Ectopic or ectopic pregnancy is considered one of the unpredictable, and therefore insidious, pathological gynecological conditions. The incidence of such pregnancies is about 0.8-2.4% of the total number of pregnancies. The most common option is considered to be ectopic tubal localization (about 98-99% of cases). After an ectopic conception, a woman may not have children at all if the pathology occurred with complications such as ruptures, etc. Pain during an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages helps to understand the presence of a problem in a timely manner.
A serious approach to planning is very important
Description
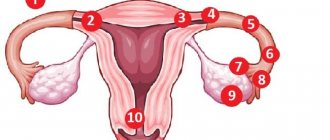
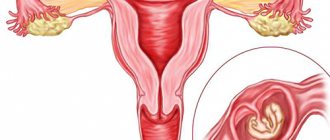
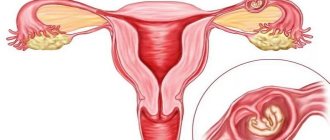
In a normal pregnancy, the egg implants in the fundus or body of the uterus. The difference between an atypical pregnancy is that the egg is not in the uterus. It has a different localization: in the fallopian tubes, ovary, abdominal cavity. Such a pregnancy cannot develop; it is life-threatening and is a medical indication for its termination. It has been noted that pain during ectopic pregnancy in the early stages is very severe.
The woman herself cannot suspect the pathology. After all, it is clinically no different from a normal pregnancy. Many people ask: “Do the breasts hurt during an ectopic pregnancy? Is there toxicosis? Is there sleepiness?
Yes, sure! Everything is the same here: menstruation is delayed, the mammary glands become enlarged, the milky passages are outlined, dizziness, weakness, nausea, vomiting, and drooling are possible. An alarming complication of such a pregnancy may be bleeding and loss of consciousness, and the woman should immediately consult a doctor.
What is the danger of a pipe rupture?
The problem gets worse when the embryo begins to develop and grow. This is a serious complication of ectopic pregnancy and is dangerous for women. Typically, a pipe rupture is accompanied by pain and internal bleeding, which can be fatal.
It is possible that it will be very difficult for a woman to become pregnant in the future. Especially if she did not see a doctor or received untimely medical care for an ectopic pregnancy. There is a risk of losing the opportunity to have children for life.
If an ectopic pregnancy has been diagnosed at least once, difficulties may arise in subsequent conception. Therefore, if you have severe pain in the lower abdomen or abdominal cavity, you should urgently consult a doctor. The saddest outcome of fallopian tube rupture is death.
Types of ectopic pregnancy
Causes
The cause of this pathology is an obstruction in the path of a fertilized egg from the ovary to the uterus. This obstacle is associated with a decrease in the patency of the fallopian tubes (inflammation after abortion, endometriosis, miscarriage, use of an intrauterine device as a means of contraception), anomalies of their development, as well as the ovaries or uterus, oncological changes in the internal genital organs, hormonal disorders or difficult childbirth, after which adhesions form in the tissues.
In addition, women of the older age category (after 35 years) can also be considered at risk, since by this age a woman has a fairly “rich” set of both general somatic and gynecological diseases and disorders, changes in hormonal status and often the presence of abortions in stories.
At what time do they start to appear?
Women who suspect they are pregnant are in no hurry to contact an antenatal clinic early and register.
There may be multiple reasons for this: from family circumstances to work. However, it is precisely this inattention to one’s health that leads to great complications in the future.
It is impossible to notice the first signs of ectopic fertilization on your own without the qualified help of a doctor. Moreover, often the pathology is not even visualized on ultrasound. Doctors, if they suspect an ectopic location of the fetus, always perform surgical intervention.
How to recognize?
If you have an ectopic pregnancy, your breasts hurt, the test strips will show a positive result. Pathology is difficult to suspect. However, the hCG level will constantly fluctuate and deviate from the normal level corresponding to a certain period.
This interesting condition is usually accompanied by unilateral, unpleasant pain in the lower abdomen. The unpleasant condition may intensify with changes in the position of the body. Pain during an ectopic pregnancy can be similar to menstrual pain or cramping.
But the only reliable method for determining the place of attachment of the future fetus is ultrasound diagnostics through transvaginal access.
With timely diagnosis and treatment methods, ectopic pregnancy does not cause a significant impact on the body. And with qualified follow-up therapy, a woman can resume trying to become a mother in just 3-6 months after the termination of such a pregnancy.
The arrest of the fertilized egg in the fallopian tube is dangerous because its tissues are not elastic enough and cannot stretch simultaneously with the embryo increasing in size. The tube ruptures, blood along with tissues and the fertilized egg enters the abdominal cavity, which can lead to peritonitis. In addition, rupture of any organ will be accompanied by acute pain during an ectopic pregnancy and heavy bleeding. This puts the woman’s life at risk and requires immediate hospitalization in the intensive care unit under constant medical supervision.
Removal of an ectopic pregnancy is usually performed by laparotomy. Through a small incision in the abdomen, the surgeon gains access to the fertilized egg. Moreover, all instruments have sensors, and any manipulation by a specialist is displayed on the monitor. Depending on the stage of pregnancy, the doctor can remove only the fertilized egg, the egg with part of the damaged tissue, or the entire uterine tube. Therefore, the sooner a woman consults a doctor, the less harm will be caused to her health. Pain after an ectopic pregnancy will remain in a woman’s memory for a long time.
However, the treatment does not end there. It is necessary to undergo a course of restorative therapy, as well as eliminate possible causes of recurrent ectopic pregnancy. It is necessary to treat infections, inflammatory processes, and restore hormonal imbalance.
With timely diagnosis and termination, as well as competent subsequent treatment and rehabilitation, a woman will be able to forget the pain of an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages. She will be able to recover and give birth to a healthy baby.
Diagnostics
The most informative method for diagnosing ectopic pregnancy is ultrasound. It allows you to determine the location of the fertilized egg. In the early stages, the fertilized egg attached to the ovary or peritoneum is extremely difficult to visualize with ultrasound, but the fact of its absence in the uterine cavity against the background of hormone levels characteristic of pregnancy indicates an ectopic localization.
The nature of the course of VB is determined in several ways, each of which is designed to confirm the absence or presence of a fertilized egg in the uterus. If you experience bloody discharge, swollen breasts, or toxicosis, then there is every reason to visit a doctor.
A positive pregnancy test and the occurrence of at least one of the familiar symptoms should prompt a woman to go to the doctor. Research procedures will be prescribed to make a diagnosis.
An ultrasound performed transvaginally will be more effective. The doctor will determine the concentration of human chronic gonadotropin. If the hCG level is 1500, but during diagnostic examinations the fertilized egg is not detected, then a diagnosis is made - pregnancy outside the uterus.
An ultrasound performed transvaginally will be more effective. The doctor will determine the concentration of human chronic gonadotropin. If the hCG level is 1500, but during diagnostic examinations the fertilized egg is not detected, then a diagnosis is made - pregnancy outside the uterus.
Risk factors
There are cases in which the fertilized egg attaches outside the uterus due to some malfunction of the tubal canal. This is a complication and is called an ectopic pregnancy. Unfortunately, such a fetus has no chance of survival. This phenomenon is very dangerous for a woman’s health, as it is fraught with bleeding and, if ignored, can cost her life.
Under normal conditions, the fertilized egg descends into the uterus and attaches to its wall. But with an ectopic pregnancy, everything happens the other way around, it moves away from it and attaches either to the tube, or to the ovary, or even to the abdominal cavity. The lack of a favorable environment for the development of the unborn baby provokes the growth of the fetus into the organ to which it is attached. As a result, internal bleeding occurs.
Such a pregnancy is divided into ovarian, tubal or abdominal. It all depends on the place of attachment of the embryo. Of course, such situations are extremely rare and occur in 1-2 cases out of 100.
There are some risk factors:
- if there was an operation in the abdominal area;
- hormonal imbalance;
- due to diseases of the female reproductive organs;
- benign or malignant tumor of the reproductive organs.
It begins in the same way as usual, and the first weeks proceed in a similar way. Suspicious symptoms begin to appear from 3 to 9 weeks. What are the pains during an ectopic pregnancy? These include the following symptoms.
- Pain syndrome with aching, stabbing pain during ectopic pregnancy. It occurs in the lower abdomen, in the area where the embryo is attached. Pain may be present during bowel movements.
- There is bleeding of the vessels of the organ where the fertilized egg is located, and there may also be uterine bleeding. Basically reminiscent of menstruation, but not as heavy.
Can breasts hurt during an ectopic and frozen pregnancy? Causes and symptoms
To the question: “Do the breasts hurt during an ectopic pregnancy?”
– you can give a clear positive answer. The processes that occur in the mammary gland in this case are no different from changes in the breast during normal pregnancy. In the first stages, similar hormonal changes occur in a woman’s body. Including the release of human chorionic gonadotropin, a specific hormone that is responsible for the successful bearing of a baby. First you need to understand what an ectopic pregnancy is? Normally, a fertilized egg is implanted inside the uterine cavity. But if for some reason the fetus ends up outside of it (in the fallopian tube, ovary, peritoneal cavity or cervix), then a pathology occurs, which is called an ectopic pregnancy. At the same time, there can be no talk of normal pregnancy and childbirth. In 97% of cases of pathology, the fertilized egg remains in the fallopian tube. If it is not diagnosed in the initial stages, there is a possibility of fetal growth, which can lead to stretching and further rupture of the organ in which it is located. This is a very dangerous condition that threatens a woman’s life.
In the first days, a woman experiences the same symptoms as during normal pregnancy.
- Delayed menstruation.
- Increased basal temperature.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Early toxicosis.
- Pain and swelling of the breast.
But there are certain signs that are present only in a pathological condition and appear a month after fertilization.
The presence of an ectopic pregnancy can be detected using the following changes:
- Insufficient concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin. This is reflected on the test strip. Usually it is faintly colored or may be completely absent, but there are signs of conception. This is explained by the slow increase in the amount of the hormone. During a normal pregnancy, the volume of human chorionic gonadotropin doubles every 48 hours, and during an ectopic pregnancy it grows very slowly. The situation is the same with progesterone. This symptom cannot be called accurate; it can only suggest the presence of pathology.
- Minor bleeding. A fairly common sign during an ectopic pregnancy, which misleads a woman. It differs from menstruation in its scarcity, blurry nature of discharge and long continuation. The reason for its appearance is a decrease in the level of progesterone in the blood.
- Pain in the lower abdomen. This symptom does not appear immediately. Usually the pain is localized on the side where the embryo is attached and can radiate to the rectum. It often intensifies when changing body position, bending over and fast walking. How soon the symptom appears depends on in which part of the fallopian tube the fertilized egg is located. If it is located in the wide part of the fallopian tube (ampule), pain will occur at 8 weeks. When the fertilized egg is fixed in the isthmus, discomfort can be felt already from the 5th week. When the embryo is localized in the cervix, the woman may not feel any symptoms for a long time, and pain rarely appears.
In any case, the listed symptoms alone are not enough to confidently diagnose an ectopic pregnancy. It can be difficult to determine even with the help of ultrasound. As a rule, an ultrasound examination determines the presence or absence of an embryo in the uterus, since it is very difficult to examine it in the peritoneal cavity or tube. Then the doctor will refer the woman to analyze the level of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood. This is one of the most informative signs. If its concentration is less than during normal conception, this may indicate the presence of an ectopic or frozen pregnancy. In this case, an appointment to a hospital is necessary to conduct additional studies, including laparoscopy.
During the development of pathology, the mammary gland behaves exactly as during normal pregnancy. The signs of changes that occur to her are of a purely individual nature and are not present in all women. Some of them go through this period painlessly and do not notice any external changes in the chest.
But those pregnant women with sensitive mammary glands usually experience the following symptoms:
- Feeling of heaviness and increase in breast volume.
- Soreness and excessive sensitivity.
- Colostrum release.
- The nipples become darker in color.
- The appearance of a venous network (the skin becomes thinner due to an increase in breast volume, and blood circulation becomes more intense).
These signs are not a deviation, but indicate that the mammary gland is preparing for future feeding of the baby. A specific “improvement” of the breast occurs, additional milk lobules and ducts develop.
Symptoms are usually less severe during a second pregnancy. According to women who were carrying a second child, there is no excessive pain or swelling. In some cases, it is possible to discharge colostrum from the nipples. This is explained by the fact that the breasts have already gone through the processes of preparation for lactation once and returned to their original parameters. Therefore, the second time the changes are much easier.
Degrees
Doctors divide it into several degrees. The first is when the embryo, during its growth, digs into the walls of the tube and tears it. The second degree is divided into two types.
The first is when an ectopic pregnancy, where the pain is usually severe, aborts on its own, and the egg is released into the abdominal area. Accompanied by bleeding and pain. The uterus is enlarged, but does not coincide with the due date. Such a pregnancy is usually accompanied by unilateral pain in the lower abdomen. Discomfort may increase with changes in body position. Pain during an ectopic pregnancy resembles contractions or menstrual cramps. Bloody or spotting discharge appears.
The second is a rupture of the fallopian tube. It happens at 7-10 weeks. In this case, it is important to seek help immediately! This is life threatening.
A woman is required to undergo a rehabilitation course, which is aimed at restoring reproductive function after such an unsuccessful pregnancy. On average, the rehabilitation course lasts six months, after which a woman can start planning a child.
What causes this pregnancy?
The fertilized egg does not reach the uterus, resulting in its incorrect location and pathological development. Maturation of the egg can occur in the fallopian tube, ovary or abdominal cavity. The reason is:
- Abortion.
- Underdevelopment or abnormal development of the reproductive system.
- Lack or excess of hormones.
- Blockage of the fallopian tubes or disruption of their innervation.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Contraception.
Symptoms
At the very beginning, an ectopic pregnancy is difficult to distinguish from a normal one. A woman has identical symptoms: increased appetite - she can eat day or night, toxicosis - nausea can occur immediately or a little later, weakness, drowsiness, swelling of the mammary glands, lack of menstruation. Only after 3-6 weeks do symptoms begin to appear, indicating that the woman has a pregnancy pathology.
- Pain during ectopic pregnancy. A terrible state when everything aches and there is no strength to endure it all. What are the pains during an ectopic pregnancy? Cramping pain in the abdominal area. They are usually aching and cramping in nature. Urination becomes painful, sometimes mixed with blood.
- Bleeding. Bleeding during an ectopic pregnancy occurs in the abdominal cavity. Uterine bleeding is also possible. The reason for this is a sharp decrease in progesterone levels. It is the hormone progesterone in women that stimulates the growth of the uterus. It blocks uterine contractions and, during pregnancy, stops the menstrual cycle.
- State of shock. A pregnant woman's blood pressure drops. A drop in blood pressure is also associated with a decrease in levels of the hormone progesterone. The skin is of an unhealthy color, heavy bleeding begins, and as a result, loss of consciousness. Pain in the lower abdomen also occurs during an ectopic pregnancy.
The right side hurts during pregnancy and radiates to the lower back: what does this mean?
First, determine the nature of the pain. If your right side hurts during pregnancy and radiates to the lower back with an aching, nagging pain, this may mean that a hitherto dormant chronic disease has decided to worsen. Acute sharp pain with aching in the lower back most likely indicates problems with the spine. Weak back muscles and lumbar radiculitis may also be to blame (in this case, pain in the right side and lower back also radiates to the leg).
If the pain disappeared after the 20th week of pregnancy, the culprit was probably hormonal changes in the body and the muscles getting used to the new position. Pain in the right side and lower back in the later stages may be a symptom that the significantly enlarged uterus is pressing on the nerve endings located in the lower part of your spine.
Many women wonder if their lower back hurts during an ectopic pregnancy. Yes, during an ectopic pregnancy, the lower back may also hurt, but such pain, as a rule, radiates to the abdomen and not necessarily to the right side. It will be given to where the fertilized egg is attached. In addition, ectopic pregnancy is most often accompanied by spotting, a sharp decrease in blood pressure and attacks of dizziness.
Treatment
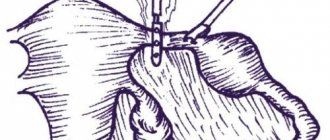
The only way to solve the problem is surgery. Laparoscopy is common. During the operation, the fertilized egg attached outside the uterus is removed. In case of difficulties, plastic surgery is used. Plastic surgery will restore the integrity of the fallopian tube. The fallopian tubes are significant for pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancy diagnosed in the early stages is treated with chemotherapy. Gradual resorption of the ovum is performed with methotrexate. Removing the fallopian tube is dangerous. This increases the likelihood of infertility or recurrent ectopic pregnancy.
What are the dangers of an ectopic pregnancy?
As mentioned above, the fertilized egg enters the fallopian tube and begins to develop there. The problem is that the tube is not suitable for fetal growth, since its wall does not have sufficient elasticity and extensibility, and also has a relatively small diameter.
Accordingly, having reached a certain point (4-6th week of pregnancy), the chorionic villi grow into the wall of the tube, after which it ruptures and an outpouring of blood occurs into the abdominal cavity (hemoperitoneum with the possible further development of peritonitis). Clinically, this is manifested by sharp “dagger” pain in the lower abdomen, pallor, dizziness, cold sticky sweat, and loss of consciousness. When a large vessel ruptures, bleeding can be life-threatening, requiring immediate attention.
In some cases, the wall of the fertilized egg ruptures, after which it is expelled into the abdominal cavity. The clinical picture is similar to that of a pipe rupture, but may be less pronounced or take longer to develop over time.