When should you wear a bandage?
The bandage is not a mandatory device to wear during pregnancy. As a rule, the doctor prescribes it in certain cases. Initially, this device was developed to reduce stress on the spine and ease back pain.
In addition, an elastic bandage is prescribed for underdeveloped cervix, threat of miscarriage, scars on the uterus as a result of cesarean section or other operations, as well as for twins or triplets.
It is recommended to wear a bandage when the fetus is in a low position, especially if the abdominal muscles are weak, this is necessary in order to prevent the baby from going down too early. Very often, a bandage helps with lower back pain due to a pinched nerve; without it, the pain can intensify so much that it becomes difficult to walk.
The device is prescribed by an obstetrician-gynecologist; it is recommended that pregnant women start wearing the bandage when they reach 22-30 weeks. In some cases, it may be prescribed later, when lower back pain appears.
If the abdominal muscles are well developed, there are no indications for using a bandage, it is not necessary to wear one, especially since the belt replaces the work of the muscles, and this is not always useful.
Among other things, in some cases an elastic belt is completely contraindicated. With a pelvic or transverse presentation of the fetus, it interferes with the free movement of the child, which is why the baby will not be able to turn into the desired position. If after 24 weeks the presentation is incorrect, the belt cannot be worn.
Low placentation in pregnant women: when will it rise?
The degree and likelihood of danger directly depends on how many centimeters remain between the lower edge of the placenta and the uterine os.
However, even with a distance of 2-3 cm, when the diagnosis is made unconditionally, there is a possibility that everything will get better. Therefore, you should never make darkening conclusions and get upset: it is possible to safely carry and give birth to a baby! Moreover, this is what happens most often. As the uterus increases in size and rises higher into the abdominal cavity, it will “pull” the baby’s place with it. This natural movement is called placental migration. Most often it occurs at a later stage, closer to the 30th week of pregnancy or even later - at 32-34 weeks. But positive dynamics can also be observed in the second trimester. All these changes are well determined during ultrasound.
The placenta takes its final place at 36 weeks. Therefore, there is no reason to worry ahead of time: everything can change for the better!
Types of bandages
Bandages can be prenatal, postnatal, universal, or mixed.
Prenatal ones are available in the form of panties and a belt. The panties are quite comfortable to wear and easy to put on, but they need to be washed daily, like any underwear. The elastic insert in them is located inside, it is not as dense and wide as in the belt.
Panties can be high or low. It is better to put on a prenatal corset while lying down in order to properly distribute the pressure, more at the bottom, less at the top. Among the panties there are models with a clasp between the legs.
The belt is very popular among expectant mothers; pregnant women really like it, as it is almost invisible under clothes and is not so hot in the summer. It is worn over underwear, provides good support from below and fixes the uterus.
The belt prevents the baby's head from dropping prematurely and causing premature birth. Thanks to the side flaps, you can adjust the size of the belt, this is very convenient if you need to tighten it or loosen it. You can put on the corset while lying down or standing.
A universal or mixed corset can be worn during pregnancy and continued after childbirth. The universal belt is an elastic tape with Velcro, which is narrow on one side and wide on the other.
During pregnancy, the tape is worn with the wide part on the lower back and the narrow part under the belly. This ensures spine strengthening, load distribution and abdominal support.
After childbirth, the tape is worn in reverse, the narrow part is located on the lower back, and the wide part holds the stomach.
A postpartum bandage is usually prescribed after a caesarean section. There are special postoperative belts and regular postpartum ones. A regular one can be worn if you had a second or third birth.
The postoperative corset is specially designed for women who have had a caesarean section. It looks like a wide belt and has a clasp across the entire width.
If the birth took place without complications and naturally, it is better not to wear a belt, since it causes the muscles to come into shape more slowly.
How to put on and wear a bandage
It is very important to know how to wear a bandage during pregnancy, how to put it on correctly and how long a day to walk in it. The main thing is that the belt does not put too much pressure. If you feel discomfort, it means it is not worn correctly.
When purchasing a device, it is recommended to try it on to feel whether it is comfortable or not. The doctor helps determine the size; to do this, he must measure the circumference of the abdomen. It is also the doctor’s job to show how the prenatal bandage is worn, since the illustrations on the packaging are not always correct.
When trying on for the first time, you need to put on the corset in a lying position, the device should pass along the lower part of the butt, go under the stomach and rest against the hips, capturing the pubic bone in front.
As the belly grows, the model must be adjusted so that the belt does not press too hard or too lightly. Over time, when the skill of tying is mastered to perfection, you can put it on while standing.
How long should you wear the brace?
The antenatal belt is usually worn from the moment it is prescribed until the birth, especially if the woman walks, stands or sits a lot. There is disagreement among doctors about how long to wear the device during the day.
Wearing a brace during pregnancy can greatly help not only the woman, but also her baby. However, there is no consensus among doctors on the question of whether it is worth resorting to his help.
To make a decision, you need to listen to different points of view. And if you still want to wear a bandage, then you will immediately have many questions: what they are, how to put them on, why they are needed at all, and others. Let's try to figure it out.
Types of bandages
Bandages belong to the category of underwear, which, depending on the purpose, are worn during pregnancy or after childbirth, that is, there are prenatal and postpartum bandages. There are also universal models that are suitable for wearing in both periods.
In addition, the bandage can be of various shapes:
- Bandage panties with an elastic support insert in the front above the abdomen: worn like panties, but inconvenient because daily wearing is impossible or difficult, since such a bandage needs to be washed every day.
- The bandage belt is worn on underwear. It looks like an elastic band that supports the stomach and prevents the appearance of stretch marks. Very easy to use, special flaps on the sides allow you to adjust the size and tightness of the fit.
- The corset bandage is considered a relic of the past - very impractical.
- The combined bandage is used both before and after childbirth. It is also made in the form of a belt - from rubberized fabric that stretches. This bandage is fastened with Velcro: during pregnancy, the wide part strengthens the back, and the narrow part supports the stomach. After childbirth, the belt is fastened in reverse - with the narrow part back, while the wide part tightens the stomach.
Arguments for the bandage
- Significantly facilitates pregnancy, especially multiple pregnancies.
- Helps avoid feelings of fatigue and pain in the legs.
- Removes and.
- Reduces the load on the spine and pelvic organs.
- May prevent the appearance of stretch marks.
- Prevents premature descent of the fetus (which normally should occur at 38 weeks of pregnancy).
- Reduces risks in case of threat of miscarriage.
- Supports the abdomen while relaxing the abdominal muscles.
- Helps the baby to take the correct position in utero.
- Modern technologies have made it possible to create special breathable materials, so it will not be hot in the bandage even in the summer.
- Very convenient and easy to use (each model comes with detailed instructions with a description).
- Invisible under clothes.
Main reasons
Low placentation in pregnant women can be caused by the following factors:
Heavy physical activity on the female body before conception and in the first months of pregnancy.- Abortions (they always cause damage to the endometrium).
- The woman's age is over 35 years.
- Operations on the uterus.
- Previous infections and inflammations of the pelvic organs and reproductive system.
- The presence of congenital defects of the uterus and structural features of the female internal genital organs.
In other words, any cleansing, abortion and inflammation greatly injure the endometrium. An egg that has been fertilized passes through the uterus in search of the best and safest place for attachment. And the lower it is located, the worse the condition of the endometrium.
Arguments against"
Some doctors are sure that wearing a bandage causes the abdominal muscles to become lazy and more difficult to recover after childbirth. Therefore, you can wear a bandage only according to strict indications:
- back pain;
- threat of miscarriage;
- underdevelopment of the cervix;
- low position of the fetus with weak abdominal muscles;
- a scar on the uterus (after a previous cesarean or other gynecological operation);
- abdominal surgery within one and a half years before pregnancy;
- neurological pain caused by a pinched nerve in the lumbar spine;
- multiple pregnancy.
If you do not have any of the indications, the bandage cannot be worn. After all, nature has thought out everything, and a woman can easily bear such a burden (a growing fetus) without additional help - the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall are able to cope with this on their own. In addition, women often buy synthetic bandages, which can cause allergic skin reactions.
Doctors also say that the appearance of stretch marks is caused by hormonal changes and loss of skin elasticity. And a bandage cannot help with this, some say.
However, in some cases, the bandage is completely contraindicated. This applies more to the last trimester of pregnancy, when the baby suddenly turns over and takes an incorrect position, for example, sitting on his butt. The bandage will be a serious obstacle to turning over again as needed before giving birth. But in the case when the baby’s position becomes normal again, the bandage, on the contrary, will keep the child in this state, not giving the opportunity for unwanted “independent activities”. Therefore, it will be necessary to wear it.
Decisive factor
Only you can make a decision about wearing a bandage, but it would still be a good idea to consult a doctor. The decisive factor in making a decision (if there are no obvious contraindications) may be your feelings.
You should buy a bandage at a pharmacy, a specialty store or directly at a antenatal clinic. Choose several types of bandages for yourself and try them on. If you have enough patience, you can try everything. Let the consultant help you with this, choosing the right size and showing you how to put on this or that model correctly.
You should choose the option that is most convenient for you. You should not feel any pressure or any other discomfort. If you are uncomfortable in any of the proposed bandages, you should not buy any at all.
Why is it dangerous?
The low location of the placenta conceals a large number of dangers, but depending on the type, the tactics for managing a pregnant patient are selected.
- With a posterior position, there is a high probability of the placenta moving upward, and the birth canal opens completely.
- Anterior - causes difficulties when carrying a large child. There is an increased risk of getting entangled in the umbilical cord.
- Complete or central placenta previa is the most dangerous condition for the baby. The cervical canal is completely closed, hypoxia may develop. Pregnant women with this diagnosis are prepared for surgical delivery.
Due to low placentation, the blood supply to the embryonic placenta deteriorates, a lack of essential microelements and oxygen starvation appear.
Consequences:
- Hemorrhagic anemia;
- Frequent bleeding due to poor quality hemoglobin;
- Deterioration of uteroplacental blood flow;
- Fetoplacental insufficiency;
- Threat of interruption even over long periods;
- Impaired oxygen supply to the fetus;
- Incorrect position of the baby in the womb (occipital presentation);
- Placental abruption is a pathological condition that threatens the life of the child and mother;
- Incomplete descent of the head due to the closure of the birth canal, resulting in complicated childbirth and negative consequences;
- Possible late gestosis;
- Large blood loss during cesarean section.
If the process is severe, the pregnant woman is allowed to give birth before 40 weeks (37-38 weeks of gestation).
Rules for wearing a bandage
- You cannot wear a bandage continuously, much less sleep in it. It is recommended to take a 30-40 minute break after every 3 hours of wearing.
- However, if the bandage was prescribed to you for serious reasons and it just suits you perfectly (you feel noticeable relief and comfort), then there is no need to take breaks.
- The bandage should not compress the abdominal cavity - only support the abdomen.
- A woman should not experience any uncomfortable sensations (regardless of the position taken or body movements) - only relief.
- It is advisable to wear the bandage until the very end of pregnancy. But you should be guided by your feelings and testimony.
If the doctor does not prohibit it, and you decide to wear a bandage, do not worry. When put on, worn and used correctly, it poses absolutely no danger to either you or your baby.
Especially for
— Elena Kichak
From Guest
I have been wearing a B.Well maternity bandage for the last few months. I felt very comfortable with it, relieved back pain, nice light material, did not rub or press anywhere.
From Guest
I’ve been wearing it since 24 weeks, because pain appeared between the shoulder blades, and my tummy began to actively grow forward. My husband started doing massage and I wear a bandage belt for 4-5 hours a day, with breaks of course. The relief is unreal: my stomach doesn’t pull down, and if my back starts to ache, it’s only a little. But! Before choosing the perfect bandage, I searched for a long time
From Guest
During my first pregnancy, I couldn’t wear a bandage because the baby protested so clearly that the skin hurt after his legs. Now I'm pregnant 2 5 months. The stomach is large and the ligaments hurt every time I move my legs. I found a solution: panties with a wide elastic band for support, like a bandage. And it’s comfortable to drive and a pleasure to walk around. But I only wear it outside if I'm staying for a long time. They are worn over cotton linen, so there is no need to wash them often.
From Guest
The bandage helped me a lot. During my first pregnancy I couldn’t do without it because my belly was huge. And now we are 23 weeks old and our belly is already big, again the bandage saves us, at work I spend a lot of time on my feet or the whole day in a sitting position, after which my back is simply unbearable it hurts, and the bandage helps prevent it.
From Guest
I wear a bandage (in the form of panties with a wide elastic band and plastic rods in an elastic band on the back) from about 15-17 weeks. It relieves stress from the lower back very well and supports the stomach. I wear it all day and only take it off at night. My lower back is weak and gets tired quickly, and my stomach is a little low this time, and there’s a stitch from a caesarean section, so I can’t do without a bandage. I recommend bandage panties; I wear them over regular panties, so you don’t have to wash them every day.
From Guest
You also forgot to write about symphysitis! This is when a baby, after 3 months of pregnancy, puts pressure on the bones of the pelvis and pubic symphysis and pain occurs due to the load. Yoga exercises, wearing a bandage and a swimming pool helped me! Don’t forget that you need to take small steps, carefully climb the steps and do not open your hips during this period.
From Guest
From Guest
I bought a good quality bandage from a specialty store. But, unfortunately, I couldn’t wear it. A couple of times I even took it to a consultation so that the doctor would put it on for me herself. At home I asked for my husband.. The feeling that he was dressed, however, incorrectly, did not leave me, because... There was no comfort that should have appeared; on the contrary, there was a certain feeling of constriction and fear of harming the baby. I didn’t wear it, and, in my opinion, there was no need for it, I wasted my money...
From Guest
I'm having twins, now 23 weeks. Lower back pain is terrible, but the belt makes it even worse. I tried to put it on about 4 weeks ago - my back hurt even worse. During sedentary work, my lower abdomen began to choke and began to ache... In general, the bandage did not suit me.
From Guest
I am very pleased that I was advised to wear a bandage. I chose the universal one - it helped both during pregnancy and after childbirth, when I unrolled it to tighten my tummy. During pregnancy it made walking very easy, because... The tummy was slightly pulled down. And with the bandage it was easy and comfortable. The main thing is to dress it correctly, then there will be no problems. I bought it at the pharmacy and tried it on first. I am sure that if you choose the right bandage and understand how to wear it correctly, then there will be no problems or discomfort - only assistance to expectant mothers in carrying their baby.
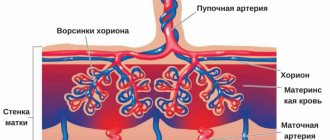
The placenta supplies the baby with oxygen, vitamins and microelements, and cleanses the amniotic fluid from waste products. Its formation begins at 10–12 weeks of gestation, but attachment to the lining of the uterus occurs much earlier, at the chorion stage. Low placentation during pregnancy occurs due to the placement of the placenta in the lower region of the uterus, which threatens a number of complications both during gestation and at the time of birth.
The transformation of the chorion into the placenta lasts until 16–17 weeks. However, the growth of the organ, which is important for the baby, continues in parallel with the development of the baby - until the 36th week. The low location of the placenta may move upward by the time of birth, then the risk of negative consequences will decrease. But if the placenta shifts towards the internal uterine os, is located less than 5-6 cm from it, or partially or completely blocks the lumen, this will already be called low placenta previa. Then the danger will increase.
What does low placentation mean in pregnant women?
The placenta is a unique organ that is formed and exists only during pregnancy. It acts as an intermediary between the embryo and the uterus, which performs a number of important functions, the main of which are nutrition and protection of the fetus.
The placenta is located at the site of attachment of the embryo to the uterine epithelium (therefore it is also called the baby's place). Normally, this is the area closer to the top point of the uterus (its bottom), and more often the attachment occurs along the back wall. If for some reason the fertilized egg settles lower, then they speak of low placentation. The diagnosis is made if the distance between the placenta and the uterine pharynx (the opening in the cervix) does not exceed 5-6 cm. If its edge does not reach the pharynx by only 1-2 cm, then this attachment is called marginal low placentation. If the baby's place overlaps the uterine pharynx, then placenta previa is diagnosed - partial or complete, depending on the degree of closure of the pharynx.
Compared to breech presentation, low placentation is not as dangerous, but still carries multiple risks. Usually, the normal attachment of the fertilized egg and placenta is hampered by the condition of the uterine endometrium. If it is damaged and its functions are impaired, then implantation occurs with disruption. The causes of such damage are most often sexually transmitted infections, inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity (for example, endometriosis), surgical interventions (abortion, previous births), and anatomical features of the female organ. Other risk factors include smoking, age over 35, multiple pregnancies, multiple or complicated births in the past.
There is also a version about the “psychological” reason for this violation: as if the placenta is located low in women who are very afraid of losing the child, thus closing the exit from the uterus and “protecting” the baby.
This pathology only means that the placenta is located lower than with normal attachment, but does not block the birth canal, as happens with its presentation. However, this feature immediately places a woman at risk for abortion.
Is low placentation dangerous for the expectant mother and baby?
The placenta attachment site is determined at the beginning of pregnancy. If a low-lying placenta was diagnosed, and by 24, 25 or 26 weeks it has not moved, complications may arise for the mother and baby. There is a danger associated with an increase in fetal weight by the 2nd trimester, which causes pressure on the embryonic organ. It drops even lower, and the risk of blocking the cervical canal increases.
This can lead to the following consequences:
- Frequent bleeding will cause anemia in the pregnant woman;
- low hemoglobin content in the mother’s blood will lead to hemorrhagic shock, which poses a threat to the health and life of the baby;
- when blood vessels are compressed, blood flow deteriorates, which threatens hypoxia and delayed development of the baby;
- insufficient space for the fetus in the uterus leads to incorrect presentation of the baby;
- detachment of an embryonic organ leads to impaired blood circulation in the fetus;
- premature detachment will cause premature birth;
- a low-lying placental organ prevents the baby’s head from descending into the pelvis, which will lead to difficulty in natural childbirth;
- during contractions, the embryonic organ can shift and block the birth canal, which will make natural childbirth impossible (an urgent cesarean section will have to be performed);
- if a cesarean section is necessary, low placentation along the anterior wall of the uterus makes the operation difficult and leads to large blood loss.
If a pregnant woman experiences frequent and heavy bleeding in the third trimester, or there is a danger of fetal hypoxia, the mother is left in the hospital under round-the-clock medical supervision until labor begins.
If it is impossible to carry the child to term (40 weeks), they try to maintain the pregnancy until 37 weeks. A caesarean section is then prescribed, since natural delivery in this situation is not recommended. If there is an urgent need, the operation is performed earlier.
Placement on the rear wall: features
Low placentation along the posterior wall is safer for the fetus than along the anterior wall. Because in this case:
- The absolute immobility of the placenta is ensured, which reduces the risk of inflammation and abruption.
- The risk of injury to mother and fetus is reduced.
- Shocks and movements are felt easier, viral and inflammatory agents almost do not penetrate the fetus, negative environmental factors have less impact on the child’s health.
- The likelihood of birth injuries due to presentation is minimized.
- There is a chance to give birth naturally.
- Complete safety in the presence of uterine scars.
- Occurs in cases where the first child was born by caesarean section.
Symptoms of the disease
It was noted that low placentation was recorded in 15% of women aged 30–35 years.
The reasons may be different, but the main ones are:
- damage to the mucous wall of the uterus - formations of a different nature, trauma;
- physiological features - bending of the uterus, poorly developed genitals;
- inflammatory processes – endometriosis, salpingitis, urolithiasis and others;
- mechanical damage to the walls of the uterus in the past - abortions, difficult childbirth, curettage, surgical operations;
- hormonal imbalance – irregular or heavy periods;
- diseases of internal organs - cardiovascular, liver, genitourinary system.
When the baby's place is not attached very close to the uterine os, no external symptoms of pathology are observed. The threat can only be detected at 12–13 weeks with an ultrasound scan.
The lower this organ is located to the exit of the uterus, the stronger the signs of low presentation or placentation will appear:
- pain in the lower abdomen that has a pulling character;
- slight spotting after intense physical exertion;
- pain in the lower back and lower abdomen during detachment.
In addition to the above symptoms, 20% of pregnant women with low placentation experience:
- headache or dizziness;
- low pressure;
- nausea and vomiting;
- swelling.
The earlier the feature is diagnosed, the lower the risk of developing dangerous pathologies. Therefore, you should definitely visit a gynecologist in the early stages. Low placentation at the beginning of pregnancy is diagnosed in 80% of women. But after 30 weeks, for the majority, the embryonic organ rises.
Gynecological examination for women with low placentation is strictly contraindicated.
Low placenta previa
The placenta is a unique organ that appears only during pregnancy and connects the organisms of the woman and the fetus. Through the placenta, the unborn baby receives oxygen, vitamins and nutrients from the mother's body.
The formation of this organ is completed by the 16th week of pregnancy, but up to the 36th week the placenta continues to grow, as the baby’s need for the above elements increases. Like any physiological process, the development of the placenta can occur with deviations, and one of the possible pathologies is low placenta previa during pregnancy.
What is low placenta previa
To answer this question, you will have to remember how fertilization occurs. As a rule, after leaving the fallopian tubes, the embryo attaches to the back or front wall of the uterus, closer to its bottom, which is located on top. Subsequently, the placenta begins to form at this site.
But it happens that, for a number of reasons, the fertilized egg is fixed in the lower part of the uterus, in the area of the pharynx. In this case, low placentation occurs. But when the placenta shifts to such an extent that it begins to block the exit from the uterus, doctors talk about low placenta previa.
Firstly, over time, the baby begins to put more and more pressure on the lower part of the uterus. If the placenta is low, it is also subject to excess pressure from the fetus. This leads to a deterioration in blood supply and can result in placental abruption or vaginal bleeding, which, in turn, poses a threat of miscarriage.
However, there is no need to sound the alarm prematurely. In practice, only in 10% of cases the outcome of low placenta previa is a miscarriage. Often, as the gestation period increases, the placenta simply rises up and falls into place, and this can happen both in the middle of pregnancy and just before birth.
Symptoms and causes of low placenta previa
Pregnant women with this diagnosis experience low blood pressure, late gestosis, and fetal hypoxia. However, if low placentation has not had time to turn into presentation, the expectant mother may not observe pronounced signs of this pathology. As a rule, low placenta previa is determined by chance at the 20th week of pregnancy during a routine ultrasound.
In critical situations, a woman may exhibit general symptoms characteristic of a threatened miscarriage: nagging pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, bleeding from the genital tract. It is necessary to listen to the signals of your body - placental abruption occurs without severe pain, and it can only be determined by the presence of blood in the discharge.
As for the reasons, gynecologists name several prerequisites that can contribute to a low location of the placenta in pregnant women.
One of them is the anatomical features of a woman’s reproductive organs, and these can be either congenital anomalies or acquired as a result of exposure to negative pathological factors.
Chronic endometritis, uterine fibroids, complicated first births, multiple pregnancies, smoking - all these factors can provoke low placenta previa during pregnancy.
Low placentation can occur against the background of past inflammatory processes, sexually transmitted infections, vascular diseases of the pelvic organs, as well as surgical interventions in the reproductive system. Expectant mothers over 35 years of age who are giving birth to more than their first child and have had multiple abortions are also at risk.
Treatment of low placenta previa
the problem is that drug therapy for low placenta previa is impossible. In most cases, you can only wait that after some time the placenta will take a more suitable place on its own. This is not only a possible, but also the most probable option: an increase in the size of the uterus contributes to a change in the position of the placenta.
A pregnant woman who has been diagnosed by a gynecologist should follow the following recommendations:
- Avoid sudden and fast movements, do not run, do not jump, avoid physical activity;
- If possible, minimize travel on public transport;
- Refuse sexual contacts;
- When lying down or sitting, give your legs an elevated position;
- If spotting or spotting occurs, consult a doctor immediately, and in case of severe bleeding, call an ambulance;
- If the doctor insists on inpatient treatment in the pregnancy pathology department, do not refuse.
Features of childbirth with low placenta previa
If by 37-38 weeks of pregnancy the placenta has not risen to its proper place, the method of delivery is determined depending on the situation. If the distance between the cervix and the placenta is more than 6 cm, labor proceeds naturally. In the case where the distance is a little less, there is also no need to worry - most likely, the birth will proceed normally.
If the doctor thinks that the placenta is too close to the throat, he may puncture the amniotic sac, causing the placenta to be pressed against the uterus by the baby's head. However, even in such a situation, the woman in labor should be under the supervision of experienced specialists.
When the fetus is positioned incorrectly in the uterus (legs forward), a planned caesarean section is performed. When the birth canal is completely blocked, low placenta previa is also the basis for operative delivery.
Yet in most cases the prognosis is favorable. If you have been diagnosed with this, prepare yourself for the best, follow the doctor’s recommendations, and everything will be fine: the baby will be born on time, naturally and without complications.
Source: https://lady7.net/nizkoe-predlezhanie-placenty.html
How does this condition affect pregnancy?
Often the baby's place is attached to the back wall of the uterus. The norm is considered to be its attachment to the bottom (at the top). But sometimes it is attached to the front wall. If its location is very low, less than 6 cm from the edge of the exit from the uterus, this is fraught with consequences. After 23–27 weeks, the baby begins to move, and after 31, movements become more active. During this period, it can damage the placental organ or the umbilical cord, especially with breech presentation.
The second disadvantage of this feature is the poor blood supply to the lower part of the uterus, which threatens the fetus with a lack of oxygen.
If at 18–19 weeks low placentation is recorded along the posterior wall, then the placental organ by the end of the period in most cases migrates higher. But with a front attachment, the opposite may be true, since migration is directed in the opposite direction.
Another danger is the extrachorionic type of placentation, where the placenta is shifted to the center, creating a kind of shelf. This arrangement requires close monitoring of the pregnant woman throughout the entire period of gestation.
Placenta along the anterior wall
A low anterior wall placenta is a situation where the embryo is attached to the wall at the bottom of the uterus and is located 6 cm from the exit.
This phenomenon is dangerous in the following ways:
- The growing embryo presses on the front of the uterus.
- There is a risk of placenta detachment from the wall of the uterus and vaginal bleeding, which, in turn, without proper assistance, usually leads to the death of the embryo.
- Insufficient oxygen supply to the embryo.
Causes:
- damage to the uterine mucosa;
- postoperative sutures;
- anatomical features.
There is no treatment for this phenomenon. It is only recommended not to aggravate the situation.
It is necessary to refuse sex and physical activity. If bleeding is detected, consult a doctor immediately. Don’t skip trips to specialists and ultrasounds. If you follow these recommendations, the situation improves in the third trimester.
Why and how is low placentation dangerous? Sometimes emergency medical intervention is required during childbirth. Namely, the amniotic sac is punctured. If the life of the fetus is in danger, a caesarean section may be performed.
However, this diagnosis cannot be a factor leading to early termination of pregnancy. It is only necessary to strictly follow the advice of doctors.
What not to do with low placentation
Certain features of pregnancy force a woman to more closely monitor her health. In order not to aggravate the circumstances and lead to even greater prolapse, it is necessary to follow the doctor’s recommendations.
With this diagnosis the following are contraindicated:
- sudden movements;
- excessive physical activity;
- vaginal procedures;
- lifting weights;
- stress and overwork.
It is not recommended to sit with your legs crossed, as this position interferes with normal blood circulation. You also need to lie down and get up carefully, without jerking. Even coughing and sneezing can cause bleeding. Riding on public transport is also not advisable, especially during rush hour.
Sex with low placentation is possible only in the absence of obvious symptoms and contraindications - detachment of the placental organ, pain, bleeding.
When having sex with a partner, it is important to take basic precautions:
- Maintaining hygiene. Be sure to visit the bathroom before starting intimacy;
- No sudden movements. Strong shocks can cause harm, so friction must be done gently and penetration is shallow.
- Position selection. There will be less pressure on the uterus if the woman lies on her side.
If there is a threat of miscarriage or low placental presentation, sexual intercourse is contraindicated. During this period, even masturbation and anal sex can cause serious complications due to contraction of the uterus during orgasm, which will lead to placental abruption. Therefore, you also need to masturbate with caution if there are no prerequisites for pathology.
What not to do if there is low placentation during pregnancy: tips and tricks
The course and outcome of such a pregnancy mainly depends on the woman herself, on how carefully she treats herself and how diligently she follows medical prohibitions. And there are many of them...
The most important thing is to reduce any physical activity to an absolute minimum, and if there is a threat of miscarriage, eliminate it completely, that is, just lie down! Moreover, it is better to lie with your legs raised up - this promotes better blood circulation in the placenta. Playing sports, running, jumping, making sudden movements, lifting even small weights is strictly prohibited! Low placentation and physical activity are completely incompatible! It is not recommended to even raise your arms up or bend over. Yoga, swimming pool, Pilates, and other activities for pregnant women will have to be postponed until the placenta rises. And after that, perhaps the doctor will allow you to resume classes.
You also need to completely give up sex.
Any trips and trips are also generally prohibited. You can discuss this issue with your doctor, but most likely he will tell you that it is better not to even move around the city (whether by personal or public transport) unless absolutely necessary. And there is no need to talk about planes and trains at all: both travel and flight are now extremely dangerous. Therefore, unfortunately, the trip to the sea will have to be cancelled.
All kinds of thermal procedures are also contraindicated: baths, saunas, baths, hot showers and foot baths, heating pads and warming compresses in the pelvic area. All these procedures increase the risk of uterine bleeding.
In general, you need to be careful with the steam room throughout the entire gestation period. There are many contraindications for expectant mothers to visit the bathhouse, and low placentation is one of the most serious among them.
But with the bandage, not everything is so simple. Because some doctors strongly recommend wearing a prenatal bandage with low placentation (arguing that it supports the uterus and reduces stress), others prohibit it (until the placenta rises).
Therefore, if you are comfortable and want to wear a bandage, then this issue must be clarified with your doctor, and if there is such an opportunity, then with several in order to compare their recommendations.
The only thing that can be stated with certainty is that the bandage does not in any way contribute to raising the placenta, and with a pelvic or breech presentation of the fetus, the bandage can prevent this position from changing to physiological, that is, head down.
What treatment methods are there?
There is no medical treatment for this disease. According to statistics, in 8–9 out of 10 cases, the placental organ independently takes the correct position as the uterus grows. Therefore, a diagnosis made at 20–22 weeks or 32 weeks of pregnancy should not be considered critical. Until 33–36 weeks, the position of the placenta changes, which means that there is a possibility of complete disappearance of the pathology.
In order not to aggravate the process, carry the child to term and give birth naturally, you need to listen to and follow all the doctor’s instructions. Throughout pregnancy, with a low-lying placenta, it is important to be observed by a specialist and undergo regular ultrasound examinations. Three ultrasound examinations are the norm - the first at 15–17 weeks, the second at 21–24 and the last at 34–36 weeks.
Starting from 28-29 weeks of pregnancy, with severe development of pathology, a number of drugs are prescribed to maintain pregnancy until the required period:
- Papaverine and Ginipral help increase the elasticity of the muscles of the uterine walls, increase tone and relieve spasmodic impulses.
- Increases hemoglobin Ferlatum, Hemofer, Aktiferin.
- Enhances blood circulation, improves nutrition of placental tissue Curantil, folic acid and vitamins E and Magne B6.
- Increases progesterone levels - Utrozhestan.
In some cases, if there is a risk of placental abruption, the doctor advises placing a pessary.
In case of bleeding and severe pain, you must quickly call for medical help. At this time you can’t do anything, it’s better to just lie down until the ambulance arrives.
Diagnostics
When a low placenta is observed, it does not manifest itself with any special symptoms; prolapse does not mean that alarming signs of the well-being of the mother or the baby’s body will appear. The diagnosis is made through routine ultrasounds. The examination is done at 12-16, 22-25, 30-35 weeks of pregnancy. The location of the placenta is considered low if it is less than 6 cm to the os of the uterus. The earlier the diagnosis is made, the higher the likelihood of responding competently. Even in the last trimester of pregnancy, this is not a death sentence.
Enlargement of the uterus and movement occurs up to 36 weeks; the location of the placenta may still change.
Features of childbirth
If before the onset of labor the woman in labor underwent a full examination and monitoring of the course of pregnancy, natural delivery in most cases will go well.
But the course of labor is influenced by several factors:
- placenta attachment site;
- nature of pregnancy;
- the occurrence of complications during pregnancy;
- accompanying pathologies.
If the placental membrane does not cover the uterine os, the obstetrician punctures the amniotic sac. As a result, the baby’s head presses the placenta against the uterine wall, preventing it from detaching.
Caesarean section is preferable in case of placental presentation or incorrect position of the fetus - bottom down.
Childbirth with low placenta
Very often, low placentation does not appear until after birth. Many mothers are worried about how the birth will go with such a disappointing diagnosis .
- Basically, if the condition of the pregnant woman is satisfactory and there are no complications, then childbirth takes place naturally. But at the same time, the female condition is constantly monitored: the amount of discharge, blood pressure, the position of the baby in the womb, as well as its pulse are recorded.
- If the diagnosis is confirmed and after 36 weeks of gestation (the distance from the placenta to the pharynx is less than 2 cm), bleeding and various unfavorable symptoms appear, then childbirth is usually carried out by cesarean section.
Preventive measures
For prevention purposes, special attention should be paid to the mother’s diet. Increase the amount of vitamins and minerals entering the body that have a beneficial effect on pregnancy. Calcium, magnesium and iron are especially useful.
Rest more and walk in the fresh air. When resting, it is recommended to place your legs a little higher, using a pillow or bolster. This will ensure increased blood circulation in the placenta, which will help move it upward.
Excitement, overexertion and stressful situations have a bad effect on the situation. It is worth remembering that even with such symptoms, women can carry and give birth on their own, without surgery, as evidenced by numerous reviews on the Internet. You just need to follow all safety rules and listen to the supervising doctor.
You can do special gymnastics for pregnant women or go to the pool. But these issues should be discussed with a gynecologist. Exercises with low placentation should be light, without sudden movements. Heavy lifting and running are prohibited.
It is better not to engage in sexual games during this period. The placenta is located only 30–40 mm from the edge of the cervix, and rhythmic pushing can provoke its movement closer to the edge.
Is it possible to wear a bandage with low placentation? The attending physician will answer. Different types of placentation require different treatment and prevention.
Place of formation
A baby's place is formed at the site where the embryo is implanted into the wall of the uterus. It is believed that the most favorable is the fixation of the fertilized egg on the back wall of the uterus closer to its bottom. Implantation of the embryo on the anterior wall is also considered normal.
It is the posterior wall of the uterus, in the segment adjacent to its bottom, that is the most favorable place for nourishing the placenta, and therefore the fetus. This is considered so for two reasons:
- Thanks to the most intense blood circulation in this place.
- The closer the baby's place is attached to the fundus of the uterus, the less the myometrium will stretch. Consequently, the slower the placental tissue will stretch.
- This also means that this position negates the threat of detachment.
To avoid misunderstandings, it should be said that the fundus of the uterus is its upper part, located on the opposite side of the internal os.
What are the stages of placenta formation:
- The active process occurs at 5–6 weeks of gestation.
- By 7–10 weeks, the fetus switches to the placental blood supply.
- By 14–16 weeks this process is completed.
During these periods, it is important to confirm the well-being of this organ, its blood supply and place of attachment:
- A low location of the placenta during pregnancy is diagnosed as a result of ultrasound screening. This may happen at the first mandatory screening at 11, 12 or 13 weeks.
- During pregnancy, week 20 (more precisely, weeks 20–24) is the time of the second screening, when this pathology can be diagnosed.
- At the third screening (30–34 weeks), if the situation does not change for the better, the woman will be offered hospitalization and delivery by cesarean section at 37–38 weeks.
In case of placental abruption, operative delivery may be recommended at an earlier date.