Pregnancy, childbirth and lactation bring a young mother not only the joy of motherhood and positive emotions from communicating with her baby, but also a large number of new problems with her health. Similar pathologies include the condition of a woman when her stomach hurts during breastfeeding.
The causes of this pain symptom are quite diverse. And the very nature and localization of pain in nursing women is very different. To prevent abdominal pain during lactation, you should find out the cause of such manifestations.
Types of chronic gastritis
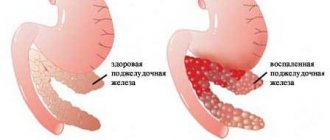
Symptoms of gastritis are renewed pain in the epigastric region, heartburn, and bloating. Any woman who has suffered from gastritis in the past can easily recognize the signs of exacerbation, although sometimes the first signs of the disease appear during pregnancy.
Chronic gastritis can be of three types, depending on the reasons that caused it:
- Chronic gastritis A. The reasons lie in the autoimmune processes occurring in the body. The gastric mucosa suffers from antibodies that the body mistakenly produces, and its own tissues are affected.
- Chronic gastritis B. Bacterial (superficial) type of gastritis caused by Helicobacter pylori on the mucous membranes.
- Chronic gastritis C occurs due to the reflux of bile acids. This type of gastritis is also called reflux gastritis.
These are the main types of chronic gastritis, although others occasionally occur: lymphocytic, granulomatous, eosinophilic. In chronic inflammation, stress and vitamin deficiency play a significant role, so a nursing woman should monitor her emotional state and take vitamin complexes.
Gastritis B and C are characterized by increased or normal acid content; with gastritis A, the acidity of gastric juice is reduced. More than 90% of all gastritis are bacterial. Atrophic (autoimmune) and reflux gastritis occur much less frequently.
Feed or treat
When the gastric mucosa is inflamed, a nursing mother is faced with the question: stop breastfeeding and treat the sore stomach or continue breastfeeding. Each choice has pros and cons. No one will dispute the importance of breastfeeding. If the symptoms of the disease are not pronounced, a woman can continue to breastfeed for up to a year, and then begin therapy. Most medications for gastritis are contraindicated in hepatitis B.
For mild pain, a woman is prescribed a gentle diet containing mineral waters, stewed and steamed vegetables, dairy products, boiled meat and fish. Meals during the treatment period are fractional, in small portions. When creating a menu, you should take into account the individual characteristics of the body: stop eating foods that cause stomach irritation and confidently eat something that does not cause nausea, pain, or discomfort. Well-cooked oatmeal and natural jelly coat the walls of the stomach well. It is recommended to drink kefir at night, limit the consumption of salt and hot spices.
To reduce the symptoms of postpartum depression, a woman is advised to get adequate sleep and avoid emotional turmoil. It can be extremely difficult to completely rest and recover in the first months after the birth of a child. The mother has to stand up to the crying baby several times. You should expect help from relatives who can take on some of the responsibilities. Before going to bed, the mother can express breast milk so that the baby's father or grandmother can cope with feeding without waking the woman in labor.
How can I relieve the painful sensations? :
To turn feeding from a painful procedure into a pleasant pastime, get rid of pain now and prevent its occurrence in the future, follow some simple instructions. 1. Make sure your baby is attached to the breast correctly. 2. Buy a special lotion for nipples - using it 1-2 times a day, you will get rid of dryness, and thereby prevent the formation of cracks. 3. Lubricate the nipples with a few drops of breast milk and leave until completely dry. 4. You may need to change your feeding regimen: if you put your baby to your breast more often, you will prevent milk from stagnating in the ducts. 5. First of all, place the baby on the breast that hurts less. 6. Try to gently remove your baby from the breast at the end of the feeding session. 7. Change the position of the baby each time when feeding - this way he will suck milk from different areas of the breast. 8. Apply heat to the mammary glands before feeding.
Treatment with drugs and herbal medicine
Taking herbs with an enveloping and analgesic effect is not contraindicated: chamomile, flax seed, oats, dill, licorice root. Such infusions can really safely relieve pain. But mint can reduce lactation and should be taken with caution. To reduce pain, taking a spoonful of flaxseed oil on an empty stomach is recommended.
To treat gastritis during breastfeeding, decoctions of other herbs are often used. They may provide mild analgesic and sedative effects, but their effectiveness has generally not been proven. Such herbs include deyasil, buckthorn, and calamus powder.
There are a number of drugs that are sometimes used to treat gastritis during breastfeeding, but their effect on the infant body is unknown or research is being conducted but not yet completed. Of these drugs, it is worth noting Gastrosidin (famotidine), Digestal, Mezim forte, Pancreatin, Festal.
Unsafe medications are harmful because they pass into breast milk and can cause various degenerative changes in the baby. Do not take Controloc (pantoprazole), De-Nol, Gerusil Lac, Helicocin while breastfeeding. Cimetidine, Enterosgel, Gasterin are recognized as safe. Smecta helps reduce pain a little, but it does not eliminate the cause of the disease.
Use Maalox, Almagel, Gastal, Gaviscon with caution. To relieve pain, you can use No-shpu (it is also used during pregnancy), Papaverine.
After breastfeeding
Superficial gastritis during breastfeeding does not require treatment, as does acute gastritis caused by Helicobacter pylori. Treatment of bacterial gastritis must be started after finishing feeding.
If the pain is unbearable, you can begin treatment by switching the child to complementary foods. During treatment, if a woman plans to breastfeed in the future, every effort should be made to preserve milk supply. To maintain lactation, you need to take vitamins for nursing mothers, massage your breasts, express milk regularly, and drink plenty of fluids.
When treating bacterial gastritis, therapeutic measures must be comprehensive. Painkillers and enveloping drugs must be combined with antibiotics. Treatment is aimed at reducing the content of hydrochloric acid, eliminating the inflammatory process and spasm, and eliminating bacteria. The Helicobacter bacterium, having entered the body, settles in it until it is destroyed by an antibacterial drug.
Could the pain be infectious in nature? :
If you experience breast pain along with symptoms such as fever, chills, and reddened breasts, you may have an infection of the milk ducts called mastitis. You should urgently consult a specialist - most often mastitis requires antibiotics. Thrush, which can affect the nipples, also has an infectious genesis. Thrush is manifested by itching or burning in the breast area, which intensifies during or after feeding. Painful cracks in the nipples may form. At the same time, the child easily picks up an infection from you: a white or yellow coating on the baby’s lips, tongue or inner surface of the cheeks most likely indicates a fungal infection.
The main causes of abdominal pain during breastfeeding
The weight of the uterus after childbirth decreases by 10-20 times
In most cases, the appearance of discomfort is associated with the restoration of the uterus. Immediately after the baby is born, it begins to shrink and gradually return to its previous size. This process usually lasts two to three months. The intensity of pain increases during feeding. This is explained by the fact that lactation stimulates the production of the hormone oxytocin, which is responsible for the contraction of smooth muscles - the myometrium of the reproductive organ. The more often a woman puts the baby to her breast, the more hormone is produced, the faster the uterus is restored.
At first, severe pain is felt in the lower abdomen. In nature, they resemble contractions before childbirth. The spasm weakens during pauses between feedings. Such discomfort is present for two weeks after discharge from the maternity hospital. A full bladder can increase discomfort, so women are advised to empty it when the first urge appears.
If a caesarean section was performed, aching pain in the lower abdomen will persist longer. At the initial stage of scarring they are pronounced, then they become periodic. Complete tissue fusion occurs within two to three months. All this time, one way or another, discomfort will make itself felt. If there are no signs of suppuration or suture dehiscence, there is no need to worry. If there is oozing or discharge of ichor, you should immediately seek medical help.
Strict adherence to personal hygiene rules, limiting physical activity, and following doctors’ recommendations can speed up the recovery process.
Digestive disorders
If after two months the aching pain in the lower abdomen has not disappeared on its own, but has become more intense and pronounced, you should be examined for diseases associated with the gastrointestinal tract. Very often they occur against the background of hormonal changes, which begin again after childbirth. It causes a disturbance in the acidity of the stomach, which leads to the formation of dysfunction of the liver and pancreas, and to the development of inflammatory reactions. They have characteristic symptoms:
- heartburn,
- increased gas formation,
- bloating,
- nausea,
- vomiting after eating,
- decreased appetite.
Another possible cause of pain is constipation. They occur in most women who breastfeed due to forced dietary restrictions. The consumption of fruits and raw vegetables is limited, the secretion of milk dries out the body, so the described problem is familiar to many. The pain is caused by abdominal distension, severe bloating and flatulence. These are constant companions of constipation. Even after bowel movement, women do not experience relief: the feeling of rectal blockage persists. This causes some concern.
Overeating also often causes pain in the lower abdomen. Girls who followed a diet during pregnancy, after its completion, begin to eat more varied foods, which causes indigestion.
When preparing a diet, a nursing mother must find a clear balance that will allow her to receive the necessary nutrients herself and provide them to her child.
Inflammatory diseases
If a nursing woman's body temperature rises and spotting appears, endometriosis may be suspected. This is a dangerous pathology that occurs due to infection of the inner walls of the uterus by bacteria during a cesarean section or curettage.
Another pathology is salpingitis - inflammation of the fallopian tubes. It develops when pieces of amniotic membranes remain. They begin to rot, the woman’s condition rapidly deteriorates, and she must be hospitalized immediately.
A nagging pain in the lower abdomen that radiates to the back may indicate damage to the spinal column or tailbone. This often happens after a difficult birth. Trauma does not manifest itself immediately, but after some time. Only an instrumental diagnostic examination can detect it.
There is a set of alarming symptoms that should force you to seek medical help: pain in the lower abdomen has been bothering you for more than two weeks, its intensity is constantly increasing, weakness occurs, and body temperature rises. Delay in such situations poses a threat to life.
What you should know about the postpartum period
The postpartum period begins in the first hours after birth. Even in the maternity room, an ice tank is placed on the stomach to stop bleeding. Then women are recommended to lie on their stomach - this position helps to reduce the size of the uterus. At this moment, the woman experiences aching pain in the lower abdomen. If the birth occurred by caesarean section, then this position (lying on your stomach) should not be taken. Natural childbirth is beneficial for a woman’s health; you should not insist on a cesarean section without sufficient medical indications. There is debate about the consequences of this operation for the child. Of course, there are situations in which cesarean section is the only method of delivery.
In the first hours after childbirth, it is dangerous for a woman in labor to get up, as this can cause loss of consciousness. If you feel an urgent need to get up, seek help from medical personnel. Throughout the week spent in the maternity hospital, the nursing mother will be accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, which will intensify while feeding the baby. This is fine. When the baby suckles at the breast, the hormone oxytocin is released, which causes contractions of the uterus, which is necessary for its restoration. The better the uterus contracts, the faster the woman will recover after childbirth.
Two weeks after birth, pain during feeding becomes almost imperceptible. The amount of bleeding also decreases. These discharges differ from menstrual discharge; they have a specific smell and are larger in volume. They can last for several weeks, but if their volume does not decrease, and the woman feels excessive fatigue and drowsiness, then this may be a bleeding that threatens the woman’s life.
During the postpartum period, a woman should not be exposed to physical and emotional stress. Lifting heavy objects can lead to serious health problems for a woman. In the first month after childbirth, a woman should be given more assistance with housekeeping than before childbirth. It is necessary to monitor the nutrition of a nursing mother. The diet should be complete and nutritious and exclude foods that can cause allergies in the child.
Return to contents
Is it possible to use analgesics for breastfeeding?
Doctors reason like this: if you can endure the discomfort, it is better to give up the pills. If not, you should know which drugs are strictly prohibited for breastfeeding mothers:
- "Analgin" and its analogues "Sedalgin", "Tempalgin".
- "Aspirin" and "Acetyl acid".
- "Citromon" and its substitutes "Citropak", "Askofen".
Medicines in this group can cause severe allergic reactions in a newborn baby; they negatively affect the baby’s internal organs.
Relatively safe, approved painkillers for a nursing mother are drugs that contain the active ingredient ibuprofen (Advil, Nurofen) or paracetamol (Strimol, Panadol). They are prescribed for the treatment of children from the moment of birth, so mothers can also use them as an ambulance.
It is periodically allowed to take “No-shpu”, “Ultracaine”. The latter drug is used for pain relief after caesarean section. Before use, be sure to consult a doctor.
How to get rid of abdominal pain during lactation
To eliminate discomfort, you need to clearly understand what could provoke it.
- Stomach pain is relieved with Smecta or Enterosorbent. Taking them helps eliminate heartburn and remove toxins from the body. Almagel relieves heaviness and the feeling of fullness well.
- If you have symptoms of pancreatic dysfunction (nausea, vomiting after eating, impaired bowel movements), you need to take an enzyme preparation. Pancreatin is allowed for breastfeeding women. The maximum dose is three tablets. Exceeding doubles the likelihood of constipation or diarrhea in infants.
- Dill water and Espumisan help relieve symptoms of intestinal colic.
- You can fight constipation with Regulax. This laxative does not pass into breast milk.
It is important to create a menu correctly and include safe products in it. During lactation, a woman should eat:
- lean meat;
- sea fish (except sturgeon and caviar);
- cereal porridge.
You cannot eat onions and garlic, marinades and spices, spicy and salty foods, fatty and fried foods, confectionery, or drink tonic drinks. Only by following a diet can you improve digestion and get rid of nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
First, you need to determine where exactly the breastfeeding mother is experiencing pain. If it's at the top, it's most likely the stomach. Remember what you ate during the day to see if you could have been poisoned. This may be an exacerbation of gastritis or another stomach disease. If your upper abdomen suddenly hurts after a heavy meal, this may well be the cause of overeating. In addition to poisoning from low-quality products, the stomach can also get sick from an abundance of too fatty or spicy foods, especially if up to this point you have been following a nursing diet. Pain in the upper abdomen is also often associated with problems with the pancreas, which, for example, has ceased to produce enough elements necessary for digesting food.
As for pain in the lower abdomen, it can be caused by colic, gas, intestinal obstruction or inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs. If you did not protect yourself while breastfeeding, the pain may be caused by an ectopic pregnancy or a threatened miscarriage (if, for example, you did not know you were pregnant). If a nursing mother has a stomach ache, she should also think about how long ago she had a bowel movement. When following a nursing diet, some people get too carried away and practically exclude fruits and vegetables from the diet for fear of colic or allergies in the child. As a result, the nursing mother does not receive enough fiber and begins to suffer from constipation. Infectious diarrhea or diarrhea due to poisoning is also often accompanied by pain in both the upper and lower abdomen. And finally, if the stomach hurts on the right side, the nursing mother may have appendicitis.
Negative consequences of not eating properly
Constipation in a nursing mother can occur due to changes in the position of the intestines. Pregnancy makes adjustments to all systems of the body, changing them and adapting them to your needs. The growing fetus gradually takes up more and more space, pressing and displacing other organs. The intestines are no exception to this process. The approaching birth puts more and more pressure on him. To restore its full functionality, it also takes some time, during which constipation may occur in nursing mothers.
An improper diet is one of the main criteria for the formation of constipation. In most cases, women suddenly change their diet for fear of eating something wrong or even refuse food in the first days after childbirth. Both of these approaches are fundamentally wrong, since they only aggravate the situation. After suffering stress, the body needs to restore not only its strength, but also all damaged tissues. Fasting or poor nutrition leads to the fact that the regeneration process is prolonged for a significant period of time. A weakened body cannot fully perform its functions and therefore limits some of them. The same applies to sudden changes in nutritional patterns. The fear of eating something extra, so as not to cause allergic reactions in the child, also plays a role. Thanks to this, the meager set of products is reduced even more.
Constipation in a nursing mother can be a consequence of stress. In some cases, the psychological factor comes first. Constant worries and tests endured in the last months of pregnancy leave an imprint on the mental state of the new mother. Childbirth is the final stage of this process. Only now, on top of everything else, there is also fear for the health of the little person. This decisive factor can create all the prerequisites for entering a state of severe stress. It also affects the functioning of all systems and organs. The intestines are no exception to the general list. So the formation of constipation when feeding a child may well be associated with this generally negative factor.
Stomach pills while breastfeeding
When a nursing mother has a stomach ache, all necessary measures must be taken so that she does not end up in the hospital, far from the child. If you have heartburn or suspect that you have eaten some low-quality foods, take smecta. This is an absolutely safe feeding drug that adsorbs all excess and eliminates the symptoms of stomach problems. If this is overeating or lack of enzymes, take pancreatin (preferably only after consulting a doctor), but only once. Systematically overeating, saving yourself with enzymes, is not at all beneficial for the pancreas.
If abdominal pain is caused by gases and colic, there is dill water for this (you probably already saved it for the child) and espumisan. For constipation, nursing mothers can take Regulax or use one of the folk remedies (castor oil, etc.). If you have severe pain in the lower abdomen or right side, it is better to consult a doctor. Painkillers taken for “female” pain are for the most part contraindicated during lactation, and for appendicitis it is contraindicated to take anything at all and you should immediately head towards the nearest hospital.
During breastfeeding, a woman’s body may experience various sensations that cause discomfort and anxiety. One of these sensations is pain in the lower abdomen.
Pain in the lower abdomen during breastfeeding is a common occurrence that occurs for a number of reasons related to poor health of the young mother and hormonal changes after childbirth.
Eliminate pain without harming the baby, perhaps knowing the etiology of the process and the treatment algorithm. Do not forget that first of all you need to consult a specialist.
Changes in hormonal levels and weakened abdominal muscles
The first factor causing constipation in a nursing mother is hormonal changes and general background disorders that affect the female body as a whole. This process begins during the first months of pregnancy, when all systems and processes begin to be rebuilt in anticipation of the development of a new life. The entire duration of bearing a child is marked by hormonal changes. Over nine months they deviate significantly from the natural level. Everyone knows that after childbirth, hormonal systems cannot quickly and most effectively restructure according to the previous parameters. This process occurs gradually and can take several months. As a result, metabolic disorders can cause constipation after childbirth.
The physiology of the process of eliminating used food involves some muscle activity. The work involves mainly the abdominal muscles, which create the necessary pressure on the rectum. Pregnancy makes some adjustments to their location and subsequent work. A gradually growing belly stretches the rectus and transverse abdominal muscles, causing them to lose some of their functions. The childbirth procedure puts excessive stress on weakened areas, which leads to their overload. As a result, the muscles simply cannot apply pressure to the intestine with the necessary force. As a result, constipation may occur during breastfeeding.
The pressure of the uterus on the intestines can also cause fecal stagnation. During pregnancy, the uterus gradually stretches. This is due to the growth of the baby. After his birth, she cannot instantly return to her previous condition, therefore she remains in an enlarged form and only over time gradually returns to her original state. During this period, the uterus can press on some parts of the intestine, thereby disrupting its function.
Causes of discomfort
The occurrence of pain in the lower abdomen during breastfeeding is physiological in nature
(associated with natural processes occurring in the body of a young mother after childbirth) or a pathological nature (due to diseases of the intestines, urinary organs or reproductive system).
Like menstruation
Cramping, pulling, aching, dull, reminiscent of pain during menstruation - such sensations may be natural and do not require treatment. Discomfort in the lower abdomen in the early postpartum period is associated with the production of the hormone oxytocin, which leads to contractions of the uterus after the baby is born.
Over the first 6-8 weeks, the muscular organ decreases from 1 kg to 50 g, causing pain in the young mother, as during menstruation. Due to the contraction of the muscles of the uterus, the cleansing process occurs
(mucous secretions mixed with blood come out - lochia) and pain receptors of the body and blood vessels of the organ are irritated.
By decreasing in size, the reproductive organ affects the tension of the uterine ligaments, irritates the pain receptors of the peritoneum and causes heaviness in the lower abdomen, similar to premenstrual syndrome.
Pain of a physiological nature can occur throughout the entire period of breastfeeding: this is due to the baby’s grasping of the areola and nipple, causing uterine tone. Usually the discomfort goes away 60 seconds after the start of feeding
: if the discomfort lasts longer, the baby is not attached to the breast correctly.
If unbearable cramping pain occurs, radiating to the lower back, or increased bleeding in the absence of a menstrual cycle, you should consult a doctor for examination and possible treatment.
In some young mothers, during the first year after childbirth, despite lactation, pain in the lower abdomen may indicate the onset of ovulation
, caused by the extinction of estrogen hormone production and the onset of menstruation. This phenomenon is not a pathology and usually occurs in connection with the introduction of complementary foods and a decrease in the frequency of the baby's feeding to the breast.
For functional bowel disorder
Unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen occur in nursing women when the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted:
Such pain occurs in a nursing mother for no apparent reason and often depends on:
- emotional state of a woman;
- nature of nutrition and volume of fluid drunk;
- the presence of traumatic and psychologically difficult events (stress).
The causes of discomfort are usually difficult to determine:
they are not associated with physiological or organic disorders of the digestive system and are diagnosed based on patient complaints.
Pain in the lower abdomen during breastfeeding, caused by a functional intestinal disorder, manifests itself as spastic discomfort in different parts of the anterior abdominal wall.
The occurrence of a functional bowel disorder is not uncommon
in nursing mothers: difficult childbirth, sleepless nights, disordered eating lead to disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and, as a result, to abdominal discomfort.
For various pathologies
Unpleasant sensations in the peri-umbilical, suprapubic and iliac regions can be observed in the case of pathological processes caused by the reasons given below.
Endometritis
The inflammatory process in the inner layer of the uterine mucosa (endometritis) is associated with the consequences of a difficult birth and a weakening of the immune defense of the new mother.
The penetration of infection into the cavity of the reproductive organ and the proliferation of bacteria leads to the formation of a focus of inflammation
and the appearance of constant intense nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
Against the background of breastfeeding, the intensity of the unpleasant sensations increases, and the process is accompanied by copious bloody and purulent discharge, increased body temperature, and chills.
The lack of qualified treatment for endometritis leads to the transition of the disease to a chronic form, the development of cysts, uterine adhesions and infertility.
Diseases affecting the lower urinary tract
Diseases of the urinary system may worsen during breastfeeding
. It's connected:
- with reduced immunity after pregnancy and during lactation;
- with the introduction of pathogenic flora due to insufficient hygiene or during childbirth;
- with impaired blood supply to the bladder and decreased muscle tone;
- with hypothermia, stress, trauma to the urethra during childbirth when a urinary catheter is placed.
Inflammatory diseases of the lower urinary tract, leading to pain in the lower abdomen in a nursing mother, include:
Pathologies are accompanied by frequent urge to urinate, the appearance of blood in the urine and symptoms of intoxication, requiring specialized therapy.
Pain in the lower abdomen during breastfeeding is also a consequence of cesarean section
, injuries to the pubic bone and spine during childbirth, discrepancy of the pubic symphysis, fissures of the external genitalia.
Regardless of the cause of the discomfort, a woman needs to visit a doctor for diagnosis and possible treatment of the pathology.
Preventive measures and drug therapy
Preventative measures are extremely important to restore normal functions of the digestive system. First of all, these include physical exercises that a new mother should do. In the first days after childbirth, you absolutely don’t want to do any physical work, and your muscles ache and feel sore. However, as paradoxical as it may sound, it is feasible exercises for muscle development that are the best way to eliminate constipation. They should start with several bends or twists, which will engage weakened muscles and give an impetus to the normalization of all body systems.
There are times when there is no other choice but to use medications. As a rule, these are various complications that block intestinal function for a long period. In such circumstances, the best solution would be to report the problem to your doctor, who will make his recommendations and give an opinion. In most cases, doctors prescribe special glycerin suppositories for constipation, which are designed to eliminate the problem at the local level. The principle of their use is to insert into the anus and rest briefly, during which the elements dissolve. The effect on the body begins its process from the moment the capsules dissolve. As soon as this happens, the active elements begin to be absorbed into the rectum, helping it to contract and push out feces. This leads to the passage of stool.
However, it should be remembered that suppositories for constipation should be used only on the recommendation of a doctor who is observing a woman. Such an appointment, as a rule, is made in the most extreme cases, when the effectiveness of other methods is practically zero.
How to help a nursing woman during lactation?
Abdominal discomfort in a nursing mother is complicated by the inability to take most medications that are contraindicated during lactation.
Depending on the cause of the pain, the specialist selects treatment and gives recommendations on nutrition and treatment of symptoms of the disease that does not have a negative impact on the baby.
Correction of diet and nutrition system
So what should you do if you are breastfeeding and suffer from lower abdominal pain? In case of dyspeptic symptoms caused by digestive disorders, it is first necessary to change the diet and nutrition system:
If an exacerbation of a chronic disease (pancreatitis, gastritis, cholelithiasis) has led to digestive disorders, it is necessary to engage in targeted treatment of this pathology, which contributes to the appearance of abdominal pain and dyspepsia.
Diet
Proper nutrition for a nursing mother can reduce abdominal pain
for functional intestinal disorders. A woman does not have to limit herself in food (after all, her body spends about 500 kcal to produce milk). It is enough to consume healthy foods that do not cause gas formation, fermentation and putrefactive processes in the intestines:
- lean meat and fish;
- boiled or stewed vegetables;
- gluten-free cereals (rice, buckwheat, corn);
- fermented milk products with a low fat content (cottage cheese, kefir);
- unsweetened fruits;
- eggs;
- whole grain bread croutons;
- vegetable oils;
- weak tea and dried fruit compote.
For abdominal pain, the nursing diet excludes the consumption of:
- sweets, fresh bread and pastries;
- salted, smoked, pickled delicacies;
- fried, fatty;
- canned food;
- fresh white cabbage and legumes;
- alcohol, strong tea and coffee, carbonated drinks;
- whole milk and fatty fermented milk products.
How to get rid of pain?
Abdominal pain during lactation, regardless of the cause, must be eliminated in accordance with the recommendations of a specialist. If discomfort occurs after curettage of the uterine cavity, a woman is recommended to:
- apply a cold compress;
- visit a gynecologist or (in case of heavy bleeding) call an ambulance;
- agree to examination and treatment in a specialized department.
If you suspect a pathology of the digestive organs, a young mother needs to call a doctor or visit a specialist herself
. You should not take painkillers and antispasmodics - in case of acute pathology, the drugs will change the picture of the disease and complicate diagnosis.
- The doctor will conduct an examination (examination, instrumental diagnostics, prescribe tests).
- Depending on the cause of the illness, he will prescribe drugs approved for lactation (enzymes, antispasmodics, carminatives).
- If necessary, decide on the use of antibiotics or surgical treatment.
- Inflammation of the uterine mucosa is treated in a hospital setting with antibiotics, immunomodulators, vitamins and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- In this case, a nursing mother needs to stop (or suspend) breastfeeding, follow a diet and get more rest.
If signs of endometritis occur, you should consult a doctor for examination and treatment.
Therapy for urinary system diseases should be determined by a specialist
. To relieve pain from cystitis and urethritis, a woman needs to increase the volume of fluid consumed to 2 liters, refuse junk food, and avoid hypothermia.
- preparations based on herbal components (Canephron, Phytolysin);
- injection of antiseptics directly into the bladder in a clinical setting;
- in case of ineffective treatment - suspension of lactation and antibiotic therapy.
Can analgesics be used?
It is possible to eliminate abdominal pain with the help of medications, but not all medications are allowed during breastfeeding. Painkillers are not recommended for nursing mothers due to the content of active substances that are contraindicated during lactation (they pass into breast milk and have a negative effect on the baby’s body).
Pain in the lower abdomen is a sign of organ dysfunction
and systems that cause discomfort to a nursing mother. Despite the constant hassle associated with the baby and breastfeeding, a woman should not forget about her health and consult a doctor in time for diagnosis and treatment of the disease in order to avoid dangerous complications of a possible pathology.
Almost every person faces problems with indigestion and intestinal obstruction. This problem does not escape breastfeeding women either.
The drug market offers a lot of drugs to eliminate the symptoms that accompany indigestion and are aimed at effective treatment, but if a nursing mother has a stomach ache, not all medications are approved for use. The fact is that the milk used to feed the baby will contain medications taken by the mother, and not all of them will benefit the child. It is very important to carefully consider the issue of choosing a drug, and, above all, take into account that it should not harm the health of the newborn.
Start of treatment measures
Treatment of primary symptoms of constipation during breastfeeding is based on the introduction of a special diet and preventive methods. More serious degrees of the disease may require minor drug intervention.
The first and most important factor in helping to treat constipation is following the principles of proper nutrition and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. These two criteria can quickly neutralize constipation and remove its unpleasant consequences. Some are wary of eating different foods to avoid negative effects on the baby. In general, there is some truth in this. However, the main thing is to remember that most natural products can still be eaten, you just need to subject them to special processing.
Some women stop eating meat immediately after giving birth. Such a decision will not bring anything good, since the body, at the time of tissue regeneration and organ restoration, needs an abundance of light protein, which meat products are rich in. Refusal to use them entails the fact that the body has nowhere to take this building element, and it simply cannot recover normally and effectively. Eating meat is not only possible, it must be done. Fried, smoked, fatty, heavy versions of this dish, of course, will have to be excluded so that this does not negatively affect the quality of breast milk. But boiled or steamed rabbit or chicken will be the optimal solution for creating the necessary supply of energy and building material.
Vegetables are also extremely important foods for both mother and baby. They contain many vitamins and mineral compounds that are responsible for normalizing metabolic processes and tissue restoration. Of course, it is not recommended to consume them raw, but it is quite possible to do so in a boiled version. The general principles of nutrition during breastfeeding include avoiding heavy and fatty foods, as well as reorienting the diet to simpler foods. Various cereals and boiled meat are the main allies in the fight against constipation and the best helpers in normalizing all metabolic processes in the body, as well as ensuring adequate nutrition for the baby.
Causes and symptoms of indigestion
Dyspepsia or indigestion is characterized by disruption of food digestion processes and the occurrence of constipation during breastfeeding in mothers.
The causes of dyspepsia can be different, namely:
- Binge eating;
- Chronic inflammatory disease of the digestive system;
- Eating poor quality, heavy or fatty foods;
- Lack or decreased activity of digestive enzymes produced by the pancreas.
The result of these reasons is that the digestive system is simply not able to cope with its functions, and as a result, pain, belching, constipation, heaviness in the stomach, loose stools, heartburn, bloating, mild nausea, general weakness of the body and dizziness occur - symptoms dyspepsia.
Spasms
Another common cause of abdominal pain is cramping. Experts note that the causes of the disease still remain unknown. With this disorder, no pathological changes in the functions and tissues of the organ are observed. Treatment is based on relieving muscle spasms. Presumably the disease develops against a background of nervous shock and stress. It is noted that only adults suffer from spasms.
If this disorder occurs, it is necessary to undergo a thorough diagnosis of the abdominal organs in order to exclude other causes of pain. Only after analyzing the condition of all organs and systems will the doctor be able to prescribe adequate treatment.
However, there is no need to attribute any pain to a spasm. Pain is a signal that some kind of disorder is occurring in the body.
It doesn’t just arise and go away. Our body is designed in such a way that we can learn about problems in the functioning of organs in time and eliminate them.
Drugs used for stomach pain in a nursing mother
Since the causes of abdominal pain, constipation and diarrhea in a nursing mother are different, the drugs aimed at neutralizing these symptoms are different from each other.
If a nursing mother has a stomach ache due to a lack of digestive enzymes, then their balance can be replenished only after consultation with a gastroenterologist with the help of medications such as Pancreatin, Vestal and Creon 10000. These drugs are indicated for use by women during lactation and are made from the pancreas animals. The drug Pancreatin contains enzymes such as lipase, protease and amylase, which not only promote the breakdown of fats, proteins and carbohydrates, but also normalize digestive processes.
Most often, a deficiency or decrease in the activity of digestive enzymes is accompanied by dysfunction of the liver and biliary tract, so medications containing components that normalize bile secretion, absorption and other indicators, such as Digestal, Festal, Panzinorm Forte and Digestal Forte, may be required. These drugs are allowed to be taken by women during lactation and pregnancy. The most effective and mildly acting drug, the effect of which is aimed at relieving symptoms if the stomach hurts during breastfeeding, is Mezim Forte - these tablets can be taken even by very young children.
In cases where a nursing mother has a stomach ache, heartburn may occur, the appearance of which is due to the fact that gastric contents enter the esophagus. To neutralize heartburn, it is necessary to use antacids, which, by neutralizing hydrochloric acid, reduce the acidity of gastric juice. There are a large variety of drugs that have this effect on the drug market, but drugs such as Almagel, Maalox and Phosphalugel are suitable for use by women during lactation.
The causes of flatulence in nursing mothers may be the consumption of large portions of foods such as fried potatoes, brown bread, milk and vegetables, since during childbirth the tone of the stomach muscles is lost, or insufficient absorption of gases in the intestine occurs due to gastrointestinal diseases. tract. Often, flatulence (excessive gas formation) is accompanied by a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the abdomen, hiccups, bad breath, belching and paroxysmal pain in the abdomen, which disappears after the gases pass. Traditionally, if a nursing mother has a stomach ache and flatulence develops, various infusions of cumin fruits, chamomile flowers, garden or dill seeds, as well as dill oil or fennel oil are used. These drugs facilitate the passage of gas due to their ability to relax smooth muscles and at the same time stimulate intestinal motility. Infusions made from the above ingredients can be combined, and nursing mothers are also allowed to use drugs such as Espumisan and Sab Simplex.
Constipation during breastfeeding is usually accompanied by symptoms such as malaise, weakness, headache, insomnia, irritability and decreased appetite, which are caused by toxic substances that are absorbed from retained stool. Constipation during breastfeeding can lead to an increase in the number of pathogenic bacteria, which interferes with the absorption and synthesis of B vitamins. If constipation occurs, laxatives are used, among which the main ones are herbal remedies such as rhubarb root, buckthorn bark, joster fruits, senna leaves , anise and castor oil, sabur, aloe juice, seaweed, flaxseed, agar-agar and various bran, defecation after consumption of which occurs within 12-20 hours. In addition to the above herbal remedies, if a nursing mother has a stomach ache and constipation occurs, indicated for use are such medications as Regulax, Mucofalk and saline laxatives such as magnesium hydroxide, sodium phosphate and Carlsbad salt, the effect of which - defecation - occurs 3-6 hours after use.
Why can the lower abdomen hurt after childbirth?
Unusual sensations may occur immediately after childbirth or several months later. If there are any doubts about the cause of the illness, it is better to consult a specialist and undergo a full examination.
Physiological reasons
With the birth of a child, a woman’s body begins to release large amounts of oxytocin into the blood. This hormone is responsible for the production of breast milk and the restoration of the uterus.
The reproductive organ should return to its normal state in a couple of months. The uterus needs not only to restore its shape and size, but also to take its original place in the pelvis. It is quite natural that this process causes discomfort - the uterine ligaments hurt.
Many people feel contractions of the uterine muscles while feeding the baby. Oxytocin is actively produced when the nipples are stimulated, which is what happens when the baby suckles. Experts advise feeding a newborn with milk on demand, including for this reason. The more often a woman puts her baby to her breast, the faster the body will recover.
The most severe pain is observed within a few hours after childbirth, then the pain gradually subsides. In the first week, the pain can be so intense that it even frightens the woman in labor, as it resembles the contractions she has experienced. Then the pain returns periodically when the necessary hormone enters the blood.
The neighboring organs, which have been under pressure from the uterus for several months, will also have to return to their previous state. This also applies to the bladder, due to its overcrowding, sometimes the lower abdomen aches and hurts. Doctors advise emptying it as often as possible immediately when you feel the urge to go to the toilet.
Those who gave birth by cesarean section will continue to experience pain in the suture area for a long time. This is an abdominal operation that requires long-term rehabilitation. A woman must follow all doctors’ recommendations and take good care of the stitch. If there are no complications, the pain will go away in 2-3 months.
When parts of the placenta or other objects remain in the uterus, the doctor will prescribe special IVs for the woman in labor. With the help of medications, the uterine cavity will be cleared, but this does not always happen. Sometimes a woman needs to have her uterus cleaned, a painful procedure performed under anesthesia. After aspiration, the organ needs a recovery period, and pain may be felt for a long time.
Stomach hurts when breastfeeding: diet for a nursing mother
The occurrence of abdominal pain, constipation and diarrhea in a nursing mother is often due to poor nutrition.
The most common diet myth for breastfeeding mothers is that they need a strict diet. It is very important to consider that a woman during lactation spends at least 500 kcal per day on feeding her baby, and this is not the only thing she has to do during the day. Carrying out household chores, shopping and going to markets, caring for a child, and working part-time indicate that nursing mothers should eat a nutritious and varied diet in order to replenish the calories expended in the body, and following a strict diet during this period will only lead to depletion of the body.
So, if a nursing mother has a stomach ache, you should definitely remember that this indicates mistakes made when preparing the diet. What the mother absorbs during the day is passed on to the baby through breast milk, so in order for none of them to have health problems, a woman’s diet during lactation should be as balanced as possible.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Main symptoms
“What could be easier than treating constipation?” - many of us can say. However, for an organism that has undergone the pangs of giving birth to a new life, this aspect can become a huge problem. It is quite simple to determine such a condition, since it is characterized by obvious signs:
- bloating;
- difficulty in excreting feces;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- pain in the intestinal area.
As a rule, these signs do not appear separately. They have the character of a gradual spread, which depends on the time spent without the toilet. Basically, constipation in a nursing mother begins to manifest itself 1-3 days after birth. It can continue for a considerable period of time, and its neutralization requires special preventive measures.