Fetal hypoxia is a pathological process that is characterized by insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus. This disease can appear either suddenly or gradually (with the expression of symptoms). This disorder is not independent, but occurs due to abnormal processes occurring in the female body. The time of formation, course and intensity of symptoms directly affect the development and general health of the child. If the pathology is not treated, the consequences can be disastrous.
- Etiology
- Varieties
- Symptoms
- Complications
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
This disease can appear at any stage of pregnancy. The sooner intrauterine fetal hypoxia makes itself felt, the more seriously it will affect the development of the child (both mental and physical). It can also cause damage to the central nervous system, but this is in case of untimely or improper treatment.
Medical statistics show that 10% of all pregnancies experience oxygen deficiency. Therapy for such a disease is primarily aimed at normalizing blood flow to the uterus and placenta, but in case of acute fetal hypoxia, it is recommended to induce labor artificially rather than using any treatment methods.
Many women, when they learn about such a problem, are horrified because they mistakenly think that this will certainly lead to the death of their child. Nevertheless, there is a way to determine fetal hypoxia yourself. This can be done starting from the second trimester of pregnancy (the moment the first signs of baby movement appear). In a normal state, the intensity of movements should not be less than ten manifestations per day, and not one separate movement is considered, but their repetition over several minutes.
To avoid any complications, it is necessary to begin treatment of the disease no later than the seventh day of oxygen deficiency in the child.
Etiology
The causes of intrauterine fetal hypoxia are pathologies that occur in the maternal body, as well as the impact of external unfavorable factors. The risk of this disorder may arise due to such diseases of the woman as:
- heart disease;
- hypertension;
- various kidney diseases;
- chronic bronchitis or bronchial asthma;
- diabetes;
- preeclampsia and eclampsia.
Causes of fetal hypoxia
If for some reason the gestational age exceeds nine months, this may also cause fetal hypoxia.
The second group of reasons consists of processes taking place directly in the womb:
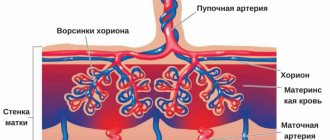
- disruption of blood flow in the placenta;
- wrapping the umbilical cord around the baby's neck;
- obstruction of the birth canal from the uterus by the placenta;
- intrauterine infection of a child;
- pregnancy with two, three or more fetuses;
- increased volume of amniotic fluid;
- complication of the baby’s passage through the birth canal, most often due to large volumes or incorrect posture of the baby;
- prolonged compression of the child’s head and neck during childbirth;
- damage to the integrity of the uterus.
In addition, external factors can serve as causes of fetal hypoxia:
- abuse of alcohol, nicotine or drugs by a woman during pregnancy;
- chemical poisoning;
- taking a large number of medications;
- poor ecology and high air pollution in the place where the expectant mother lives.
Causes of hypoxia
To prevent this phenomenon, it is necessary to know for certain about the reasons contributing to the development of the pathology. In medicine, it is customary to divide them into 3 groups :
- Some disturbances in the functioning of a pregnant woman's organs. These include: diseases of the cardiovascular system, incorrect functioning of the lungs, compression of the inferior genital vein, anemic condition, poisoning, large loss of blood and excess carbon dioxide in the body. Metabolic processes are also adversely affected by the consumption of alcoholic beverages, smoking and drug addiction of the expectant mother.
- In case of pathology of the placenta : threat of miscarriage, gestosis, post-term fetus, vascular thrombosis, placental infarction, premature detachment. Also, prerequisites for O deficiency are the child being entangled in the umbilical cord or damaged.
- Infections in the fetus , intrauterine anemia, developmental abnormalities, severe head obstruction during childbirth.
The effect of hypoxia on a child’s development is always negative, so the problem must be noticed promptly.
Varieties
Depending on how fast it progresses, hypoxia can be:
- short-term, that is, it occurs unexpectedly and quickly;
- moderate severity – expressed directly during childbirth;
- acute - signs of the disease are observed several days before the upcoming birth;
- Chronic fetal hypoxia often develops - it appears with severe toxicosis, intrauterine infections of the fetus, incompatibility of blood groups or Rh factors of the mother and child. In this case, the fetus usually adapts and gets used to the lack of oxygen, but this entails many irreversible consequences.
Based on the time of occurrence, this disorder is divided into:
- formed in the first months of pregnancy;
- in the second half of the allotted time;
- during childbirth;
- after childbirth it occurs very rarely, most often it is a sign of congenital pneumonia.
Why is acute hypoxia dangerous?
Chronic oxygen starvation is established at least several weeks before birth, which means specialists will monitor the baby’s condition throughout the rest of the pregnancy and during labor.
The acute syndrome often occurs within a couple of minutes and none of the symptoms have time to manifest properly, resulting in death. The prerequisites for the development of this type of pathology arise within 2-3 hours , so specialists have a chance to save the fetus if they act promptly.
Symptoms
It is quite difficult to determine the first signs of the disease, since it can appear unexpectedly, but at the same time, it is very important to do this in the early stages, because this will allow you to quickly begin treatment and avoid consequences.
The main symptom of fetal hypoxia is a slow heartbeat, but this cannot be noticed at home. The first sign to consult with a doctor is a change in the intensity of fetal kicks. Every woman feels movement, but if the child makes itself felt less than three times a day, you should immediately contact a specialist, because this indicates chronic intrauterine fetal hypoxia. The acute form, which occurs suddenly, is characterized by completely opposite signs - the child is too active, pushing hard.
Signs of fetal hypoxia in the first three months of pregnancy are very difficult to determine, so it would be better for the woman and the fetus to be examined by a doctor weekly.
Hypoxia of the fetus and newborn
The above reasons are associated not only with fetal hypoxia, but also with asphyxia of the newborn. A baby is considered a newborn in the first week after birth. During this period, all organs begin to actively work and are reconfigured to work independently, without the help of the mother’s body. So, if a child has intrauterine hypoxia, then it is likely that the same problem may arise in the first days of life.
The fact is that, with a lack of oxygen in the womb, the child tried to compensate for it by breathing through an open glottis. Amniotic fluid, mucus, and blood could get there, which after birth will lead to blockage of the respiratory organs, and suffocation will occur - asphyxia of the newborn. That is why such children require every second supervision in the first days of life.
Hypoxia and fetal malnutrition
We figured out what hypoxia is, and malnutrition is a lack of nutrition and underdevelopment of the fetus. This may be due to the same lack of oxygen, which is so necessary for the development of each organ, and the lack of proper nutrition. In most cases, malnutrition is a consequence of untreated or undetected hypoxia.
Fetal hypoxia: signs
In the first stages of pregnancy, it is impossible to determine fetal hypoxia without Doppler examination (intrauterine examination of the fetal heartbeat) and ultrasound, since the fetus is not yet fully formed and cannot “tell” you that something is not satisfactory in your lifestyle and your condition.
This is where the diagnosis of fetal hypoxia comes to the rescue thanks to frequent and unscheduled examinations. Indicators of this may include your chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, bronchitis, constant cough and others), your general condition if you work in a stuffy room, and no one will exempt you from working there unless there are certain contraindications.
In later stages of pregnancy, the mother should observe the baby's movements. When you ask your doctor about fetal movements, you get an answer on how to determine fetal hypoxia yourself. “ Methodology 10 ” is the name of an assistant for identifying signs of intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
Mom, waking up in the morning, having greeted the baby, begins to count his movements. There should be at least 10 episodes per day. That is, you felt a stirring for 2 minutes - the first series, then another minute - the second series, and so on.
Some doctors believe that increased fetal movements and hiccups are also symptoms of fetal hypoxia. But in reality, this may be a second indicator of anxiety: the mother lay down unsuccessfully (on her back, for example, which is unacceptable during pregnancy) or walked very quickly and now she also lacks air. If these phenomena quickly pass in the baby, then there is no reason to worry. But a decrease in the number of movements is already the most important symptom of intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
The development of acute fetal hypoxia is indicated by turbid amniotic fluid, which is determined by their analysis.
How to recognize fetal hypoxia
The first method for detecting oxygen starvation was indicated above. The remaining methods are associated with the examination of a pregnant woman by a gynecologist during a scheduled or unscheduled examination.
The doctor, listening to the fetal heartbeat, pays attention to its frequency. If it is below normal, then there is a need to conduct additional examination. Listening to the fetal heartbeat using a statoscope through the mother’s abdominal cavity begins in the second half of pregnancy.
Heart rhythm can be more accurately monitored using CTG (cardiotocography). This is an ECG for the fetus.
Signs of fetal hypoxia according to CTG are:
- absence or decrease in the number of heart beats;
- the presence of increased heart rate with involuntary contractions of the uterus and with fetal movements. The absence of such an increase indicates fetal stress and exhausted adaptive reactions.
And the third method is a study using Doppler ultrasound - intrauterine ultrasound, which allows you to examine the blood flow in the uterine arteries.
Also, a routine ultrasound examination can tell the doctor about the development of hypoxia - these could be disturbances in the development of the placenta, its premature maturation, or too thick or thin walls.
The appointment of some blood tests: hormonal and biochemical make it possible to detect the presence of enzymes in higher concentrations, fat oxidation products and other trace elements that indicate the development of a pathology such as fetal hypoxia.
Treatment of intrauterine fetal hypoxia
Having heard the diagnosis of “fetal hypoxia,” the mother becomes scared and the first thing that worries her is what she should do in case of fetal hypoxia. The main thing is to remain calm and follow the doctor’s recommendations. The mother’s peace of mind is the key to the health of the child, not only the one already born, but also the one in her tummy.
If fetal hypoxia is diagnosed in time, and there are no indications for immediate cesarean section, then fetal hypoxia is treated. First of all, when treating fetal hypoxia during pregnancy, they try to get rid of as much as possible the illness of the mother that led to oxygen starvation (if it is revealed that it is the cause of this).
Depending on the severity, treatment can take place in a hospital or outpatient setting. Rest and bed rest, taking medications prescribed by a doctor that help improve oxygen supply to the fetus, and drinking oxygen-rich water are the main areas of treatment for intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
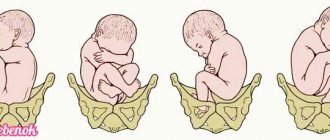
Fetal hypoxia during childbirth
During labor, the obstetrician-gynecologist who delivers the baby periodically listens to the baby's heartbeat. So here the symptoms of hypoxia are tachycardia, fetal bradycardia, as well as the appearance of dull tones and arrhythmias in the fetal heartbeat.
The degree of bradycardia and tachycardia during different periods of labor may vary. In the first period, hypoxia is indicated by bradycardia up to 100 beats per minute, and in the second it is already 98 beats.
In response to a contraction with the development of hypoxia during labor, a decrease in heart beats to 50 per minute can be observed using a radiotocograph.
The consequence of hypoxia during labor may be the child swallowing amniotic fluid, which further leads to disruption of the respiratory organs of the newborn.
Complications
If you ignore all the symptoms or go to the clinic late, hypoxia has a number of consequences for the development of the fetus and the health of the unborn child. Complications of chronic fetal hypoxia can include:
- delay in fetal development;
- internal hemorrhages;
- intracellular edema;
- disorders of the development and formation of internal organs, bones and brain of the fetus.
For a newborn child, the consequences are no less serious:
- cerebral palsy;
- psychical deviations;
- mental retardation;
- neurological diseases;
- inability to independently perform functions characteristic of the first days after birth;
- changes in the structure and structure of some internal organs;
- hemorrhages.
In addition, both acute and chronic fetal hypoxia can lead to fetal death in the womb or death of the child during the first week of life.
For a woman, the consequences of such a disorder are more mental than physical, except in cases where the causes of fetal hypoxia were diseases that had already occurred before pregnancy. Complications may include:
- prolonged depression associated with the death of a child;
- refusal of subsequent pregnancies;
- postpartum mental trauma.
Chronic fetal hypoxia
Sometimes, in the absence of monitoring of a pregnant woman (if she is not registered), in case of untimely diagnosis and treatment of this pathology, prolonged oxygen starvation occurs - chronic fetal hypoxia. The consequences of chronic fetal hypoxia are: disturbances in the formation of fetal organs and embryo development.
At later stages, this pathology causes damage to the central nervous system, a violation of physical development, which is characterized by growth retardation, poor adaptation of the child to existence outside the womb. Children born after chronic hypoxia inside the womb experience poor appetite, anxiety and disorders of the autonomic nervous system.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing fetal hypoxia starting from the fifth month of pregnancy is not difficult. It is much more difficult to do this in the first three months, but the earlier the diagnosis is made, the greater the chances of avoiding the consequences of the disease.
Diagnosis of this disease consists of:
- monitoring the intensity of fetal movements;
- listening to heart rate through a stethoscope;
- CTG;
- Ultrasound;
- Doppler ultrasound, which allows you to track the speed of blood flow in the umbilical cord and placenta;
- Using special gynecological diagnostic techniques, the transparency, color and amount of amniotic fluid is assessed.
Fetal Doppler
Treatment
At the first manifestation of symptoms of fetal hypoxia, a pregnant woman is immediately hospitalized. The first thing treatment is aimed at is stabilizing the oxygen supply to the fetus and reducing the tone of the uterus. To do this, the patient is prescribed strict bed rest and medications that will improve oxygen permeability and metabolism.
When the first improvements in the condition of the fetus are observed, the woman can perform gymnastics, various breathing exercises, and attend aqua gymnastics. If no measures to normalize the supply of oxygen to the fetus have had the desired effect or symptoms of fetal hypoxia persist for more than twenty-eight weeks of pregnancy, it is best to immediately perform a cesarean section. In case of acute hypoxia, a newborn child requires the help of a resuscitator.
Timely treatment and normalization of pregnancy can avoid dangerous consequences for the child.
Treatment and prevention of hypoxia
Lack of oxygen and its consequences are detrimental to the fetus at any time from the moment of conception. If problems cannot be avoided and the first symptoms of hypoxia appear, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment under the guidance of a doctor. First of all, eliminate the causes of the problem and relieve its symptoms.
The chronic form of the pathology is eliminated with the help of medications that improve blood supply to the uterus. The diet of a pregnant woman is enriched with a complex of vitamins; in most cases, a diet is prescribed that limits fatty foods, salt and sugar.
As a preventive measure, rest, regular walks in the fresh air, and light exercises are recommended.
Clothing should be comfortable and loose enough to avoid squeezing the limbs and impairing blood circulation. The diet should be balanced and high in iron to prevent anemia. It is better to give up bad habits completely, at least during pregnancy.
The consequences of hypoxia can significantly complicate the life of a little person and his parents, so it is always necessary to keep health under control. Any signs of lack of oxygen should be a reason to consult your doctor.
Pregnancy is a wonderful time, but it will end quite quickly, and then a new life will begin, and what it will be like depends largely on the sanity of the expectant mother. To prevent unpleasant consequences, you need to undergo prescribed examinations in a timely manner and follow the recommendations.
Author: Yulia Prokofieva, obstetrician-gynecologist, especially for Mama66.ru
Prevention
Prevention of fetal hypoxia should be carried out by a woman who has decided to become a mother, namely:
- plan pregnancy and carefully prepare for it, through examination by doctors, treatment of chronic, infectious or gynecological diseases;
- register with an obstetrician-gynecologist on time;
- be regularly observed at the antenatal clinic;
- lead a healthy lifestyle, give up alcohol, nicotine and drugs;
- rationalize nutrition by consuming large amounts of vitamins and calcium;
- rest enough time;
- avoid strong physical exertion, only breathing exercises;
- timely treatment of diseases that accompany pregnancy;
- choose the right way to give birth to a child. With a caesarean section there is less chance of fetal hypoxia than with a natural birth.
Why does hypoxia occur?
Factors contributing to the development of hypoxia are numerous. First of all, these are diseases of the mother. Among them, anemia is a decrease in the total amount of hemoglobin. With anemia, the main function of red blood cells is impaired - the delivery of oxygen to the tissues of the body.
In the presence of acquired and congenital heart defects, myocardial diseases, chronic lung diseases in conditions of increased load on these organs, pregnant women most often experience circulatory failure, in which microcirculation in the tissues is disrupted, as a result of which the phenomena of hypoxia and disturbances in the functioning of the “mother - mother” system gradually develop. placenta - fetus."
Diseases of the respiratory system (bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis, etc.) also adversely affect the course of pregnancy. They cause respiratory failure, which results in hypoxia of the woman’s organs and tissues and, accordingly, the fetus. Kidney disease and diabetes can also cause problems with oxygen supply to the fetus.
Other causes of hypoxia are disturbances of the fetal-placental blood flow, which occurs during postterm pregnancy, the threat of premature birth, pathology of the placenta and umbilical cord, abnormalities of labor, and other complications of pregnancy and childbirth.
Fetal diseases also lead to hypoxia: hemolytic disease (a condition that occurs when the blood type of the fetus and mother is incompatible), intrauterine infection, congenital malformations, prolonged compression of the head during childbirth. As you can see, there are enough reasons.