Is it possible to give birth with uterine fibroids?
Many ladies are interested in whether pregnancy is possible after fibroid removal.
To preserve reproductive function, conservative methods are more often used to treat the tumor. When removing fibroids in a gentle way, where only a node or part of the uterine tissue is removed, reproductive function is preserved. A woman can conceive and give birth to children. During surgery, the ability to bear children is sometimes impaired. It all depends on what type of operation was chosen. For example, after a conservative myomectomy, reproductive function may recover over time, but if the organ is completely removed, it may disappear forever. But pregnancy after a myomectomy, in which the uterus is completely removed, is no longer possible.
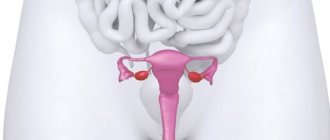
Myoma is a hormonal-dependent benign neoplasm that grows from the smooth muscle elements of the uterus.
Its main causes are considered to be an increase in the level of ovarian hormones and metabolic disorders. This condition can occur when:
- Physiological fluctuations in the synthesis of ovarian hormones: pregnancy, perimenopause.
- Diseases of the endocrine glands: hormonally active tumors and ovarian cysts, pathologies of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland.
- Lesions of the central nervous system affecting the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
- Obesity.
- Smoking and alcoholism.
- Chronic stress.
- Long-term use of hormonal drugs.
Under the influence of unfavorable conditions, atypical cells appear in the muscle layer of the uterus, which begin to divide randomly, forming a node. It can grow in the thickness of the myometrium (interstitial), extend to the surface of the organ (subserous) or protrude into the cavity (submucosal).
For a long time, the disease is asymptomatic and is detected when the node reaches 30 mm or more in diameter. The main manifestations of fibroids are:
- Long, heavy periods.
- Pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen.
- Compression of the adjacent intestines and bladder by the tumor, causing problems with defecation and urination.
- Acute pain and signs of inflammation of the peritoneum due to malnutrition in the nodes.
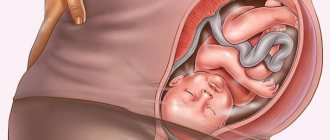
A node on the uterus can complicate the process of childbirth. It disrupts the contractility of the organ, makes it difficult for the child to pass through the birth canal; with cervical fibroids, its mobility and transformation for a successful birth are impaired.
Complications
The main complications caused by uterine neoplasms during childbirth are:
- Weakness or absence of contractions and pushing.
- Discoordinated labor activity.
- Bleeding.
- High risk of uterine rupture.
- Creating an obstacle to the birth of a fetus.
- Delayed separation of placenta.
Childbirth with fibroids can occur naturally with a small diameter of the node, its localization near the fundus of the uterus and the absence of mechanical barriers to the birth of the fetus.
Delivery of fibroids by cesarean section is carried out when large nodes are located in the lower segment, complications occur, and after myomectomy.
It is possible to give birth safely with fibroids. The birth process must be supervised by qualified medical personnel. At the same time, contractions and fetal heartbeat are constantly monitored. If complications occur, emergency surgical delivery is used. After childbirth, uterine bleeding and retained placenta are more common. Therefore, it also requires constant medical supervision.
The main danger of fibroids for the fetus is its compression by large nodes, causing deformations and deformities. And also, when the placenta is adjacent to pathological tissues, it is possible that the blood circulation between the uterus and the placenta may be impaired, leading to delayed fetal development and oxygen starvation of varying severity.
However, with medical supervision over the course of the gestation period, such complications are extremely rare. Despite all the frightening possible consequences, fibroids and childbirth are compatible if the woman is under the supervision of doctors and follows all their instructions.
This formation is considered benign; it is a tumor that grows on the muscles of the uterus. Experts have not yet been able to give specific answers as to why this is happening. But there are suggestions as to what causes uterine fibroids - it could be increased hormonal stimulation and increased secretion of estrogen. In other words, the tumor forms due to low levels of progesterone in the body and grows due to an excess balance of estrogen.
But if no hormonal imbalance is detected in the blood, this does not mean that a tumor cannot form. The level of estrogen in the uterus may increase slightly and not be reflected in a blood test. In almost all cases, the formation consists of several nodes in various sizes of seals. A tumor of this type is considered common, but it is extremely undesirable for an expectant mother.
Causes
This disease occurs as a result of hormone imbalance. The amount of estrogen increases, which contributes to rapid cell division and the formation of unwanted nodes. Nodes can grow in different places on the uterus in multiple numbers. If a tumor is detected and treated in time, then it does not pose any danger.
Reasons for the rapid production of estrogen by the ovaries:
- genetics (if women had such a disease, then it is difficult for the next generation of women to avoid it);
- infections that inflame the genitals;
- intentional termination of pregnancy;
- cyst on the ovaries;
- birth control pills;
- excess weight;
- chemotherapy.
Uterine fibroids often cause infertility. But there are cases when pregnancy is still possible. Practice suggests that this disease affects each organism differently. Doctors cannot fully answer why some women give birth when fibroids form in the uterus, while others are unable to conceive a child with this benign multiple formation.
Symptoms
A formation on the uterus is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the menstrual cycle is very painful;
- women very often feel slight pressure in the lower abdomen;
- abdominal pain intensifies and has a pulling character;
- sexual intercourse often becomes painful for a woman;
- the bladder often makes you want to go to the toilet;
- the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted;
- belly growth.
To be able to give birth to a baby, you need to contact a specialist for examination at the first sign of these symptoms. He will order an ultrasound to detect fibroids on the muscle layer of the uterus. Ultrasound examination will help to detect tumor formations in time. Also, using this procedure, the doctor will find out:
- the number of nodes that have formed on the uterus;
- condition of myomatous nodes;
- their place of growth;
- exact size of fibroids;
- exact location of lesions;
- structure of tumors.
These characteristics are necessary to determine the answer to the question - whether a woman has the opportunity to give birth to a child. Conception can occur if nothing blocks the entry of sperm into the uterus and does not disrupt the ovulation process. For a successful pregnancy, the cervix should not be blocked by this tumor formation. As you can see, there is a possibility of pregnancy with this diagnosis.
Diagnostics
At the very beginning of the diagnosis, doctors ask the woman a number of questions. They find out how many times the woman was pregnant and how many times she terminated the pregnancy. Also, specialists need to find out whether there have been uterine surgeries or miscarriages. One of the questions may be about the birth of a non-living child. After clarifying all the nuances, the woman is sent for research, which uses various diagnostic methods.
General clinical examinations and tests are carried out. Doctors find out the main aspects of this disease. Diabetics and hypertensive patients are examined very carefully, because these diseases have a great impact on the entire treatment process. In addition to general examinations, the woman is referred to a gynecologist.
The gynecologist must clarify through research all the sizes of the formed nodes and changes in the fibroids. Also, the exact location of fibroids. In addition, with the help of an ultrasound machine, a specialist monitors the development of the fetus if a pregnant woman is diagnosed. Ultrasound also determines where the tumors are located.
Treatment
At the very beginning of treatment for a woman who has been diagnosed with a tumor, doctors try to stop further growth of the tumor. All methods of stopping the development of a benign tumor depend on the individual characteristics and structure of the fibroid. Also, the reason why the disease was diagnosed plays an important role.
Prevention
Prevention consists of taking iron, ascorbic acid and various vitamins. Proper nutrition, which includes food with plenty of protein. Carbohydrates should be limited, and you should also stop eating animal fats. Fresh juices, vegetables and fruits have a beneficial effect on disease prevention.
In the uterus, fibroids often form with many nodes. After removing all the nodes, there may be no healthy tissue left on the uterus, so planning conception and pregnancy may be accompanied by difficulties. But doctors can remove precisely the nodes that interfere with the development of the fetus, which will lead to various complications. Pregnancy with fibroids can proceed smoothly after removal of such nodes. And after the birth, the doctor will remove the remaining nodes that have formed.
The surgical method is used to treat fibroids. Laparoscopy is an operation that is performed with the necessary instruments and a camera to take video of the abdominal cavity. This operation prevents the formation of adhesions and increases the patency of the tubes, so that a woman can become pregnant. This technique is safer than, for example, laparotomy.
The surgery to remove fibroids, called laparotomy, involves a manual process that may carry the risk of adhesions. This can lead to consequences such as infertility and even intestinal obstruction. But with the first type of operation, if the fibroid nodes are large, it will not be possible to stitch the uterus. This is solely due to the use of specific technology.
Treatment of fibroids
Treatment of fibroids involves a set of measures aimed at eliminating the tumor and its effects on the uterine tissue and pelvic organs. Since nodes often interfere with successful conception, it is recommended to get rid of it before fertilization.
You can get pregnant even after 40 with uterine fibroids if you prevent its further growth. Treatment of the formation involves both surgical intervention, in later stages, or in particularly difficult cases, and medicinal treatment of the nodes.
Surgical
Surgical intervention is carried out at those stages of the development of the disease when heavy bleeding, anemia appears, urination is disrupted, the functioning of the intestinal tract is disrupted, and the uterine cavity is blocked. The presence of scars and adhesions formed after surgery can cause infertility, which is why specialists more often prescribe drug treatment during childbearing years.
Surgical methods include myomectomy—removal of the tumor while preserving the uterus—and uterine artery embolization, which cuts off the blood supply to dry out the tumor.
Medication
Drug therapy is based on eliminating the cause of the tumor. Depending on the case, antibiotics are used to eliminate inflammation, hormonal drugs to normalize hormonal levels and the cycle, drugs against anemia and complex vitamins that accelerate endometrial regeneration. Hormonal drugs are prescribed by a doctor after analyzing the level of hormones in the blood, since self-prescription can aggravate the situation.
Lifestyle
The doctor can adjust your diet to increase vitamin levels and limit physical activity. Abdominal exercises promote a rush of blood to the pelvis and have a negative effect; before playing sports, you should consult a doctor. The presence of fibroids requires adherence to a strict diet, especially if you are obese. You should also avoid thermal procedures and stress, it is recommended to sleep at least 8 hours.
General information about the disease
Myoma is a benign tumor that is located in the muscle layer of the uterus. The neoplasm resembles an oval-shaped node. There may be several reasons why the disease occurs. Most often it occurs due to hormonal imbalance in the body when the amount of estrogen is exceeded.
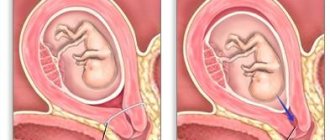
- Submucosal - occurs in the submucosal layer of the uterus.
- Intramural - located inside the myometrium, its growth occurs outward or inward.
- Subserous - formed on the outer wall of the reproductive organ, growth occurs outward.
Patients experience the following symptoms:
- Heavy discharge during menstruation;
- The appearance of painful sensations;
- Inability to bear a child;
- Problems with conception;
- Infertility;
- Compression of the pelvic organs, problems with urination and defecation.
Often, fibroids are not one tumor, but several. Most often, neoplasms form in the body of the uterus and extremely rarely occur in the cervix.
Read this article for more details.
In the practice of some obstetricians and gynecologists, cases have arisen when a pregnant woman’s fibroids resolve. However, such situations are extremely rare.
Therefore, all women with a history of this pathology should plan pregnancy and, if necessary, treat the pathology at the stage of preconception preparation.
A pregnant woman can have many symptoms. When the baby is pregnant, the tumor can disrupt the placenta and its functions. A woman may have a stomach ache. These pains in the lower abdomen are caused by poor circulation in the nodes. Also, increased blood pressure is observed. A benign tumor can be easily recognized using echo signs of ultrasound examination.
When a woman plans to conceive a baby, she needs to take into account all the characteristics of the tumor. It is important to know how it is located and where. Also, the size of the nodes and their predisposition to growth play an important role. If the uterus is deformed due to formation, then conception is impossible. In this case, it is necessary to remove the nodes. When planning pregnancy, fibroids should be carefully examined.
If the nodes are small and do not affect the uterus, then the likelihood of pregnancy becomes high. But during pregnancy, problems can arise. A woman may not be able to bear a child. Miscarriage or termination of pregnancy is highly likely.
Removal of fibroids by a doctor during a cesarean section is possible:
- in case of single education;
- abdominal tumor, which has a stalk;
- if there are structural changes in the tumor;
- large intermuscular formation.
But it happens that after a cesarean section, it is necessary to completely remove the uterus. This is necessary for women over forty years of age. Also, with necrosis of fibroids and recurrence of tumors. If during a cesarean section it was possible to remove the formation, then the woman can safely plan another conception of a child.
For each woman with a tumor, the choice of childbirth is individual. Natural childbirth can take place in the absence of contraindications. For example, the formation does not grow and will not interfere with the birth process. For such births, only pain medication is used. But often the doctor recommends a cesarean section to his patient. During a caesarean section, the fibroids can be removed by a doctor.
Caesarean section is necessary:
- if the tumor is located low;
- many nodes;
- if there is a scar on the uterus after surgery;
- the blood circulation of the tumor is impaired.
But is it necessary to remove fibroids before pregnancy? Yes, because then the pregnancy can proceed in the most normal way, without any intervention. But this is provided that the nodes were small. It is also necessary to undergo a gynecological examination before planning a conception to ensure that the scar is in good condition. The age of the pregnant woman also plays an important role in this matter.
There are many women's forums where they talk about pregnancy with a benign tumor. Very often you can find positive reviews when a woman carried and gave birth to a baby without any problems. But every case is different. Some were maintained throughout the entire pregnancy period under the constant supervision of a gynecologist. Some doctors observed their patients with fibroids as ordinary women in labor, because the pregnancy went smoothly.
Tatyana, 23 years old.
Ida, 34 years old.
Lilia, 31 years old.
Pregnancy affects benign formations in such a way that they can even resolve. There are many cases when the tumor resolved itself during pregnancy. This may be due to the fact that progesterone levels in the body increase. But no one can answer for sure whether fibroids can resolve in all pregnant women. It all depends solely on individual characteristics.
In order for the process of bearing a child to go well and calmly, it is necessary to lead a moderate lifestyle. Strong physical activity is as undesirable as constant lying in bed. The health of pregnant women and their babies depends on their diet. You need to take a lot of vitamins and choose exclusively healthy foods. Pregnancy management should be accompanied by constant monitoring by a specialist, because fibroids may increase during pregnancy.
Doctors believe that it is not always possible to conceive a baby during such an illness. Also, there are cases when doctors confuse fibroids with pregnancy. A pregnancy test may show a positive result. This happens because the tumor synthesizes hormones in the same way as during pregnancy. The test, in turn, is very sensitive to hCG, so it often shows a false result.
A myomatous node on the uterus is an area of overgrown atypical cells of the muscle layer. It is covered with a pseudocapsule and has its own vasculature. The tumor has a benign appearance - it does not spread metastases and does not destroy neighboring tissues.
It disrupts the contractility of the myometrium, provoking uterine bleeding, and when large in size, it manifests itself as pain and signs of compression of the intestines and bladder. In nodes that grow on a thin stalk or reach large sizes, there may be insufficient blood supply, leading to necrosis and inflammation.
Ovarian hormones – progesterone and estrogen – are responsible for the active growth and development of fibroids. In addition to them, the cause of the appearance of a tumor is a violation of metabolic processes, trauma and infection of the uterus, and an unhealthy lifestyle.
Pregnancy management
The main rule when managing pregnancy with uterine fibroids is regular ultrasound examinations. Using ultrasound, the doctor monitors the growth of myomatous nodes. As a rule, studies are carried out at 6-10, 14-16, 22-24, 32-34 and 38-39 weeks. But the doctor may prescribe more frequent ultrasounds. To monitor the functioning of the placenta, Doppler ultrasound is additionally prescribed.
The main task of obstetricians with fibroids is to maintain pregnancy and ensure the healthy development of the child. Doctors often recommend that expectant mothers go to the hospital during critical periods of pregnancy. Treatment will be aimed at normalizing hormonal status, relieving uterine hypertonicity and maintaining healthy placental metabolism. Do not neglect your doctor’s recommendations; for any fibroids, it is safer to be under the daily supervision of specialists.
Take the first step - make an appointment!
or call 8 800 550-05-33
free phone in Russia
How pregnancy affects fibroids
It is not always possible to detect fibroids at the stage of preconception preparation. And if a woman with this pathology has already become pregnant, myomatous nodes can complicate its course.
The gestation period is accompanied by changes throughout the body. The uterus undergoes significant changes: its epithelial lining thickens, muscle fibers lengthen and hypertrophy, allowing the organ to greatly stretch as the size of the fetus increases.
These changes are controlled by hormones that are actively produced by the ovaries, and after 12 weeks of gestation, by the placenta. And often this provokes intensive growth of a hormonally dependent pathological structure.
The percentage of spontaneous abortions during early pregnancy in women with this pathology is significantly higher than in women without myometrial nodes. At the same time, the risk of miscarriage increases significantly with numerous myomatous tumors.
For the same reason, delays and abnormalities in fetal development are often observed. Large nodes in the uterine cavity can put pressure on the baby, leading to various deformities.
The second third of the gestational age may be complicated by placental insufficiency, which provokes insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus (hypoxia). Placenta previa to the cervical canal contributes to frequent bleeding and the threat of spontaneous abortion. Also, with further development of pregnancy, preeclampsia may occur. This is a pathological condition characterized by:
- High blood pressure.
- The appearance of protein in the urine.
- Swelling of the face and limbs.
- Neurological disorders.
With the development of hypertensive crisis and convulsions (eclampsia), urgent delivery is required, regardless of gestational age.
In the third trimester of pregnancy, fibroids can cause abnormal positioning of the baby. Large nodes prevent him from taking a head position towards the entrance to the pelvis. The baby is positioned transversely or feet first, which will significantly complicate the birth process. This may be an indication for cesarean section for fibroids.
It is no secret that such formation is negative during pregnancy. It can cause a miscarriage due to a lack of placenta, because the fetus must be surrounded by the placenta. Due to fibroids, the baby may receive little oxygen and all nutrients. The effects may also cause severe bleeding due to placental abruption.
But if uterine fibroids are detected, you should not immediately terminate the pregnancy. After all, this disease and pregnancy are compatible. You just need to constantly be examined by a specialist. There are many examples where women carried a healthy child, and the pregnancy period was absolutely calm. But it’s better not to take risks, because the child may be born with a small weight or a deformed body. The negative impact of fibroids on pregnancy cannot be ruled out at all, even despite many successful cases.
After 40 years, pregnancy is more difficult, because at this age hormonal imbalance is very likely. Also, the rapid growth of fibroids can significantly outpace the capillaries, which causes bleeding. If no disturbances were observed over the course of 12 weeks, this does not mean that after 20 weeks the same result will occur.
The first trimester can pass without any symptoms. But complications can appear at any time. There is a high probability that blood circulation will be impaired in the later stages because myomatous nodes grow. Therefore, it is recommended to perform a caesarean section when the pregnancy is 39 weeks.
Nowadays, most women give birth after 30. At this age, hormonal imbalances begin to progress. Therefore, before conception, it is necessary for doctors to discover the location and size of the formation. If they reach 4 cm or 5 cm, then pregnancy is possible. But if the fibroid is 7 cm or 8 cm, then this significantly complicates the process of treatment and pregnancy.
Doctors cannot guarantee exactly how the formation on the uterus will change during pregnancy. We have not yet found out exactly why the formation decreases during pregnancy, which happens in most cases. But there is a small percentage that the tumor can almost double in size. However, it does not always interfere with pregnancy and childbirth. Perhaps progesterone increases and fibroid development decreases. But scientists cannot fully answer this question.
Is it possible to conceive a child?
Women with uterine nodes do not know whether it is possible to get pregnant with fibroids and are afraid of infertility. Gynecologists say that it is possible to get pregnant, but in some cases conception can be complicated. If a tumor forms on the inner uterine lining, the movement of sperm is limited and ovulation is disrupted.
Large fibroids also do not promote pregnancy; they compress the fallopian tubes, blocking their lumen. This prevents the sperm from meeting the egg.
In such cases, IVF is indicated.
Other reasons for not getting pregnant include:
- localization of the tumor near the cervix;
- fibroid size exceeding 8 cm;
- woman's age over 45 years;
- increased uterine tone.
The type of tumor also affects conception. Submucous fibroids are the most unfavorable for pregnancy; they can cause infertility or failure to carry a fetus to term. Women who have a pedunculated node are not recommended to become pregnant, since such formations can twist.
If a woman is diagnosed with fibroids, she may try to conceive for up to a year. After 40 years, this period is halved. If fertilization does not occur during this time, it is necessary to begin therapy.
The best option is to remove the formation before planning a pregnancy. But only those fibroids that have reached a size corresponding to 12 weeks of pregnancy are removed.
The parameters of the nodes are measured over weeks. If surgical intervention is performed, then it is allowed to start planning conception 6 months after the operation.
Consequences for the child
The disease does not always lead to infertility. There are three possible cases in which it interferes with conceiving a child:
- If the fibroid is located in the uterine cavity and does not allow the fertilized egg to attach to the mucous membrane.
- The process of conception becomes difficult when the tumor becomes an obstacle to the passage of sperm and prevents them from reaching the egg.
- If the nodes have a large diameter, the likelihood of pregnancy is negligible.
A neoplasm no larger than three to four centimeters in size most often allows you to conceive a baby. But there is a possibility that problems will arise with bearing the fetus and a miscarriage may occur. There is also a possibility of complications occurring during childbirth. It is possible to become pregnant more if there is a subserous node located outside the uterus.
In this case, the chances of conceiving and bearing fruit are high. If the neoplasm is located intramurally, a woman can become pregnant, but if it is located at the site of attachment of the fertilized egg, there is a risk of placental abruption and the death of the unborn baby. With a subbucous and intramural location, it is possible to carry a child to term, but how high the chance is depends on the number and size of neoplasms.
Modern representatives of the fairer sex give birth later, some plan to have children at 40 years old. But it happens that women want to give birth even at 50 years old. Conceiving at a late age is quite possible, provided that the ovulation process occurs regularly. And, of course, it is important that the tumor is small in size and does not interfere with the attachment and full development of the fertilized egg. However, reviews from mothers in labor indicate that it is possible to give birth to a healthy child.
Women who are candidates for surgery to remove fibroids often ask the question about when they can get pregnant. Usually, no special difficulties are observed during pregnancy if no new lesions have arisen. After removal of the tumors, you can become pregnant with uterine fibroids after 8-12 months. In this case, it does not matter what type of operation was performed.
The number of months depends on the size of the removed tumor. If the diameter is small, 3-4 cm, then you can get pregnant after 8 months so that the uterus can fully recover. It takes 90 days for the sutures to dissolve after the operation. In some situations, a cesarean section will be necessary, depending on the size of the remaining scar, the age of the pregnant woman, and the suture data shown by ultrasound. If no complications arise during the removal of small fibroids, then childbirth can be natural.
It is worth noting that tumors after childbirth may stop growing and developing. The uterus returns to its original position, and accordingly, fibroids and nodes also change. Uterine leiomyoma is found in almost every fifth woman, so the process of bearing a child and the postpartum period can be complicated by various processes.
There may be no consequences for the baby. But if pregnancy is not managed correctly, all sorts of complications can arise. The mother will observe all the consequences of the child after birth, when a deformation of the skull or insufficient development is discovered. The tumor does not allow the placenta to fully function and can put pressure on the walls of the uterus. Therefore, all these difficulties may arise in the newly born baby.
Many young women faced with a tumor are frightened by the prospect of infertility. A common question asked to a gynecologist is whether pregnancy is possible with fibroids?
Fibroids actually reduce the chances of getting pregnant safely. This is due to deformation of the walls of the uterus by nodes, as well as disruption of the normal blood supply to the organ.
Women with nodes that are located intramurally (in the thickness of the myometrium) or grow into the uterine cavity have low chances of becoming pregnant. Such submucous fibroids, especially large ones, severely deform the uterine cavity, disrupting the attachment of the fertilized egg.
Nodes located at the entrance to the tubes or in the cervical area also significantly reduce the possibility of getting pregnant. They prevent the fertilization of the egg by blocking the pathways for sperm to enter the fallopian tubes.
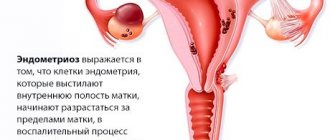
This pathology is characterized by the resettlement of endometrial cells and their growth outside the inner layer of the uterus. It is impossible to get pregnant with widespread endometriosis, which grows into the muscular layer of the uterus, affecting the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
If you still manage to get pregnant with these pathologies, then the period of gestation may be accompanied by the following complications:
- Low attachment and placenta previa.
- High risk of early pregnancy loss.
- Threat of premature birth.
- Chronic hypoxia and intrauterine growth retardation due to impaired formation of the placenta.
During childbirth, women with large fibroids may experience discoordinated contractions and weak pushing due to impaired uterine contractility. In such cases, delivery by cesarean section or vacuum extraction of the fetus may be required.
It is much easier to get pregnant if you have small uterine fibroids located on the surface of the organ. Subserous fibroids do not deform the cavity and do not interfere with fertilization and attachment of the egg to the wall of the uterus.
The superficial location of the nodes can complicate the course of pregnancy only if they are large. In this case, they and the pregnant uterus intensely compress the organs and neurovascular plexuses of the pelvis, leading to constipation, frequent urination, pelvic pain and compression syndrome of the inferior vena cava.
Single myomatous nodes up to 3 cm located in the body of the uterus are also not an obstacle to successfully becoming pregnant and bearing a child. There are cases when fibroids decrease during pregnancy, which may be due to changes in hormonal levels.
Even in full health, it is more difficult for a woman aged 40 or older to become pregnant than for a woman aged 20-30. This is due to a significant decrease in eggs capable of fertilization and a physiological decrease in the synthesis of sex hormones. In primiparous women over the age of 40, the risk of chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus and complications of the gestation period increases sharply.
Reduces the possibility of pregnancy after 40 and fibroids. The older the woman and the closer the age of perimenopause, the greater the risk of developing tumor-like nodes on the uterus. Every year their number and size increase, which leads to complete deformation of the organ and the impossibility of conception.
At the stage of prenatal preparation the following is carried out:
- Complete examination of the patient, identification and treatment of somatic diseases and foci of chronic infection.
- Treatment of acute and chronic diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Hormonal therapy for ovarian dysfunction.
- Removal of tumors in the uterus that can complicate pregnancy.
Pregnancy should be under the supervision of an obstetrician-gynecologist. It is necessary to regularly undergo a medical examination, ultrasound of the uterus and fetus, and all diagnostic and laboratory tests necessary during pregnancy. Any deviation in a woman’s health requires urgent consultation with a doctor.
Surgeries to remove fibroids are of the following types:
- Laparotomy myomectomy - involves a wide surgical approach through an incision in the anterior abdominal wall. The operation is extremely traumatic, often complicated by adhesions, and has a long rehabilitation period.
- Laparoscopic myomectomy is performed with special endoscopic instruments that are inserted into the abdominal cavity through small punctures in the navel area. It is much easier to tolerate and has a low percentage of complications.
- Uterine artery embolization is the introduction of an embolic drug into the vessels of the uterine node through the femoral artery. The tumor quickly regresses, the rehabilitation period is short and easy.
A full-fledged and wealthy scar should form on the uterus, the menstrual cycle should normalize. Only in this case is it possible to get pregnant, safely carry and give birth to a child.
It is believed that at least a year must pass after myomectomy for the body to be completely ready for pregnancy. At this time, the woman should be regularly monitored by a gynecologist; a control ultrasound is performed 6 and 12 months after the operation. This is necessary to monitor the condition of the sutures on the uterus and possible postoperative complications (adhesions, infection, injuries).
What is fibroid and why does it occur?
Uterine fibroids are a benign tumor that affects the middle layer of the reproductive organ - the myometrium. This disease is diagnosed in every second patient after 40 years. In recent years, the disease has become younger, appearing even in nulliparous women. Statistics show that fibroids account for about 25% of all gynecological diseases. According to unofficial data, tumor growth in the myometrium is observed in 7 out of 10 representatives of the fairer sex. Uterine fibroids can be called the most common benign female disease.
There are several types of tumor process:
- submucous - grows in the submucosal layer of the myometrium, located closer to the endometrium (may have a stalk, descend into the uterus and even vagina);
- intramural – located in the muscular layer of the myometrium;
- interstitial – affects the intermuscular layers of the uterus;
- subserous - grows on the outer area of the uterus, extends into the abdominal cavity;
- cervical – formed in the muscle layer of the cervix (accounts for 5% of all cases of diagnosed myometrial tumors).
Myoma complicated by endometriosis is dangerous. The main reason for the development of these diseases is hormonal imbalance. Diagnosing it is not difficult. It is enough to contact a gynecologist and tell about your complaints. In most patients, myometrial tumors are accompanied by pain and pressure in the pelvic area, pulling sensations in the lower back and menstrual irregularities. The causes of the proliferation of myomatous nodes are:
- hormonal imbalance;
- delayed puberty;
- no pregnancy or breastfeeding;
- abortions and diagnostic interventions in the uterine cavity;
- inappropriate or independent use of hormonal medications;
- gynecological diseases;
- genetic predisposition;
- lack of physical activity and poor diet;
- stress, emotional distress, chronic fatigue;
- bad habits.
Is it possible to confuse fibroids with pregnancy?
Often myomatous nodes are symptomatically similar to the gestation period. They can be confused with pregnancy due to the following symptoms:
- Delay of the next menstruation.
- Bloody discharge during the intermenstrual period.
- Enlarged belly.
If these signs occur, you should definitely consult a doctor to make a correct diagnosis.
Most accurately, a uterine tumor can be detected by examining the uterine cavity with ultrasound. Confusion on ultrasound can only occur if the pedunculated submucous fibroid has a small volume.
It can be mistaken for an embryo. In such cases, it is necessary to determine the concentration of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) in the urine or blood. This hormone is a marker of pregnancy and with fibroids its concentration is close to zero.
How to distinguish
Pregnancy can be distinguished from myomatous tumor by the following features:
- Weekly increase in the concentration of hCG in the blood and urine.
- The appearance of a bluish tint of the vagina and cervix, softening of the tissues of the organ when palpated.
- Ultrasound: detection of fetal heartbeat from 6-12 weeks, movements from 16 weeks of gestation.
In the early stages, it is quite possible to confuse a myomatous node with a fertilized egg. The reason may be old ultrasound equipment, unclear images, or the doctor’s lack of competence may play a role. If the specialist is highly qualified, he will never confuse the neoplasm with a fertilized egg.
There are a number of different studies that help determine what is happening in a woman's body. A gynecological examination allows you to determine whether the patient is pregnant or not. The doctor prescribes the necessary hCG, blood and urine tests. You can understand your condition by the menstrual cycle. If you have menstruation and discharge appears between them, then most likely this is due to the formation of fibroids.
Course of pregnancy
Uterine fibroids in pregnant women have their own characteristics. From the first days of pregnancy, hormonal changes occur in the female body, provoking the growth of myomatous nodes. The nutrition of the uterus also improves, this is an additional factor in their development. Possible complications of pregnancy depend on the initial location of the myomatous nodes, their number, size and dynamics of development.
If the size of the nodes is small, they are well located inside the uterus, far from the placenta, the risks are minimal. If the nodes are large, and at least one of them is located next to the placenta or in the lower parts of the uterus, complications are possible.
The main complications of pregnancy with fibroids: placental insufficiency, spontaneous termination of pregnancy in the first trimester, miscarriage and premature birth in the second. If the placenta does not have enough nutrition due to rapidly growing fibroid nodes, the child may experience oxygen starvation and developmental inhibition. Large myomatous nodes can deform the uterus, reduce its ability to stretch, and increase excitability and tone. The growth of the baby in the uterus can lead to disruption of the blood supply to the nodes, their inflammation and intrauterine infection of the child.
Contraindications
The growth of fibroids while carrying a child can lead to many complications. The development of all kinds of pathologies and diseases sometimes has to be stopped through emergency childbirth or termination of pregnancy. Therefore, pregnancy must be taken very seriously. Constant examination by specialists is necessary to avoid unpleasant unexpected situations.
For this disease, gynecological massage is contraindicated. Also, the lower abdomen should not be allowed to warm up in any way. That is, a bathhouse, solarium, sauna, etc. are contraindicated. Do not lift weights over 3 kg and drink a lot of water before bed. The latter can lead to swelling of the uterus.
Uterine fibroids and pregnancy - features of the course
Yesterday we started talking about such a common pathology of the female reproductive system as uterine fibroids.
Today, fibroids have become much younger, and their occurrence is quite possible in fairly young women who plan to become pregnant and have children. In this part we will continue the conversation about the mutual influence of pregnancy and childbirth on fibroids, which began yesterday. We have already talked about how fibroids can affect the course of pregnancy, and today we will continue the conversation, focusing in more detail on some other aspects. The influence of fibroids on childbirth. Myoma is a tumor of muscle tissue and therefore, it will somehow affect the process of childbirth. The thing is that childbirth occurs as a result of the fact that the muscular elements of the uterus actively contract, the cervix opens and the fetus is expelled. If there is a tumor in the wall of the uterus, even if it is small in size, this can definitely affect the birth process for the worse. And in fact this is so, most women with fibroids experience difficulties in childbirth in the form of a protracted process with a long water-free interval. Often, in the presence of myomatous nodes, there is a need to carry out or complete the labor that has begun by caesarean section. Although, in principle, fibroids themselves, if they do not interfere with the gestation of the fetus, as a rule do not represent a true obstacle to the birth of the fetus, but the formation of myomatous nodes, especially if they are large, can lead to abnormalities in the position of the fetus and in its presentation
The fetus may take a transverse position in the uterus, may be in a pelvic or facial presentation; with such positions of the fetus, the natural birth of a child is impossible, and a caesarean section must be performed. When performing a caesarean section, in some circumstances, if the incision area is in the area of the node, doctors will simultaneously remove the tumor at the birth of the child. During childbirth with the presence of uterine fibroids, complications such as premature placental abruption often occur, especially if the location of the fibroids is not very favorable, it is located behind the placenta (retroplacentally). When planning the management of childbirth, doctors must take into account all these circumstances and think through in advance the options for the development of events and the provision of assistance.
Features of the postpartum period
The presence of uterine fibroids cannot go unnoticed by the body, and can significantly affect the postpartum period, leading to various kinds of complications. Both early and late postpartum complications can be associated with the presence of myomatous nodes in the uterine wall. The main early complications of the postpartum period include the development of postpartum hemorrhage, which occurs as a result of uterine hypotonicity, as well as tight attachment of the placenta itself to the uterine wall, or a complication such as placenta accreta. Late complications include incomplete involution of the uterine walls, when the size of the uterus does not completely return to its original size. There is also an increased risk of developing infectious and inflammatory complications.
The influence of pregnancy and childbirth on the course of uterine fibroids
Naturally, not only the fibroid itself affects the course of pregnancy and childbirth, but there is also an inverse interaction - the development of pregnancy and childbirth also affect the course of the fibroid. Thus, in order for pregnancy to develop and continue, increased levels of both the amount of estrogen and increased amount of progesterone are necessary (and progesterone is even more important). Both substances significantly affect the course of fibroids, which can lead to progression of the process.
In addition to the occurrence of certain hormonal changes, during pregnancy certain mechanical changes also occur in the area of the uterus and especially its muscle layer. There is an active increase in muscle fibers, their quite pronounced stretching in the longitudinal and transverse direction, increased blood flow in the area of the uterine walls, which leads to a change in the shape and size of the fibroids. But in any case, the effect of pregnancy on fibroids largely depends on the extent to which the fibroids have reached in their development and how much they have grown in the uterus. It is believed that fibroids also grow during pregnancy, but there is an opinion that this apparent growth is associated with an increase in the entire uterus as a whole. Typically, a slight increase in the size of fibroids occurs during the first and second trimester, but in the third trimester, usually all fibroids tend to decrease. In general, the trends in the development of fibroids are as follows: they rarely grow during pregnancy and practically do not interfere with pregnancy with their growth.
Often during pregnancy, another phenomenon can be observed - it is called fibroid degeneration (destruction of fibroids), but you should not be too happy about this fact, since the process of destruction of fibroids can be directly related to the extremely unpleasant processes of necrosis (death) of tumor tissues, and cysts can form. , swelling and bleeding. Degeneration of fibroids can occur at any stage of pregnancy, and can also form during the postpartum period - this directly depends on the location of the uterine fibroids. The exact reasons for this phenomenon of degeneration have not yet been clarified. The influence of an increased amount of progesterone (hormonal influences) is assumed, in addition, vascular and mechanical phenomena - there may be circulatory disorders in the tumor due to thrombosis of the vessels that feed the tumor vessels.
The main signs of impaired blood circulation in the uterus may be pain in the area where the myomatous nodes are located, increased tone of the uterus, and the temperature may rise. In the blood test, leukocytes are elevated and ESR is accelerated. The diagnosis is confirmed by ultrasound of the uterus, and this phenomenon continues for one to two weeks. During this process, doctors usually choose conservative treatment tactics, use analgesics and prescribe strict bed rest. If abdominal pain occurs and increased uterine tone persists, hospitalization and active inpatient treatment with continued pregnancy are necessary.
During pregnancy, surgical operations on uterine fibroids are performed extremely rarely and only for health reasons, when a high fever does not subside, acute abdominal pain or severe bleeding from the uterus occurs. Sometimes minimal surgical interventions are enough to preserve pregnancy. Only in rare cases, problems with fibroids can lead to spontaneous miscarriage and the formation of premature labor with the birth of a premature baby. But the changes in fibroids that occur in the first months after childbirth can be completely different. It is impossible to predict their development, and fibroids that were dangerous during pregnancy may disappear after childbirth and not appear at all, and as the uterus develops back, the location of the fibroids can change greatly.
How are fibroids diagnosed in pregnant women?
One of the classic manifestations of fibroids can be bleeding during and between periods, but during pregnancy there are no periods at all. Diagnosing fibroids during pregnancy can be somewhat more difficult than outside of it, but it is quite possible to make a diagnosis. First of all, fibroids are detected by two-handed examination, palpating the uterus and identifying a node, if it is large. But during pregnancy, the uterus can already be enlarged due to the growth of the fetus, and the last word in diagnosis belongs to an ultrasound examination of the uterus. But radiography, hysterography and hysteroscopy are not performed during pregnancy, they are prohibited!
How should fibroids be treated during pregnancy?
Complications
Why fibroids are dangerous:
- insufficient power supply to nodes;
- neoplasms begin to grow rapidly;
- placental insufficiency;
- vein thrombosis;
- miscarriage;
- anemia.
Myoma during pregnancy threatens miscarriage. The risk is quite high. The percentage reaches the sixty mark. 25% of women give birth prematurely. To prevent the threat, patients take vitamins and special medications. Doctors recommend staying in bed and limiting yourself in physical activity to prevent the occurrence of various complications.
To remove or not to remove fibroids during pregnancy
If fibroids and pregnancy are proceeding well, then conservative treatment, prescribed only by a doctor, is suitable. It is strictly forbidden to use any folk remedies. Myoma is a new growth and no one knows how it will behave under the influence of herbal infusions. When conservative treatment does not help and the fibroid grows, it is worth doing surgery - laparoscopy.
Tags: women's health, treatment of polyps in the uterus, fibroids, uterine fibroids, fibroids during pregnancy, the formation of polyps in the uterus, Uterine polyp, Polyps, Polyps in the uterus, Causes of polyps in the uterus, symptoms of polyps in the uterus
- Related Posts
- Thrush during pregnancy: how to treat?
- What tests should be taken throughout pregnancy?
- Utrozhestan during pregnancy until what week should I take it?
« Previous entry