and position of the fetus, listen to the fetal heartbeat with a special obstetric stethoscope (Fig. 66). Usually, the fetal heartbeat can be heard starting from the end of the fifth lunar month of pregnancy, and then with each month it can be heard more and more clearly. The heartbeat can be clearly heard closer to the head and on the side where the back of the fetus is facing. So, for example, if the back is facing to the left and the head is down (cephalic presentation, first position), the fetal heartbeat is most clearly heard to the left of the midline of the abdomen, below the navel; When presented with the pelvic end, the fetal heartbeat is best heard above the navel. When the fetus is in a transverse position, the heartbeat is heard at the level of the navel, on the right or left, closer to the head. Depending on the type of location of the fetus, its heartbeat will be heard more clearly, either closer to the midline of the abdomen, or further from it (Fig. 67); in front view - closer, Fig. 67. The place where the fetal heartbeat is most clearly audible in its various positions. 1 and 2 - with breech presentation in the second position; 3 and 4 - with cephalic presentation of the second position: 5 and 6 - with breech presentation of the first position; 7 and 8 - with cephalic presentation in the first position. in posterior view, further from the midline of the abdomen. As the presenting part of the fetus moves and descends into the pelvis, the place of a distinct heartbeat also moves - it gradually drops lower and gets closer and closer to the midline. The fetal heart rate at the end of pregnancy is usually 120-130 rhythmic beats per minute. When listening, in addition to the fetal heartbeat, a blowing noise of the uterine vessels can be heard, which occurs when blood flows through the tortuous vessels of the pregnant uterus. The nature of this noise does not correspond to the fetal heartbeat; in frequency and rhythm it corresponds to the mother’s pulse. The pulsation of the abdominal aorta is also heard, coinciding in frequency with the mother’s pulse. Vaginal examination is performed in some cases in late pregnancy and childbirth (p. 198). In late pregnancy, especially shortly before childbirth, vaginal examination poses a great danger due to the possibility of infection in the birth canal; if, according to available indications, it is necessary to resort to a vaginal examination, the midwife is obliged to apply the strictest measures of asepsis and antisepsis in relation to both her hands and the external genitalia of the pregnant woman. A vaginal examination (Fig. 68) makes it possible to determine the condition of the vagina, cervical canal, the degree of opening of the external pharynx, to establish whether the amniotic sac is intact, which part of the fetus is presented, how it is presented, in which part of the pelvis it is located; with a high-standing head, a diagonal conjugate is certainly determined (p. 149).
- Back
- Forward
How to recognize pregnancy by the cervix yourself
The method of self-diagnosis of conception is based on palpation of the organ. Determining the gestational age at home:
- Take a squatting position or placing one foot on the edge of the bathtub.
- Insert your middle finger deep into the vagina.
- If you feel a round, moist and soft tubercle with a small hole - this is a raised cervix, the probability of pregnancy is high.
Self-diagnosis of conception is carried out in extreme cases. It increases the risk of pathologies. Recommendations:
- Carry out self-diagnosis if there is no infection.
- Wash your hands and cut the nails on your middle or index finger.
- Use the same pose, time to explore.
On one's own
If you ask a specialist a question about how to palpate the uterus during pregnancy, with a high degree of probability he will be against carrying out such a procedure at home. But even if such restrictions do not stop the patient, she must adhere to the following rules:
- It is strictly forbidden to perform actions too often;
- No movement should be accompanied by pain or discomfort;
- All actions must be performed slowly and smoothly;
- During the examination, you need to relax as much as possible.
After careful preparation, the girl should take a horizontal position, relax the muscles of the lower abdomen and pelvis, and begin to gently palpate the abdomen from above in the place where the uterus is supposed to be located. If pain occurs, the procedure should be stopped.
Self-diagnosis is carried out in a relaxed state. Source: zdorovia.net.ua
If during the diagnosis the walls were soft to the touch, we can tentatively assume that pregnancy has occurred. However, only a doctor can confirm this fact after examining the woman in a chair. At about 3-4 months of gestation, the uterus descends to the bottom.
Also, sometimes girls ask how to feel the uterus at 11 weeks of pregnancy. At this time, in the lower abdomen of most expectant mothers, a tubercle appears under the palm of the hand. It is very important not to press too hard so as not to injure the child. Actually, starting from this period, most likely, the position of the reproductive organ will be determined without difficulty.
Cervical position
The beginning of the menstrual cycle is characterized by the female body preparing for conception. After the end of menstruation, the cervix begins to pull up and close the cervical canal . The discharge stops, and in the meantime the endometrium begins to grow in the uterus. Gradually, the cervix can descend into the vagina, but the canal continues to be tightly closed. This is necessary to prevent infection from entering the woman’s body.
In the days before ovulation, the cervix rises sharply and the canal opens. The period of ovulation is characterized by copious mucous discharge. In gynecology they are called “egg whites”. The discharge is similar in consistency.
If conception does not take place, then the cervix begins to prepare for the arrival of menstruation. It goes down into the vagina and changes the degree of its hardness. Shortly before menstruation, the cervix becomes dry and hard. The cervical canal is completely compressed, which prevents sperm from entering the uterus . A woman's fertility is reduced during this period. With the onset of menstruation, the cervix rises and pushes out the rejected layers of the endometrium.
What does the cervix look like before menstruation?
In accordance with the day of the cycle, the cervix not only changes its position every month, but also becomes different to the touch. Its structure also changes.
What does the cervix look like before menstruation? To understand this, you need to understand what processes occur in the female body. After ovulation, which occurs in the middle of the cycle, the woman’s body and uterus prepare to fertilize the egg. Additional endometrium appears. There is a gradual change in shape and enlargement of the uterus before the onset of menstruation. Before ovulation, the cervical canal opens so that sperm can freely penetrate to their target. When ovulation ends, the canal gradually narrows and the uterus begins its preparation for a possible pregnancy. Find out the norms for endometrial thickness by day of the cycle in the article at the link.
Determination of pregnancy by touch, normal
In the very first weeks of pregnancy, an experienced doctor can determine its presence by looking at the cervix. This is also possible through independent palpation .
A gynecologist determines pregnancy according to the following criteria:
- Size of the uterus and cervix;
- Shape of the cervix;
- Position of the cervix in the vagina;
- Hardness degree;
- Neck color;
Only a doctor can determine the color of the cervix using special instruments. During pregnancy, the cervix loses its pink tint and becomes bluish . This occurs due to active blood flow to the genitals. The position of the cervix during pregnancy is high. The cervical canal narrows because ovulatory or menstrual flow is not expected. To the touch, the neck becomes soft and even slightly loose in texture.
Determination of position by self-palpation
There are situations in which it is extremely important for a woman to find out about the presence of pregnancy even before the delay and before going to the gynecologist. In this case, independent palpation of the cervix can provide partial assistance. It must be carried out strictly with clean, disinfected hands, as there is a risk of infection. For a more accurate result, it is recommended to conduct the study regularly over several cycles . You can understand what position and texture the neck has only based on comparison.
To avoid unpleasant consequences, you should pay attention to the rules for self-palpation of the cervix.
- Hands must be clean and disinfected. If this is not possible, then you should wear sterile gloves.
- The nails of the middle and index fingers should not be long, as there is a risk of damaging the surface of the vagina.
- The most comfortable postures for diagnosis are lying on your back, spreading your legs and squatting.
- You should push two fingers into the vagina until they rest against the cervix.
Disadvantages of the home diagnostic method
Despite the simplicity of manipulation, determining an interesting position by touch, at home, contains some negative aspects.
They are as follows:
- Lack of proper sterility leads to the emergence of infectious diseases ;
- Careless movement can result in damage. As a result, erosion may form, which is difficult to cure;
- The reliability percentage of the method is not as high as consulting a gynecologist or using pregnancy tests;
- If you are pregnant, you can cause harm by palpating the tone of the uterus ;
What is a short cervix during pregnancy?
Pregnancy may not always proceed without problems. There is a pathology called shortened cervix .
This condition carries a risk of miscarriage. The cervix becomes short under the influence of various injuries or excessive pressure due to the size of the fetus. This is also typical for polyhydramnios. This pathology can be detected by examining and palpating the cervix. Its texture becomes too soft. The neck itself becomes more mobile. The cervical canal is not closed; a gap is visible in it. The degree of anomaly may vary. Early diagnosis allows you to take timely measures and maintain the pregnancy.
Sources:
https://empiremam.com/beremennost/opredelenie-beremennosti/kak-po-sheyke-matki-opredelit-beremennost.html https://mosmama.ru/10838-kak-po-shejke-matki-opredelit-beremennost-metodika -samodiagnostiki.html https://mamavika.com/beremennost/zdorove/sheyka-matki-pri-beremennosti-na-rannih-srokah-na-oshhup.html
Possible complications and treatment of abnormalities
Complicated situations during pregnancy are shortening and lengthening of the cervix.
Short
The fact that in an interesting position the organ becomes softer causes a decrease in its length. However, a gradual reduction in length should not occur too quickly: only before birth the size can be 1-1.5 cm, the rest of the time - no less than 3 cm. Particularly dangerous periods for bearing an unborn child are 6-7 weeks and 23-25 weeks .
Too rapid reduction in length during pregnancy is called a “short cervix.” This condition is dangerous due to premature birth or miscarriage.
A woman should closely monitor the deterioration of her health, especially after the 16th week, when the progressive growth of the fetus begins.
We also advise you to learn about such diseases of the uterus as: metroendometritis, endometritis, leukoplakia, dysplasia, erosion
Long
If the length of the organ exceeds the norm, this may be caused by:
- congenital anomalies;
- regular inflammatory processes;
- previous injury;
- operations.
In this case, the organ remains hard and narrowed, which causes prolonged contractions and weak labor. The baby cannot get out and feels a lack of oxygen, so doctors have to use additional stimulation.