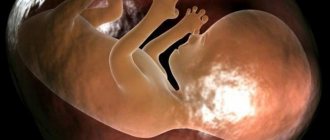
A low position of the fetal head is not a disorder, but only a diagnostic sign indicating the anatomical features of the body. This is a conditionally dangerous condition that can become a deviation only with concomitant disturbances in intrauterine development and fetal position.
The cephalic presentation of the fetus is a favorable position for the child, and the low position of the head is only a feature that doctors pay attention to, but do not classify as a deviation. This sign requires increased attention from specialists and the woman herself to the course of pregnancy, but there is no need to worry about this. This feature is revealed during a routine examination by a gynecologist and an ultrasound examination.
How should the embryo (fetus) normally be located in the uterus at different stages of pregnancy?
A few days after conception, the embryo descends into the uterine cavity and attaches to the endometrial layer of the uterine wall. Normally, this occurs closer to the bottom of the organ - the upper convex part, which protrudes above the line of connection with the uterus of the fallopian tubes.
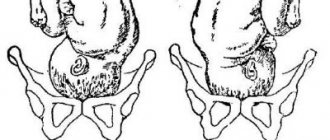
By the end of the third trimester, before birth, the fetus takes the position in which it will pass through the birth canal. Its head descends lower to the cervix and presses against the entrance to the pelvis. A cephalic presentation is considered normal, in which the baby’s head is positioned towards the exit. Pelvic, transverse and oblique presentation are pathologies, with the latter two a cesarean section is indicated.
Types of fetal presentation
Presentation, like the position of the fetus, can change throughout pregnancy, but starting from the 33rd week the baby almost always remains in a certain presentation. This is explained by its size, because it becomes more and more difficult to spin, and there is less and less space every day. And already from the 34th week the fetus gradually prepares for birth. The expectant mother begins to feel preliminary (training) contractions, and the baby gradually descends. At the last ultrasound, the presentation of the fetus is determined, in which it will be born.
Let's consider the types of fetal presentation.
Head presentation of the fetus
This is the most common position for giving birth. According to statistics, almost 95% of women give birth to babies head first. A child in a cephalic presentation is in a longitudinal position.
This presentation, in turn, is further divided depending on the level of extension of the head:
- occipital;
- anterocephalic;
- frontal;
- facial.
Occipital cephalic presentation of the fetus is the norm, in which all women give birth on their own, without additional intervention.
Anterior cephalic presentation is worse because the head enters the small pelvis at its largest size; such births are much more difficult. But there were cases when the child adapted and changed the position of the head during the birth process, making its way into the world easier. Such a presentation may be an indication for a caesarean section, but this issue is very individual. Each case is considered separately, taking into account other aspects.
Frontal presentation is very rare; it is an average degree of extension of the head. With this position of the fetus, natural childbirth is impossible, only with surgical intervention.
Facial presentation - maximum extension of the head. Technically, such a birth can take place naturally, but with trauma for both the child and the mother, which in most cases determines the tendency to have a cesarean section.
For a better perception of information, we suggest looking at a photo of a cephalic presentation of a child with varying degrees of head extension.
Breech presentation of the fetus
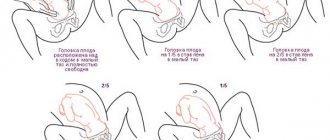
The second name for this type of presentation is breech. In this case, the baby is turned with his butt towards the exit of the uterus. That is, the butt and legs enter the small pelvis first. The baby is born either buttocks or legs forward, so breech presentation is divided:
- pure breech presentation (position a in the picture);
- mixed (position b);
- foot (position c).
Such presentation during childbirth does not occur very often (only about 5%). In most cases, when determining breech presentation, gynecologists give recommendations or perform manipulations themselves to turn the baby over.
Birth in a breech presentation is considered pathological, as it is accompanied by complications. It is quite possible to carry out such births naturally, but in some cases a decision is made to have a caesarean section.
It all depends on many characteristics of pregnancy:
- The size of the mother's pelvis.
- Child's weight.
- Gender of the child (in boys, the genitals may be damaged during childbirth).
- What type of breech presentation (breech, mixed or foot).
- What age is the woman?
- What kind of births were there, the history of previous births.
Transverse or oblique presentation of the fetus
Transverse and oblique presentation of the fetus is an indication for cesarean section. It is impossible to give birth to a child in such a presentation naturally.
Previously, during childbirth, twisting of the child's limbs was used, but in our time this is prohibited, because this procedure can cause irreparable harm to both the child and the mother. The only case when these manipulations can be used is only at the birth of twins. When the first child is born, and the second takes an incorrect position in a transverse or oblique presentation.
In what case is it considered that the baby is located low?
When do doctors talk about low placentation and the location of the baby? If in the second trimester the placenta is attached at a distance of less than 7 cm from the internal os of the uterus, and in the third trimester - less than 5 cm, then placentation is considered low.
Is it possible to independently determine how the baby is positioned in the womb? A woman may experience characteristic symptoms:
- aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- bloody, spotting discharge;
- problems with stool;
- bloating.
However, these symptoms only allow one to suspect that the fetus lies at the internal os. Diagnosis is made during a gynecological examination, during which the doctor can assess the distance between the fetus and the cervix. The diagnosis can be confirmed using ultrasound.
Causes of low position of the embryo (fetus)
Why is the embryo, and subsequently the fetus, located in the womb too close to the internal os? The reasons for the low position of the fetal head may vary depending on the trimester, and they do not always indicate pathological processes. In some situations, a low position of the fetal head indicates a normal pregnancy.
Early in pregnancy
Why is the embryo positioned too low at the beginning of pregnancy? In the first trimester, the close location to the os of the uterus is explained by the mechanism of attachment of the blastocyst to the endometrium. For implantation to be possible, the blastocyst must approach a suitable area of the endometrium. When the inner layer of the walls is covered with scars, attachment will be difficult. In some cases, implantation of the embryo is impossible, and it is brought out - a miscarriage occurs.
Reasons for attachment at the entrance to the uterus:
- scars on the endometrium after surgical abortion or surgery;
- inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- endometriosis.
At the beginning of pregnancy, low chorion attachment does not show itself in any way. A woman may not know about this feature until mid-term.
In the second trimester
If the fetus is located low in the second trimester, starting from the 20th week of pregnancy, characteristic symptoms appear in the form of nagging pain in the lower abdomen, frequent urination, and spotting. Risk factors:
- anatomical features of the structure of the woman’s pelvis;
- heavy physical labor in early pregnancy;
- inflammatory processes in the internal genital organs;
- multiple pregnancy.
Even more interesting:
Tongue with HIV infection photo
Yarina or Dimia
At the end of pregnancy and before childbirth
Shortly before birth, at 37–38 weeks, the baby takes a position convenient for passing through the birth canal. Its head descends closer to the internal os of the uterus and seems to be pressed into it. During this period, the stomach drops. The pregnant woman's heartburn goes away, it becomes easier for her to breathe, but other unpleasant symptoms arise: frequent urination, bloating, a feeling of fullness in the perineum.
The descent of a child before delivery is a normal physiological process. Obstetricians call it a harbinger of childbirth and advise preparing for the imminent birth of the baby.
Transverse presentation of the fetus during pregnancy
The transverse arrangement does not in any way threaten the course of gestation and normal development. The danger is the premature onset of contractions caused by bleeding.
With this pathology, the water drains very quickly, which immobilizes the baby, who blocks the pelvic area with his shoulder joints. Prolonged dehydration (more than 12 hours) leads to hypoxia and suffocation. Therefore, a complete diagnosis of the woman’s body is carried out in order to identify the causes of this pathology. Also, a decision is made on the method and timing of delivery.
In case of transverse, corrective gymnastics is recommended, which helps to turn the baby’s head towards the os of the uterus:
- lying down, roll from side to side for 10 minutes;
- stands in a knee-elbow position, raising the pelvis;
- rest with pillows under your hips.
If there is a threat of miscarriage or interruption, exercises are performed only under the supervision of obstetricians.
In most cases, transverse localization involves birth by cesarean section. The main deciding factor will be the presence of additional threats to pregnancy and the formation of pathologies.
Why is it dangerous for a baby to be in a low position at different stages?
In itself, this situation is not a pathology; it is dangerous only in combination with other symptoms - increased myometrial tone and a shortened cervix (up to 2 cm). In this case, the pregnant woman is constantly monitored, she visits the gynecologist more often than others and has an ultrasound scan.
If the baby's head is very close to the internal os, and this is accompanied by pathology of the cervix, this condition can provoke a miscarriage. In a hospital setting, the woman’s cervix is sutured or a special support ring is placed - an obstetric pessary (for more details, see the article: obstetric pessary: what is it and why is it placed?).
With low placentation, the likelihood of placental abruption and uterine bleeding increases. The child is at constant risk of oxygen starvation.
Low presentation of the fetus during pregnancy
Low presentation indicates the body is preparing for birth. In the early stages, such a diagnosis threatens to interrupt pregnancy. The reasons are mainly due to diseases of the female body:
- infectious processes;
- surgical interventions in the past (abortion, caesarean section);
- structural features of the uterus;
- heredity;
- age category over 35 years.
Failure to maintain a healthy lifestyle and previous diseases of the female genital organs also contribute to the fact that the fetus is low-lying.
The position inside the womb can be corrected with the help of a bandage and special exercises, which should only be done on the recommendation of a doctor, so as not to aggravate the condition. In particularly complicated cases, a decision is made to hospitalize and prescribe drug therapy. Sometimes it requires suturing the cervix or using a special ring.
Can a child get up and what to do in this situation?
If, during an examination by a gynecologist, it was discovered that the fetal head is low, do not panic, because the baby can still rise. To do this, you should follow the following recommendations from doctors:
- Limiting physical activity. A woman should stop playing sports and avoid physical labor. The maximum permissible activity is leisurely walking. Also, the expectant mother should give up heels and choose comfortable, loose clothing.
- Sexual abstinence. There is no strict ban on intimate life, but penetrative sexual contact should be avoided. During sexual intercourse, there is an additional impact on the cervix, which can lead to its premature dilatation.
- Wearing a bandage. It is recommended to wear the bandage starting from the 20th week. It can be purchased at any pharmacy and in specialized stores and departments for pregnant women.
Causes of low fetal position
Low fetal position can be diagnosed at any stage. At the end of pregnancy (after 37 weeks) this is the absolute norm and even has a good prognostic value. This means that the baby is already preparing for childbirth, its head (presenting part) corresponds to the size of the woman’s pelvis and descends.
Being low, the child exerts mechanical pressure on the lower segment of the uterus and cervix, thereby helping to prepare them - shortening and opening the cervical canal.
Detection of a low position of the child before 37 weeks is fraught with premature birth; the reasons for this condition may be hidden in the following:
- Increased uterine tone. At the same time, the myometrium puts pressure on the child, and it rushes down.
- Anomalies of the structure of the uterus. For example, the presence of a septum, bicornuate or unicornuate uterus prevents the baby from positioning at the top, at the bottom of the uterine body, as a result it puts additional pressure on the lower part and moves towards the exit of the pelvis.
- Physical exercise. Overwork, heavy lifting and other similar activities predispose to low fetal position.
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency. In this case, the cervix loses its closure function. The lower segment takes on the structure as on the eve of childbirth. This allows the child to fall down under the influence of gravity.
- Multiple pregnancy. Two or three babies need extra space in the uterus, so they put more pressure on the lower segment of the uterus and cervix. As a result, the cervical canal may open slightly earlier than expected, which helps the fetus move downwards.
Causes of fetal malposition
There can be many reasons why incorrect positions and fetal presentation occur. Most often this occurs with polyhydramnios, when an excess amount of fluid gives the child the opportunity to actively move, preventing him from being fixed in a normal position. Twins and triplets are also often born in the wrong position. It’s good if at least the first child walks head first, but often all the children are positioned incorrectly. Also quite common are the causes of abnormal fetal position, such as a narrow pelvis, placenta previa, pathologies of fetal development, prematurity, insufficient weight of the child (less than 2500 grams), abnormalities in the structure of the uterus, bicornuate uterus, tumors of the uterus or appendages, decreased tone of the uterus and weak muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. Often, problems with fetal fixation occur during repeated pregnancy, when the abdominal muscles have already been stretched previously and have not regained their elasticity. Heredity is also a serious risk factor. If a mother was born in a breech position, the chances of repeating the same situation with her own baby increase significantly.
Gymnastics for abnormal fetal position
If during an ultrasound at 30 weeks of pregnancy you were told that the baby was lying incorrectly, you should not be upset. According to statistics, 90% of babies manage to change their position to a more comfortable cephalic presentation before birth. Although about 3% of children are still born in a breech position. Therefore, after 32 weeks of pregnancy, doctors recommend that expectant mothers perform special exercises if the fetus is in abnormal position. A woman should lie down on a hard sofa or rug and lie on one side for 10 minutes, then she should turn over and spend 10 minutes on the other side. Then the exercise is repeated 2-3 more times. This should be done several times a day, and after 1-2 weeks you can expect results. It is also very useful to lie with your legs and lower back elevated on pillows. You can spend 10-15 minutes in this position after breakfast, lunch and dinner. But before eating, expectant mothers are recommended to stand in a knee-elbow position, also with the pelvis raised up. The logic of the exercises is to place the child in an uncomfortable position with his head down, and thereby stimulate him to roll over and press against the entrance to the pelvis. For the same reason, pregnant women are recommended to sleep on the side where the fetal head is located. The baby will feel discomfort and try to roll over. In addition, as you know, swimming and water aerobics are very beneficial for all expectant mothers. With breech presentation it is doubly useful.
The effectiveness of these exercises is 70-90%. That is, the result is usually always positive. But there are cases when gymnastics with an incorrect position of the fetus is strictly contraindicated. Therefore, any actions must be previously agreed with the doctor. A doctor may prohibit a pregnant woman from performing exercises if she has been diagnosed with: placenta previa, uterine fibroids, other serious diseases not related to the reproductive system, and also if she has scars on her uterus from previous operations. If there are no contraindications to gymnastics, it can also be done for preventive purposes. In addition, some mothers additionally turn to various methods of alternative medicine, such as reflexology, light therapy and music therapy. It is believed that even while in the womb, the child already reacts to light and sound. Therefore, some parents bring a light source, as well as a player with light, pleasant music to the lower abdomen to encourage the baby to move his head closer to the pelvis. This is not only very cute, but extremely useful. After all, the more naturally the child turns into the correct position, the safer and easier it is for him and for the mother.
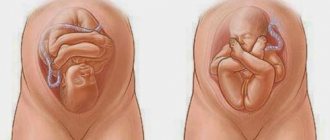
If the baby is in a head-down, occiput-to-stomach position (anterior view of the fetal position, cephalic occipital presentation), labor is likely to be faster and easier. By the end of pregnancy, most babies take exactly this position.
In the anterior position, the fetus curls up “comfortably” with its head towards the pelvis. During birth, the baby rounds his back, pointing and pressing his chin to his chest. Childbirth will be easy because:
- The top of the baby's head puts even pressure on the cervix during contractions. This helps it expand and the body to produce the hormones necessary for childbirth.
- During pushing, the baby moves at such an angle that the smallest area of the head appears first. (Try wearing a tight turtleneck without retracting your chin and you will understand the mechanism).
- When the baby hits the lower part of the pelvis, he turns his head slightly so that the widest part of the head is at the widest part of the pelvis. The back of the head slips under the pubic bone. During birth, the baby's face passes through the area between the vagina and the perineum.
How dangerous is the situation for mother and child?
The low position of the fetal head or other parts of it (usually the buttocks and legs) leads to additional pressure on the lower segment of the uterus and cervix. As a result of this, the following may occur:
- the tone of the uterus increases primarily or secondarily;
- The cervical canal may open, which provokes the rupture of amniotic fluid.
As a result, premature birth may occur. The consequences for the mother are usually minimal. Such early births are dangerous for the child: the immaturity of all systems and organs threatens his life after birth, a high percentage of disability, and serious health problems in the future.
In some cases, a woman can undergo and successfully carry a pregnancy, having a low position of the child in the womb. However, until the 37th week she still faces the risk of giving birth to a premature baby.
Is there any danger
Incorrect position of the child's head does not pose any danger if it is not associated with other, but already pathological, characteristics of the fetus. Childbirth with an anterior type of occipital presentation will be favorable. This position ensures easy passage of the head, as an optimal relationship between its size and the woman’s pelvis is created.
When entering the small pelvis, the head bends, the chin approaches the chest. As the child progresses, the small fontanel becomes the leading point. When bent, it passes through its smallest part and straightens at the exit, then the shoulders turn, and the head turns towards the mother’s thigh. After passing through the shoulder girdle, the baby’s torso and legs come out with ease.
In the case of frontal presentation, natural childbirth is extremely rare. They take a long time to pass and can lead to damage to the child and the woman’s pelvic organs. Frontal presentation during natural childbirth has an unfavorable prognosis, there is a risk of uterine rupture and fetal asphyxia.
How to tell if your baby is lying low
Sometimes a woman may not be bothered by anything at all if the head or buttocks of the fetus are low, but most likely she simply does not pay attention to her condition or is already accustomed to it. The main manifestations of pathology include the following:
- feeling of pressure in the lower abdomen, in the perineum;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- the stomach drops: the height of the uterine fundus has become lower than it was, as a result, heartburn decreases, it is easier to breathe, and shortness of breath is not as severe during exertion as it was recently;
- periodic or constant uterine tone.
If such complaints occur, you should consult a doctor. To confirm the status, you must do the following:
- Examination on a gynecological chair. Normally, up to 37 weeks, the lower part of the fetus should be high and easily pushed away with slight pressure on it through the vaginal vaults. When the presenting part is lowered, it is already fixed, as it were. In addition, structural changes in the cervix are very often determined; it softens and shortens. All these are signs of a threat of premature birth.
- Ultrasonography. In this case, the presenting part is determined low, as happens on the eve of childbirth. When measuring the length of the cervix, its shortening is determined, and the internal os and cervical canal open slightly.
How a bandage will help
A bandage for a low-lying fetus is not a treatment, it is just one of the possible measures to prevent premature birth and further lowering of the child. It is especially important to use it in the following cases:
- with a low position of the fetal head (pelvis) after 35-36 weeks;
- during multiple pregnancy.
You can use a universal pre- and postpartum bandage. It must be selected according to size, removed at night and when in a horizontal position.
In other cases, in addition to the bandage, additional treatment is necessary.
Watch this video about how to wear a prenatal bandage correctly and for what purpose:
Other methods of maintaining pregnancy
Depending on the period at which the low location was detected, the condition of the cervix and the woman’s complaints, the following treatment options are possible:
- Bed rest . This is the most common and simple recommendation for women. If the position of the child is very low and there are structural changes in the cervix, strict bed rest is prescribed. You can only go up to the toilet, eat and shower. In a horizontal position, the presenting part of the fetus does not exert such strong pressure on the lower segment as in a vertical position. This helps maintain pregnancy.
- Installation of a pessary (abbreviated as RAP - unloading obstetric pessary). This ring for the cervix can be hard plastic, silicone, of various sizes (selected based on the anatomy of the woman’s genital organs).
- After installing the pessary, pressure from the presenting part of the fetus is applied not only to the cervix, but also to the entire surface of the product. This slows down structural changes in the cervix, helping to maintain pregnancy. Can be installed at any time up to the 32-35th week if necessary.
- Suture on the cervix . Apply at a period of 16 to 20-22 weeks. It is used for isthmic-cervical insufficiency, in which case the presenting part of the fetus may also be low. It is a circular suture in the area of the internal pharynx, which literally prevents the cervix from opening even with pressure on it from the fetus. Apply only in hospital settings.
If, after examining a doctor and establishing the fact that the baby is low, the threat of premature birth is confirmed, in addition to the above, additional conservative therapy is carried out. It includes the following (sometimes several points at the same time):
- magnesium therapy: magnesium solution is dripped intravenously for up to 10-12 days;
- antispasmodic treatment: drugs such as “No-shpa”, “Papaverine”, “Drotaverine” are used according to an individual regimen;
- tocolytic therapy: Ginipral is used in the form of intravenous injections or tablets for oral administration; it relieves the tone of the uterus and thus helps maintain pregnancy.
And here is more information about what abnormalities of the placenta and umbilical cord may be.
A low position of the baby in the uterine cavity can result in premature birth. Therefore, if a condition is detected or suspected, it is necessary to consult a doctor for qualified medical care, which will primarily be aimed at maintaining the pregnancy. Options and methods of therapy are selected individually, based on the timing and clinical situation.
Longitudinal and oblique position of the fetus during pregnancy
Oblique - involves the baby being diagonally inside the womb, with the head and pelvic bone located on opposite sides of the main axis of the woman’s abdomen. Only after 31 weeks of pregnancy can this situation be considered a pathology. The cause of the oblique position is considered to be polyhydramnios or, conversely, oligohydramnios, as well as various neoplasms that prevent the baby from coming out. If head down movement does not occur before the 36th week, then delivery by cesarean section is used.
Useful video
Watch this video about how to install an obstetric pessary:
The location of the fetus in the uterus is always individual - it may also be that the child is too low in the mother’s womb. This article will tell you what low presentation of the fetus is and whether it is dangerous during pregnancy.
Head presentation of the fetus
The position of the fetus with its head towards the pelvis is the most favorable for natural childbirth. There are several types of this position, but in any case, during childbirth, the head will come out first. There are facial, occipital, frontal, anterior cephalic presentations. With any type, the head can be lowered and strongly pressed against the pelvis, which is defined as a low position of the fetus.
This type of presentation is divided into several subtypes, depending on the extension of the head:
- Anterior cephalic - the wire point is the large fontanel, and this option for the fetal position is favorable, but there remains a risk of injury to the child and mother, since labor is long, it is necessary to exclude hypoxia.
- Frontal low presentation of the fetus - this option is characterized by the entry of the baby’s head into the pelvis, the frontal part, the widest, serves as the wire. In this case, natural childbirth is in jeopardy, and a caesarean section is prescribed.
- Facial low presentation - this type of placement is diagnosed when the leading area is the chin. Natural birth is possible provided the mother's pelvis is sufficiently wide; otherwise, surgical delivery is indicated.
An abnormal position can be caused by disorders on the part of the mother, complicated pregnancy, underdevelopment of the fetus, polyhydramnios and other intrauterine anomalies. The hereditary factor also plays a role. The risk of malpresentation increases when similar cases have already been observed in the family.
Features of the pathology
Low presentation of the fetus is quite common in obstetric practice. Typically, this clinical condition is detected in the second trimester of pregnancy, when the fetus is already quite large.
There are several ways to determine how low the baby is in the uterus. The first of them is manual. It has been used by doctors for many centuries, dating back to ancient times. An obstetrician-gynecologist conducts such a study.
During this diagnostic procedure, the doctor evaluates where the baby's head is located. If it is located too low, a conclusion is made about the presence of a low presentation of the baby in the uterus. An experienced doctor also determines the position of the placenta, as well as which wall of the uterus it is predominantly attached to. The placenta can be attached to the anterior, posterior, or lateral walls of the uterus.
How should the fetus be positioned depending on the week of pregnancy?
The position of the baby in the early stages depends on where the egg is implanted. Most often it is implanted to the back wall of the uterus; this position is considered the best, since the woman begins to feel movements earlier, and it is easier for the doctor to track the fetal pulse. Less commonly observed is the location on the anterior wall of the uterus; it is a variant of the norm and does not cause dangerous deviations.
A low position can be dangerous. If this option is noted for placing the baby in the stomach for weeks until 31-32 weeks, the doctor does not consider it a deviation: often the baby moves to the upper parts of the uterus. In cases where this does not happen, the doctor diagnoses placenta previa, which is an indication for a cesarean section.
The position of the baby in relation to the birth canal may also be different. In the early stages it can easily change; up to 32 weeks, the norm is a constant change in the position of the fetus. However, before birth, the baby should lie head down; otherwise complications will arise. It is better if the back is pressed against the anterior uterine wall, the position will be longitudinal (the line from the tailbone to the back of the baby's head is parallel to the uterine axis).
The oblique and transverse position is considered incorrect in the later stages.
At what time does the issue of presentation become relevant?
Since the fetus is constantly moving and changing its location in space, in the first and second trimesters you should not worry if the ultrasound results show that the baby is lying head up or perpendicular to the birth canal. The child will have time to move many times.
In the third trimester, the fetus increases greatly. The space in the uterus becomes insufficient for active movements. By week 34, the baby most often takes its final position. At this stage, it is important that the baby is positioned head down. If a pelvic or transverse presentation is noted, complications are possible; this phenomenon is observed in approximately 4-6% of cases. If the position of the baby in the stomach at this stage is incorrect, the doctor prescribes a caesarean section.
Symptoms
The course of pregnancy with a low presentation of the fetus can be different. One woman will experience multiple uncomfortable symptoms, while another tolerates the period of bearing a child quite calmly. The development of pregnancy depends on numerous factors.
In some cases, the expectant mother may experience abdominal pain. It usually develops after lifting some heavy objects or after fast walking. As a rule, at rest this symptom develops much less frequently.
If abdominal pain is accompanied by bleeding from the genital tract, this can be very dangerous. In such a situation, a pregnant woman should not hesitate to seek medical help. If severe cramping pain in the abdomen occurs, you should not make any active movements. It’s better to lie down on the sofa at this time and try to breathe deeply.
Pregnancy occurring with a low presentation of the fetus can be complicated by the occurrence of periodic small bleeding from the genital tract. In this case, a woman will usually notice the appearance of dark red or brown discharge on her underwear.
If this situation repeats again and again, the expectant mother must inform her obstetrician-gynecologist about this.
Repeated, even minor bleeding can lead to the development of an anemic condition. Anemia is an extremely unfavorable pathology for both the pregnant woman herself and her baby. In such a situation, the supply of oxygen to the child’s vital organs is reduced, which subsequently negatively affects his development.
Possible consequences
With low presentation of the fetus, it is very important to monitor the course and development of pregnancy. For an expectant mother whose doctors identify this feature, they are required to draw up an expanded set of recommendations. A pregnant woman must observe them until the birth.
Pregnancy occurring with a low presentation of the fetus can proceed quite normally. Its course largely depends on the lifestyle that the expectant mother leads, as well as her initial condition. If a woman’s body was weakened even before pregnancy, then the likelihood of complications developing during pregnancy increases.
During pregnancy that occurs with the development of low presentation of the fetus, it is very important to reduce the risk of premature birth. Many women who are diagnosed with low presentation of the fetus may face the threat of miscarriage. If doctors determine such a condition, the expectant mother may be hospitalized in a hospital. The main goal of therapy is to maintain pregnancy as long as possible.
In order for a baby to be born viable, he needs a certain time for intrauterine development. During this time, the fetus's lungs are finally formed and even a small heart begins to function. If the baby’s vital organs are not yet fully formed during spontaneous early labor, there is a real threat to his life in his new environment. Such underdevelopment of organs also threatens the formation of serious developmental defects in the child.
If the fetus is presenting low, infection is dangerous. It is important to understand that the closer the baby is to the external genitalia, the higher the risk of possible infection entering the uterine cavity. For expectant mothers who have been diagnosed with low presentation of the fetus during pregnancy, it is very important to monitor compliance with the rules of personal hygiene.
If the threat of premature birth is too high, and the pregnancy is still short, the pregnant woman can have a special retaining ring installed - it is inserted into the genitals and provides additional fixation of the child in the uterus.
This method allows you to carry the pregnancy to the moment when the child can be born already viable.