Every woman should know the signs of a frozen pregnancy so that if such a situation arises, she can respond to it in time. How dangerous is a frozen pregnancy? Its symptoms are not specific and do not appear immediately after development stops. There are also quite a few reasons for this pathology. We’ll talk about the main risk factors, as well as how a frozen pregnancy manifests itself, in today’s article.
Photo: Serova V. Atlas of human anatomy. - M.: White City, 2020. - 104 p.
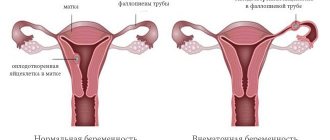
What is a frozen pregnancy, is it a pathology?
If the pregnancy proceeds normally, but for a certain reason the woman does not carry the fetus to term, a pathology occurs, which in the scientific world has a special term - frozen pregnancy. This means that the embryo stops developing and eventually dies. The most likely time frame for this pathology to occur is from conception to seven months.
The danger is that a frozen pregnancy, as a rule, proceeds without any suspicion.
Frozen pregnancy, why it is dangerous
If a frozen fetus remains in the mother's womb for a long time, this threatens the development of intoxication, and then intense pain appears, the temperature rises, and the pregnant woman feels weak. Without attaching importance to such manifestations and not rushing to see a doctor, a woman makes an irreparable mistake.
Since the fertilized egg, which is in the uterus for more than 1.5 - 2 weeks, can cause DIC syndrome - disseminated intravascular coagulation, and this is extremely life-threatening. This diagnosis indicates that the blood is not able to activate coagulation. In this case, bleeding that may open will most likely lead to death.
It happens that the pregnant woman’s body itself rejects the frozen fetus, and it all ends in a miscarriage. But if a woman does not seek medical help in time, and the above symptoms have already appeared, urgent hospitalization will be necessary. The woman will be prescribed a special drug that provokes uterine contractions, after which a miscarriage will occur. There is no time to delay in carrying out this procedure.
If you suspect a frozen pregnancy, you should immediately consult a doctor
Treatment
The consequences of a frozen pregnancy for a woman’s health can be unfavorable. If timely measures are not taken, then decomposition of the fetus is possible, which will lead to the development of intoxication and sepsis. Sometimes bleeding occurs. In case of fetal death before 16 weeks of pregnancy, curettage is performed. This is a surgical intervention during which the gynecologist removes the fetus, amniotic structures and the functional layer of the endometrium using a curette - a sharp surgical instrument. The cervical canal is first expanded using dilators of different diameters. So the operation is quite painful, it is performed only under general anesthesia.
Abortive material is sent for bacteriological examination and histology. To establish the causes of miscarriage, it is recommended to conduct a cytogenetic study of the obtained abortive material. If a frozen pregnancy is detected in the early stages, then a medical abortion may be performed. However, if the uterus does not empty completely, then curettage will have to be done. In addition, it is possible to perform vacuum aspiration, which is performed under general anesthesia.
After 16 weeks, medications are used to expel the fetus, after which the uterine cavity is curetted.
What are the signs of a frozen pregnancy?
Knowing the signs of a frozen pregnancy will help you recognize it in time and avoid serious consequences.
Characteristic pain appears
Pain in the lower abdomen can be similar to menstrual pain. But this symptom, as a rule, makes itself felt after a considerable period of time, sometimes several weeks pass after the embryo dies. But nagging pain in the lower abdomen, which is accompanied by bloody discharge, is most often evidence of a spontaneous miscarriage.
Basal temperature decreases
If the basal temperature decreases (i.e., if it becomes less than 37 ° C, usually 36.4-36.9), a frozen pregnancy should be suspected. However, based on the above sign, in the first trimester it is impossible to accurately determine whether the pregnancy has frozen, since incorrect measurement or thermometer error is possible.
No toxicosis in the first trimester
If morning sickness and vomiting suddenly stop during this period, as a rule, this is also a sign of a frozen pregnancy. But women often do not pay attention to this phenomenon, deciding that the unpleasant symptoms have simply passed and the body has adapted to the presence of the unborn child. This symptom may not appear immediately after the death of the fetus, but only after several days or weeks.
Body temperature rises
If, due to the decay of a dead fetus, an infectious process has begun in the uterus, the pregnant woman’s body temperature rises (from 37 to 38 ° C). But if the process becomes systemic, hyperthermia is possible up to 41° C, and then the woman’s general condition becomes severe.
Spotting vaginal discharge appears
Such discharge streaked with blood can also signal a frozen pregnancy. Still, most often, this sign is evidence of a spontaneous miscarriage.
The breasts return to a state corresponding to what they were before the child was conceived
Another sign of a frozen pregnancy is the absence of swelling of the mammary glands, as well as hyperpigmentation of the nipples. Such changes are also characterized by a sharp manifestation. Among other things, colostrum ceases to be released if it was previously secreted.
Nagging pain in the lower abdomen may be a sign of a frozen fetus
Change in uterine volume
This sign can only be detected during a gynecological examination. The doctor measures the volume of the uterus and if the pregnancy is frozen, the uterus stops enlarging. However, one cannot “rely” on the presence of such a sign in the first weeks of the gestational period: the volume of the uterus at this time is almost no different from its dimensions prior to conception.
The hCG hormone stops increasing
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is produced by chorionic tissue after embryo implantation - about a week after the egg has been fertilized. This is one of the indicators of a normal pregnancy. If it freezes, hCG stops increasing after the fetus dies, and even later it decreases altogether. Therefore, if this pathology is suspected, it is necessary to track the dynamics of hCG and take the test again after a few days.
Absence of heartbeat and lag in fetal size on ultrasound
Ultrasound is rightly considered the ideal method for detecting frozen pregnancy. Therefore, if the doctor diagnosed the above signs, unfortunately, the pregnancy has stopped.
Where to look for the guilty
Who is to blame for such a pathology? Mom or future father? Without additional medical history and tests, no doctor can tell. There can be many reasons. Pregnancy can develop perfectly, but one day the fetus simply dies in the womb, remaining there until the expectant mother suspects it. That is why the second name for a frozen pregnancy is a failed miscarriage.
Such an interruption usually occurs in the first trimester, so for the first time after conception you need to especially listen to your health, take care and go to the antenatal clinic more often for examination.
I think you should know about the most common causes of freezing, so I tried to collect as fully as possible all medical observations on this matter.
- Genes/chromosomes. All sorts of genetic anomalies that are not detected in time can play a cruel joke on the mother and fetus. So, if a child has, for example, an extra chromosome or some kind of gene mutation that is incompatible with life, death may occur. It's sad, but that's natural selection. Having been born, such a baby would still not be viable, and Mother Nature had already decided his fate herself.
- Infectious diseases. Rubella, herpes, chickenpox, toxoplasmosis and even the common cold can affect and damage the baby's vital organs and systems. You especially need to try to take care in the first trimester, when the baby is very susceptible to various negative influences and there is a high probability of death.
- Women's hormones, in particular, the main hormone of all pregnant women, can also cause the fetus to freeze. If there is critically little of it in the mother’s body, then the probability of a miscarriage is about 80%.
- Various pathologies of an autoimmune nature, when the mother’s body suddenly begins to produce antibodies to her own child, as to a foreign “object”. They quickly kill the cells of the baby’s still maturing body.
- Abnormal structure of the father's sperm. Unfortunately, many couples are now experiencing problems conceiving, and teratozoospermia (pathology of sperm composition) is one of the reasons. A woman becomes pregnant, but due to abnormal sperm, the baby's development quickly stops. Sometimes pregnancy even stops after IVF, when the fertilized egg implanted into the woman refuses to grow and develop.
- Bad habits, poor nutrition, improper daily routine, and poor living conditions in general not only do not contribute to the normal development of pregnancy, but also force it to stop at the initial stage. This is also a kind of natural selection.
- Taking medications when you are pregnant must be agreed with your doctor, otherwise the consequences may be unpredictable.
- The age of a woman giving birth over 35-40 years is quite risky, especially for the first pregnancy, so you should prepare especially carefully for conception and undergo all examinations and tests.
Why embryo development stops, possible causes of pathology
Doctors cannot always determine exactly why a pregnancy stalls. However, the main causes of pathology may be as follows:
- genetic failure - in the majority of women (70%), if fetal fading occurs during pregnancy up to 2 months, it is due to chromosome abnormalities in the fetus. Such anomalies appear quite early and are almost always incompatible with life. Bad genetics can be passed on from both the mother and the father, and an unsuccessful combination of parental genes is also possible. And if a woman’s fetus freezes more than 3 times, then this is precisely because of a genetic failure;
- hormonal disorders - in this case, the fetus freezes for 2 reasons: 1 - due to a deficiency in the female body of the hormone progesterone, without which it can neither survive nor develop in the uterus; 2 – on the contrary, excess androgen hormones;
- infections. A pregnant woman's immunity often weakens, and she becomes vulnerable to various bacteria and viruses. In this case, infectious diseases worsen, the vaginal flora becomes more active, and then a dangerous moment comes for the unborn child, threatening infection;
- ARVI is usually quite severe, since the immune system works at half capacity. Moreover, the danger is not the causative agent of the disease, but precisely its symptoms: intoxication of the body and an increase in temperature (it leads to a malfunction in the circulatory system: the fetus does not receive the required amount of oxygen and nutrients);
- rubella and cytomegalovirus. They are dangerous in case of infection during pregnancy; with early infection, on the contrary, antibodies have already been developed that prevent the exacerbation of the disease;
- bleeding disorders;
- incorrect and inadequate diet, lack of exercise, insufficient exposure to fresh air, etc. harmful factors - in this case, the first signs of a frozen pregnancy may appear without delay.
Fetal freezing can also occur at a later stage
Who is at risk
It is worth noting that not a single woman is insured against a frozen pregnancy. And even in absolutely healthy representatives of the fair sex this pathology can be detected. So women may be at risk:
- over 40 years of age with an untreated sexually transmitted infection;
- exposed to increased emotional and physical stress. loads;
- having in their honey. biographies of abortion or recurrent miscarriage;
- with somatic diseases such as diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis or thyroid dysfunction.
Pregnant women are also at risk if the embryo has abnormalities incompatible with life.
Prevention measures
Preventive measures at the planning stage will help reduce the risk or completely avoid the repetition of negative experiences.
The first and main measure is individual treatment prescribed by a specialist after determining the cause of fetal death.
It will be necessary to get vaccinated if a woman is at risk. For example, if she works in children's educational institutions, where it is easy to become infected.
A woman planning a future pregnancy needs to strengthen her immunity. Lead a healthy lifestyle, completely abandon all bad habits.
It is possible that treatment after the incident will not be required at all. But the gynecologist will most likely recommend undergoing a number of examinations before starting planning:
- study of the pelvic organs using ultrasound;
- determination of homocysteine level, presence of antibodies;
- smear to detect hidden infections;
- study of thyroid hormones;
- analysis for TORCH infections.
Find out more about what tests you need to take when planning a pregnancy to ensure a successful and healthy pregnancy. Stretch marks often appear during pregnancy and after childbirth. Find out what ways you can get rid of them.
Read about how to get pregnant with twins right away in our other material:
What is done if you suspect a frozen pregnancy, what therapy is indicated
Of course, the subjective symptoms of a frozen pregnancy are the “marker” that notifies you of the need to immediately consult a doctor in order to conduct a thorough diagnosis. And if the diagnosis is confirmed using appropriate tests, the embryo is removed from the uterine cavity.
Sometimes the body itself gets rid of the frozen fetus - a spontaneous miscarriage occurs
Frozen pregnancy - treatment
Medical tactics for managing a woman with this pathology can be different: it depends on the gestational age, as well as the psychological and physical state of the pregnant woman.
If the diagnosis is made early, doctors often take a wait-and-see approach: there is a considerable probability that a spontaneous onset of miscarriage will occur. The woman is placed in a hospital setting under the supervision of specialists, and a spontaneous miscarriage is expected over the course of several days. But if this does not happen (this happens if the fetus died long enough), then an abortion is performed.
In particular, during early pregnancy, vacuum aspiration is often used - this is the safest method; for a period of less than 2 months, an artificial miscarriage is performed using appropriate medications.
And already in the later weeks of pregnancy, the frozen fetus is removed by cleaning the uterine cavity: the procedure is carried out under general anesthesia, and the resulting materials are sent for histological examination.
After which the woman remains in the clinic for some time: she is prescribed a course of antibiotics, hormone therapy (if there are indications), as well as sedatives. Hormonal tests are necessarily carried out, smears are taken for hidden infections, and general blood counts are identified using tests.
A woman may be prescribed hormones after a missed abortion
Frozen pregnancy - consequences for a woman
It is worth noting that serious complications in women occur only if she consults a doctor late. And a timely diagnosis, correctly prescribed treatment - all this in the future will help a woman become pregnant again and give birth to full-fledged offspring.
A particular difficulty in the case of a frozen pregnancy is determining the reason for its termination (unfortunately, this can only be established absolutely precisely in very rare cases), because every effort must be made to ensure that this does not happen again.
Many women who have already encountered this pathology are interested in whether a repeat frozen pregnancy is possible? Experts are unanimous in the opinion that this can be repeated more than once if the cause of fetal death has not been established.
Accordingly, a woman should approach solving the problem comprehensively: undergo a serious examination, visit a geneticist, and cure existing ailments. And, of course, the attitude towards a positive outcome of the next pregnancy is very important.
The loss of an unborn child is a heavy blow for any woman. This is reflected in her reproductive system, and, of course, on the psycho-emotional background. In such a difficult period, a woman urgently needs the support of loved ones, and possibly psychological help from a specialist. In any case, it will take a long time to accept what happened.
For every woman who wants to have a child, the miscarriage of pregnancy is a heavy blow.
Possible consequences
Unfortunately, no matter at what stage a frozen pregnancy is discovered, its consequences are not always favorable. All complications that accompany intrauterine fetal death and related gynecological manipulations can be divided into two groups - early and late.
The first group includes:
- perforation of the uterus during curettage;
- intense bleeding;
- infectious diseases of the internal genital organs.
Late complications include:
- chronic inflammatory processes;
- disruption of ovarian function;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- infertility.
New pregnancy after fetal growth arrest
Doctors' predictions that reconception will lead to a successful birth can only take place if the couple:
- will not ignore visiting all necessary specialists;
- be sure to undergo treatment;
- in the next six months to a year after the miscarriage has occurred, she will not make attempts to become parents again (this is the period that is optimal both for identifying the causes of the pathology and for a detailed examination, as well as the woman’s recovery).
Tests required after a frozen pregnancy
A second (after a frozen) pregnancy should be planned, having in hand the results of the following tests:
- vaginal smear for sexually transmitted diseases;
- a blood test that determines the levels of progesterone and estrogen.
To try to get pregnant again after a missed pregnancy, you need to take several tests
Recommendations for a pregnant woman
Following simple recommendations will help the child’s successful prenatal development
- take folic acid before conception;
- take a general strengthening course of vitamins;
- balance your diet;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- monitor the microflora of the genital organs;
- do not self-medicate;
- Follow your doctor's recommendations.
Statistics show that in most cases, repeated pregnancy ends in the birth of a healthy baby, so do not despair and blame yourself or your partner.