a brief description of
Renal failure (RF) is a pathological process of the urinary system.
In which the death of nephrons and the inability of the renal parenchyma to perform the functions assigned to it are noted. The kidneys completely or partially lose their main function - excretory. Excretion of end products of metabolism in urine. Depending on the stage and type of disease.
There are acute and chronic forms of the disease. The acute form is an acute violation of the filtration capacity of one or two kidneys as a result of exposure to exo- and endogenous negative factors. Chronic PN is the gradual death of nephrons.
The most dangerous disease is diagnosed during pregnancy. Women with kidney pathologies are at risk for complicated pregnancy and childbirth.
Carrying a child with chronic renal failure carries many risks for the fetus and mother.
Progressive depression of kidney function leads to poisoning of the female body, disruption of the level of balance and fatal changes in the process of hemostasis.
In severe cases of the process and acute kidney pathologies, women are prohibited from becoming pregnant and giving birth to children, because the load on the urinary system and in particular on the kidneys increases.
When planning a pregnancy, specialists thoroughly examine the patient and issue a “verdict.”
Chronic kidney failure can cause:
- Emergency childbirth;
- Early birth (before 28 weeks of pregnancy);
- Intrauterine fetal death;
- Stillbirth;
- Blood loss;
- Violation of child development and difficult postpartum recovery period.
Acute renal dysfunction during pregnancy is diagnosed in the first and last trimester of gestation.
- Kidney failure stage 3 treatment
Kidney failure develops sharply and rapidly, threatening the life and health of the pregnant woman and the fetus.
An increase in the amount of toxic chemical components (uric acid, urea and creatinine) is associated with provocative factors in the development of the pathological process.
What are the dangers of urinary tract infections in pregnant women?
In most cases, the prognosis for all forms of infections is favorable. In a complicated course, infectious-toxic shock, respiratory failure and hypoxia of the extremities associated with low blood pressure may develop. The effect on the fetus is not very pronounced, since the bacteria do not enter the fetal bloodstream directly. However, phenomena such as maternal dehydration, low blood pressure, anemia and the direct effect of bacterial toxins can cause disruption of the blood supply to the fetal brain. If urinary system infections are not treated, then there is a high risk of developing arterial hypertension, preeclampsia, anemia, premature birth, and inflammation of the membranes - amnionitis. Naturally, all these factors seriously increase the risks of an unsuccessful pregnancy and childbirth.
Introduction. Blog of user AnastasiCFfond on 7ya.ru
Hello! I want to keep a blog here from the Charitable Foundation “In the Name of Life” Help for patients with cystic fibrosis.” I will talk here about assistance campaigns, about the fund’s activities, about the needs and opportunities to provide assistance to families with a child diagnosed with Cystic Fibrosis. but first I’ll tell you a little about the foundation itself: The “In the Name of Life” Charitable Foundation was created in 2006 by parents of children, as well as people who lost their loved ones who suffered from this disease. “In the name of life” is currently…
Vitamin preparations have both fans and opponents. With ideal health, ecology and a balanced diet under the age of 50, we are able to obtain from food or synthesize almost all vitamins in sufficient quantities. Everything in this story is wonderful, except that the average person does not eat 800 grams of cottage cheese and 200 grams of heart per day, as well as several bowls of salad from beets, carrots, green leaves and broccoli with a dressing of crushed nuts and herbs and...
Prevention of kidney diseases in expectant mothers
Pregnant women can protect themselves from the occurrence of kidney diseases by taking preventive measures. By following simple rules, you can survive the period of waiting for a baby without consequences for your body.
- Every day, drink at least a glass of cranberry or lingonberry juice. These berries are good not only for the treatment of kidney diseases, but also for prevention.
- From the first days when you find out about pregnancy, you need to adhere to a diet that will help maintain kidney health. Avoid everything salty, smoked, fried, and fatty. Eliminate white bread and all legumes from your diet.
- You need to drink at least 2 liters of water per day.
- Go to the toilet as often as possible, do not tolerate it under any circumstances.
- Clothes should be loose; remove all tights and swimming trunks that are tight or cause discomfort.
- Buy underwear only from natural cotton; this can be found in departments for pregnant women.
- Don't take a bath, use a shower.
- Don't forget about gymnastics for pregnant women.
If you don’t have the opportunity, time or simply desire to attend gymnastics in a group, then be sure to do one exercise at home - stand on all fours. Take this pose 3-4 times a day, hold for 15 minutes. The uterus in this position will not put pressure on the urinary tract and kidneys, the organs will rest a little from the heaviness. This exercise also helps with back pain.
Causes, development and complications
During pregnancy, changes are observed in the female body: immune defense decreases, diseases appear that the woman had not previously suspected.
The pressure exerted by the fetus on all internal organs forces the body to work in double mode. The process is aggravated by acute or chronic forms of renal failure.
The main factors provoking the development of chronic renal failure in pregnant women:
- Diseases that cause damage to the glomerular system. Diabetes mellitus, glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis in the chronic stage, rheumatic diseases and arterial hypertension.
- advanced acute form of renal failure.
Causes of acute renal failure in pregnant women:
- malignant neoplasms of the pelvic organs;
- established pyelonephritis before the gestational period;
- postpartum consequences (blood loss, abortion in late stages of gestation, antenatal death of the fetus and its long stay in the uterine cavity;
- cystitis (possible development of a postrenal form of the disease);
- curettage of the uterine cavity with non-sterile instruments;
- toxicosis and drug poisoning;
- candidiasis;
- operations involving transfusion of red blood cells with an inappropriate Rh factor;
- urinary system injuries;
- a sharp change in weight upwards.
The development of acute renal failure occurs in different ways, depending on the diagnosed form of the process:
- prerenal – resulting from a violation of the blood supply to the organ;
- renal – characterized by the development of a violation of the functional duties of organ cells;
- postrenal - develops when the urinary ducts are blocked. Stones or salt crystals.
Consequences (complications) as a result of kidney failure in pregnant women, regardless of stage:
- Kidney failure - symptoms and signs. Treatment of acute and chronic renal failure
- indication for ACS;
- premature birth;
- threat of miscarriage;
- the child's subsequent stay in intensive care wards to eliminate
- negative consequences;
- impaired hemostasis, which threatens extensive blood loss on the part of the mother;
- intrauterine death of a child for a long period of time;
- threat of sepsis and uremic coma;
- myocardial or cerebral ischemia;
- swelling of the limbs;
- anemia;
- if treatment is refused, death will occur.
Causes of chronic renal failure
The reasons why chronic renal failure occurs are kidney pathologies: chronic glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis.
Chronic renal failure is a rather complex form of kidney disease that requires constant treatment and a number of preventive measures to prevent negative consequences. If you ignore the recommendations of your doctor and do not follow therapy, chronic renal failure develops into kidney failure and nephrosclerosis. The reasons why chronic renal failure occurs:
- kidney pathology: chronic glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis, kidney tuberculosis, polycystic kidney disease, organ cancer and nephrlithiasis;
- diseases of the urinary tract:
- urethral stricture, urolithiasis;
- cardiovascular diseases: atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, angiosclerosis of renal vessels;
- endocrine diseases: diabetes, thyroid problems;
- systemic pathologies: hemorrhagic vasculitis, renal amyloidosis.
How is the development of a pathological process determined?
Diagnosis of renal failure includes tests and hardware examination.
When the first symptoms develop, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor or report any warning signs during a routine examination. To determine the cause, a set of studies will be prescribed that will help establish the cause of the deviations:
- blood and urine collection for general analysis;
- biochemical study of blood;
- microbiological analysis of urine;
- Ultrasound of the bladder;
- MRI.
Return to contents
Prevention
For women who are planning a pregnancy or are already pregnant, it is important to adhere to rules that will help avoid the occurrence of urinary tract infections. To begin with, for women who are just planning a pregnancy, it is important to treat chronic diseases and eliminate possible sources of infection and inflammatory processes. In situations where women have endocrine pathologies, you need to consult a doctor who will prescribe a set of medications with the help of which the hormonal levels will return to normal.
During pregnancy, you should drink plenty of fluids. Not only water is taken into account, but also all liquids that enter the body, for example, teas, compotes, herbal decoctions and soups. However, it is important to note that only those pregnant women who do not have severe edema should follow a heavy drinking regime. It is important to empty your bladder on time when you feel the urge, even when it is not full. This rule plays a key role, since accumulated urine in the bladder puts pressure on the uterus, which can lead to miscarriage.
In addition, during pregnancy the patient is prohibited from douching. Instead, you should consult your doctor and choose a different path to treat your illnesses. The patient also needs to take care of personal hygiene. During pregnancy, it is forbidden to take a bath, and it is better to change underwear every day. We should not forget that pregnancy should proceed under the constant and careful supervision of the attending physician. If the patient experiences changes in her condition and new symptoms appear, she should immediately consult a doctor and find out the cause.
etopochki.ru
Symptoms of the disease
- latent phase (hidden): fatigue, weakness, dry mouth. Minor abnormalities in urine analysis;
- compensated phase: increased diuresis to 2.5 l, severe apathy and weakness;
- intermittent phase: a persistent change in nitrogen metabolism in the biochemical analysis of venous blood. Nausea, vomiting, tremors, increased thirst and unpleasant taste in the mouth. The skin turns yellow and a specific urinary odor appears.
- terminal phase: complete absence of urine, puffiness of the face, skin acquires a gray-yellow tint, defecation is disrupted. Fatal disorders of the internal secretion organs, nervous system disorders, encephalopathy, irreversible changes in the coagulation system.
- nagging pain in the lower back;
- cessation of urine output;
- adynamia;
- lethargy;
- proteinuria;
- azotemia;
- body hyperthermia;
- muscle weakness;
- change in the color of urine (when it is excreted);
- ari smell from a pregnant woman;
- change in skin color.
A pregnant woman can determine the initial symptoms herself and immediately contact a gynecologist.
Causes of kidney enlargement
Whether the right kidney is enlarged during pregnancy or the left one, there are a variety of reasons for this:
- Pyelonephritis. This is the most common disease among pregnant women. We will talk about this disease in more detail below.
- Glomerulonephritis. This disease is an immune-inflammatory disease and often occurs as a complication after influenza or tonsillitis. Symptoms may include swelling in the face and legs, frequent urination, and a dull ache in the lower back.
- Kidney stones also form quite often during pregnancy, and it is they that cause the organ to expand. A stone can become an obstacle to the outflow of urine by getting stuck in the ureter or when leaving the renal pelvis, which is how the organ enlarges. If there are stones in the kidneys, the first sign of this will be unbearable pain, especially when urinating. Small grains will be visible in the urine - finer than sand, reminiscent of powder.
The kidneys may be enlarged during pregnancy due to many medical conditions that require a more detailed review. We suggest moving on to familiarize yourself with the most common ailments that occur during pregnancy.
Diagnostic methods
To determine the cause of kidney dysfunction, you need to see a doctor. After examining and studying the medical history, the doctor will prescribe the examinations necessary to verify the diagnosis. Kidney disease and pregnancy are a dangerous combination and can cause serious complications for the fetus. Therefore, the doctor must decipher the research results. To make a correct diagnosis, an assessment of the indicators together is required. The main tests that are prescribed for the progression of pathological disorders in the kidneys are:
- general (clinical) blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko,
- urine analysis according to Zimnitsky;
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys.
With pyelonephritis, the following changes are characteristic: in a clinical blood test - an increase in leukocytes, ESR and a decrease in hemoglobin concentration; in a general urine test - an increase in the number of leukocytes, the presence of protein and bacteria, a possible increase in red blood cells. In complicated courses of the disease, according to the results of biochemistry, an increase in the concentration of urea and creatinine is noted. In the Nechiporenko study, the growth of leukocytes is determined. The results of the Zimnitsky analysis indicate a violation of the concentration function.
Glomerulonephritis is characterized by an increase in the number of leukocytes, eosinophils and a decrease in the level of platelets in a general blood test. Based on the results of biochemistry, an increase in indicators such as creatinine, gamma globulin, and urea is determined. Indicators of urine analysis are deviated from the norm as follows: increase in density, presence of protein and traces of blood, change in color, decrease in volume. According to the results of the coagulogram, a decrease in PTT and an increase in PTI are noted. If an immunological study has been carried out, then most likely an increase in the level of immunoglobulins M and A will be determined.
To confirm asymptomatic bacteriuria, in addition to basic studies, urine culture for microflora is also prescribed. The analysis allows you to determine the type of pathogenic microorganisms and their sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. It is more difficult to detect urolithiasis during pregnancy due to the fact that X-ray examination is contraindicated. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor is guided by ultrasound data of the urinary system, a positive Pasternatsky symptom and an increase in the level of red blood cells, white blood cells and crystals in a general urine test.
Treatment of urinary tract infections in pregnant women
Depending on the severity of the disease, treatment can be carried out on an outpatient basis or in a hospital setting.
It is imperative to treat asymptomatic bacteriuria, since it is the main cause of the development of more severe diseases. Treatment can be divided into behavioral methods and antibiotic therapy.
Behavioral methods include simple hygiene rules:
- You can't take a bath during pregnancy, only shower
- You can wipe the perineum after urination or defecation only from front to back
- Wash your hands thoroughly before using the toilet
- Do not use washcloths to wash the perineum
- Use only liquid soap to prevent bacteria from growing in the soap bars.
- When showering, the first thing to do is wash the area around the urethra.
For antibiotic treatment, drugs from the group of penicillins, cephalosporins, sulfonamides and nitrofurans are used. Typically, the duration of therapy is 14 days. Second-line drugs include fosfomycin (monural).
The choice of drug, frequency of administration, dosage and duration of administration is determined by the attending physician.
ultraclinic.com.ua
Inflammatory diseases of the lower urinary system include: acute urethritis, acute cystitis, asymptomatic bacteriuria
.
Inflammatory diseases of the upper urinary system are: pyelonephritis, abscess and kidney carbuncle
. Inflammatory diseases that occur against the background of an existing pathology of the urinary system (urolithiasis, ureteral stricture, renal failure, etc.) are characterized as complicated.
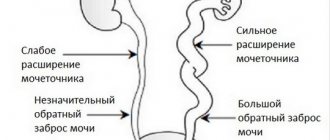
The reasons that influence women's susceptibility to infection are: short urethra, proximity of the urethra to the rectum and external genitalia, hormonal changes. During pregnancy, conditions are additionally created for stagnation of urine and disruption of its outflow due to significant expansion of the renal pelvis, lengthening of the ureters, decreased tone and contractility of the muscles of various parts of the urinary system, and displacement of the kidneys. In addition, the outflow of urine from the kidneys is impaired due to the mechanical pressure of the pregnant uterus on the ureters. In this regard, in 1/3 of pregnant women, urine backflow from the bladder into the ureters occurs, which contributes to the spread of infectious agents to the upper parts of the urinary system.
Risk factors for the development of urinary system infections are: disordered sex life and frequent changes of sexual partners, non-compliance with the rules of personal and sexual hygiene, previous inflammatory diseases of the genital organs (inflammation of the cervix, uterus and uterine appendages), the presence of foci of chronic infection in the body, endocrine pathology ( diabetes mellitus), pathology of the urinary system ( urolithiasis, chronic cystitis, kidney development abnormalities
).
Taking into account the predisposing circumstances and risk factors for the development of inflammatory diseases of the urinary system for all pregnant women, when registering at the antenatal clinic, it is advisable to conduct a screening examination, including a urine test using bacterial culture
.
The most common causative agent of inflammatory diseases of the urinary system is Escherichia coli
(80%).
Other typical pathogens of this group of diseases are Klebsiella
,
Enterobacter
(10-15%), as well as
staphylococci
and
streptococci
(5-10%).
Asymptomatic bacteriuria
characterized by the presence of bacteria in the urine without clinical manifestations of infection. This pathology is a risk factor for the development of acute pyelonephritis and requires specific antibacterial therapy. Diagnostic signs of asymptomatic bacteriuria include the detection in urine of bacteria belonging to the same species, in quantities greater than and equal to 105 CFU/ml in two samples taken with an interval of more than 24 hours (3-7 days) in the absence of clinical signs of infection.
Cystitis
Acute cystitis is one of the most common inflammatory diseases of the urinary system in pregnant women and occurs mainly in the first trimester. Typical symptoms of acute cystitis
are: painful urination, frequent imperative urges, pain above the pubis, the presence of blood elements in the last portion of urine. These phenomena are accompanied by such general symptoms as weakness, malaise, and a slight increase in body temperature. A urine test reveals leukocytes and bacteria.
Treatment of pregnant women, the choice of drug and its dose is carried out only by the attending physician. In the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the lower urinary tract in pregnant women, the use of antibacterial drugs
If possible, it should be delayed beyond 12 weeks.
In the 2nd trimester, it is possible to use amoxicillin/clavulanate, 2nd generation cephalosporins (cefaclor, cefuroxime axetil), in the 3rd trimester it is advisable to use 3rd and 4th generation cephalosporins
(cefotaxime, ceftazidime, ceftibuten, cefepime, cefaperazone/sulbactam). In this case, a single dose of the drug or a short 3-day course is sufficient, after which it is necessary to conduct a repeat cultural study after 7-14 days in order to assess the effectiveness of treatment. In cases where the therapy is ineffective, a second course of treatment is carried out using other drugs. If, after the second course, there is an increase in microorganisms, it is necessary to exclude urolithiasis, diabetes mellitus and other urinary tract diseases with further appropriate treatment using monural at a dose of 3 g every 10 days or furagin at a dose of 50-100 mg once a day. In addition, repeat urine tests are performed until the due date. After completion of antibacterial therapy, it is advisable to use herbal uroantiseptics (phytolysin, canephron, lingonberry leaf, cranberry juice).
www.art-med.ru
Causes of acute renal failure
1. Shock kidney. Acute renal failure develops during traumatic shock with massive tissue damage, due to a decrease in the volume of circulating blood (blood loss, burns), and reflex shock. This is observed in accidents and injuries, severe operations, damage and decay of liver and pancreas tissue, myocardial infarction, burns, frostbite, transfusion of incompatible blood, abortion.
2. Toxic kidney. ARF occurs when poisoned by nephrotropic poisons, such as mercury, arsenic, Berthollet's salt, snake venom, insect venom, and mushrooms. Intoxication with drugs (sulfonamides, antibiotics, analgesics), X-ray contrast agents. Alcoholism, drug addiction, substance abuse, professional contact with salts of heavy metals, ionizing radiation.
- Chronic renal failure: stages of development and consequences
3. Acute infectious kidney. Develops in infectious diseases: leptospirosis, hemorrhagic fever. Occurs in severe infectious diseases accompanied by dehydration (dysentery, cholera), and bacterial shock.
4. Obstruction (obstruction) of the urinary tract. Occurs with tumors, stones, compression, trauma to the ureter, with thrombosis and embolism of the renal arteries.
5. Develops in acute pyelonephritis (inflammation of the renal pelvis) and acute glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the renal glomeruli).
Postpartum acute renal failure
The disease develops due to large blood loss, trauma, infection, and the administration of broad-spectrum medications. As the disease develops, a woman experiences an increase in body temperature, pain in the kidney area, difficulty urinating, and lack of appetite.
The liver may become enlarged and abdominal pain may be felt. Acute renal failure is often accompanied by other disorders associated with dysfunction in other body systems. If additional disturbances occur in the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, death may occur.
Symptoms of kidney disease
The symptoms of the pathology are as follows: a change in appearance due to impaired glomerular filtration
. The stage of renal failure, symptoms and general condition directly depend on the nature and morphology of the disease. The first symptoms of the disease appear in anemia, the chemical content of nitrogen and potassium substances, as well as an increase or decrease in the volume of urination per day. The symptoms of the pathology are as follows:
Recommended reading:
How to find a kidney recipient and who can become a donor?
- Changes in appearance due to impaired glomerular filtration; due to anemia, the skin color changes, it becomes pale and painful, dryness appears, and elasticity decreases. Spontaneous hemorrhages and itching may also appear. Due to impaired renal function, swelling, puffiness appears, muscle mass loses its elasticity and becomes flabby;
- Nervous system disorder. This symptom manifests itself in sleep disturbances, the appearance of apathy, memory deterioration, and the formation of limb disorders;
- A violation of the urinary system manifests itself in the form of a sharp increase in the volume of urine, over time the volume decreases and may disappear altogether;
- An imbalance in the water-salt balance in the body manifests itself in constant thirst, dry mouth, breathing is impaired, arrhythmia appears, the heartbeat quickens, the patient feels unwell and weak;
- An increased level of parathyroid hormone production, as a result of which the level of phosphorus prevails over calcium in the blood, where softening of bone tissue and the formation of fractures occurs;
- Violation of the nitrogen balance leads to the formation of an ammonia taste in the mouth, affecting the small and large intestines with severe pain attacks;
- A disorder of the cardiovascular system manifests itself in the form of an increase in blood pressure, damage to the heart, heart rate, shortness of breath, swelling of the extremities, the liver increases in size, acute heart failure and death may occur;
- A disorder of the blood system manifests itself in insufficient production of erythropoietin by the kidneys.
Disturbance of the digestive system manifests itself in the form of decreased appetite, attacks of nausea and severe vomiting, and inflammation of the salivary glands.
The mechanism of urinary tract infections during pregnancy
Infection in the urinary tract of women during pregnancy occurs from the surface of the perineum, where there is a high concentration of bacteria living in the rectum and vagina. Predisposing factors are weakened muscle tone of the ureters due to the influence of progesterone, stagnation of urine caused by compression of the ureters by the uterus, and increased urine output during pregnancy.
An increase in urine volume and a decrease in the tone of the ureters and pelvis leads to their expansion and even greater stagnation of urine. In 86%, the pelvis and calyx of the kidneys expand on the right side. These processes begin at 10 weeks of pregnancy and only progress over time. Accordingly, in the first trimester, acute pyelonephritis occurs in only 2% of pregnant women, in the second trimester - in 52%, and in the third trimester - in 46%.
In addition to stagnation of urine and expansion of the components of the urinary system, the chemical properties of urine change during pregnancy: glucose and some amino acids may appear. The mechanism for increasing the excretion of certain amino acids in the urine during pregnancy is not completely clear, but their appearance in the urine predisposes to an increase in the pathogenic properties of Escherichia coli, one of the most common causative agents of urinary tract infections.
Chronic renal failure during pregnancy
With this type of pathology, the process of bearing a child is difficult for a woman, and complications develop with double the frequency. This condition can trigger preterm labor, which will require a cesarean section. Subsequently, the baby will have to undergo intensive therapy to maintain his health. Pregnancy with chronic renal failure (CRF) goes smoothly if the form of the deviation is not complex. Otherwise, a miscarriage may occur, premature labor and large blood loss may develop during childbirth.
Return to contents
Description of the problem
Renal eclampsia is characterized by peculiar convulsions, which are similar to epileptic seizures, but have a different basis, causes and nature of the disease. In this case, attacks appear against the background of serious kidney diseases. Blood circulation in the brain is impaired due to swelling of the brain tissue and microcirculation disorders occur. This occurs due to water and sodium retention.
Causes of the syndrome and pathogenesis
Symptoms
The syndrome is characterized by convulsive attacks; a person may lose consciousness at such moments. Unreasonable lethargy of the body occurs, appetite disappears, urination becomes rare. The disease is also accompanied by headache, nausea and vomiting. Vision often deteriorates and sometimes disappears completely. Seizure attacks can occur suddenly or after the above symptoms. The disease includes the following stages:
- Time before cramps. During this period, the muscles of the face and eyelids are seized by spasms. The stage lasts about 30 seconds.
- Tonic cramps (muscle tension). The duration of this stage is from 10 to 30 seconds.
- Clonic convulsions (muscle tone changes). At this stage, the patient may rush from side to side. Duration - up to 2 minutes.
- Comatose period when the patient comes to his senses.
Eclampsia of the kidneys is mainly manifested by seizures.
During stages 1–3, a person has poor control of himself and faints. The pulse and pressure rise, the pupils stop responding to light. During such attacks, it is necessary to fix the tongue so that it does not sink or the patient does not bite it. You may foam at the mouth and the veins in your neck will be swollen. It also happens that during an attack (most often at the 4th stage), a person may involuntarily wet himself or be unable to hold back his feces. The attack lasts several minutes and can happen 2-3 times or up to 40 times a day.
Gradually the patient regains consciousness, but for some time he remains in a foggy state. After the attack, the patient does not remember anything about his condition; at first he thinks and speaks inhibited. But such consequences do not always occur; some may experience an attack while conscious, and sometimes it can lead to coma.
Symptoms of urinary tract infections in pregnant women
With asymptomatic bacteriuria, nothing worries the pregnant woman. With the development of an infection of the lower parts of the urinary system, pain in the lower abdomen, frequent urge to urinate, and hematuria appear. These symptoms are not strictly characteristic, since they can also be caused in healthy pregnant women due to compression of the bladder and pelvic organs by the growing uterus, an increased rate of urine formation and an increase in the volume of circulating fluid in pregnant women.
With pyelonephritis, body temperature often rises (above 38 degrees), pain in the side, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting occur. Sometimes body temperature may, on the contrary, drop.
Treatment
At the first stage of treatment for acute renal failure, it is urgent to restore homeostasis and eliminate disturbances in kidney function. Carrying out detoxification therapy helps cleanse the blood of waste and toxins and establish normal urine flow.
For these purposes, the following procedures are used:
Detoxification is accompanied by the introduction of drugs with a high content of sodium, potassium, calcium in order to restore the water and electrolyte balance in the body. Dopamine helps improve blood flow to the kidneys.
To better remove harmful metabolic products, gentle diuretic drugs (Gyrothiazide, Trigrim, Diacarb) are used. An associated bacterial infection is eliminated by a course (10–14 days) of antibiotics: cephalosporins, Amoxiclav, Clarithromycin.
Chronic renal failure requires long-term therapy. After eliminating the cause of the disease, treatment is aimed at strengthening the woman’s body and eliminating any health problems that have arisen:
In the final stages of the disease, patients require continuous hemodialysis in a hospital. If the kidney cannot be saved, then such blood purification becomes a lifelong necessity. An alternative may be a donor kidney transplant.
Source: https://2pochki.com/lechenie/pochechnaya-nedostatochnost-zhenshchin
Treatment method for disease during pregnancy
Kidney failure and pregnancy is a complex process that requires constant monitoring and supervision by specialists.
To prevent the formation of negative consequences and eliminate complications of renal failure in pregnant women, do the following:
- eliminate ectopic bleeding and hemodynamic disorders;
- with a normal gestational age, rapid delivery is performed to avoid stillbirth and fetal growth arrest;
- during the period of perenal acute renal failure, the intravascular volume of fluid should be restored, restoration is carried out by introducing a zotonic solution of sodium chloride;
- treatment of acute tubular necrosis is aimed at eliminating ischemia and infection, maintaining fluid balance and restoring blood supply to the organ;
- the early stage of cortical necrosis is eliminated with anticoagulant therapy; if there is no result, hemodialysis is used;
- During the development of obstructive acute renal failure, detoxification and antibacterial therapy is performed.
Kidney failure and pregnancy are a complex process that requires constant monitoring and supervision by specialists. With timely observation by specialists and implementation of recommendations, a positive result in bearing a fetus is possible.
Pregnancy and kidney pathology
Kidney failure and pregnancy significantly increases the load on a woman's entire renal system.
Kidney failure and pregnancy significantly increases the load on a woman's entire renal system. In chronic renal failure, pregnancy significantly worsens the morphology of the disease and entails its progression. Causes of complications:
- during pregnancy, strong blood flow increases and stimulates the tension of the renal tangles, some of which die;
- the process of normal absorption of salt by the renal tubules is disrupted, as a result of which the protein breaks down in large volumes, and its particles are toxic to the kidney tissue;
- due to increased work of the blood coagulation system, small blood clots are formed in the renal capillaries;
- Arterial hypertension increases, resulting in kidney necrosis.
During the period of deterioration of the filtration process by the kidneys, the level of creatinine increases, which complicates the conditions and course of pregnancy, and the gestation of the fetus becomes unfavorable. Complications of chronic renal failure for a pregnant woman:
- nephrotic syndrome with the formation of severe swelling;
- arterial hypertension;
- complex form of anemia;
- delay and defects in fetal development;
- inability to bear a fetus, premature birth;
- infectious pathologies of the urinary system.
Sources used:
- https://kakrodit.ru/pochechnaya-nedostatochnost-pri-beremennosti/
- https://tuberkulezkin.ru/pochki/pochechnaya-nedostatochnost-i-beremennost-simptomy-formy.html
- https://prourinu.ru/zabolevaniya/vazhnoe/pochechnaya-nedostatochnost-i-beremennost.html
- https://stranacom.ru/article_3486/
- https://lecheniepochki.ru/zabolevaniya/pochechnaya-nedostatochnost/pochechnaya-nedostatochnost-i-beremennost.html